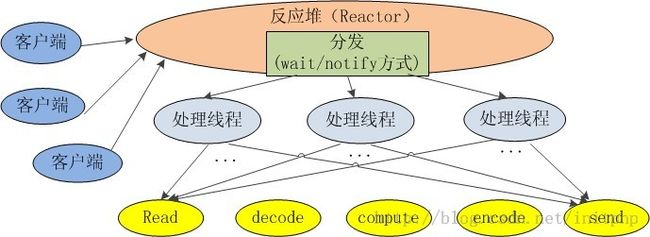
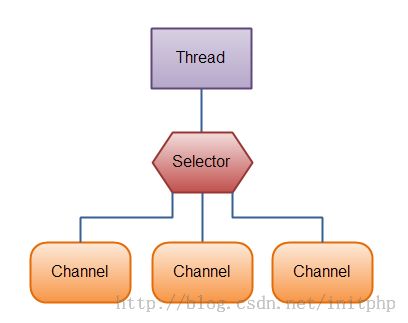
Java深入 - Java Socket和NIO
关于TCP和UDP协议
TCP:是一种面向连接的保证可靠传输的协议。通过TCP协议传输,得到的是一个顺序的无差错的数据流。发送方和接收方的成对的两个socket之间必须建 立连接,以便在TCP协议的基础上进行通信,当一个socket(通常都是server socket)等待建立连接时,另一个socket可以要求进行连接,一旦这两个socket连接起来,它们就可以进行双向数据传输,双方都可以进行发送 或接收操
UDP:是一种无连接的协议,每个数据报都是一个独立的信息,包括完整的源地址或目的地址,它在网络上以任何可能的路径传往目的地,因此能否到达目的地,到达目的地的时间以及内容的正确性都是不能被保证的。
比较:
TCP在网络通信上有极强的生命力,例如远程连接(Telnet)和文件传输(FTP)都需要不定长度的数据被可靠地传输。但是可靠的传输是要付出代价的,对数据内容正确性的检验必然占用计算机的处理时间和网络的带宽,因此TCP传输的效率不如UDP高。
UDP操作简单,而且仅需要较少的监护,因此通常用于局域网高可靠性的分散系统中client/server应用程序。例如视频会议系统,并不要求音频视频数据绝对的正确,只要保证连贯性就可以了,这种情况下显然使用UDP会更合理一些。
Java Socket编程
网络上的两个程序通过一个双向的通讯连接实现数据的交换,这个双向链路的一端称为一个Socket。Socket通常用来实现客户方和服务方的连接。Socket是TCP/IP协议的一个十分流行的编程界面,一个Socket由一个IP地址和一个端口号唯一确定。在Java环境下,Socket编程主要是指基于TCP/IP协议的网络编程。
Socket通信过程
Socket服务端监听某个端口是否有连接请求。当客户端发出Connect连接请求,并且和服务端的IP和端口建立连接,服务端就会向客户端发挥Accept接受消息的请求。四个步骤:
1. 创建Socket
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8090);
2. 打开socket连接的输出和输入流
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream(); //获取输入流 OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream(); //获取输出流
3. 进行数据读写 Read和Write
//使用BufferReader的方式读取输入流
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
//打印出输出流
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(out, true);
writer.println("Thread ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
//读取一行客户端的输入
String line = reader.readLine();
4. 关闭Socket
serverSocket.close();
Socket创建的方法
Socket常用的创建方法在java.net包中。提供了一些常用的创建方法:
Socket(InetAddress address, int port);
Socket(InetAddress address, int port, boolean stream);
Socket(String host, int prot);
Socket(String host, int prot, boolean stream);
Socket(SocetImpl impl)
Socket(String host, int port, InetAddress localAddr, int localPort)
Socket(InetAddress address, int port, InetAddress localAddr, int localPort)
ServerSocket(int port);
ServerSocket(int port, int backlog);
ServerSocket(int port, int backlog, InetAddress bindAddr)
直接用Java Socket最大的弊端
1. 直接使用socket进行编程,因为socket是阻塞式的,所以如果你直接编写代码的话,不能让多个用户同时进行连接到你的服务端
2. 如果我们采用线程的方式,来支持多用户(客户端)的连接,但是当用户连接数非常多了之后,需要N多的线程,服务器性能会下降
看一个服务器端的Socket实现例子:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Java Scoket Server Run...");
//创建一个固定大小的线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
try {
//启动一个8090端口的Socket服务
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8090);
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); //wait等待
pool.execute(new MyRunable(socket)); //线程池
}
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
pool.shutdown(); //关闭线程池
}
}
}
public class MyRunable implements Runnable {
private Socket socket = null;
public MyRunable(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream(); //获取输入流
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream(); //获取输出流
//使用BufferReader的方式读取输入流
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
//打印出输出流
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(out, true);
writer.println("Thread ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
//读取一行客户端的输入
String line = reader.readLine();
//如果客户端输入bye 则退出
while (!"bye".equals(line)) {
writer.println("ECHO:" + line);
line = reader.readLine();
}
reader.close();
writer.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
简单的客户端例子:
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
String host = "192.168.136.100"; //要连接的服务端IP地址
int port = 8787; //要连接的服务端对应的监听端口
Socket client = new Socket(host, port);
InputStream in = client.getInputStream();
OutputStream out = client.getOutputStream();
String str = "Hello Wolrd[]woasodsadsadsad";
out.write(str.getBytes());
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int n = in.read(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, n));
String str2 = "----------[]sadasdsad=======[]";
out.write(str2.getBytes());
byte[] bytes2 = new byte[1024];
int n2 = in.read(bytes2);
System.out.println(new String(bytes2, 0, n2));
byte[] bytes3 = new byte[1024];
int n3 = in.read(bytes3);
System.out.println(new String(bytes3, 0, n3));
in.close();
client.close();
}
Java Nio
Java Nio原理
NIO是非阻塞的IO。
1. NIO有一个专门的线程来处理多个IO。这样就保障了线程资源的合理利用。
2.事件驱动的形式。事件到了才会触发。
3. 线程通讯:线程之间通过 wait,notify 等方式通讯。保证每次上下文切换都是有意义的。减少无谓的线程切换。
Java NIO的重要的核心模块
1. Channels
2. Buffers
3. Selectors
Channels 有点像流,可以将数据写入buffers,也可以读取到Channels,也可以读取到,主要包含:FileChannel,DatagramChannel,SocketChannel,ServerSocketChannel。我们这里主要将ServerSocketChannel。
Buffers包含:ByteBuffer,CharBuffer,DoubleBuffer,FloatBuffer,IntBuffer,LongBuffer,ShortBuffe。
