Android开发学习之路--Service之初体验
android最后一个组件便是service了,终于学习到最后一个组件了,从年前的开发环境的搭建,到现在学到最后一个组件花了三周的时间,期间记录的点点滴滴,照着书本学习编写的代码都受益匪浅,这里要感谢第一行代码这本书。三个星期除了三十和初一没有学习,其余时间坚持每天学习一个知识点,总算慢慢地学习了个大概,接下去继续学习其他的东西。说了这么多还是开始学习Service组件吧。
Service从字面上理解就是服务的意思,也就是为应用程序提供服务,比如我们在播放一首歌的时候,我又想把它下载下来,那么我们就可以把他交给Service去处理。播放歌曲是在后台运行的,那么它也是个服务,还是来个例子吧。先新建工程ServiceTest。编写布局如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:padding="10dp"
tools:context="com.example.jared.servicetest.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/startService"
android:text="启动Service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/stopService"
android:text="停止Service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"/>
</LinearLayout>
这里实现了两个按钮启动和停止Service。接着新建一个MyService类,继承Service,代码如下:
package com.example.jared.servicetest;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* Created by jared on 16/2/18.
*/
public class MyService extends Service{
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "onCreate is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.d(TAG, "onStartCommand is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "onStartCommand is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "onDestroy is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
这里重写了onCreate方法,onStartCommand方法和onDestroy方法,这里在各个方法里加了些调试信息,接着我们再实现MainActivity的代码:
package com.example.jared.servicetest;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Button mStartServiceBtn;
private Button mStopServiceBtn;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mStartServiceBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startService);
mStopServiceBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopService);
mStartServiceBtn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
mStopServiceBtn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
}
private class myOnClickListener implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.startService:
Intent mStartIntent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), MyService.class);
startService(mStartIntent);
break;
case R.id.stopService:
Intent mSopIntent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), MyService.class);
stopService(mSopIntent);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
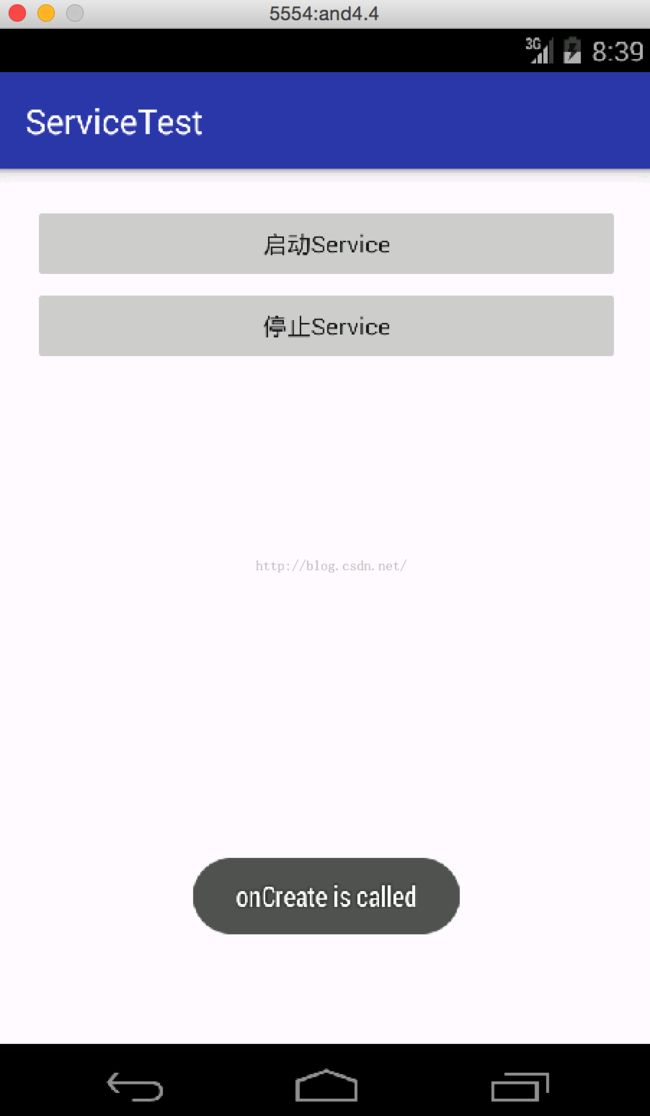
这里当按start的时候启动service,按stop的按钮的时候停止服务。先来运行下看下效果,先启动Service吧,效果如下:
从上可知先调用了onCreate方法,然后调用onStartCommand方法。然后我们看下在运行着的服务,打开手机的setting下的apps里的running:
从图可知ServiceTest已经在了,然后这个时候我们再点击启动Service的话,是不会再调用onCreate方法的,只会调用onStartCommand方法,只有stop了Service才可以,那我们先stop掉Service,效果如下:
如图调用了onDestroy方法。接着再启动Service的话,就和上述一样了。
上面代码中还有个方法那就是onBind方法了,从字面可以理解到这个方法是把Activity和Service绑定了,那样就可以通过Activity控制Service了。下面实现下代码,修改layout如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:padding="10dp"
tools:context="com.example.jared.servicetest.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/startService"
android:text="启动Service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/stopService"
android:text="停止Service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/startDownloadService"
android:text="绑定Service Download"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/stopDownloadService"
android:text="解绑Service Download"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/startGetProgressService"
android:text="绑定Service GetProgress"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/stopGetProgressService"
android:text="解绑Service GetProgress"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAllCaps="false"/>
</LinearLayout>
这里添加了启动下载的服务和获取当前下载状态的服务。Service中添加Binder,代码如下:
package com.example.jared.servicetest;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* Created by jared on 16/2/18.
