C++ Primer 学习笔记_51_STL剖析(六):移除性算法(remove)、变序性算法(rotate)、排序算法(sort)、已序区间算法、数值算法(accumulate)
回顾
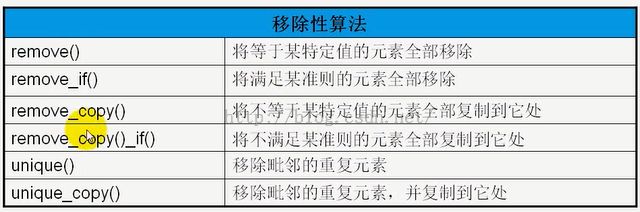
3、移除性算法是一种特殊的变动性算法。移除性算法是在一区间内移除某些元素,这些算法并不能改变元素的数量,它们只是以逻辑上的思考,将原本置于后面的“不需要移除元素”向前移动,覆盖那些被移除元素而已。它们都返回新区间的逻辑终点。移除性算法也可以在复制的过程中执行移除。注意,目标区间不能是关联式容器。
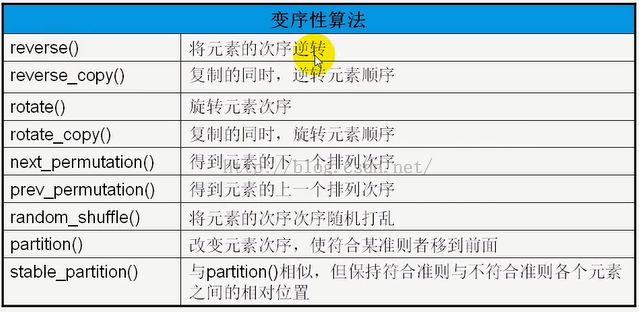
4、变序性算法改变元素次序,但不改变元素值。这些算法不能用于关联式容器,因为关联式容器中,元素有固定的次序。
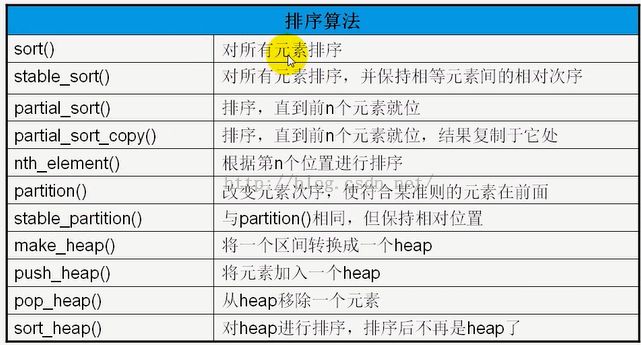
5、排序算法,排序算法是一种特殊的变序算法。但比一般的变序性算法更复杂,花费更多的时间
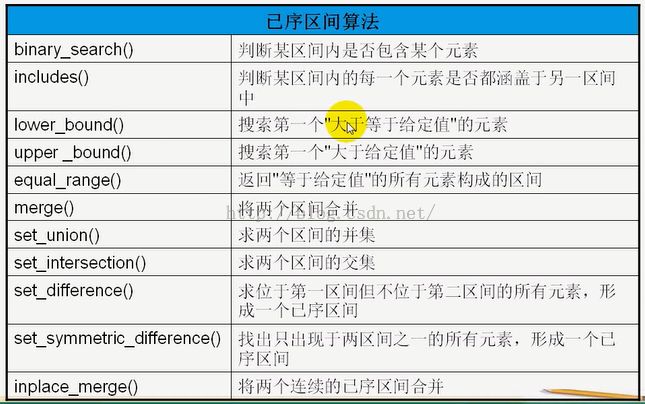
6、已序区间算法,一般来说这些算法的结果,仍然是已序的。
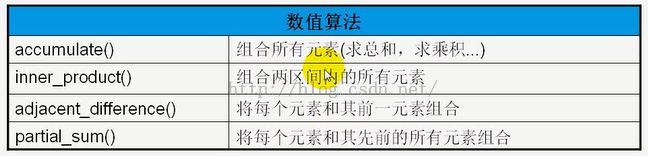
7、用来处理数值的算法,需要加上头文件 #include<numeric>
1、示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print_element(int n)
{
cout << n << ' ';
}
int main(void)
{
int a[] = { 1, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
vector<int> v(a, a + 6);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
/*remove(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout<<endl;*/
v.erase(remove(v.begin(), v.end(), 3), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
// TEMPLATE FUNCTION remove_copy
template < class _InIt,
class _OutIt,
class _Ty > inline
_OutIt _Remove_copy(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last,
_OutIt _Dest, const _Ty &_Val, _Range_checked_iterator_tag)
{
// copy omitting each matching _Val
_DEBUG_RANGE(_First, _Last);
_DEBUG_POINTER(_Dest);
for (; _First != _Last; ++_First)
if (!(*_First == _Val)) //如果相等,则if不成立,不做拷贝
*_Dest++ = *_First;
return (_Dest);
}
template < class _InIt,
class _OutIt,
class _Ty > inline
_OutIt unchecked_remove_copy(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last,
_OutIt _Dest, const _Ty &_Val)
{
// copy omitting each matching _Val
return _STD _Remove_copy(_CHECKED_BASE(_First), _CHECKED_BASE(_Last), _Dest, _Val,
_STD _Range_checked_iterator_tag());
}
// TEMPLATE FUNCTION remove
template < class _FwdIt,
class _Ty > inline
_FwdIt remove(_FwdIt _First, _FwdIt _Last, const _Ty &_Val)
{
// remove each matching _Val
_First = find(_First, _Last, _Val);
if (_First == _Last)
return (_First); // empty sequence, all done
else
{
// nonempty sequence, worth doing
_FwdIt _First1 = _First;
return (_STDEXT unchecked_remove_copy(++_First1, _Last, _First, _Val));
}
}
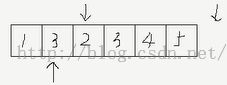
如下图所示:
假设现在想要remove 的元素是3,则传入到 _Remove_copy 函数的3个参数如上图第一行所示,Val 即3。
接着遍历First ~ Last 区间的元素,将非移除元素拷贝到前面,覆盖前面的元素,最后的指向如图,函数返回的是Dest 位置,如下代码所示:
for (; _First != _Last; ++_First)
if (!(*_First == _Val))
*_Dest++ = *_First;
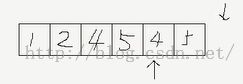
由上图可看出移除性算法并没有改变元素的个数,如果要真正删除,可以将remove 的返回值传入erase 进行删除,如:v.erase(remove(v.begin(), v.end(), 3), v.end()); 即会将后面两个元素4 和 5 删除掉。
在这里顺便提一下,erase 会使当前迭代器失效,但可以返回下一个迭代器,故如果需要在遍历中删除。
1、示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print_element(int n)
{
cout << n << ' ';
}
int main(void)
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
