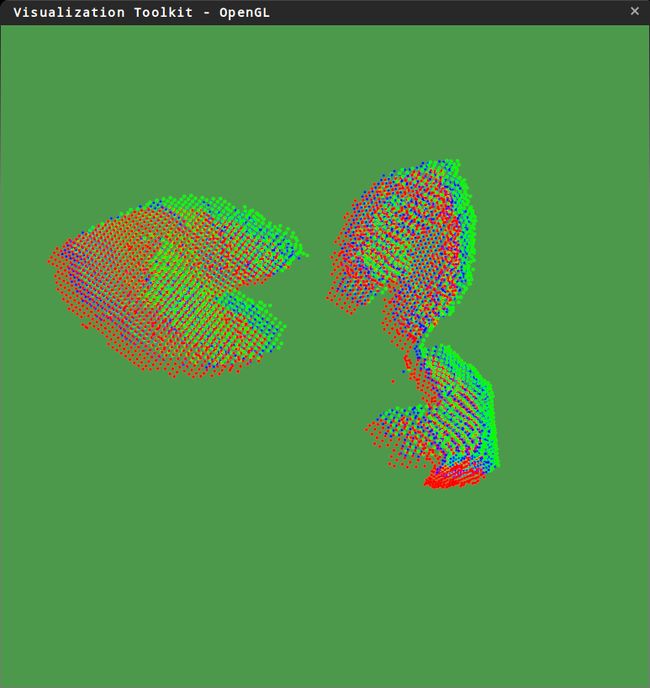ICP in VTK
提要
ICP算法简介
ICP算法最初由Besl和Mckey提出,是一种基于轮廓特征的点配准方法。基准点在CT图像坐标系及世界坐标系下的坐标点集P = {Pi, i = 0,1, 2,…,k}及U = {Ui,i=0,1,2,…,n}。其中,U与P元素间不必存在一一对应关系,元素数目亦不必相同,设k≥n。配准过程就是求取2个坐标系间的旋转和平移变换矩阵,使得来自U与P的同源点间距离最小。其过程如下:
(1)计算最近点,即对于集合U中的每一个点,在集合P中都找出距该点最近的对应点,设集合P中由这些对应点组成的新点集为Q = {qi,i = 0,1,2,…,n}。
(2)采用最小均方根法,计算点集U与Q之间的配准,使得到配准变换矩阵R,T,其中R是3×3的旋转矩阵,T是3×1的平移矩阵。
(3)计算坐标变换,即对于集合U,用配准变换矩阵R,T进行坐标变换,得到新的点集U1,即U1 = RU + T
(4)计算U1与Q之间的均方根误差,如小于预设的极限值ε,则结束,否则,以点集U1替换U,重复上述步骤。
数学描述(感觉更好理解一些)
VTK中有一个类vtkIterativeClosestPointTransform实现了ICP算法,并将ICP算法保存在一个4×4的齐次矩阵中。下面就跟着官方demo来实践一下。
安装库
升级cmake
编译VTK6.1需要cmake2.8.8以上。
下载cmake2.8.12.2
解压终端cd进目录
sudo ./bootstrap
make
sudo make install
编译VTK6.1
官网下载解压终端cd进目录
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo make install
实战
ICP的输入是两个点云,这两个点云必须是针对同一个场景,而且必须有重叠部分。
这里关乎格式转换、读取的问题的。,对新手来说,xyz是做好的读取文件了,只含有坐标信息,而且是文本信息。如果不是.xyz格式,用meshlab导出一个ply,把文件头部的说明去掉,扩展名改成xyz就可以了。
代码:
#include <vtkVersion.h>
#include <vtkSmartPointer.h>
#include <vtkTransform.h>
#include <vtkVertexGlyphFilter.h>
#include <vtkPoints.h>
#include <vtkPolyData.h>
#include <vtkCellArray.h>
#include <vtkIterativeClosestPointTransform.h>
#include <vtkTransformPolyDataFilter.h>
#include <vtkLandmarkTransform.h>
#include <vtkMath.h>
#include <vtkMatrix4x4.h>
#include <vtkXMLPolyDataWriter.h>
#include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h>
#include <vtkActor.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindow.h>
#include <vtkRenderer.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h>
#include <vtkXMLPolyDataReader.h>
#include <vtkProperty.h>
#include <vtkPLYReader.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> sourceTmp =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> targetTmp =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> source =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> target =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New();
if(argc == 3)
{
// Get all data from the file
std::string strSource = argv[1];
std::string strTarget = argv[2];
std::ifstream fSource(strSource.c_str());
std::ifstream fTarget(strTarget.c_str());
std::string line;
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> sourcePoints =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> targetPoints =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New();
while(std::getline(fSource, line))
{
double x,y,z;
std::stringstream linestream;
linestream << line;
linestream >> x >> y >> z;
sourcePoints->InsertNextPoint(x, y, z);
}
sourceTmp->SetPoints(sourcePoints);
