设计模式
设计模式分为三种类型
-
创建型模式:简单工厂、工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、建造者模式、原型模式、单例模式
-
结构型模式:适配器模式、桥接模式、装饰模式、组合模式、外观模式、享元模式、代理模式。
-
行为型模式:模版方法模式、命令模式、迭代器模式、观察者模式、中介者模式、备忘录模式、解释器模式、状态模式、策略模式、职责链模式、访问者模式。
创建型模式
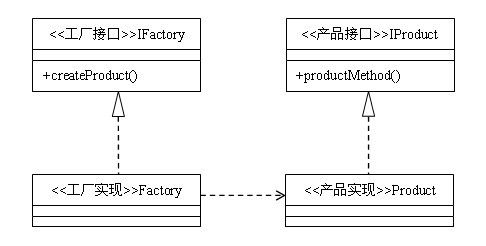
一、简单工厂模式
模式说明
简单工厂模式又称之为静态工厂方法,属于创建型模式。在简单工厂模式中,可以根据传递的参数不同,返回不同类的实例。简单工厂模式定义了一个类,这个类专门用于创建其他类的实例,这些被创建的类都有一个共同的父类。
模式结构图
代码示例
1 namespace DesignPattern 2 { 3 public class SimpleFactory 4 { 5 public static Operation GetOperation(op op, double a, double b) 6 { 7 switch (op) 8 { 9 case op.add: return new Add(a, b); 10 case op.sub: return new Sub(a, b); 11 case op.mul: return new Mul(a, b); 12 case op.div: return new Div(a, b); 13 default: return new undef(a, b); 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 18 public enum op 19 { 20 add = '+', 21 sub = '-', 22 mul = '*', 23 div = '/' 24 } 25 26 public abstract class Operation 27 { 28 public double a, b; 29 public Operation(double a, double b) 30 { 31 this.a = a; 32 this.b = b; 33 } 34 public abstract double GetResult(); 35 } 36 37 public class Add : Operation 38 { 39 public Add(double a, double b) : base(a, b) { } 40 41 public override double GetResult() 42 { 43 return a + b; 44 } 45 } 46 47 public class Sub : Operation 48 { 49 public Sub(double a, double b) : base(a, b) { } 50 51 public override double GetResult() 52 { 53 return a - b; 54 } 55 } 56 57 public class Mul : Operation 58 { 59 public Mul(double a, double b) : base(a, b) { } 60 61 public override double GetResult() 62 { 63 return a * b; 64 } 65 } 66 67 public class Div : Operation 68 { 69 public Div(double a, double b) : base(a, b) { } 70 71 public override double GetResult() 72 { 73 try 74 { 75 return a / b; 76 } 77 catch (DivideByZeroException e) 78 { 79 throw e; 80 } 81 } 82 } 83 84 public class undef : Operation 85 { 86 public undef(double a, double b) : base(a, b) { } 87 88 public override double GetResult() 89 { 90 throw new NotImplementedException(); 91 } 92 93 } 94 }
二、工厂方法模式
模式说明
工厂方法模式定义了一个创建对象的接口,但由子类决定要实例化的类是哪一个。工厂方法模式让实例化推迟到子类。
和简单工厂区别在于,每个工厂只管生产自己对应的产品,而简单工厂是一个工厂生产各种产品。
模式结构图
代码示例
1 namespace DesignPattern 2 { 3 public interface ILogger 4 { 5 void write(string log); 6 } 7 public class EventLogger : ILogger 8 { 9 public void write(string log) 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine("EventLog:" + log); 12 } 13 } 14 public class FileLogger : ILogger 15 { 16 public void write(string log) 17 { 18 Console.WriteLine("FileLog:" + log); 19 } 20 } 21 22 public interface ILoggerFactory 23 { 24 ILogger CreateLogger(); 25 } 26 public class EventLoggerFactory : ILoggerFactory 27 { 28 public ILogger CreateLogger() 29 { 30 return new EventLogger(); 31 } 32 } 33 public class FileLoggerFactory : ILoggerFactory 34 { 35 public ILogger CreateLogger() 36 { 37 return new FileLogger(); 38 } 39 } 40 }
三、抽象工厂模式
模式说明
抽象工厂模式提供一个接口,用于创建相关或者依赖对象的家族,而不需要明确指定具体类。
抽象工厂允许客户端使用抽象的接口来创建一组相关的产品,而不需要关系实际产出的具体产品是什么。这样一来,客户就可以从具体的产品中被解耦。
和工厂方法主要区别于,抽象工厂内要像像定义中说的一样,‘创建一组相关的产品’。
感觉像是(不知道这样理解对否):简单工厂是一个工厂生产多个产品;工厂方法是拆分成子工厂,分别生产各自产品;抽象工厂整合工厂方法和简单工厂,随着子工厂规模变大,也可以生产多个类似产品。
模式结构图
代码示例