vector<int> v(a, a + 6);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
rotate(v.begin(), v.begin() + 2, v.end()); //将1 2 转到末尾
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
template <class ForwardIterator>
void rotate (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator middle,
ForwardIterator last)
{
ForwardIterator next = middle;
while (first != next)
{
swap (*first++, *next++);
if (next == last) next = middle;
else if (first == middle) middle = next;
}
}
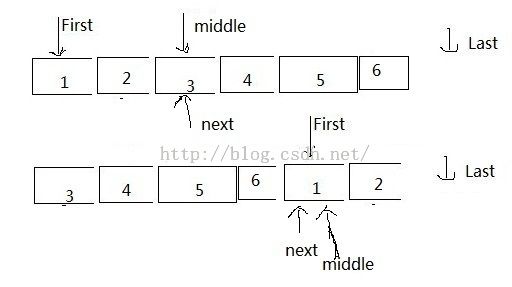
假设一个容器有 1 2 3 4 5 6 六个元素,现在想把 1 2 放到后面去,可以这样写 rotate(v.begin(), v.begin()+2, v.end()); 如下图所示:
1、示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print_element(int n)
{
cout << n << ' ';
}
bool my_greater(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
}
int main(void)
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
vector<int> v(a, a + 6);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
rotate(v.begin(), v.begin() + 2, v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), my_greater);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2、源代码分析
template<class _RanIt> inline
void sort(_RanIt _First, _RanIt _Last)
{
// order [_First, _Last), using operator<
_DEBUG_RANGE(_First, _Last);
std::_Sort(_CHECKED_BASE(_First), _CHECKED_BASE(_Last), _Last - _First);
}
template < class _RanIt,
class _Pr > inline
void sort(_RanIt _First, _RanIt _Last, _Pr _Pred)
{
// order [_First, _Last), using _Pred
_DEBUG_RANGE(_First, _Last);
_DEBUG_POINTER(_Pred);
std::_Sort(_CHECKED_BASE(_First), _CHECKED_BASE(_Last), _Last - _First, _Pred);
}
sort 重载了两个版本,第一个版本只有2个参数,默认按从小到大排序(using
operator<)
;第二个版本有三个参数,即可以自定义比较逻辑
(_Pred)。它们都调用了标准库的std::_Sort, 跟踪进去发现比较复杂,在_Sort 内会根据一些条件选择不同的排序方式,如标准库的堆排序,合并
排序,插入排序等等。站在使用的角度看,没必要去深究,但如果是想学习相关的排序,那是很好的资源。
四、已序区间算法 (lower_bound 、upper_bound)
使用这些算法的前提是区间已经是有序的。
1、示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print_element(int n)
{
cout << n << ' ';
}
int main(void)
{
int a[] = { 1, 10, 10, 14, 15, 16 };
vector<int> v(a, a + 6);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it;
it = lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 10);
if (it != v.end())
{
cout << it - v.begin() << endl;
}
it = upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 10);
if (it != v.end())
{
cout << it - v.begin() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
1 10 10 14 15 16
1
3
2、源代码分析
// TEMPLATE FUNCTION lower_bound
template < class _FwdIt,
class _Ty,
class _Diff > inline
_FwdIt _Lower_bound(_FwdIt _First, _FwdIt _Last, const _Ty &_Val, _Diff *)
{
// find first element not before _Val, using operator<
_DEBUG_ORDER_SINGLE(_First, _Last, true); //判断区间是否有序
_Diff _Count = 0;
_Distance(_First, _Last, _Count);
for (; 0 < _Count; )
{
// divide and conquer, find half that contains answer
_Diff _Count2 = _Count / 2;