vtkSmartPointer<vtkVertexGlyphFilter> vertexFilter1 =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkVertexGlyphFilter>::New();
#if VTK_MAJOR_VERSION <= 5
vertexFilter1->SetInputConnection(sourceTmp->GetProducerPort());
#else
vertexFilter1->SetInputData(sourceTmp);
#endif
vertexFilter1->Update();
source->ShallowCopy(vertexFilter1->GetOutput());
while(std::getline(fTarget, line))
{
double x,y,z;
std::stringstream linestream;
linestream << line;
linestream >> x >> y >> z;
targetPoints->InsertNextPoint(x, y, z);
}
targetTmp->SetPoints(targetPoints);
vtkSmartPointer<vtkVertexGlyphFilter> vertexFilter2 =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkVertexGlyphFilter>::New();
#if VTK_MAJOR_VERSION <= 5
vertexFilter2->SetInputConnection(targetTmp->GetProducerPort());
#else
vertexFilter2->SetInputData(targetTmp);
#endif
vertexFilter2->Update();
target->ShallowCopy(vertexFilter2->GetOutput());
}
else
{
std::cout << "Error data..." << std::endl;
}
// Setup ICP transform
vtkSmartPointer<vtkIterativeClosestPointTransform> icp =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkIterativeClosestPointTransform>::New();
icp->SetSource(source);
icp->SetTarget(target);
icp->GetLandmarkTransform()->SetModeToRigidBody();
icp->SetMaximumNumberOfIterations(20);
//icp->StartByMatchingCentroidsOn();
icp->Modified();
icp->Update();
cout<<"bitch"<<endl;
// Get the resulting transformation matrix (this matrix takes the source points to the target points)
vtkSmartPointer<vtkMatrix4x4> m = icp->GetMatrix();
std::cout << "The resulting matrix is: " << *m << std::endl;
// Transform the source points by the ICP solution
vtkSmartPointer<vtkTransformPolyDataFilter> icpTransformFilter =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkTransformPolyDataFilter>::New();
#if VTK_MAJOR_VERSION <= 5
icpTransformFilter->SetInput(source);
#else
icpTransformFilter->SetInputData(source);
#endif
icpTransformFilter->SetTransform(icp);
icpTransformFilter->Update();
/*
// If you need to take the target points to the source points, the matrix is:
icp->Inverse();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkMatrix4x4> minv = icp->GetMatrix();
std::cout << "The resulting inverse matrix is: " << *minv << std::cout;
*/
// Visualize
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> sourceMapper =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
#if VTK_MAJOR_VERSION <= 5
sourceMapper->SetInputConnection(source->GetProducerPort());
#else
sourceMapper->SetInputData(source);
#endif
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> sourceActor =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
sourceActor->SetMapper(sourceMapper);
