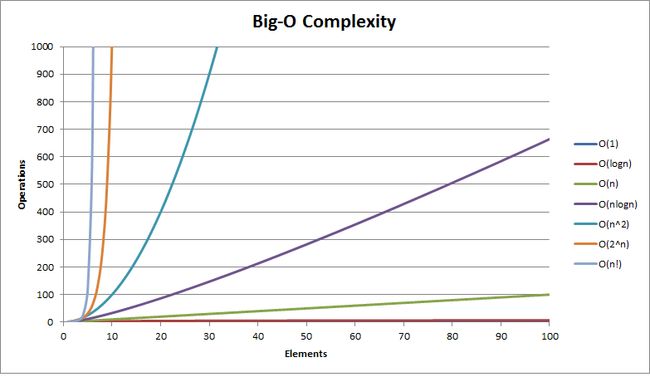
转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/gaochundong/p/complexity_of_algorithms.html
为什么要进行算法分析?
- 预测算法所需的资源
- 计算时间(CPU 消耗)
- 内存空间(RAM 消耗)
- 通信时间(带宽消耗)
- 预测算法的运行时间
- 在给定输入规模时,所执行的基本操作数量。
- 或者称为算法复杂度(Algorithm Complexity)
如何衡量算法复杂度?
- 内存(Memory)
- 时间(Time)
- 指令的数量(Number of Steps)
- 特定操作的数量
- 磁盘访问数量
- 网络包数量
- 渐进复杂度(Asymptotic Complexity)
算法的运行时间与什么相关?
- 取决于输入的数据。(例如:如果数据已经是排好序的,时间消耗可能会减少。)
- 取决于输入数据的规模。(例如:6 和 6 * 109)
- 取决于运行时间的上限。(因为运行时间的上限是对使用者的承诺。)
算法分析的种类:
- 最坏情况(Worst Case):任意输入规模的最大运行时间。(Usually)
- 平均情况(Average Case):任意输入规模的期待运行时间。(Sometimes)
- 最佳情况(Best Case):通常最佳情况不会出现。(Bogus)
例如,在一个长度为 n 的列表中顺序搜索指定的值,则
- 最坏情况:n 次比较
- 平均情况:n/2 次比较
- 最佳情况:1 次比较
而实际中,我们一般仅考量算法在最坏情况下的运行情况,也就是对于规模为 n 的任何输入,算法的最长运行时间。这样做的理由是:
- 一个算法的最坏情况运行时间是在任何输入下运行时间的一个上界(Upper Bound)。
- 对于某些算法,最坏情况出现的较为频繁。
- 大体上看,平均情况通常与最坏情况一样差。
算法分析要保持大局观(Big Idea),其基本思路:
- 忽略掉那些依赖于机器的常量。
- 关注运行时间的增长趋势。
比如:T(n) = 73n3 + 29n3 + 8888 的趋势就相当于 T(n) = Θ(n3)。
渐近记号(Asymptotic Notation)通常有 O、 Θ 和 Ω 记号法。Θ 记号渐进地给出了一个函数的上界和下界,当只有渐近上界时使用 O 记号,当只有渐近下界时使用 Ω 记号。尽管技术上 Θ 记号较为准确,但通常仍然使用 O 记号表示。
使用 O 记号法(Big O Notation)表示最坏运行情况的上界。例如,
- 线性复杂度 O(n) 表示每个元素都要被处理一次。
- 平方复杂度 O(n2) 表示每个元素都要被处理 n 次。
| Notation | Intuition | Informal Definition |
| f is bounded above by g asymptotically |
|
|
| Two definitions : f is not dominated by g asymptotically Complexity theory: f is bounded below by g asymptotically |
|
|
| f is bounded both above and below by g asymptotically |
|
例如:
- T(n) = O(n3) 等同于 T(n) ∈ O(n3)
- T(n) = Θ(n3) 等同于 T(n) ∈ Θ(n3).