*/
public class MyService extends Service{
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
private DownloadBinder mDownloadBinder = new DownloadBinder();
class DownloadBinder extends Binder {
private int progress = 0;
public void startDownload() {
Log.d(TAG, "startDownload is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "startDownload is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
progress = 0;
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0; i<=100; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
progress++;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
public int getProgress() {
Log.d(TAG, "getProgress is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "getProgress is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return progress;
}
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mDownloadBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "onCreate is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.d(TAG, "onStartCommand is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "onStartCommand is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "onDestroy is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
这里模拟了一个下载的过程,启动下载后,线程每秒更新个数值,然后可以通过getProgress去获取数值。接着修改MainActivity代码如下:
package com.example.jared.servicetest;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Button mStartServiceBtn;
private Button mStopServiceBtn;
private Button mBindService1Btn;
private Button mUnbindService1Btn;
private Button mBindService2Btn;
private Button mUnbindService2Btn;
private MyService.DownloadBinder downloadBinder;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mStartServiceBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startService);
mStopServiceBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopService);
mBindService1Btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startDownloadService);
mUnbindService1Btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopDownloadService);
mBindService2Btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startGetProgressService);
mUnbindService2Btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopGetProgressService);
mStartServiceBtn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
mStopServiceBtn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
mBindService1Btn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
mUnbindService1Btn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
mBindService2Btn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
mUnbindService2Btn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
}
private class myOnClickListener implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.startService:
Intent mStartIntent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), MyService.class);
startService(mStartIntent);
break;
case R.id.stopService:
Intent mSopIntent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), MyService.class);
stopService(mSopIntent);
break;
case R.id.startDownloadService:
Intent mBindIntent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), MyService.class);
bindService(mBindIntent, startDownloadInService, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
break;
case R.id.stopDownloadService:
unbindService(startDownloadInService);
break;
case R.id.startGetProgressService:
Intent mGetProgress = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), MyService.class);
bindService(mGetProgress, getProgressInService, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
break;
case R.id.stopGetProgressService:
unbindService(getProgressInService);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
private ServiceConnection startDownloadInService = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
downloadBinder = (MyService.DownloadBinder)iBinder;
downloadBinder.startDownload();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
}
};
private ServiceConnection getProgressInService = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
downloadBinder = (MyService.DownloadBinder)iBinder;
String progressValue = String.valueOf(downloadBinder.getProgress());
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "ProgressNow is:"+progressValue, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
}
};
}
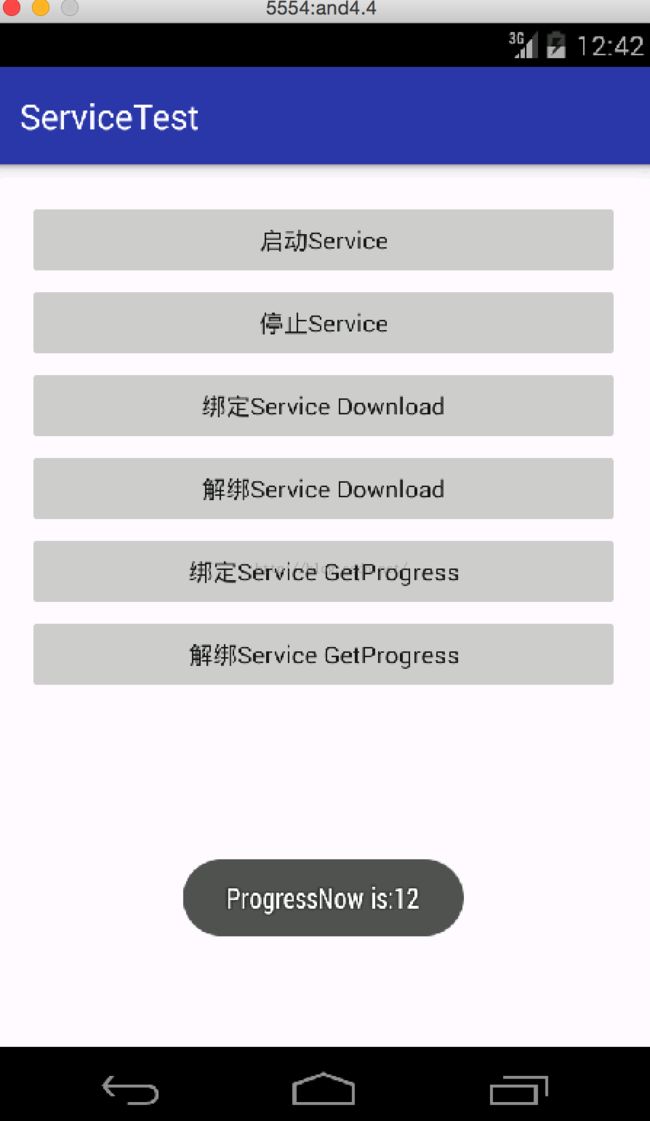
这里实例化了ServiceConnection,当通过bindService方法的时候,会通过ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected方法来调用Service中刚创建的下载类的方法。运行看下效果,先启动下载,再获取progress,运行效果如下:
这里要注意的是,服务是单例的,所谓单例就是只有一个实例,只能被new一次,不同进程也只能调用一次。当我们调用bind download的时候会直接调用Service的onCreate,当我们解绑的时候,也会调用Service的onDestroy方法。不过当我们调用了启动Service,又调用了binder的话,那就得ubind和stop方法都得调用。
上述当我们获取progress的时候,如果不解绑,那么之后的都是无效的。只有获取了一次,解绑了,再获取才有效。
android系统当内存不够的时候会自动回收优先级比较低的服务,所以为了让服务可以一直保存运行状态,而不会由于内存不足的原因导致被回收,就需要使用前台服务。前台服务就是一直运行并在状态栏显示,类似音乐播放器就会在状态栏一直保存着。简单修改Service代码如下:
package com.example.jared.servicetest;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.support.v4.app.NotificationCompat;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* Created by jared on 16/2/18.
*/
public class MyService extends Service{
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
private static final int NOTIFICATION_ID = 1;
private DownloadBinder mDownloadBinder = new DownloadBinder();
class DownloadBinder extends Binder {
private int progress = 0;
public void startDownload() {
Log.d(TAG, "startDownload is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "startDownload is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
progress = 0;
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0; i<=100; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
progress++;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
public int getProgress() {
Log.d(TAG, "getProgress is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "getProgress is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return progress;
}
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mDownloadBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "onCreate is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
NotificationCompat.Builder notification = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this);
notification.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
notification.setContentTitle("前台服务");
notification.setContentText("这是个前台服务");
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MainActivity.class);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, 0);
notification.setContentIntent(pendingIntent);
startForeground(NOTIFICATION_ID, notification.build());
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.d(TAG, "onStartCommand is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "onStartCommand is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy is called");
Toast.makeText(MyService.this, "onDestroy is called",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
stopForeground(true);
}
}
这里用到了notification,然后通过startForegroid方法来启动一个前台服务,运行看下效果:
从上图可知,当启动了前台服务的时候,在状态栏有个图标显示,当activity退出的时候,还是存在,只有当停止服务的时候才消失,那么就可以理解了为什么qq音乐退出了还在播放歌曲,还可以通过前台服务点击进入app。其实就是这个道理了。
关于Service就先学习到这里了。总算把Service学习好了。接下去继续学习别的知识点了。