sourceActor->GetProperty()->SetColor(1,0,0);
sourceActor->GetProperty()->SetPointSize(4);
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> targetMapper =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
#if VTK_MAJOR_VERSION <= 5
targetMapper->SetInputConnection(target->GetProducerPort());
#else
targetMapper->SetInputData(target);
#endif
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> targetActor =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
targetActor->SetMapper(targetMapper);
targetActor->GetProperty()->SetColor(0,1,0);
targetActor->GetProperty()->SetPointSize(4);
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> solutionMapper =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
solutionMapper->SetInputConnection(icpTransformFilter->GetOutputPort());
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> solutionActor =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
solutionActor->SetMapper(solutionMapper);
solutionActor->GetProperty()->SetColor(0,0,1);
solutionActor->GetProperty()->SetPointSize(3);
// Create a renderer, render window, and interactor
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer> renderer =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow> renderWindow =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New();
renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer);
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor> renderWindowInteractor =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New();
renderWindowInteractor->SetRenderWindow(renderWindow);
// Add the actor to the scene
renderer->AddActor(sourceActor);
renderer->AddActor(targetActor);
renderer->AddActor(solutionActor);
renderer->SetBackground(.3, .6, .3); // Background color green
// Render and interact
renderWindow->Render();
renderWindowInteractor->Start();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
PROJECT(IterativeClosestPointsTransform)
find_package(VTK REQUIRED)
include(${VTK_USE_FILE})
add_executable(IterativeClosestPointsTransform MACOSX_BUNDLE IterativeClosestPointsTransform)
if(VTK_LIBRARIES)
target_link_libraries(IterativeClosestPointsTransform ${VTK_LIBRARIES})
else()
target_link_libraries(IterativeClosestPointsTransform vtkHybrid)
endif()
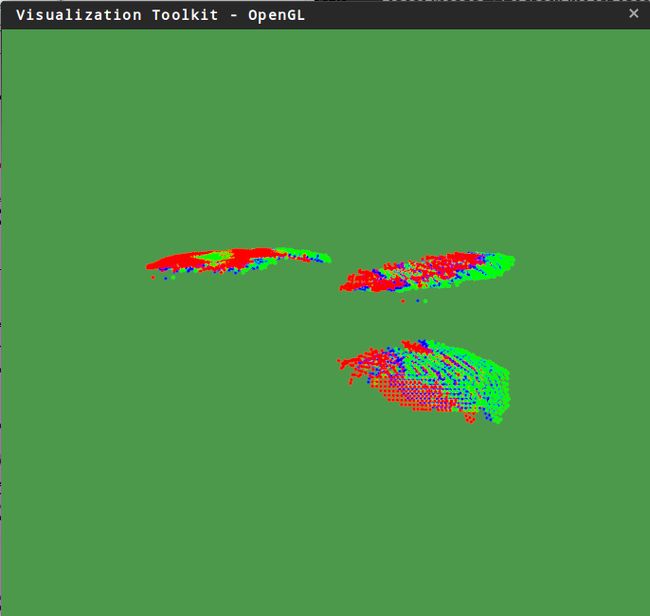
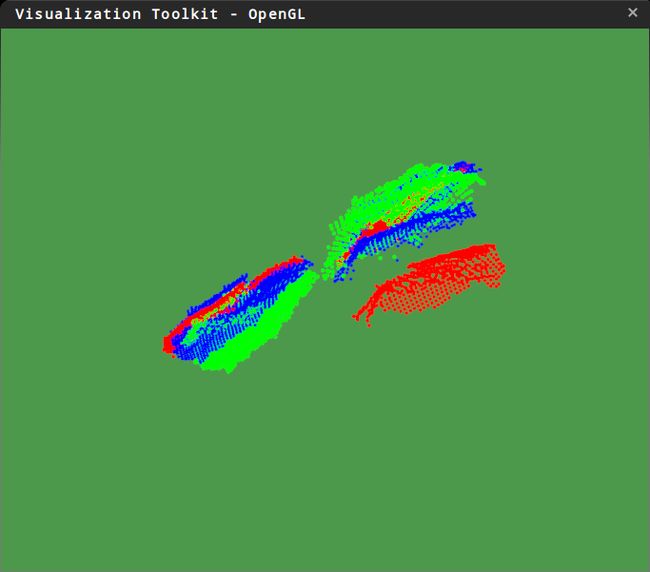
编译运行一下,用两片点云来测试,得到的结果:
微小的点云平移:
稍微大一些的平移
加入旋转量
绿色是target,红色是source,蓝色是solution。
结论和思考
和同学一起试用了几种ICP的方法,包括PCL的和VTK的,得到的结果都差不多。并不是很理想,感觉最好的Registration适用情况应该是从不同方位扫描一个物体,然后将点云进行配准,而且点云的算法的初始状态也有要求,一是要有点云的重合,二是不能分开得太远。
难道就这样结束了?
答案是No... 难道传说中的ICP这点配准都搞不定!?那也太弱了吧。
继续看论文和尝试.