1 namespace DesignPattern 2 { 3 //抽象实体 4 public abstract class absSalary 5 { 6 protected double salary; 7 protected double bonus; 8 protected double tax; 9 public absSalary(double sal, double bns, double t) 10 { 11 this.salary = sal; 12 this.bonus = bns; 13 this.tax = t; 14 } 15 public abstract double CalculateTax(); 16 } 17 public class ChineseSalary : absSalary 18 { 19 public ChineseSalary(double sal, double bns, double t) 20 : base(sal, bns, t) 21 { 22 } 23 public override double CalculateTax() 24 { 25 return (base.salary + base.bonus - 3500) * base.tax; 26 } 27 } 28 public class ForeignerSalary : absSalary 29 { 30 public ForeignerSalary(double sal, double bonus, double tax) 31 : base(sal, bonus, tax) 32 { 33 } 34 public override double CalculateTax() 35 { 36 return (base.salary + base.bonus - 4000) * base.tax; 37 } 38 } 39 40 public abstract class absSocialSecurity 41 { 42 protected double SocialSecurity; 43 44 public absSocialSecurity() 45 { 46 this.SocialSecurity = 0; 47 } 48 public virtual double GetSocialSecurity() 49 { 50 return this.SocialSecurity; 51 } 52 } 53 public class ChineseSocialSecurity : absSocialSecurity 54 { 55 public ChineseSocialSecurity(double socialsecurity) 56 : base() 57 { 58 base.SocialSecurity = socialsecurity < 1000 ? 1000 : socialsecurity; 59 } 60 } 61 public class ForeignerSocialSecurity : absSocialSecurity 62 { 63 public ForeignerSocialSecurity(double socialsecurity) 64 : base() 65 { 66 base.SocialSecurity = socialsecurity < 1500 ? 1500 : socialsecurity; 67 } 68 } 69 70 //抽象工厂,生产一系列产品(多个Create方法,分别对应不同产品) 71 public interface AbstractFactory 72 { 73 absSalary CreateSalary(double sal, double bonus, double tax); 74 absSocialSecurity CreateSocialSecurity(double socialsecurity); 75 } 76 public class ChineseFactory : AbstractFactory 77 { 78 public absSalary CreateSalary(double sal, double bonus, double tax) 79 { 80 return new ChineseSalary(sal, bonus, tax); 81 } 82 public absSocialSecurity CreateSocialSecurity(double socialsecurity) 83 { 84 return new ChineseSocialSecurity(socialsecurity); 85 } 86 } 87 public class ForeignerFactory : AbstractFactory 88 { 89 public absSalary CreateSalary(double sal, double bonus, double tax) 90 { 91 return new ForeignerSalary(sal, bonus, tax); 92 } 93 public absSocialSecurity CreateSocialSecurity(double socialsecurity) 94 { 95 return new ForeignerSocialSecurity(socialsecurity); 96 } 97 } 98 }
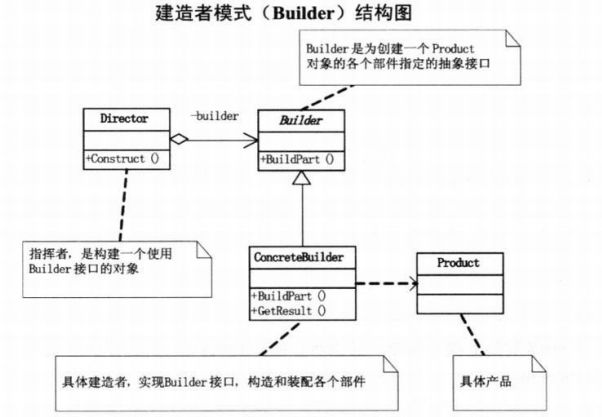
四、创建者模式
模式说明
建造者模式将一个复杂对象的构建与表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。
建造者模式构建复杂对象就像造汽车一样,是一个一个组件一个一个步骤创建出来的,它允许用户通过制定的对象类型和内容来创建他们,但是用户并不需要知道这个复杂对象是如何构建的,它只需要明白通过这样做我可以得到一个完整的复杂对象实例。
和工厂方法很像,创造者是一个builder内每个方法分别创建产品零部件,而工厂方法是每个factory生产一个产品。如果把builder的零部件当做一个完整产品呢?是不是就像 builder又再一次封装了factory~
模式结构图
代码示例
1 public abstract class PersonBulider 2 { 3 public Graphics g; 4 public Pen p; 5 6 public PersonBulider(Graphics g, Pen p) 7 { 8 this.g = g; 9 this.p = p; 10 } 11 12 public abstract void BuliderHead(); 13 public abstract void BuliderBody(); 14 public abstract void BuliderArmLeft(); 15 public abstract void BuliderArmRight(); 16 public abstract void BuliderLegLeft(); 17 public abstract void BuliderLegRight(); 18 } 19 20 public class BuliderTirn : PersonBulider 21 { 22 public BuliderTirn(Graphics g, Pen p) 23 : base(g, p) { } 24 public override void BuliderHead() { g.DrawEllipse(p, 50, 20, 30, 30); } 