Hadoop Compression解压缩架构的学习
Hadoop的Compressor解压缩模块是Hadoop Common IO模块中又一大的模块。虽然说在现实生活中,我们使用压缩工具等的使用场景并不是那么多。或许在我们潜在的意识里,压缩的概念就停留在一些压缩种类上,zip,gzip,bizp等等不同类型的压缩,分别具有不同的压缩比,效率比等等。也许当你看完本篇本人对于Hadoop的压缩框架的学习之后,你一定会有所收获。
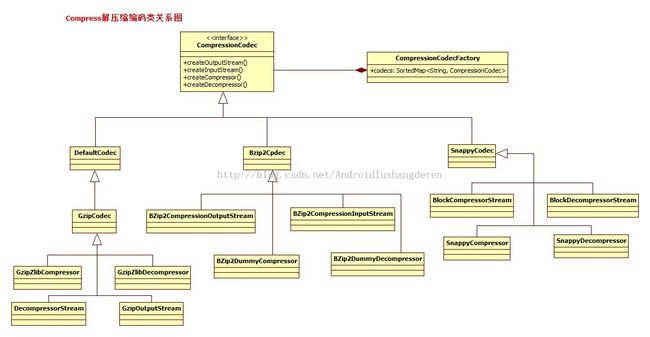
压缩对于数据的传输室至关重要的,同样对于存储来说也大大的提高了效率,在Hadoop系统中目前支持的压缩算法包括1,gzip 2.bzip 3.snappy4.default系统默认算法。这些压缩工具的体现都是通过一个叫CompressionCodec的对象来体现的。先来看看这个类:
/**
* This class encapsulates a streaming compression/decompression pair.
*/
public interface CompressionCodec {
CompressionOutputStream createOutputStream(OutputStream out) throws IOException;
CompressionOutputStream createOutputStream(OutputStream out,
Compressor compressor) throws IOException;
Class<? extends Compressor> getCompressorType();
Compressor createCompressor();
CompressionInputStream createInputStream(InputStream in) throws IOException;
CompressionInputStream createInputStream(InputStream in,
Decompressor decompressor) throws IOException;
Class<? extends Decompressor> getDecompressorType();
Decompressor createDecompressor();
String getDefaultExtension();
}这是一个接口,里面定义了很多的方法,我主要把他归为2类,
1个是Compressor和Decompressor解压缩的构造,
1个是CompressionInputStream,CompressionOutputStream压缩输入输出流。
其实2者很像,因为压缩输入输出流的很多操作也是基于上面的压缩器,解压器的操作实现的。具体压缩算法的表现都是继承与这个基类。看一下比较庞大的结构图:
可以看到在每种Codec子类中,都会有解压缩器的实现和压缩输入输出流的构造。然后把这种压缩算法类保存在了一个Codec的工厂中,通过统一的接口调用。
public class CompressionCodecFactory {
public static final Log LOG =
LogFactory.getLog(CompressionCodecFactory.class.getName());
/**
* A map from the reversed filename suffixes to the codecs.
* This is probably overkill, because the maps should be small, but it
* automatically supports finding the longest matching suffix.
* 所有的解压缩编码类放入 codecs Map图中,CompressionCodec是一个基类,
* 允许添加上其所继承的子类
*/
private SortedMap<String, CompressionCodec> codecs = null;初始化的时候,可以根据配置加入自己希望的压缩算法种类:
/**
* Find the codecs specified in the config value io.compression.codecs
* and register them. Defaults to gzip and zip.
* 根据配置初始化压缩编码工厂,默认添加的是gzip和zip编码类
*/
public CompressionCodecFactory(Configuration conf) {
codecs = new TreeMap<String, CompressionCodec>();
List<Class<? extends CompressionCodec>> codecClasses = getCodecClasses(conf);
if (codecClasses == null) {
//如果没有编码类的设置,则加入gzip,defaultCode
addCodec(new GzipCodec());
addCodec(new DefaultCodec());
} else {
Iterator<Class<? extends CompressionCodec>> itr = codecClasses.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
CompressionCodec codec = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(itr.next(), conf);
addCodec(codec);
}
}
}然后是从工厂中取出压缩算法工具的时候了,通过名字获取,其实这种模式类似于享受 模式,达到对象的复用效果了。
/**
* Find the relevant compression codec for the given file based on its
* filename suffix.
