Struts2与SpringMVC
Struts2
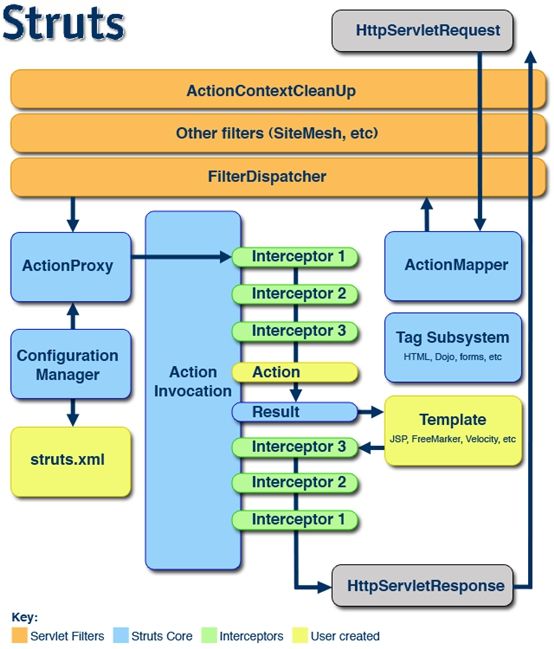
上图来源于Struts2官方站点,是Struts 2 的整体结构。
一个请求在Struts2框架中的处理大概分为以下几个步骤
1、客户端初始化一个指向Servlet容器(例如Tomcat)的请求;
2、这个请求经过一系列的过滤器(Filter)(这些过滤器中有一个叫做ActionContextCleanUp的可选过滤器,这个过滤器对于Struts2和其他框架的集成很有帮助,例如:SiteMesh Plugin);
3、接着FilterDispatcher被调用,FilterDispatcher询问ActionMapper来决定这个请是否需要调用某个Action
4、如果ActionMapper决定需要调用某个Action,FilterDispatcher把请求的处理交给ActionProxy
5、ActionProxy通过Configuration Manager询问框架的配置文件,找到需要调用的Action类
6、ActionProxy创建一个ActionInvocation的实例。
7、ActionInvocation实例使用命名模式来调用,在调用Action的过程前后,涉及到相关拦截器(Intercepter)的调用。
8、一旦Action执行完毕,ActionInvocation负责根据struts.xml中的配置找到对应的返回结果。返回结果通常是(但不总是,也可 能是另外的一个Action链)一个需要被表示的JSP或者FreeMarker的模版。在表示的过程中可以使用Struts2 框架中继承的标签。在这个过程中需要涉及到ActionMapper
在上述过程中所有的对象(Action,Results,Interceptors,等)都是通过ObjectFactory来创建的。
springmvc
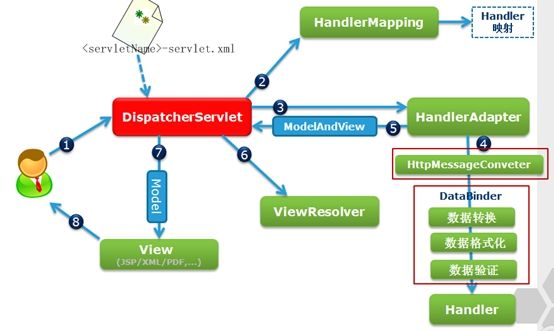
Springmvc工作流程描述
1、用户向服务器发送请求,请求被Spring 前端控制DispatcherServlet捕获;
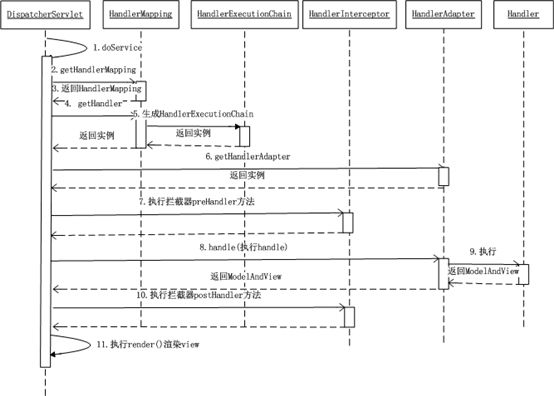
2、DispatcherServlet对请求URL进行解析,得到请求资源标识符(URI)。然后根据该URI,调用HandlerMapping获得该Handler配置的所有相关的对象(包括Handler对象以及Handler对象对应的拦截器),最后以HandlerExecutionChain对象的形式返回;
3、DispatcherServlet根据获得的Handler,选择一个合适的HandlerAdapter。(附注:如果成功获得HandlerAdapter后,此时将开始执行拦截器的preHandler(...)方法)
4、提取Request中的模型数据,填充Handler入参,开始执行Handler(Controller)。 在填充Handler的入参过程中,根据你的配置,Spring将帮你做一些额外的工作:
HttpMessageConveter: 将请求消息(如Json、xml等数据)转换成一个对象,将对象转换为指定的响应信息;
数据转换:对请求消息进行数据转换。如String转换成Integer、Double等;
数据格式化:对请求消息进行数据格式化。 如将字符串转换成格式化数字或格式化日期等;
数据验证: 验证数据的有效性(长度、格式等),验证结果存储到BindingResult或Error中;
5、Handler执行完成后,向DispatcherServlet 返回一个ModelAndView对象;
6、根据返回的ModelAndView,选择一个适合的ViewResolver(必须是已经注册到Spring容器中的ViewResolver)返回给DispatcherServlet ;
7、ViewResolver 结合Model和View,来渲染视图
8、将渲染结果返回给客户端。
/** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */ protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Error err) { triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
为什么Spring只使用一个Servlet(DispatcherServlet)来处理所有请求?