25 public override void BuliderBody() { g.DrawRectangle(p, 60, 50, 10, 50); } 26 public override void BuliderArmLeft() { g.DrawLine(p, 60, 50, 40, 100); } 27 public override void BuliderArmRight() { g.DrawLine(p, 70, 50, 90, 100); } 28 public override void BuliderLegLeft() { g.DrawLine(p, 60, 100, 45, 150); } 29 public override void BuliderLegRight() { g.DrawLine(p, 70, 100, 85, 150); } 30 } 31 32 public class PersonBuliderDirector 33 { 34 public PersonBulider person; 35 public PersonBuliderDirector(PersonBulider person) 36 { 37 this.person = person; 38 } 39 40 public void CreatPerson() 41 { 42 person.BuliderHead(); 43 person.BuliderBody(); 44 person.BuliderArmLeft(); 45 person.BuliderArmRight(); 46 person.BuliderLegLeft(); 47 person.BuliderLegRight(); 48 } 49 }
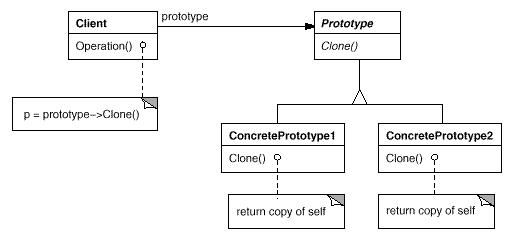
五、原型模式
模式说明
所谓原型模式就是用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过复制这些原型创建新的对象。
说到复制,就会有深/浅两种复制,这是面向对象的值类型和引用类型的差异,具体不作说明
模式结构图
代码示例
1 public abstract class ProtoType 2 { 3 public ProtoType(string Id) 4 { 5 this.Id = Id; 6 } 7 private string id; 8 9 public string Id 10 { 11 get { return id; } 12 set { id = value; } 13 } 14 15 public abstract ProtoType Clone(); 16 } 17 18 public class ConCreatProtoType : ProtoType 19 { 20 public ConCreatProtoType(string Id) 21 : base(Id){} 22 23 public override ProtoType Clone() 24 { 25 return (ProtoType)this.MemberwiseClone(); 26 } 27 }
六、单例模式
代码示例
1 public sealed class Singleton 2 { 3 private static readonly Singleton instance = new Singleton(); 4 private Singleton() { } 5 public static Singleton GetSing() 6 { 7 return instance; 8 } 9 }
结构型模式
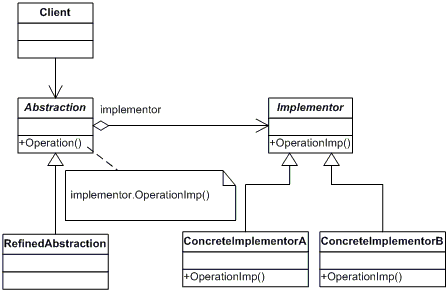
七、适配器模式
模式说明
适配器模式就是将一个类的接口,转换成客户期望的另一个接口。适配器让原本接口不兼容的类可以合作无间。
在适配器模式中,我们可以定义一个包装类,包装不兼容接口的对象,这个包装类就是适配器,它所包装的对象就是适配者。
适配器提供给客户需要的接口,适配器的实现就是将客户的请求转换成对适配者的相应的接口的引用。也就是说,当客户调用适配器的方法时,适配器方法内部将调用 适配者的方法,客户并不是直接访问适配者的,而是通过调用适配器方法访问适配者。因为适配器可以使互不兼容的类能够“合作愉快”。
模式结构图
代码示例
注:此处ILogger接口使用了【工厂方法模式】定义的接口
namespace DesignPattern { public interface IAdaptor { void writelog(string log); } public class LogAdaptor : IAdaptor { ILogger logger; public LogAdaptor(ILogger logger) { this.logger = logger; } public void writelog(string log) { this.logger.write(log); } } }
八、桥接模式
模式说明
桥接模式即将抽象部分与它的实现部分分离开来,使他们都可以独立变化。
桥接模式将继承关系转化成关联关系,它降低了类与类之间的耦合度,减少了系统中类的数量,也减少了代码量。
个人感觉,代理模式、适配器模式和桥接模式相类似,代理模式是一个代理对外表示一个特定的类,适配器模式相当于一个适配器代理多个类,而桥接模式则更加适用于多个对多个的时候
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public abstract class Color { public string name { get; set; } } public abstract class Shape { private Color color; public string name { get; set; } public void SetColor(Color c) { color = c; } public void Draw() { Console.WriteLine("draw shape {0} with color {1}", this.name, this.color.name); } } public class White : Color { public White() { this.name = "white"; } } public class Blue : Color { public Blue() { this.name = "blue"; } } public class Squre : Shape { public Squre() { this.name = "squre"; } } public class Circle : Shape { public Circle() { this.name = "circle"; } } }
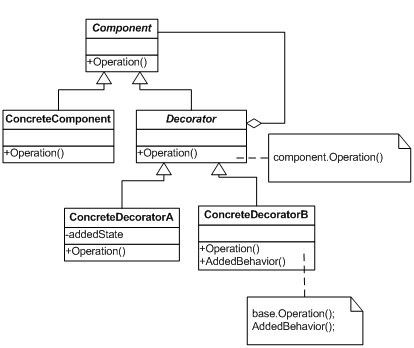
九、装饰者模式
模式说明