Selectors:Selector允许单线程处理多个 Channel。图:
Selector四种事件名称
| 事件名 | 对应值 |
| 服务端接收客户端连接事件 | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT(16) |
| 客户端连接服务端事件 | SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT(8) |
| 读事件 | SelectionKey.OP_READ(1) |
| 写事件 | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE(4) |
Selector能检测到一个或者多个通道上的事件。例如检测到客户端连接上来的信息SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT,例如检测到服务端可以读取的事件等。
例如注册一个读取事件:
channel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); //注册一个读取时间
一个简单的NIO Server和Client的例子
public class Test {
private Selector selector;
protected Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
protected CharsetEncoder charsetEncoder = charset.newEncoder();
protected CharsetDecoder charsetDecoder = charset.newDecoder();
/**
* 主函数
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
Test test2 = new Test();
test2.init(); //初始化
test2.listen(); //监听
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
private void init() throws IOException {
System.out.println("Java Nio Scoket Server Run...");
selector = Selector.open(); //打开选择器
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 获得一个Socket通道
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);// 设置通道为非阻塞
serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9000)); //绑定端口
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //注册SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT事件。
}
private void listen() throws IOException {
while (true) {
selector.select();
Iterator ite = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) ite.next();
ite.remove();
//接受连接事件,上面注册的SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT事件
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel channel = serverChannel.accept();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(new String("Welcome to nio socket").getBytes()));
channel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); //注册一个读取事件
System.out.println("有一个客户端连接上来了");
//读取时间,上面注册的SelectionKey.OP_READ事件
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
//当通道中有数据过来的时候,就执行这边的读取代码
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //一次读取1024个字符
byteBuffer.clear();
long i = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if (i == -1) {
socketChannel.close(); //读取失败
} else {
//读取
byteBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.remaining()];
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(body);
//回写
String x = "Hello";
byte[] response = x.getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(response.length);
writeBuffer.put(response);
writeBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
}
}
}
}
}
}
客户端:
public class Test3 {
private Selector selector;
protected Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
protected CharsetDecoder charsetDecoder = charset.newDecoder();
private SocketChannel channel;
public static final Test3 test3 = new Test3();
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Test3.test3.init(); //初始化
Test3.test3.listen(); //监听
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}).start();
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
test3.write("Yes.."); //发送一个数据
test3.write("Yes111");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public void init() throws IOException {
this.selector = Selector.open();
// 获得一个Socket通道
channel = SocketChannel.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9000)); //连接到一个端口
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); //注册一个连接事件
}
public void write(String str) throws IOException {
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(new String(str).getBytes()));
}
public void listen() throws IOException {
while (true) {
selector.select();
Iterator ite = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) ite.next();
ite.remove();
//是否连接事件,上面注册的SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT
if (key.isConnectable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
// 如果正在连接,则完成连接
if (channel.isConnectionPending()) {
channel.finishConnect();
}
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(new String("Hello World").getBytes()));
channel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); //连接建立成功,注册一个read事件
System.out.println("连接了...");
//读取事件
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
byteBuffer.clear();
long i = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if (i == -1) {
socketChannel.close();
} else {
byteBuffer.flip();
String msg = charsetDecoder.decode(byteBuffer).toString();
System.out.println("MSG:" + msg);
}
}
}
}
}
}