第十周 第十章 代码运行
- 学习任务
- 编译运行
cp1.c
代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> define BUFFERSIZE 4096 #define COPYMODE 0644 void oops(char *, char *); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int in_fd, out_fd, n_chars; char buf[BUFFERSIZE]; if (argc != 3) { fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s source destination\n", *argv); exit(1); } if ((in_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) == -1) oops("Cannot open ", argv[1]); if ((out_fd = creat(argv[2], COPYMODE)) == -1) oops("Cannot creat", argv[2]); while ((n_chars = read(in_fd, buf, BUFFERSIZE)) > 0) if (write(out_fd, buf, n_chars) != n_chars) oops("Write error to ", argv[2]); if (n_chars == -1) oops("Read error from ", argv[1]); if (close(in_fd) == -1 || close(out_fd) == -1) oops("Error closing files", ""); } void oops(char *s1, char *s2) { fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s ", s1); perror(s2); exit(1); }
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<termios.h> int main() { struct termios info; int rv; rv = tcgetattr( 0, &info ); /* read values from driver */ if ( rv == -1 ){ perror( "tcgetattr"); exit(1); } if ( info.c_lflag & ECHO ) printf(" echo is on , since its bit is 1\n"); else printf(" echo is OFF, since its bit is 0\n"); return 0; }

#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> void show_stat_info(char *, struct stat *); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { struct stat info; if (argc>1) { if( stat(argv[1], &info) != -1 ){ show_stat_info( argv[1], &info ); return 0; } else perror(argv[1]); } return 1; } void show_stat_info(char *fname, struct stat *buf) { printf(" mode: %o\n", buf->st_mode); printf(" links: %d\n", buf->st_nlink); printf(" user: %d\n", buf->st_uid); printf(" group: %d\n", buf->st_gid); printf(" size: %d\n", (int)buf->st_size); printf("modtime: %d\n", (int)buf->st_mtime); printf(" name: %s\n", fname ); }
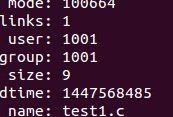
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/stat.h> int main() { struct stat infobuf; if ( stat( "/etc/passwd", &infobuf) == -1 ) perror("/etc/passwd"); else printf(" The size of /etc/passwd is %d\n", infobuf.st_size ); }#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <dirent.h> void do_ls(char []); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if ( argc == 1 ) do_ls( "." ); else while ( --argc ){ printf("%s:\n", *++argv ); do_ls( *argv ); } return 0; } void do_ls( char dirname[] ) { DIR *dir_ptr; struct dirent *direntp; if ( ( dir_ptr = opendir( dirname ) ) == NULL ) fprintf(stderr,"ls1: cannot open %s\n", dirname); else { while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL ) printf("%s\n", direntp->d_name ); closedir(dir_ptr); } }
#include <stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <dirent.h> #include <sys/stat.h> void do_ls(char[]); void dostat(char *); void show_file_info( char *, struct stat *); void mode_to_letters( int , char [] ); char *uid_to_name( uid_t ); char *gid_to_name( gid_t ); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if ( argc == 1 ) do_ls( "." ); else while ( --argc ){ printf("%s:\n", *++argv ); do_ls( *argv ); } return 0; } void do_ls( char dirname[] ) { DIR *dir_ptr; struct dirent *direntp; if ( ( dir_ptr = opendir( dirname ) ) == NULL ) fprintf(stderr,"ls1: cannot open %s\n", dirname); else { while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL ) dostat( direntp->d_name ); closedir(dir_ptr); } } void dostat( char *filename ) { struct stat info; if ( stat(filename, &info) == -1 ) perror( filename ); else show_file_info( filename, &info ); } void show_file_info( char *filename, struct stat *info_p ) { char *uid_to_name(), *ctime(), *gid_to_name(), *filemode(); void mode_to_letters(); charmodestr[11]; mode_to_letters( info_p->st_mode, modestr ); printf( "%s", modestr ); printf( "%4d " , (int) info_p->st_nlink); printf( "%-8s " , uid_to_name(info_p->st_uid) ); printf( "%-8s " , gid_to_name(info_p->st_gid) ); printf( "%8ld " , (long)info_p->st_size); printf( "%.12s ", 4+ctime(&info_p->st_mtime)); printf( "%s\n" , filename ); } void mode_to_letters( int mode, char str[] ) { strcpy( str, "----------" ); if ( S_ISDIR(mode) ) str[0] = 'd'; if ( S_ISCHR(mode) ) str[0] = 'c'; if ( S_ISBLK(mode) ) str[0] = 'b'; if ( mode & S_IRUSR ) str[1] = 'r'; if ( mode & S_IWUSR ) str[2] = 'w'; if ( mode & S_IXUSR ) str[3] = 'x'; if ( mode & S_IRGRP ) str[4] = 'r'; if ( mode & S_IWGRP ) str[5] = 'w'; if ( mode & S_IXGRP ) str[6] = 'x'; if ( mode & S_IROTH ) str[7] = 'r'; if ( mode & S_IWOTH ) str[8] = 'w'; if ( mode & S_IXOTH ) str[9] = 'x'; } #include <pwd.h> char *uid_to_name( uid_t uid ) { struct passwd *getpwuid(), *pw_ptr; static char numstr[10]; if ( ( pw_ptr = getpwuid( uid ) ) == NULL ){ sprintf(numstr,"%d", uid); return numstr; } else return pw_ptr->pw_name ; } #include <grp.h> char *gid_to_name( gid_t gid ) { struct group *getgrgid(), *grp_ptr; static char numstr[10]; if ( ( grp_ptr = getgrgid(gid) ) == NULL ){ sprintf(numstr,"%d", gid); return numstr; } else return grp_ptr->gr_name; }#include<stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include<termios.h> #define oops(s,x) { perror(s); exit(x); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { struct termios info; if ( argc == 1 ) exit(0); if ( tcgetattr(0,&info) == -1 ) /* get attribs */ oops("tcgettattr", 1); if ( argv[1][0] == 'y' ) info.c_lflag |= ECHO ; /* turn on bit*/ else info.c_lflag &= ~ECHO ; /* turn off bit */ if ( tcsetattr(0,TCSANOW,&info) == -1 ) /* set attribs*/ oops("tcsetattr",2); return 0; }#include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <dirent.h> ino_t get_inode(char *); voidprintpathto(ino_t); voidinum_to_name(ino_t , char *, int ); int main() { printpathto( get_inode( "." ) ); putchar('\n'); return 0; } void printpathto( ino_t this_inode ) { ino_t my_inode ; char its_name[BUFSIZ]; if ( get_inode("..") != this_inode ) { chdir( ".." ); inum_to_name(this_inode,its_name,BUFSIZ); my_inode = get_inode( "." ); printpathto( my_inode ); printf("/%s", its_name ); } } void inum_to_name(ino_t inode_to_find , char *namebuf, int buflen) { DIR *dir_ptr; struct dirent *direntp; dir_ptr = opendir( "." ); if ( dir_ptr == NULL ){ perror( "." ); exit(1); } while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL ) if ( direntp->d_ino == inode_to_find ) { strncpy( namebuf, direntp->d_name, buflen); namebuf[buflen-1] = '\0'; closedir( dir_ptr ); return; } fprintf(stderr, "error looking for inum %d\n", (int) inode_to_find); exit(1); } ino_t get_inode( char *fname ) { struct stat info; if ( stat( fname , &info ) == -1 ){ fprintf(stderr, "Cannot stat "); perror(fname); exit(1); } return info.st_ino; }#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> int main() { struct winsize size; if( isatty(STDOUT_FILENO) == 0) exit(1); if (ioctl(STDOUT_FILENO, TIOCGWINSZ, &size) < 0) { perror("ioctl TIOCGWINSZ error"); exit(1); } printf("%d rows %d columns\n", size.ws_row, size.ws_col); return 0; }#include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include <utmp.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #define SHOWHOST int show_info( struct utmp *utbufp ) { printf("%-8.8s", utbufp->ut_name); printf(" "); printf("%-8.8s", utbufp->ut_line); printf(" "); printf("%10ld", utbufp->ut_time); printf(" "); #ifdef SHOWHOST printf("(%s)", utbufp->ut_host); #endif printf("\n"); return 0; } int main() { struct utmp current_record; int utmpfd; int reclen = sizeof(current_record); if ( (utmpfd = open(UTMP_FILE, O_RDONLY)) == -1 ){ perror( UTMP_FILE ); exit(1); } while ( read(utmpfd, ¤t_record, reclen) == reclen ) show_info(¤t_record); close(utmpfd); return 0; }#include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include <utmp.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #define SHOWHOST int show_info( struct utmp *utbufp ) { printf("%-8.8s", utbufp->ut_name); printf(" "); printf("%-8.8s", utbufp->ut_line); printf(" "); printf("%10ld", utbufp->ut_time); printf(" "); #ifdef SHOWHOST printf("(%s)", utbufp->ut_host); #endif printf("\n"); return 0; } int main() { struct utmp current_record; int utmpfd; int reclen = sizeof(current_record); if ( (utmpfd = open(UTMP_FILE, O_RDONLY)) == -1 ){ perror( UTMP_FILE ); exit(1); } while ( read(utmpfd, ¤t_record, reclen) == reclen ) show_info(¤t_record); close(utmpfd); return 0; }使用man学习理解相关系统调用, 理解参数、返回值的含义-
1是普通的命令 2是系统调用,如open,write之类的(通过这个,至少可以很方便的查到调用这个函数,需要加什么头文件) 3是库函数,如printf,fread4是特殊文件,也就是/dev下的各种设备文件 5是指文件的格式,比如passwd, 就会说明这个文件中各个字段的含义 6是给游戏留的,由各个游戏自己定义 7是附件还有一些变量,比如向environ这种全局变量在这里就有说明 8是系统管理用的命令,这些命令只能由root使用,如ifconfig -
man page大致分为一下部分:
NAME:简单命令、数据名称说明 SYNOPSIS:简短的命令语法(sysntax)简介 DESCRIPTION:较为完整的说明,需要认真阅读 OPTION:针对SYNOPSIS中列举的所有可用选项说明 COMMANDS:当这个软件在执行的时候,可用在此软件中使用命令 FILES:这个软件或数据所使用或参考或链接到的文件 SEE ALSE:可以参考的,与这个命令有关的其他说明 EXAMPLE:一些可以参考的范例,这个最好用 BUGS:是否有相关的bug -
man中的相关操作
ctrl + F或者Page Down:向下翻页 ctrl + B或者Page Up:向上翻页 gg到第一行 GG到最后一行 /start:能在整手册中搜索start相关字符,使用n查找下一个,使用N查找上一个 j,k与vi中一样使用,j向下一行,k向上一行 d下翻半页 u上翻半页 h获取man使用帮助 q退出man -
使用带有-k选项的man命令可以根据关键字搜索联机帮助。
使用带有-f选项的man命令可以根据关键字在联机帮助中搜索完全匹配的条目。 
- 会用grep -nr xxx /usr/include 查宏定义