装饰者模式装饰者模式可以动态地给一个对象增加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,装饰者模式相比生成子类更为灵活。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public abstract class Car { public string color { get; set; } public int compartment { get; set; } public void run() { Console.WriteLine(color + " " + compartment + " compartment " + this.GetType().Name + " is running!"); } } public class Benz:Car { public Benz() { base.color = "black"; base.compartment = 1; } } public class QQ:Car { public QQ() { base.color = "black"; base.compartment = 1; } } public abstract class Decorator : Car { public Car car; public Decorator(Car car) { this.car = car; } } public class ColorDecorator:Decorator { //一般在构造函数内完成属性的修改(装饰),这里单独加了一个decorate方法 public ColorDecorator(Car car):base(car) { } public Car decorate(string color) { base.car.color = color; return base.car; } } public class CompartmentDecorator : Decorator { public CompartmentDecorator(Car car) : base(car) { } public Car decorate(int compartment) { base.car.compartment = compartment; return base.car; } } }
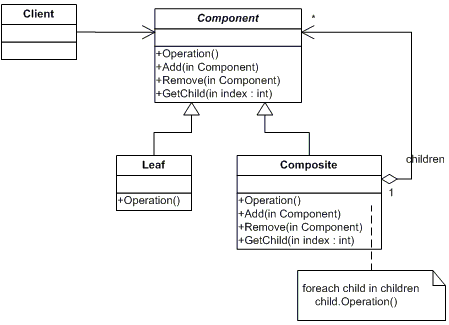
十、组合模式
模式说明
组合模式组合多个对象形成树形结构以表示“整体-部分”的结构层次。
组合模式对单个对象(叶子对象)和组合对象(组合对象)具有一致性,它将对象组织到树结构中,可以用来描述整体与部分的关系。同时它也模糊了简单元素(叶 子对象)和复杂元素(容器对象)的概念,使得客户能够像处理简单元素一样来处理复杂元素,从而使客户程序能够与复杂元素的内部结构解耦。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public abstract class File { protected string name; public File(string name) { this.name = name; } public abstract void Display(); } public class Folder : File { IList<File> list; public Folder(string name) : base(name) { list = new List<File>(); } public void AddFile(File file) { list.Add(file); } public void RemoveFile(File file) { list.Remove(file); } public override void Display() { Console.WriteLine("folder:" + this.name); foreach (File f in list) { f.Display(); } } } public class ImageFile : File { public ImageFile(string name) : base(name) { } public override void Display() { Console.WriteLine("ImageFile:" + this.name); } } }
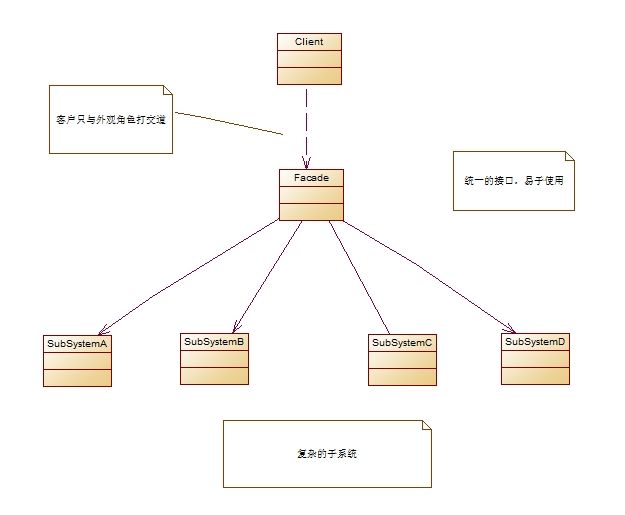
十一、外观模式
模式说明
所谓外观模式就是提供一个统一的接口,用来访问子系统中的一群接口。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public class Facade { Light _light = new Light(); TV _tv = new TV(); public void off() { _light.on(); _tv.off(); } public void on() { _tv.on(); _light.off(); } } class Light { public void on() { Console.WriteLine("light on!"); } public void off() { Console.WriteLine("light off!"); } } class TV { public void on() { Console.WriteLine("tv on!"); } public void off() { Console.WriteLine("tv off!"); } } }
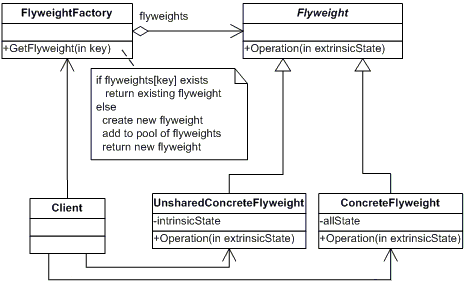
十二、享元模式
模式说明
所谓享元模式就是运行共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度对象的复用。系统使用少量对象,而且这些都比较相似,状态变化小,可以实现对象的多次复用。
FlyweightFactory内定义的实体是不变的(共享的),传入参数是状态变化。
缓存形式,传入参数已经被缓存则直接返回,否则创建参数对应实体,放入缓存并返回该新实体
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public class FlyweightFactory { static Dictionary<string, IFlyweight> pendic = new Dictionary<string, IFlyweight>(); public IFlyweight getPen(string color) { if (pendic.ContainsKey(color)) { return pendic[color]; } else { IFlyweight pen = new ConcreteFlyweight(color); pendic.Add(color, pen); return pen; } } public void Display() { foreach (KeyValuePair<string,IFlyweight> pair in pendic) { Console.WriteLine(pair.Value.GetType().FullName + ":" + pair.Key); } } } public interface IFlyweight { string GetColor(); }; public class ConcreteFlyweight : IFlyweight { string color; public ConcreteFlyweight(string color) { this.color = color; } public string GetColor() { return this.color; } } }