这次改用PCL的库来实现。
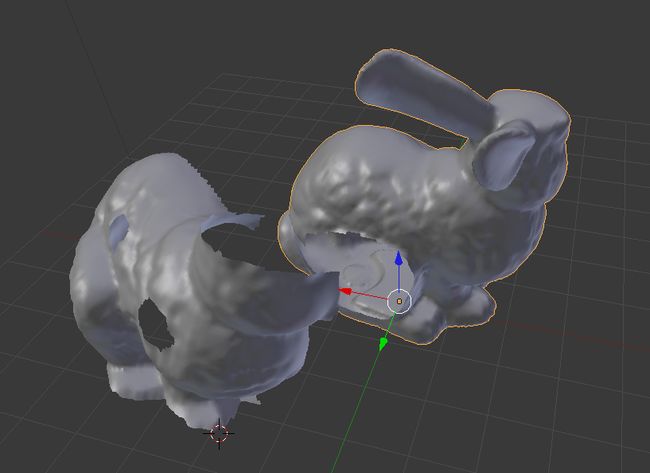
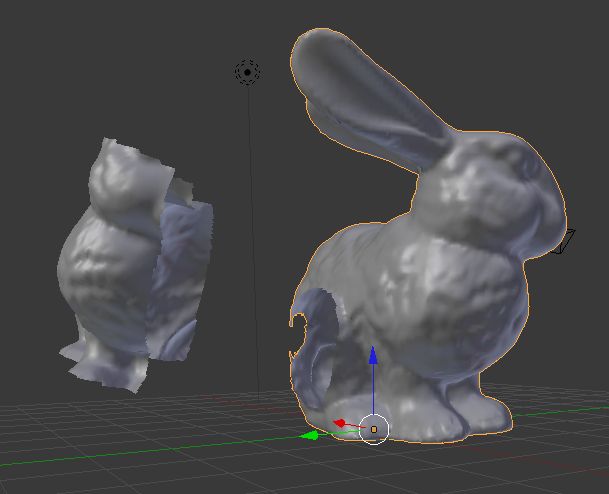
用blender基于stanford bunny来做一组测试数据
按照PCL的pipeline,首先采用的是进行一个初始化操作,将点云进行一次预处理,得到一个稍微好一点的结果,这里用到的是SAC-IA的算法,流程如下:
SAC-IA: Sampled Consesus-Initial Alignment
1. Draw n points di from the source cloud
(with a minimum distance d in between).
2. For each drawn di :
2.1 get k closest matches, and
2.2 draw one of the k closest matches as mi
(instead of taking closest match)
3. Estimate transformation (R, t) for these samples
4. Determine inlier pairs with ((Rdi + t) − mi )2 <
5. Repeat N times, and use (R, t) having most inliers
想搞懂算法的自己扒论文,只想知道怎么用的和我来看代码:
template_alignment.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/PolygonMesh.h>
#include <pcl/io/vtk_lib_io.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/features/fpfh.h>
#include <pcl/registration/ia_ransac.h>
#include <pcl/PolygonMesh.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/histogram_visualizer.h>
#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>
class FeatureCloud
{
public:
// A bit of shorthand
typedef pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> PointCloud;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal> SurfaceNormals;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33> LocalFeatures;
typedef pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ> SearchMethod;
FeatureCloud () :
search_method_xyz_ (new SearchMethod),
normal_radius_ (0.06f),
feature_radius_ (0.06f)
{}
~FeatureCloud () {}
// Process the given cloud
void
setInputCloud (PointCloud::Ptr xyz)
{
xyz_ = xyz;
processInput ();
}
// Load and process the cloud in the given PCD file
void
loadInputCloud (const std::string &pcd_file)
{
xyz_ = PointCloud::Ptr (new PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile (pcd_file, *xyz_);
processInput ();
}
// Get a pointer to the cloud 3D points
PointCloud::Ptr
getPointCloud () const
{
return (xyz_);
}
// Get a pointer to the cloud of 3D surface normals
SurfaceNormals::Ptr
getSurfaceNormals () const
{
return (normals_);
}
// Get a pointer to the cloud of feature descriptors
LocalFeatures::Ptr
getLocalFeatures () const
{
return (features_);
}
protected:
// Compute the surface normals and local features
void
processInput ()
{
computeSurfaceNormals ();
computeLocalFeatures ();
}
// Compute the surface normals
void
computeSurfaceNormals ()
{
normals_ = SurfaceNormals::Ptr (new SurfaceNormals);
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> norm_est;
norm_est.setInputCloud (xyz_);
norm_est.setSearchMethod (search_method_xyz_);
norm_est.setRadiusSearch (normal_radius_);
norm_est.compute (*normals_);
}
// Compute the local feature descriptors
void
computeLocalFeatures ()
{
features_ = LocalFeatures::Ptr (new LocalFeatures);
pcl::FPFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::FPFHSignature33> fpfh_est;
fpfh_est.setInputCloud (xyz_);
fpfh_est.setInputNormals (normals_);
fpfh_est.setSearchMethod (search_method_xyz_);
fpfh_est.setRadiusSearch (feature_radius_);
fpfh_est.compute (*features_);
}
private:
// Point cloud data
PointCloud::Ptr xyz_;
SurfaceNormals::Ptr normals_;
LocalFeatures::Ptr features_;
SearchMethod::Ptr search_method_xyz_;
// Parameters
float normal_radius_;
float feature_radius_;
};
class TemplateAlignment
{
public:
// A struct for storing alignment results
struct Result
{
float fitness_score;
Eigen::Matrix4f final_transformation;