详细见J2EE设计模式-前端控制模式
Spring为什么要结合使用HandlerMapping以及HandlerAdapter来处理Handler?
符合面向对象中的单一职责原则,代码架构清晰,便于维护,最重要的是代码可复用性高。如HandlerAdapter可能会被用于处理多种Handler。
通过以上对比发现:
- spring mvc的入口是servlet,而struts2是filter(这里要指出,filter和servlet是不同的。以前认为filter是servlet的一种特殊),这样就导致了二者的机制不同,这里就牵涉到servlet和filter的区别了。
参见:http://blog.csdn.net/zs15932616453/article/details/8832343 - 主要机制
springmvc是方法级别的拦截,一个方法对应一个request上下文,而方法同时又跟一个url对应,参数的传递是直接注入到方法中的,是该方法独有的。
struts2是类级别的拦截, 一个类对应一个request上下文, struts是在接受参数的时候,可以用属性来接受参数, 这就说明参数是让多个方法共享的,这也就无法用注解或其他方式标识其所属方法了
intercepter的实现机制。struts有以自己的interceptor机制,spring mvc 用的是独立的AOP方式。这样导致struts的配置文件量还是比spring mvc大,虽然struts的配置能继承,spring mvc使用更加简洁。
3、SpringMVC对ajax的支持上要优于struts2。
下面介绍SpringMVC对ajax的支持:
引入下面两个jar包,我用的是1.8.7,好像1.4.2版本以上都可以,其余版本未测试
jackson-core-asl-1.8.7.jar
jackson-mapper-asl-1.8.7.jar
spring的配置文件中要有这一行,才能使用到spring内置支持的json转换。如果你手工把POJO转成json就可以不须要使用spring内置支持的json转换。
<mvc:annotation-driven />
使用@ResponseBody注解
@Controller public class ajaxController extends MultiActionController { @RequestMapping("/ajax") @ResponseBody public Object queryData(User user,HttpServletRequest arg0) { System.out.println("———-ajaxController.queryData()—————"); User result=new User(); result.setUserName(user.getUserName()); result.setAge(user.getAge()); return result; } }
Jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> <!– <script type="text/javascript" src="/SpringMVC7/js/jquery-1.7.1.min.js"></script>–> <script type="text/javascript" src="/SpringMVC7/js/jquery.json-2.4.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> $(document).ready(function() { $("#btnAjax").click(function() { //系列化表单元素为Json对象 //var Jsonfields = decodeURIComponent($("form").serialize(),true); //alert($.toJSON(Jsonfields)); //var jsonuserinfo=$.toJSON(Jsonfields); var userName=$("#userName").attr("value"); var userAge=$("#age").attr("value"); var user={userName:userName,age:userAge}; $.ajax({ url : "/SpringMVC7/ajax", type : "post", data:user, success : function(data) { alert(data.userName+","+data.age); } }); }); }); </script> </head> <body> <form action="" method="post" name="form"> <h3>传递数据</h3> <input type="text" name="userName" id="userName" /> <input type="text" name="age" id="age" /> <input type="button" value="ajax请求" id="btnAjax" /> </form> </body> </html>
4、性能方面
武断的说,一般环境下,Spring MVC要优于Struts2
测试见
http://elf8848.iteye.com/blog/698217
http://developer.51cto.com/art/201104/255410.htm
http://www.iteye.com/topic/1072765
在开发中,我更倾向使用Spring MVC,理由如下:
1、基于上述对比结果
2、spring生态环境的欣欣向荣,从安全到各种服务集成具有天生的优势
3、Spring对REST的支持
4、有Spring的基础,spring mvc非常容易使用