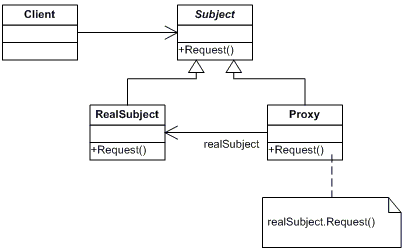
十三、代理模式
模式说明
代理模式就是给一个对象提供一个代理,并由代理对象控制对原对象的引用。
在代理模式中,“第三者”代理主要是起到一个中介的作用,它连接客户端和目标对象。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public class Girl { public string name { get; set; } public Girl(string name) { this.name = name; } } public class Boy { private Girl girl; public string name { get; set; } public Boy(string name, Girl girl) { this.name = name; this.girl = girl; } public void GiveFlower() { Console.WriteLine("boy {0} give flower to girl {1}", this.name, this.girl.name); } } public class Proxy { private Boy boy; public Proxy(Boy boy) { this.boy = boy; } public void GiveFlower() { this.boy.GiveFlower(); } } }
行为型模式
十四、迭代器模式
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public class Persons : IEnumerable { string[] m_Names; public Persons(params string[] Names) { m_Names = new string[Names.Length]; Names.CopyTo(m_Names, 0); } public IEnumerator GetEnumerator() { foreach (string s in m_Names) { yield return s; } } public int Length { get { return m_Names.Length; } } public string this[int i] { get { return m_Names[i]; } set { m_Names[i] = value; } } } }
十五、解释器模式
模式说明
所谓解释器(Interpreter)就是将一系列指令转化成代码,能够执行的代码。Interpreter本来就有翻译的意思。GoF给它的定义是:给定一个语言,定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一个解释器,这个解释器使用该表示来解释语言中的句子。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public class Context { private string msg; public Context(string msg) { this.msg = msg; } public string GetMsg() { return this.msg; } } public interface Interpreter { string Interprete(Context context); } public class UpperInterpreter : Interpreter { public string Interprete(Context context) { string msg = context.GetMsg(); return msg.ToUpperInvariant(); } } public class LowerInterpreter : Interpreter { public string Interprete(Context context) { string msg = context.GetMsg(); return msg.ToLowerInvariant(); } } }
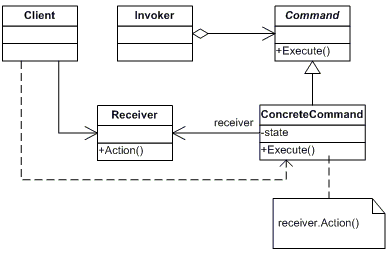
十六、命令模式
模式说明
将请求封装成对象,从而使可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可撤消的操作。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { //接受命令的对象 public class CDMachine { public void on() { Console.WriteLine("CD Machine turns on!"); } public void off() { Console.WriteLine("CD Machine turns off!"); } } //定义命令 public abstract class Command { public abstract void Execute(CDMachine cdMachine); } public class TurnonCommand : Command { public override void Execute(CDMachine cdMachine) { cdMachine.on(); } } public class TurnoffCommand : Command { public override void Execute(CDMachine cdMachine) { cdMachine.off(); } } //发送命令的对象 public class Controller { //遥控的功能 --- 可发送的命令 private TurnonCommand turnonCommand; private TurnoffCommand turnoffCommand; public Controller(TurnonCommand turnonCommand, TurnoffCommand turnoffCommand) { this.turnonCommand = turnonCommand; this.turnoffCommand = turnoffCommand; } public void turnOn(CDMachine cdMachine) { this.turnonCommand.Execute(cdMachine); } public void turnOff(CDMachine cdMachine) { this.turnoffCommand.Execute(cdMachine); } } }
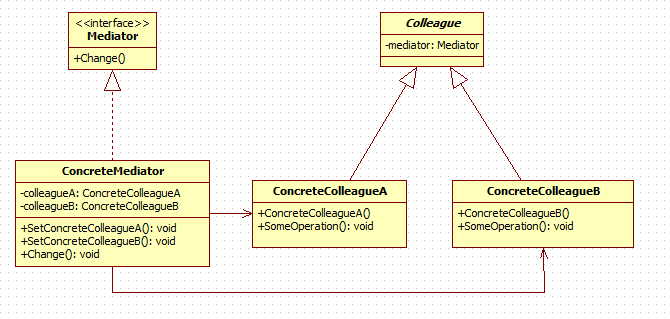
十七、中介者模式
模式说明
