HTML5新特性总结
一、HTML5 中的一些有趣的新特性:
- 用于绘画的 canvas 元素
- 用于媒介回放的 video 和 audio 元素
- 对本地离线存储的更好的支持
- 新的特殊内容元素,比如 article、footer、header、nav、section
- 新的表单控件,比如 calendar、date、time、email、url、search
二、HTML5 视频<video>
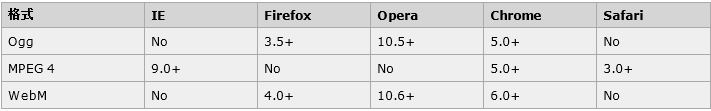
1、视频格式
Ogg = 带有 Theora 视频编码和 Vorbis 音频编码的 Ogg 文件
MPEG4 = 带有 H.264 视频编码和 AAC 音频编码的 MPEG 4 文件
WebM = 带有 VP8 视频编码和 Vorbis 音频编码的 WebM 文件
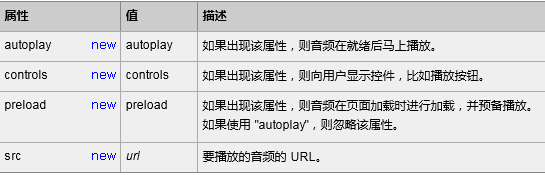
2、<video> 标签的属性
*标签<source>规定多媒体资源,可以是多个
3、实例
(1)
1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> 5 <title>视频</title> 6 </head> 7 8 <body> 9 <video src="2. HTML5音频视频-编解码工具.mp4" controls="controls" width="500px" height="500px"></video> 10 </body> 11 </html>
效果:
(2)HTML5 <video> - 使用 DOM 进行控制(用JS来控制视频的播放/暂停以及放大、缩小)
<小知识:在JS函数里输入console.log("hello");表示在浏览器控制台输出hello,若控制台可以输出hello,则表示函数是可以调用的。>
1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> 5 <title>视频</title> 6 7 </head> 8 9 <body> 10 <video id="video" src="2. HTML5音频视频-编解码工具.mp4" width="300px" height="300px"></video> 11 <button onclick="clickA()">播放/暂停</button> 12 <button onclick="clickBig()">放大</button> 13 <button onclick="clickSmall()">缩小</button> 14 15 <script><!--若此JS部分写在<head></head>中,视频将播放错误--> 16 var a = document.getElementById("video"); 17 function clickA() { 18 if(a.paused) a.play(); 19 else a.pause(); 20 } 21 function clickBig() { 22 a.width = 400; 23 a.height = 400; 24 } 25 function clickSmall() { 26 a.width = 150; <!--此处不能写150px,否则会出错,可以写成a.width = 400+"px";--> 27 a.height = 150; 28 } 29 </script> 30 31 </body> 32 </html>
效果:
点击放大、缩小视频会有相应的改变。
三、音频<audio>
1、音频格式
2、<audio>标签属性
control 属性供添加播放、暂停和音量控件。<audio> 与 </audio> 之间插入的内容是供不支持 audio 元素的浏览器显示的。(视频中也是一样)
四、HTML 5 Canvas(画布)
1、什么是Canvas?
canvas 元素用于在网页上绘制图形。
*HTML5 的 canvas 元素使用 JavaScript 在网页上绘制图像,canvas 元素本身是没有绘图能力的。所有的绘制工作必须在 JavaScript 内部完成。
*画布是一个矩形区域,您可以控制其每一像素。
*canvas 拥有多种绘制路径、矩形、圆形、字符以及添加图像的方法。
2、相关的JS知识:
(1)getContext("2d") 对象是内建的 HTML5 对象,拥有多种绘制路径、矩形、圆形、字符以及添加图像的方法。
(2)fillStyle 方法将其染色,fillRect 方法规定了形状、位置和尺寸。【fillRect 方法拥有参数 (0,0,150,75)。意思是:在画布上绘制 150x75 的矩形,从左上角开始 (0,0)】
3、实例
(1)把鼠标悬停在矩形上可以看到坐标
1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> 5 <title>画布</title> 6 <script type="text/javascript"> 7 function cnvs_getCoordinates(e) 8 { 9 x=e.clientX; <!--clientX 事件属性返回当事件被触发时鼠标指针向对于浏览器页面(或客户区)的水平坐标--> 10 y=e.clientY; 11 document.getElementById("xycoordinates").innerHTML="Coordinates: (" + x + "," + y + ")"; 12 } 13 14 function cnvs_clearCoordinates() 15 { 16 document.getElementById("xycoordinates").innerHTML=""; 17 } 18 </script> 19 </head> 20 21 <body style="margin:0px;"> 22 23 <p>把鼠标悬停在下面的矩形上可以看到坐标:</p> 24 25 <div id="coordiv" style="float:left;width:199px;height:99px;border:1px solid #c3c3c3" 26 onmousemove="cnvs_getCoordinates(event)" onmouseout="cnvs_clearCoordinates()"></div> 27 <br /> 28 <br /> 29 <br /> 30 <div id="xycoordinates"></div> 31 32 </body> 33 </html>
知识点:
*clientX 事件属性返回当事件被触发时鼠标指针向对于浏览器页面(或客户区)的水平坐标。客户区指的是当前窗口。
*innerText和innerHTML都可以给标签体里添加相应信息。
效果:
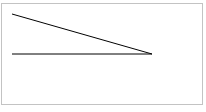
(2)绘制线条