相当于:
- T(n) 的渐近增长不快于 n3。
- T(n) 的渐近增长与 n3 一样快。
| 复杂度 | 标记符号 | 描述 |
| 常量(Constant) | O(1) |
操作的数量为常数,与输入的数据的规模无关。 n = 1,000,000 -> 1-2 operations |
| 对数(Logarithmic) | O(log2 n) |
操作的数量与输入数据的规模 n 的比例是 log2 (n)。 n = 1,000,000 -> 30 operations |
| 线性(Linear) | O(n) | 操作的数量与输入数据的规模 n 成正比。 n = 10,000 -> 5000 operations |
| 平方(Quadratic) | O(n2) | 操作的数量与输入数据的规模 n 的比例为二次平方。 n = 500 -> 250,000 operations |
| 立方(Cubic) | O(n3) | 操作的数量与输入数据的规模 n 的比例为三次方。 n = 200 -> 8,000,000 operations |
| 指数(Exponential) | O(2n) O(kn) O(n!) |
指数级的操作,快速的增长。 n = 20 -> 1048576 operations |
注1:快速的数学回忆,logab = y 其实就是 ay = b。所以,log24 = 2,因为 22 = 4。同样 log28 = 3,因为 23 = 8。我们说,log2n 的增长速度要慢于 n,因为当 n = 8 时,log2n = 3。
注2:通常将以 10 为底的对数叫做常用对数。为了简便,N 的常用对数 log10 N 简写做 lg N,例如 log10 5 记做 lg 5。
注3:通常将以无理数 e 为底的对数叫做自然对数。为了方便,N 的自然对数 loge N 简写做 ln N,例如 loge 3 记做 ln 3。
注4:在算法导论中,采用记号 lg n = log2 n ,也就是以 2 为底的对数。改变一个对数的底只是把对数的值改变了一个常数倍,所以当不在意这些常数因子时,我们将经常采用 "lg n"记号,就像使用 O 记号一样。计算机工作者常常认为对数的底取 2 最自然,因为很多算法和数据结构都涉及到对问题进行二分。
而通常时间复杂度与运行时间有一些常见的比例关系:
| 复杂度 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 1000 | 10000 | 100000 |
| O(1) | <1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
| O(log2(n)) | <1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
| O(n) | <1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
| O(n*log2(n)) | <1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
| O(n2) | <1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
2s |
3-4 min |
| O(n3) | <1s |
<1s |
<1s |
<1s |
20s |
5 hours |
231 days |
| O(2n) | <1s |
<1s |
260 days |
hangs |
hangs |
hangs |
hangs |
| O(n!) | <1s |
hangs |
hangs |
hangs |
hangs |
hangs |
hangs |
| O(nn) | 3-4 min |
hangs |
hangs |
hangs |
hangs |
hangs |
hangs |
计算代码块的渐进运行时间的方法有如下步骤:
- 确定决定算法运行时间的组成步骤。
- 找到执行该步骤的代码,标记为 1。
- 查看标记为 1 的代码的下一行代码。如果下一行代码是一个循环,则将标记 1 修改为 1 倍于循环的次数 1 * n。如果包含多个嵌套的循环,则将继续计算倍数,例如 1 * n * m。
- 找到标记到的最大的值,就是运行时间的最大值,即算法复杂度描述的上界。
示例代码(1):
1 decimal Factorial(int n) 2 { 3 if (n == 0) 4 return 1; 5 else 6 return n * Factorial(n - 1); 7 }
阶乘(factorial),给定规模 n,算法基本步骤执行的数量为 n,所以算法复杂度为 O(n)。
示例代码(2):
1 int FindMaxElement(int[] array) 2 { 3 int max = array[0]; 4 for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++) 5 { 6 if (array[i] > max) 7 { 8 max = array[i]; 9 } 10 } 11 return max; 12 }
这里,n 为数组 array 的大小,则最坏情况下需要比较 n 次以得到最大值,所以算法复杂度为 O(n)。
示例代码(3):
1 long FindInversions(int[] array) 2 { 3 long inversions = 0; 4 for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++) 5 for (int j = i + 1; j < array.Length; j++) 6 if (array[i] > array[j]) 7 inversions++; 8 return inversions; 9 }
这里,n 为数组 array 的大小,则基本步骤的执行数量约为 n*(n-1)/2,所以算法复杂度为 O(n2)。
示例代码(4):
1 long SumMN(int n, int m) 2 { 3 long sum = 0; 4 for (int x = 0; x < n; x++) 5 for (int y = 0; y < m; y++) 6 sum += x * y; 7 return sum; 8 }
给定规模 n 和 m,则基本步骤的执行数量为 n*m,所以算法复杂度为 O(n2)。
示例代码(5):
1 decimal Sum3(int n) 2 { 3 decimal sum = 0; 4 for (int a = 0; a < n; a++) 5 for (int b = 0; b < n; b++) 6 for (int c = 0; c < n; c++) 7 sum += a * b * c; 8 return sum; 9 }
这里,给定规模 n,则基本步骤的执行数量约为 n*n*n ,所以算法复杂度为 O(n3)。
示例代码(6):
1 decimal Calculation(int n) 2 { 3 decimal result = 0; 4 for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i++) 5 result += i; 6 return result; 7 }
这里,给定规模 n,则基本步骤的执行数量为 2n,所以算法复杂度为 O(2n)。
示例代码(7):
斐波那契数列:
- Fib(0) = 0
- Fib(1) = 1
- Fib(n) = Fib(n-1) + Fib(n-2)
F() = 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34 ...