所谓中介者模式就是用一个中介对象来封装一系列的对象交互,中介者使各对象不需要显式地相互引用,从而使其耦合松散,而且可以独立地改变它们之间的交互。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public abstract class Person { public string name; public Mediator mediator; public Person(string name, Mediator mediator) { this.name = name; this.mediator = mediator; } public void Contact(string msg) { //参数 this 代表 消息来自我 this.mediator.SendMsg(msg, this); } internal void GetMsg(string msg) { Console.WriteLine(this.name + " 收到消息:" + msg); } } public class HouseOwner : Person { public HouseOwner(string name, Mediator mediator) : base(name, mediator) { } } public class Tenant : Person { public Tenant(string name, Mediator mediator) : base(name, mediator) { } } public interface Mediator { void SendMsg(string msg, Person p); } public class ConcreteMediator : Mediator { HouseOwner houseOwner; Tenant tenant; public ConcreteMediator() { } public void SetHouseOwner(HouseOwner houseOwner) { this.houseOwner = houseOwner; } public void SetTenant(Tenant tenant) { this.tenant = tenant; } public void SendMsg(string msg, Person p) { if (p.GetType() == houseOwner.GetType()) { tenant.GetMsg(msg); } else { houseOwner.GetMsg(msg); } } } }
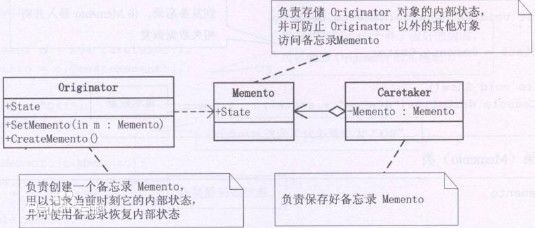
十八、备忘录模式
模式说明
所谓备忘录模式就是在不破坏封装的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态,这样可以在以后将对象恢复到原先保存的状态。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public class Memonto { public int blood { get; set; } public int magic { get; set; } } public class Caretaker { private Memonto memonto; public void SetMemonto(Memonto memonto) { this.memonto = memonto; } public Memonto getMemonto() { return this.memonto; } } public class Original { public int blood { get; set; } public int magic { get; set; } public Memonto SaveMemonto() { return new Memonto() { blood = this.blood, magic = this.magic }; } public void RestoreMemonto(Memonto memonto) { this.blood = memonto.blood; this.magic = memonto.magic; } public void display() { Console.WriteLine("blood:" + this.blood + "\tmagic:" + this.magic); } } }
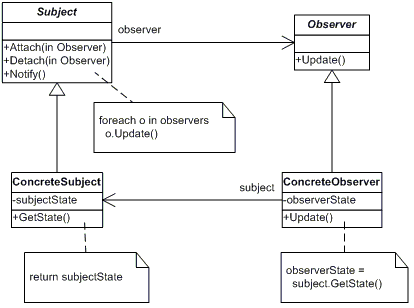
十九、观察者模式
模式说明
定义了一种一对多的关系,让多个观察对象同时监听一个主题对象,当主题对象状态发生变化时会通知所有观察者。
模式结构图
代码示例
public interface Observer { void Update(Subject subject); } public abstract class Subject { List<Observer> obsList = new List<Observer>(); public void AddObserver(Observer observer) { obsList.Add(observer); } public void RemoveObserver(Observer observer) { obsList.Remove(observer); } public void notity() { foreach (Observer o in obsList) { o.Update(this); } } private string _state; public void SetState(string state) { this._state = state; } public string GetState() { return this._state; } } public class ConcreteSubject : Subject { } public class ConcreteObserver1 : Observer { public void Update(Subject subject) { Console.WriteLine("ConcreteObserver1 get notice:" + subject.GetState()); } } public class ConcreteObserver2 : Observer { public void Update(Subject subject) { Console.WriteLine("ConcreteObserver2 get notice:" + subject.GetState()); } }
//事件委托的方式 public delegate void updateDelegate(Subject subject); public class EventSubjet : Subject { public event updateDelegate UpdateHandler; public void EventNotify() { OnUpdate(); } private void OnUpdate() { if (UpdateHandler != null) { UpdateHandler(this); } } }
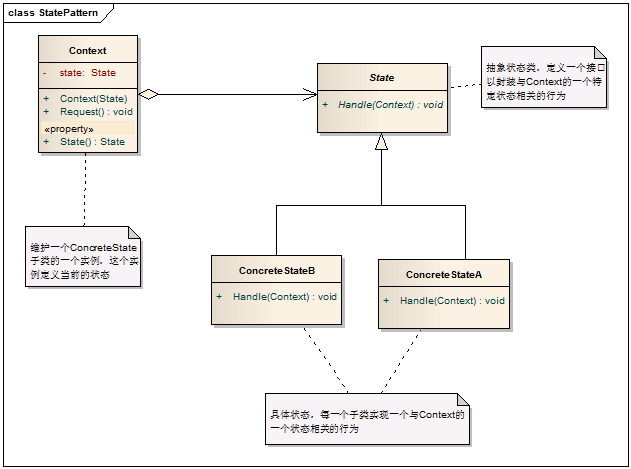
