C++ Primer 学习笔记_7_标准模板库_multiset多重集合容器
C++ Primer 学习笔记_7_标准模板库_multiset多重集合容器
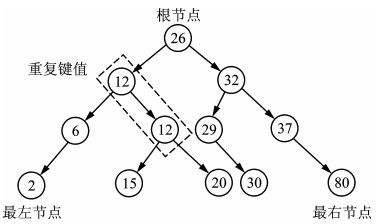
多重集合容器multiset与set一样,也是使用红黑树来组织元素数据的,唯一不用的是,multiset允许重复的元素键值插入。其结构示意图如下:
1、multiset元素插入
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
multiset<string> str;
str.insert("abc");
str.insert("123");
str.insert("111");
str.insert("aaa");
str.insert("123");
//中序遍历集合中所有的元素
for(multiset<string>::iterator iter = str.begin(); iter!=str.end(); iter++)
cout << *iter << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
111 123 123 aaa abc
2、multiset元素删除
(1)、采用erase()方法可以删除multiset对象中某个值所有重复的元素,并返回删除元素的个数。
(2)、采用clear()方法可以清空元素。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
multiset<string> str;
str.insert("abc");
str.insert("123");
str.insert("111");
str.insert("aaa");
str.insert("123");
//中序遍历集合中所有的元素
for(multiset<string>::iterator iter = str.begin(); iter!=str.end(); iter++)
cout << *iter << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
int n = str.erase("123");
cout << "删除元素的个数: " << n << endl;
cout << "输出删除后剩余元素" << endl;
for(multiset<string>::iterator iter = str.begin(); iter!=str.end(); iter++)
cout << *iter << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
str.clear();
cout << "输出删除后剩余元素" << endl;
for(multiset<string>::iterator iter = str.begin(); iter!=str.end(); iter++)
cout << *iter << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
111 123 123 aaa abc
删除元素的个数: 2
输出删除后剩余元素
111 aaa abc
输出删除后剩余元素
3、查找元素find()
使用find()方法查找元素:
如果找到,则返回该元素的迭代器位置(如果该元素存在重复,则返回第一个元素重复元素的迭代器位置);如果找到,则返回该元素的迭代器位置(如果该元素存在重复,则返回第一个元素重复元素的迭代器位置);
如果没有找到,则返回end()迭代器位置。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
multiset<string> str;
str.insert("abc");
str.insert("123");
str.insert("111");
str.insert("aaa");
str.insert("123");
//中序遍历集合中所有的元素
for(multiset<string>::iterator iter =str.begin(); iter!= str.end(); iter++)
cout << *iter << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
multiset<string>::iterator iter;
iter = str.find("123");
if(iter != str.end()) //找到
cout << *iter << endl;
else //没有找到
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
iter = str.find("bbb");
if(iter != str.end())
cout << *iter << endl;
else
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
111 123 123 aaa abc
123
没有找到
4、自定义比较函数
默认情况下,按照键值由小到大的顺序插入元素。由于内部数据结构都是红黑树,因此编写比较函数与set是一致的。编写方法有两种,
(1)如果元素不是结构体,那么可以编写比较函数。下面实现键值由大到小的顺序将元素插入mutlset中:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct myComp
{
bool operator()(string a, string b)
{
return a > b;
}
};
int main()
{
multiset<string, myComp> str;
str.insert("abc");
str.insert("123");
str.insert("111");
str.insert("aaa");
str.insert("123");
//中序遍历集合中所有的元素
for(multiset<string, myComp>::iterator iter = str.begin(); iter!=str.end(); iter++)
cout << *iter <<"";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
abc aaa 123 123 111
(2)如果元素是结构体,那么,可以直接把比较函数写在结构体里面。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Info
{
string name;
float score;
bool operator < (Info a) const
{
return a.score < score;
}
};
int main()
{
multiset<Info> str;
//插入元素
Info info;
info.name = "Jack";
info.score = 60;
str.insert(info);
info.name = "Bomi";
info.score = 80;
str.insert(info);
info.name = "Peti";
info.score = 80;
str.insert(info);
info.name = "Kity";
info.score = 70;
str.insert(info);
for(multiset<Info>::iterator iter = str.begin(); iter !=str.end(); iter++)
cout << (*iter).name<< ""<< (*iter).score << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
Bomi 80
Peti 80
Kity 70
Jack 60