* @param file the filename to check
* @return the codec object
*/
public CompressionCodec getCodec(Path file) {
CompressionCodec result = null;
if (codecs != null) {
String filename = file.getName();
String reversedFilename = new StringBuffer(filename).reverse().toString();
SortedMap<String, CompressionCodec> subMap =
codecs.headMap(reversedFilename);
if (!subMap.isEmpty()) {
String potentialSuffix = subMap.lastKey();
//根据比对名字,从codecs Map中取出对应的CompressionCodec
if (reversedFilename.startsWith(potentialSuffix)) {
result = codecs.get(potentialSuffix);
}
}
}
return result;
} 下面应该仔细分析的是具体解压缩怎么实现的步骤,我从3种算法中选了zlib/gzip算法作为底层实现例子。他们都先继承了下面这个接口:
/**
* Specification of a stream-based 'compressor' which can be
* plugged into a {@link CompressionOutputStream} to compress data.
* This is modelled after {@link java.util.zip.Deflater}
*
*/
public interface Compressor {
/**
* Sets input data for compression.
* This should be called whenever #needsInput() returns
* <code>true</code> indicating that more input data is required.
* 输入待压缩的数据
*
* @param b Input data
* @param off Start offset
* @param len Length
*/
public void setInput(byte[] b, int off, int len);
/**
* Returns true if the input data buffer is empty and
* #setInput() should be called to provide more input.
* 判断缓冲区中能否再输入数据
*
* @return <code>true</code> if the input data buffer is empty and
* #setInput() should be called in order to provide more input.
*/
public boolean needsInput();
/**
* Sets preset dictionary for compression. A preset dictionary
* is used when the history buffer can be predetermined.
*
* @param b Dictionary data bytes
* @param off Start offset
* @param len Length
*/
public void setDictionary(byte[] b, int off, int len);
/**
* Return number of uncompressed bytes input so far.
* 返回未压缩的数据的字节长度
*/
public long getBytesRead();
/**
* Return number of compressed bytes output so far.
* 返回已压缩字节的大小
*/
public long getBytesWritten();
/**
* When called, indicates that compression should end
* with the current contents of the input buffer.
* 代表输入的结束
*/
public void finish();
/**
* Returns true if the end of the compressed
* data output stream has been reached.
* @return <code>true</code> if the end of the compressed
* data output stream has been reached.
* 判断压缩器中还有没有未取出的压缩后的数据
*/
public boolean finished();
/**
* Fills specified buffer with compressed data. Returns actual number
* of bytes of compressed data. A return value of 0 indicates that
* needsInput() should be called in order to determine if more input
* data is required.
* 压缩处理方法,将输入的压缩数据压缩处理后输出到传入的输出缓冲中
*
* @param b Buffer for the compressed data
* @param off Start offset of the data
* @param len Size of the buffer
* @return The actual number of bytes of compressed data.
*/
public int compress(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException;
/**
* Resets compressor so that a new set of input data can be processed.
* 压缩器重置方法
*/
public void reset();
/**
* Closes the compressor and discards any unprocessed input.
* 关闭压缩器,一般在结束的时候调用
*/
public void end();
/**
* Prepare the compressor to be used in a new stream with settings defined in
* the given Configuration
* 根据配置重新初始化压缩器的实现
*
* @param conf Configuration from which new setting are fetched
*/
public void reinit(Configuration conf);
}
里面的每一个方法都很关键,因为后面压缩,解压操作都是基于上面的函数实现。在这里,先看一下zlib中的一些关于压缩的变量的设置:
public class ZlibCompressor implements Compressor {
//默认的缓冲区64k
private static final int DEFAULT_DIRECT_BUFFER_SIZE = 64*1024;
// HACK - Use this as a global lock in the JNI layer
private static Class clazz = ZlibCompressor.class;
private long stream;
/**
* 定义了压缩水平,可以是无损压缩,可以是追求效率的快速的压缩等等类型
*/
private CompressionLevel level;
/**
* 定义了压缩策略,有比如常见的哈弗曼编码方式,filterd方式,或者其他
*/
private CompressionStrategy strategy;
/**
* 定于了压缩的头部格式信息,比如一般前面都会有个checksum校验和的信息,当然可以选择NO_HEAEDER
*/
private final CompressionHeader windowBits;还有缓冲区的设置,定义了未压缩缓冲区的设置,已压缩缓冲区等等:
private int directBufferSize; private byte[] userBuf = null; private int userBufOff = 0, userBufLen = 0; //未压缩的缓冲 private Buffer uncompressedDirectBuf = null; private int uncompressedDirectBufOff = 0, uncompressedDirectBufLen = 0; //已压缩缓冲数据 private Buffer compressedDirectBuf = null; //输入结束标识,压缩结束标识 private boolean finish, finished;默认zlib压缩器的构造:
/**
* Creates a new compressor with the default compression level.