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
};
TemplateAlignment () :
min_sample_distance_ (0.02f),
max_correspondence_distance_ (0.001f*0.001f),
nr_iterations_ (1000)
{
// Intialize the parameters in the Sample Consensus Intial Alignment (SAC-IA) algorithm
sac_ia_.setMinSampleDistance (min_sample_distance_);
sac_ia_.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance (max_correspondence_distance_);
sac_ia_.setMaximumIterations (nr_iterations_);
}
~TemplateAlignment () {}
// Set the given cloud as the target to which the templates will be aligned
void
setTargetCloud (FeatureCloud &target_cloud)
{
target_ = target_cloud;
sac_ia_.setInputTarget (target_cloud.getPointCloud ());
sac_ia_.setTargetFeatures (target_cloud.getLocalFeatures ());
}
// Add the given cloud to the list of template clouds
void
addTemplateCloud (FeatureCloud &template_cloud)
{
templates_.push_back (template_cloud);
}
// Align the given template cloud to the target specified by setTargetCloud ()
void
align (FeatureCloud &template_cloud, TemplateAlignment::Result &result)
{
sac_ia_.setInputCloud (template_cloud.getPointCloud ());
sac_ia_.setSourceFeatures (template_cloud.getLocalFeatures ());
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> registration_output;
sac_ia_.align (registration_output);
result.fitness_score = (float) sac_ia_.getFitnessScore (max_correspondence_distance_);
result.final_transformation = sac_ia_.getFinalTransformation ();
}
// Align all of template clouds set by addTemplateCloud to the target specified by setTargetCloud ()
void
alignAll (std::vector<TemplateAlignment::Result, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Result> > &results)
{
results.resize (templates_.size ());
for (size_t i = 0; i < templates_.size (); ++i)
{
align (templates_[i], results[i]);
}
}
// Align all of template clouds to the target cloud to find the one with best alignment score
int
findBestAlignment (TemplateAlignment::Result &result)
{
// Align all of the templates to the target cloud
std::vector<Result, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Result> > results;
alignAll (results);
// Find the template with the best (lowest) fitness score
float lowest_score = std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity ();
int best_template = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < results.size (); ++i)
{
const Result &r = results[i];
if (r.fitness_score < lowest_score)
{
lowest_score = r.fitness_score;
best_template = (int) i;
}
}
// Output the best alignment
result = results[best_template];
return (best_template);
}
private:
// A list of template clouds and the target to which they will be aligned
std::vector<FeatureCloud> templates_;
FeatureCloud target_;
// The Sample Consensus Initial Alignment (SAC-IA) registration routine and its parameters
pcl::SampleConsensusInitialAlignment<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::FPFHSignature33> sac_ia_;
float min_sample_distance_;
float max_correspondence_distance_;
int nr_iterations_;
};
int main()
{
// pcl::PolygonMesh::Ptr obj_in (new pcl::PolygonMesh);
// //Read obj file.
// if(pcl::io::loadPolygonFileOBJ("tree/tarotemplate.obj",*obj_in)==-1)
// {
// PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file template.obj");
// return -1;
// }
// std::cout<<"Loaded "
// <<obj_in->cloud.width * obj_in->cloud.height
// << " data points: "
// << std::endl;
//Transform obj to source PCD.