1 int Fibonacci(int n) 2 { 3 if (n <= 1) 4 return n; 5 else 6 return Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n - 2); 7 }
这里,给定规模 n,计算 Fib(n) 所需的时间为计算 Fib(n-1) 的时间和计算 Fib(n-2) 的时间的和。
T(n<=1) = O(1)
T(n) = T(n-1) + T(n-2) + O(1)
fib(5) / \ fib(4) fib(3) / \ / \ fib(3) fib(2) fib(2) fib(1) / \ / \ / \
通过使用递归树的结构描述可知算法复杂度为 O(2n)。
示例代码(8):
1 int Fibonacci(int n) 2 { 3 if (n <= 1) 4 return n; 5 else 6 { 7 int[] f = new int[n + 1]; 8 f[0] = 0; 9 f[1] = 1; 10 11 for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) 12 { 13 f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2]; 14 } 15 16 return f[n]; 17 } 18 }
同样是斐波那契数列,我们使用数组 f 来存储计算结果,这样算法复杂度优化为 O(n)。
示例代码(9):
1 int Fibonacci(int n) 2 { 3 if (n <= 1) 4 return n; 5 else 6 { 7 int iter1 = 0; 8 int iter2 = 1; 9 int f = 0; 10 11 for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) 12 { 13 f = iter1 + iter2; 14 iter1 = iter2; 15 iter2 = f; 16 } 17 18 return f; 19 } 20 }
同样是斐波那契数列,由于实际只有前两个计算结果有用,我们可以使用中间变量来存储,这样就不用创建数组以节省空间。同样算法复杂度优化为 O(n)。
示例代码(10):
通过使用矩阵乘方的算法来优化斐波那契数列算法。
1 static int Fibonacci(int n) 2 { 3 if (n <= 1) 4 return n; 5 6 int[,] f = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } }; 7 Power(f, n - 1); 8 9 return f[0, 0]; 10 } 11 12 static void Power(int[,] f, int n) 13 { 14 if (n <= 1) 15 return; 16 17 int[,] m = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } }; 18 19 Power(f, n / 2); 20 Multiply(f, f); 21 22 if (n % 2 != 0) 23 Multiply(f, m); 24 } 25 26 static void Multiply(int[,] f, int[,] m) 27 { 28 int x = f[0, 0] * m[0, 0] + f[0, 1] * m[1, 0]; 29 int y = f[0, 0] * m[0, 1] + f[0, 1] * m[1, 1]; 30 int z = f[1, 0] * m[0, 0] + f[1, 1] * m[1, 0]; 31 int w = f[1, 0] * m[0, 1] + f[1, 1] * m[1, 1]; 32 33 f[0, 0] = x; 34 f[0, 1] = y; 35 f[1, 0] = z; 36 f[1, 1] = w; 37 }
优化之后算法复杂度为O(log2n)。
示例代码(11):
在 C# 中更简洁的代码如下。
1 static double Fibonacci(int n) 2 { 3 double sqrt5 = Math.Sqrt(5); 4 double phi = (1 + sqrt5) / 2.0; 5 double fn = (Math.Pow(phi, n) - Math.Pow(1 - phi, n)) / sqrt5; 6 return fn; 7 }
示例代码(12):
插入排序的基本操作就是将一个数据插入到已经排好序的有序数据中,从而得到一个新的有序数据。算法适用于少量数据的排序,时间复杂度为 O(n2)。
1 private static void InsertionSortInPlace(int[] unsorted) 2 { 3 for (int i = 1; i < unsorted.Length; i++) 4 { 5 if (unsorted[i - 1] > unsorted[i]) 6 { 7 int key = unsorted[i]; 8 int j = i; 9 while (j > 0 && unsorted[j - 1] > key) 10 { 11 unsorted[j] = unsorted[j - 1]; 12 j--; 13 } 14 unsorted[j] = key; 15 } 16 } 17 }
本篇文章《算法复杂度分析》由 Dennis Gao 发表自博客园,任何未经作者同意的爬虫或人为转载均为耍流氓。