* Compressed data will be generated in ZLIB format.
* 默认构造出压缩器,压缩水平,策略等都是默认值
*/
public ZlibCompressor() {
this(CompressionLevel.DEFAULT_COMPRESSION,
CompressionStrategy.DEFAULT_STRATEGY,
CompressionHeader.DEFAULT_HEADER,
DEFAULT_DIRECT_BUFFER_SIZE);
}最后悔跑到一个大的重载函数上:
public ZlibCompressor(CompressionLevel level, CompressionStrategy strategy,
CompressionHeader header, int directBufferSize) {
this.level = level;
this.strategy = strategy;
this.windowBits = header;
stream = init(this.level.compressionLevel(),
this.strategy.compressionStrategy(),
this.windowBits.windowBits());
//设置直接缓冲区的大小为64*1024个字节
this.directBufferSize = directBufferSize;
//申请2个一样大小的64k的缓冲区
uncompressedDirectBuf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(directBufferSize);
compressedDirectBuf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(directBufferSize);
//把压缩缓冲的位置挪到最后面
compressedDirectBuf.position(directBufferSize);
}上面的关键是定义了2个64k的缓冲区,我们初步可以断定,压缩的实现过程一定是从用户的输入,放入uncompressedDirectBuf,调用Compress压缩方法后转入compressedDirectBuf,最后拷贝到外界的缓冲中。
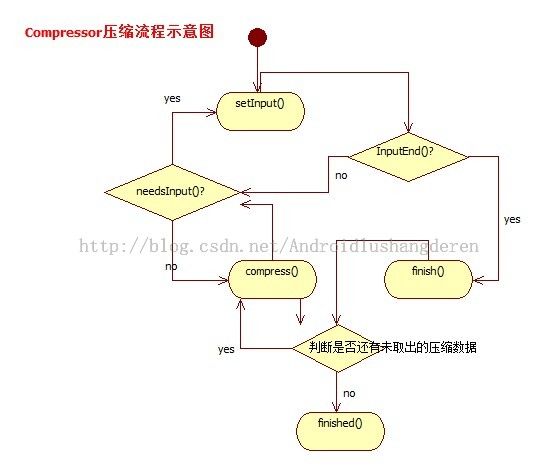
下面是一个压缩器中的压缩步骤
1.调用setInput()向里面输入待压缩数据
2.调用needsInput()判断是否能够输入,如果不能输入,则调用Compress取出已压缩的数据,才能再次输入数据
3.执行上述2步骤直到全部输入数据,调用finish(),代表输入结束
4.最后调用Compress连续取出压缩好的数据直到调用finished()方法判断已压缩缓冲中无数据了。
下面是一个流程图
流程搞清楚了之后,我们才能知道里面到底是怎么做的。首先setInput()方法,
public synchronized void setInput(byte[] b, int off, int len) {
if (b== null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (off < 0 || len < 0 || off > b.length - len) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
//设置用户缓冲数据变量
this.userBuf = b;
this.userBufOff = off;
this.userBufLen = len;
setInputFromSavedData();
// Reinitialize zlib's output direct buffer
//重新初始化已压缩缓冲的位置
compressedDirectBuf.limit(directBufferSize);
compressedDirectBuf.position(directBufferSize);
}里面关键的方法是setInputFromSavedData()
synchronized void setInputFromSavedData() {
uncompressedDirectBufOff = 0;
//更新未压缩缓冲数据的长度为用户buf的长度
uncompressedDirectBufLen = userBufLen;
if (uncompressedDirectBufLen > directBufferSize) {
//如果超过最大值,则变为最大值
uncompressedDirectBufLen = directBufferSize;
}
// Reinitialize zlib's input direct buffer
uncompressedDirectBuf.rewind();
//将用户数据存入uncompressedDirectBuf
((ByteBuffer)uncompressedDirectBuf).put(userBuf, userBufOff,
uncompressedDirectBufLen);
// Note how much data is being fed to zlib
//加上用户缓冲区的偏移量
userBufOff += uncompressedDirectBufLen;
//减少用户缓冲区的数据长度
userBufLen -= uncompressedDirectBufLen;
}就这样把用户数据放入了uncompressedDirectBuf中了,但是有最大缓冲值的限制。下面看看needsInput()判断是否能输入的判断:
public boolean needsInput() {
// Consume remaining compressed data?