_FwdIt _Mid = _First;
std::advance(_Mid, _Count2);
_DEBUG_ORDER_SINGLE(_Mid, _Last, false);
if (_DEBUG_LT(*_Mid, _Val))
_First = ++_Mid, _Count -= _Count2 + 1;
else
_Count = _Count2;
}
return (_First);
}
template < class _FwdIt,
class _Ty > inline
_FwdIt lower_bound(_FwdIt _First, _FwdIt _Last, const _Ty &_Val)
{
// find first element not before _Val, using operator<
_ASSIGN_FROM_BASE(_First,
_Lower_bound(_CHECKED_BASE(_First), _CHECKED_BASE(_Last), _Val, _Dist_type(_First)));
return _First;
}
lower_bound() 返回第一个“大于等于给定值" 的元素位置,其实还重载了另一个low_bound 版本,如下:
// TEMPLATE FUNCTION lower_bound WITH PRED
template < class _FwdIt,
class _Ty,
class _Diff,
class _Pr > inline
_FwdIt _Lower_bound(_FwdIt _First, _FwdIt _Last,
const _Ty &_Val, _Pr _Pred, _Diff *)
由于是已序区间,所以函数内用的是二分查找,而两个版本主要的代码不同在于:
_DEBUG_LT(*_Mid, _Val)
_DEBUG_LT_PRED(_Pred, *_Mid, _Val)
upper_bound 与 lower_bound 类似,不过返回的是第一个”大于给定值“ 的元素位置。
五、数值算法(accumulate)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
void print_element(int n)
{
cout << n << ' ';
}
int mult(int a, int b)
{
return a * b;
}
int main(void)
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
vector<int> v(a, a + 5);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
// 累加,默认,必须有三个参数
cout << accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0) << endl; //1+...+5 + 0,再加上0
// 累乘
cout << accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 1, mult) << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1 2 3 4 5
15
120
2、源代码分析
// TEMPLATE FUNCTION accumulate
template < class _InIt,
class _Ty > inline
_Ty _Accumulate(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, _Ty _Val)
{
// return sum of _Val and all in [_First, _Last)
_DEBUG_RANGE(_First, _Last);
for (; _First != _Last; ++_First)
_Val = _Val + *_First;
return (_Val);
}
template < class _InIt,
class _Ty > inline
_Ty accumulate(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, _Ty _Val)
{
// return sum of _Val and all in [_First, _Last)
return _Accumulate(_CHECKED_BASE(_First), _CHECKED_BASE(_Last), _Val);
}
// TEMPLATE FUNCTION accumulate WITH BINOP
template < class _InIt,
class _Ty,
class _Fn2 > inline
_Ty _Accumulate(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, _Ty _Val, _Fn2 _Func)
{
// return sum of _Val and all in [_First, _Last), using _Func
_DEBUG_RANGE(_First, _Last);
_DEBUG_POINTER(_Func);
for (; _First != _Last; ++_First)
_Val = _Func(_Val, *_First);
return (_Val);
}
template < class _InIt,
class _Ty,
class _Fn2 > inline
_Ty accumulate(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, _Ty _Val, _Fn2 _Func)
{
// return sum of _Val and all in [_First, _Last), using _Func
return _Accumulate(_CHECKED_BASE(_First), _CHECKED_BASE(_Last), _Val, _Func);
}
accumulate 重载了两个版本,第一个版本实现的是累加,第二个版本带_Func 参数,可以自定义计算,比如累乘等。代码都比较好理解,就不赘述
了。
参考:
C++ primer 第四版
Effective C++ 3rd
C++编程规范