XIV (2)--Logical system concepts
传统的存储架构都存在几个问题:
1),多个controller做cluster,但是某个controller出现问题后会failover造成performance下降
2),需要性能调优
3),某个盘坏后重构时间很长,而且重构过程中极有可能出现更多的盘坏,造成数据丢失
4),当容量不够后,扩展需要停机,而且虽然容量增加了,但是性能却降低了
而XIV的核心特点是:数据是分布在所有盘上的,没有RAID,没有热点盘,不需要人工介入,不需要调优。这种特性是由XIV的逻辑架构决定的。
先来看看几个XIV中最基本的概念:
Partitions
The fundamental building block of a logical volume is known as a partition.
Partition是1MB(1024KB)有两份,包括a primary copy 或者 secondary copy of data,存放在两个不同module的两块不同disk上。
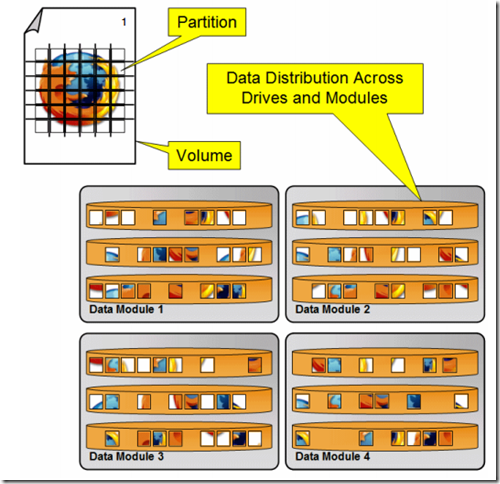
Logical volumes
1,每个Volume都是由N个1MB的Partition组成,每个volume都是分布在所有的disk上。XIV的分布式算法自动将partition随机分布在系统里所有disk上,这就使得XIV不存在hot-spot
Slice
-Each Partition belongs to a bucket of partitions-a slice
-Slices reside in a disk
-One slice belongs to only one disk.Slice cannot span disks!
-There are 16411 slices in Gen3 system(Gen2 - 16384)
Storage pools
While the hardware resources within the BM XIV Storage System are virtualized in a global sense, the available capacity in the system can be administratively portioned into separate and independent storage pools.
Essentially, storage pools function as a means to effectively manage a related group of similarly provisioned logical volumes and their snapshots.
Storage Pools are Logical
�CAllocates hardware resources
�CSame performance for all storage pools
�CVolumes can be moved between Storage Pools
�CVolumes and their clones moved together
�CNo data movement involved… immediate results
Storage Pools control the storage resources
�CUse for specific applications or departments
�CPhysical and Virtual storage used by volumes
�CLimits physical space for clones
�CCan be resized as needed… depending on available resources
下图是Storage Pool和Logical Volume的关系
查看module1上的disk,其中省略了3-11
XIV_1300023>>disk_list module=1:Module:1
Component ID Status Currently Functioning Capacity (GB) Target Status Model Size Serial Firmware Fru Temperature
1:Disk:1:1 OK yes 1TB Hitachi-HUA721010KLA330 924772 PAJ1TBSF GKAOAB0A 30
1:Disk:1:2 OK yes 1TB Hitachi-HUA721010KLA330 924772 PAHYBJTE GKAOAB0A 28
1:Disk:1:12 OK yes 1TB Hitachi-HUA721010KLA330 924772 PAHV2J4F GKAOAB0A 31
XIV_1300023>>pool_list
Name Size (GB) Hard Size (GB) Snapshot Size (GB) Empty Space (GB) Used by Volumes (GB) Used by Snapshots (GB) Locked
prd_db_pool 1013 1013 103 85 0 0 no
Bro_pool 8899 8899 910 5033 309 0 no
可以看到prd_db_pool这个pool里有8个volume
XIV_1300023>>vol_list pool=prd_db_pool
Name Size (GB) Master Name Consistency Group Pool Creator Used Capacity (GB)
prd_db_001 103 prd_db_pool admin 0
prd_db_002 103 prd_db_pool admin 0
prd_db_003 103 prd_db_pool admin 0
prd_db_004 103 prd_db_pool admin 0
prd_db_005 103 prd_db_pool admin 0
prd_db_006 103 prd_db_pool admin 0
prd_db_007 103 prd_db_pool admin 0
prd_db_008 103 prd_db_pool admin 0
Distribution table
distribution table在系统启动的时候创建,包含了Primary和Secondary Partition的映射,还有Module和相应Disk的mapping。当硬件改动时,会创建新的distribution table然后deliver到每个Module上。每个Module都包含了一份distribution table。
XIV Running state
当volume的两份Copy(Primary Copy和Secondary Copy)同时都在时,系统就是在Full Redundancy 状态。
When the full redundancy of data is compromised due to a disk or module failure, the XIV Storage System immediately identifies the non-redundant partitions and begins the rebuild process. The rebuild process consists of the following activities:
--Creates a new target data distribution
--Makes a copy of the non-redundant partitions and writes them according to the new target distribution. This process is known as rebuilding.
--Simultaneously begins to redistribute the redundant data according to the new target data distribution. This process is known as redistributing.
Important: After an XIV Storage System component failure, rebuild and redistribution begin immediately and at the same time.