二十、状态模式
模式说明
当一个对象的内在状态改变时允许改变其行为,这个对象看起来像是改变了其类。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public interface IState { void display(); } public class WorkState:IState { public void display() { Console.WriteLine("Working State"); } } public class RestState:IState { public void display() { Console.WriteLine("Rest State"); } } public class Programmer { IState _state; public void Doing(DateTime dt) { if(dt.Hour<7 || dt.Hour > 22) { _state = new RestState(); } else { _state = new WorkState(); } _state.display(); } } }
二十一、模板模式
模式说明
定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义算法的某些特定步骤。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public abstract class Template { protected void boilWater() { Console.WriteLine("boil water"); } protected virtual void brew() { Console.WriteLine("brew"); } protected void pourInCup() { Console.WriteLine("pour into cup"); } protected virtual void addOther() { Console.WriteLine("add other"); } public void makeBeverage() { boilWater(); brew(); pourInCup(); addOther(); } } public class Tea : Template { protected override void brew() { Console.WriteLine("tea"); } protected override void addOther() { Console.WriteLine("add lemon"); } } public class Coffee : Template { protected override void brew() { Console.WriteLine("coffee"); } protected override void addOther() { Console.WriteLine("add sugar"); } } }
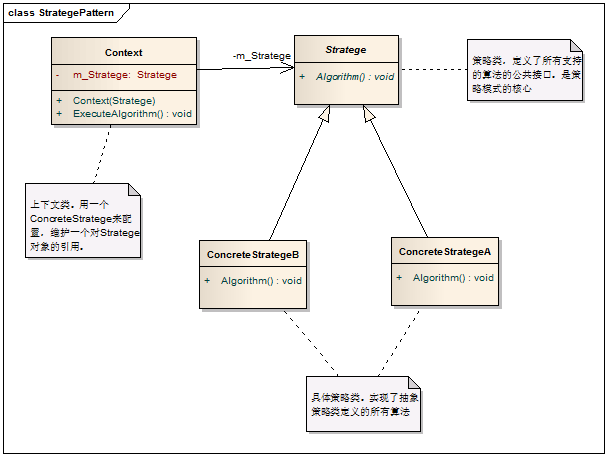
二十二、策略模式
模式说明
定义算法家族并且分别封装,它们之间可以相互替换而不影响客户端。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public abstract class OrderStrategy { public List<int> orderList; public abstract void Order(); public void display() { foreach (int i in orderList) { Console.Write(i + "\t"); } Console.WriteLine(); } } public class BubbleStrategy : OrderStrategy { public override void Order() { for (int i = 0; i < orderList.Count; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < orderList.Count; j++) { if (orderList[i] < orderList[j])//冒泡降序 小的冒上去 { int temp = orderList[i]; orderList[i] = orderList[j]; orderList[j] = temp; } } } } } public class SelectionStrategy : OrderStrategy { public override void Order() { for (int i = 0; i < orderList.Count; i++) { int smallvalue = orderList[i]; int smallposition = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < orderList.Count; j++) { if (orderList[j] < smallvalue) { smallposition = j; smallvalue = orderList[j]; } } //将最小值放到当前要排序的位置 orderList[smallposition] = orderList[i]; orderList[i] = smallvalue; } } } public class InsertionStrategy : OrderStrategy { public override void Order() { for (int i = 1; i < orderList.Count; i++) { int temp = orderList[i];//当前要插入的值,相当于位置I是个空白位置,供对比进行后移 int j = i; //j之前的序列已经排序好,选一个位置把当前值插入 while (j > 0) { //i从1开始,是因为这里j要比较前一个值 if (temp < orderList[j - 1]) //插入过程中,每次比较的值大于当前值则向后移动 { orderList[j] = orderList[j-1]; j--; } else { break; } } //找到位置(break)或者循环正常结束(说明当前值最小)则赋值。 orderList[j] = temp; } } } public class StrategyManager { OrderStrategy strategy; public void SetStrategy(OrderStrategy strategy) { this.strategy =strategy; } public void Sort(List<int> list) { this.strategy.orderList = list; this.strategy.Order(); this.strategy.display(); } } }
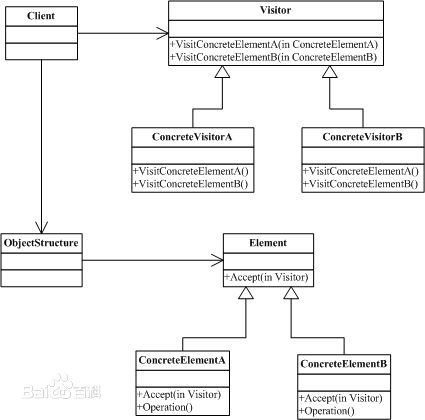
二十三、访问者模式
模式说明