1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> 5 <title>画布</title> 6 7 8 </head> 9 10 <body> 11 <canvas id="myCanvas" width="200" height="100" style="border:1px solid #c3c3c3;"> 12 Your browser does not support the canvas element. 13 </canvas> 14 <script type="text/javascript"> 15 var c=document.getElementById("myCanvas"); 16 var cxt=c.getContext("2d"); 17 cxt.moveTo(10,10); 18 cxt.lineTo(150,50); 19 cxt.lineTo(10,50); 20 cxt.stroke(); 21 </script> 22 </body> 23 </html>
知识点:
*moveto是移动到某个坐标,lineto是从当前坐标连线到某个坐标。这两个函数加起来就是画一条直线。画线要用“笔”,那么MoveToEx()把笔要画的起始位置固定了(x,y)然后要固定终止位置要用到LineTo函数确定终止位置(xend,yend),这样一条线就画出来了。每次与前面一个坐标相连。
*stroke() 方法会实际地绘制出通过 moveTo() 和 lineTo() 方法定义的路径。默认颜色是黑色。
效果:
(3)绘制圆形
*fill() 方法填充当前的图像(路径)。默认颜色是黑色。
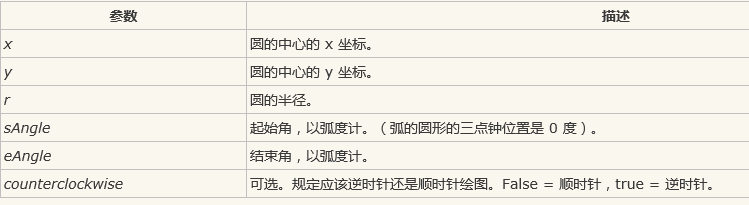
*arc() 方法创建弧/曲线(用于创建圆或部分圆):context.arc(x,y,r,sAngle,eAngle,counterclockwise);
- 中心:arc(100,75,50,0*Math.PI,1.5*Math.PI)
- 起始角:arc(100,75,50,0,1.5*Math.PI)
- 结束角:arc(100,75,50,0*Math.PI,1.5*Math.PI)
* Cxt. beginPath() :开启路径,开启后可以从新设置相关属性 。 Cxt.closePath():关闭一条路径。
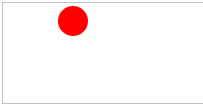
1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> 5 <title>画布</title> 6 7 </head> 8 9 <body> 10 <canvas id="myCanvas" width="200" height="100" style="border:1px solid #c3c3c3;"></canvas> <!--不能放在JS代码之后,否则效果出不来--> 11 <script type="text/javascript"> 12 var c=document.getElementById("myCanvas"); 13 var cxt=c.getContext("2d"); 14 cxt.fillStyle="#FF0000"; 15 cxt.beginPath(); 16 cxt.arc(70,18,15,0,Math.PI*2,true); 17 cxt.closePath(); 18 cxt.fill(); 19 </script> 20 21 </body> 22 </html>
效果:
(4)颜色渐变
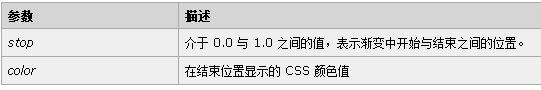
*createLinearGradient() 方法创建线性的渐变对象。渐变可用于填充矩形、圆形、线条、文本等等。使用 addColorStop() 方法规定不同的颜色,以及在 gradient 对象中的何处定位颜色。JS语法:context.createLinearGradient(x0,y0,x1,y1):
*addColorStop() 方法规定 gradient 对象中的颜色和位置。JS语法:gradient.addColorStop(stop,color);
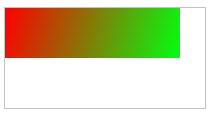
1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> 5 <title>画布</title> 6 7 </head> 8 9 <body> 10 <canvas id="myCanvas" width="200" height="100" style="border:1px solid #c3c3c3;"></canvas> 11 <script type="text/javascript"> 12 var c=document.getElementById("myCanvas"); 13 var cxt=c.getContext("2d"); 14 var grd=cxt.createLinearGradient(0,0,175,50); 15 grd.addColorStop(0,"#FF0000"); 16 grd.addColorStop(1,"#00FF00"); 17 cxt.fillStyle=grd; 18 cxt.fillRect(0,0,175,50); 19 </script> 20 21 22 </body> 23 </html>
效果:
(5)把一幅图像放置到画布上
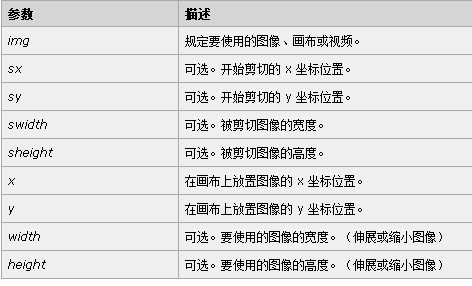
*drawImage() 方法在画布上绘制图像、画布或视频。也能够绘制图像的某些部分,以及/或者增加或减少图像的尺寸。
*JS语法1:在画布上定位图像:context.drawImage(img,x,y);
*JS语法2:在画布上定位图像,并规定图像的宽度和高度:context.drawImage(img,x,y,width,height);
*JS语法3:剪切图像,并在画布上定位被剪切的部分:context.drawImage(img,sx,sy,swidth,sheight,x,y,width,height);
1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> 5 <title>画布</title> 6 7 </head> 8 9 <body> 10 <canvas id="myCanvas" width="200" height="100" style="border:1px solid #c3c3c3;"></canvas> 11 <script type="text/javascript"> 12 var c=document.getElementById("myCanvas"); 13 var cxt=c.getContext("2d"); 14 var img=new Image(); 15 img.src="11.png"; 16 cxt.drawImage(img,0,0); 17 </script> 18 </body> 19 </html>