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree_template(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
//pcl::fromROSMsg(obj_in->cloud, *tree_template);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("source.pcd",*tree_template);
FeatureCloud object_template;
object_template.setInputCloud(tree_template);
//Load taget point cloud.
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("target.pcd",*cloud);
FeatureCloud target_cloud;
target_cloud.setInputCloud(cloud);
TemplateAlignment template_align;
template_align.addTemplateCloud(object_template);
template_align.setTargetCloud(target_cloud);
TemplateAlignment::Result best_alignment;
template_align.align(object_template, best_alignment);
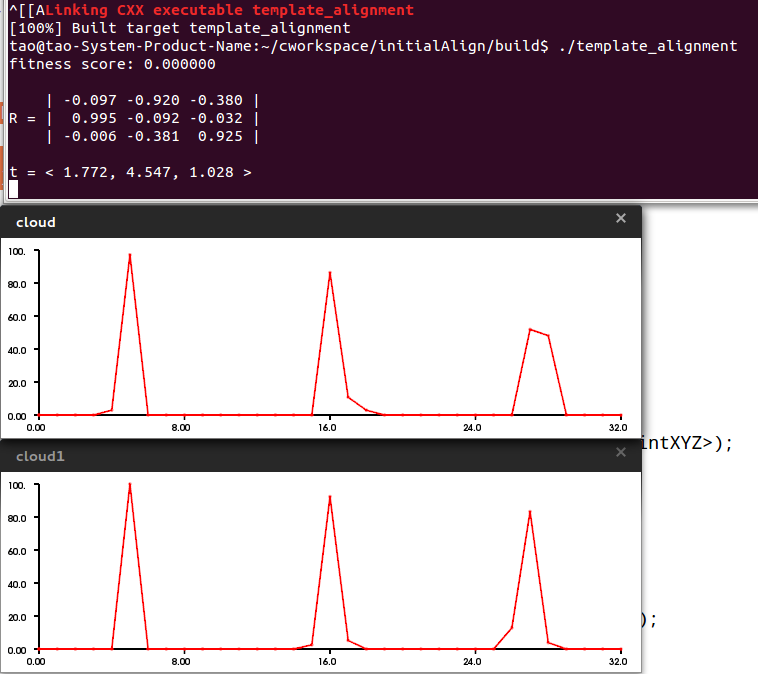
// Print the alignment fitness score (values less than 0.00002 are good)
printf ("fitness score: %f\n", best_alignment.fitness_score);
// Print the rotation matrix and translation vector
Eigen::Matrix3f rotation = best_alignment.final_transformation.block<3,3>(0, 0);
Eigen::Vector3f translation = best_alignment.final_transformation.block<3,1>(0, 3);
printf ("\n");
printf (" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", rotation (0,0), rotation (0,1), rotation (0,2));
printf ("R = | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", rotation (1,0), rotation (1,1), rotation (1,2));
printf (" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", rotation (2,0), rotation (2,1), rotation (2,2));
printf ("\n");
printf ("t = < %0.3f, %0.3f, %0.3f >\n", translation (0), translation (1), translation (2));
// Save the aligned template for visualization
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> transformed_cloud;
pcl::transformPointCloud (*object_template.getPointCloud (), transformed_cloud, best_alignment.final_transformation);
pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary ("output.pcd", transformed_cloud);
pcl::visualization::PCLHistogramVisualizer hViewer;
hViewer.addFeatureHistogram(*target_cloud.getLocalFeatures(),"fpfh",0);
hViewer.addFeatureHistogram(*object_template.getLocalFeatures(),"fpfh",0,"cloud1");
while(1)
{
hViewer.spinOnce(100);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(100000));
}
return 0;
}
CMakeList.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8 FATAL_ERROR)
project(template_alignment)
find_package(PCL 1.2 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS})
add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
add_executable (template_alignment template_alignment.cpp)
target_link_libraries (template_alignment ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
编译运行,得到结果:
参考
【3D】迭代最近点算法 Iterative Closest Points
ICP算法(Iterative Closest Point)及VTK实现
ICCV2011-registration 下载
ICCV2011-initial_registration 下载