访问者模式即表示一个作用于某对象结构中的各元素的操作,它使我们可以在不改变各元素的类的前提下定义作用于这些元素的新操作。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public interface Element { void accept(Visitor visitor); } public class ConcreteElementA : Element { string name; public void SetName(string name) { this.name = name; } public string GetName() { return this.name; } public void accept(Visitor visitor) { visitor.visitElementA(this); } } public class ConcreteElementB : Element { int ID; public void SetID(int id) { this.ID = id; } public int GetID() { return this.ID; } public void accept(Visitor visitor) { visitor.visitElementB(this); } } public interface Visitor { void visitElementA(ConcreteElementA ea); void visitElementB(ConcreteElementB eb); } public class ConcreteVisitorA : Visitor { public void visitElementA(ConcreteElementA ea) { Console.WriteLine("ConcreteVisitorA visit ElemantA:" + ea.GetName()); } public void visitElementB(ConcreteElementB eb) { Console.WriteLine("ConcreteVisitorA visit ElemantB:" + eb.GetID()); } } public class ConcreteVisitorB : Visitor { public void visitElementA(ConcreteElementA ea) { Console.WriteLine("ConcreteVisitorB visit ElemantA:" + ea.GetName()); } public void visitElementB(ConcreteElementB eb) { Console.WriteLine("ConcreteVisitorB visit ElemantB:" + eb.GetID()); } } public class objectStructure { List<Element> elementlist = new List<Element>(); public void Attach(Element e) { elementlist.Add(e); } public void Dettach(Element e) { elementlist.Remove(e); } public void Accept(Visitor visit) { foreach(Element e in elementlist) { e.accept(visit); } } } }
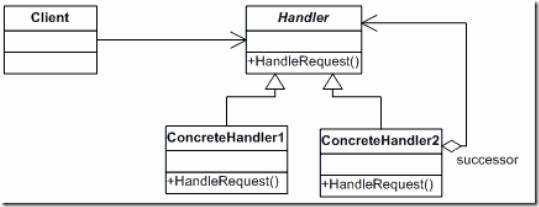
二十四、责任链模式
模式说明
避免请求发送者与接收者耦合在一起,让多个对象都有可能接收请求,将这些对象连接成一条链,并且沿着这条链传递请求,直到有对象处理它为止,这就是职责链模式。
模式结构图
代码示例
namespace DesignPattern { public class Request { int days; string name; public Request(int days, string name) { this.days = days; this.name = name; } public int GetDays() { return days; } public string GetName() { return name; } } public abstract class Responsibility { protected Responsibility responsibility; public Responsibility(Responsibility responsibility) { this.responsibility = responsibility; } public abstract void HandleRequest(Request request); } public class Leader : Responsibility { public Leader(Responsibility responsibility) : base(responsibility) { } public override void HandleRequest(Request request) { if (request.GetDays() < 3) { Console.WriteLine("Leader passed {0}'s {1} days request", request.GetName(), request.GetDays()); } else { this.responsibility.HandleRequest(request); } } } public class Department : Responsibility { public Department(Responsibility responsibility) : base(responsibility) { } public override void HandleRequest(Request request) { if (request.GetDays() < 8) { Console.WriteLine("Department passed {0}'s {1} days request", request.GetName(), request.GetDays()); } else { this.responsibility.HandleRequest(request); } } } //责任链终端必须处理 public class Boss : Responsibility { public Boss() : base(null) { } public override void HandleRequest(Request request) { if (request.GetDays() < 15) { Console.WriteLine("Boss passed {0}'s {1} days request", request.GetName(), request.GetDays()); } else { Console.WriteLine("Boss refused {0}'s {1} days request", request.GetName(), request.GetDays()); } } } }