if (compressedDirectBuf.remaining() > 0) {
//如果已压缩缓冲区中有数据,必须先取出其中的数据,才能输入
return false;
}
// Check if zlib has consumed all input
if (uncompressedDirectBufLen <= 0) {
//判断未压缩缓冲的大小是否小于等于0
// Check if we have consumed all user-input
if (userBufLen <= 0) {
//判断之前用户的缓冲数据都已经出来完毕了
return true;
} else {
setInputFromSavedData();
}
}
return false;
}
里面经过了很多层的判断,比如第一个过滤条件就是首先取出压缩好后的数据,才能允许再次输入,而且要解决掉上次的输入数据,我看完这段代码之后,跟原先的根据未压缩缓冲区是否满不满来判断能否输入的设想完全不一样,因为某些资料就是这么说的,一想还挺有道理的,看完代码之后才发现真理不是这样的。如果是判断未压缩缓冲区是否满判断,第二个判断直接就不符号,返回false了。
下面是finish()代表输入的结束标记,操作很简单:
public synchronized void finish() {
//输入结束标识改为true
finish = true;
} 下面是关键的Compress压缩操作的执行了:
public synchronized int compress(byte[] b, int off, int len)
throws IOException {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (off < 0 || len < 0 || off > b.length - len) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
int n = 0;
// Check if there is compressed data
//判断已压缩缓冲区中是否还有数据
n = compressedDirectBuf.remaining();
if (n > 0) {
n = Math.min(n, len);
//取出放入传入的输出缓冲中
((ByteBuffer)compressedDirectBuf).get(b, off, n);
return n;
}
// Re-initialize the zlib's output direct buffer
//如果已压缩缓冲中没有数据了,重新设置compressedDirectBuf
compressedDirectBuf.rewind();
compressedDirectBuf.limit(directBufferSize);
// Compress data
//调用压缩数据的native方法,最后未压缩的数据就会被压缩后转入已压缩的缓冲中
n = deflateBytesDirect();
compressedDirectBuf.limit(n);
// Get atmost 'len' bytes
n = Math.min(n, len);
//将此时压缩好后的数据再从已压缩缓冲中取出
((ByteBuffer)compressedDirectBuf).get(b, off, n);
return n;
}操作比较多,归归类
1.如果已压缩缓冲区中还有数据,先取出compressedDirectBuf到输出缓冲中,就是传入的b中,操作结束
2.如果已压缩缓冲区中没有数据,则会deflateBytesDirect()调用方法压缩数据,然后再执行1操作,取出缓冲数据,操作结束
我们找到关键的deflateBytesDirect方法,发现如下:
private native static void initIDs();
private native static long init(int level, int strategy, int windowBits);
private native static void setDictionary(long strm, byte[] b, int off,
int len);
private native int deflateBytesDirect();
private native static long getBytesRead(long strm);
private native static long getBytesWritten(long strm);
private native static void reset(long strm);
private native static void end(long strm);
发现了一堆的native的方法,也就是说,这些更加底层的实现是通过JNI的方式被调用的,但是我们基本能猜到,在这个方法里就是2个缓冲区方法的压缩转移处理。最后一个方法是判断是否结束方法
public synchronized boolean finished() {
// Check if 'zlib' says its 'finished' and
// all compressed data has been consumed
//判断压缩过程是佛结束,判断已压缩缓冲中是否还有未取出的数据
return (finished && compressedDirectBuf.remaining() == 0);
}
以上就是压缩操作的主要步骤,解压操作思路类似,不展开分析了。