Spring MVC 3.0简介
1. 背景介绍
Spring 框架提供了构建 Web 应用程序的全功能 MVC 模块。使用 Spring 可插入的 MVC 架构,可以选择是使用内置的 Spring Web 框架还是 Struts 这样的 Web 框架。通过策略接口,Spring 框架是高度可配置的,而且包含多种视图技术,例如 JavaServer Pages(JSP)技术、Velocity、Tiles、iText 和 POI。Spring MVC 框架并不知道使用的视图,所以不会强迫您只使用 JSP 技术。Spring MVC 分离了控制器、模型对象、分派器以及处理程序对象的角色,这种分离让它们更容易进行定制。
2. 常见MVC框架比较
运行性能上
Jsp+servlet>struts1>springmvc>struts2+freemarker>>struts2,ognl,值栈。
开发效率上
基本正好相反。值得强调的是,springmvc开发效率和struts2不相上下。
Struts2的性能低的原因是因为OGNL和值栈造成的。所以,如果你的系统并发量高,可以使用freemaker进行显示,而不是采用OGNL和值栈。这样,在性能上会有相当大得提高。
3. 核心原理
4. 开发实战(Spring+SpringMVC+Hibernate)
我们采用springMVC开发项目时,通常都会采用注解的方式(当然也可用配置文件方式),这样可以大大提高我们的开发效率。实现零配置。下面我们采用注解方式从零开始重新做一个spring MVC的配置。步骤如下:
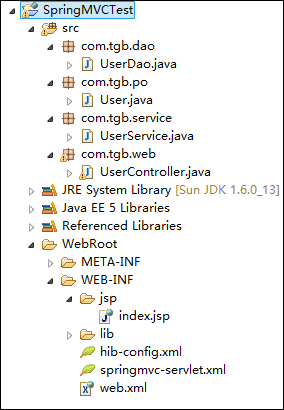
建立web项目,并建立整个项目的包结构和相关类。如下图所示:
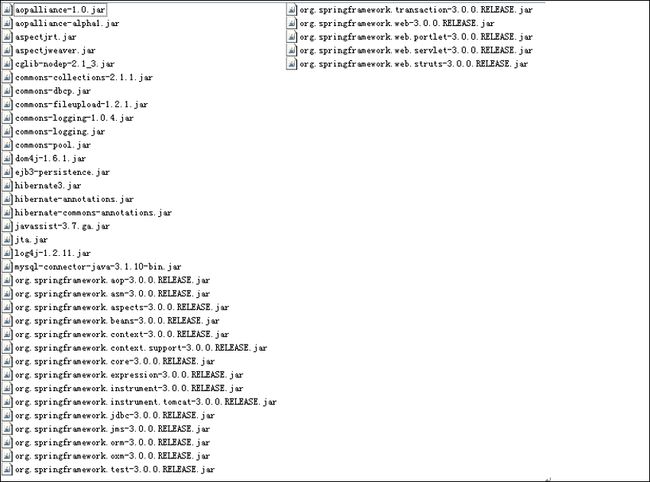
导入相关jar包,如下:(下载spring-framework-3.0.0.RELEASE,其它为Hibernate相关的jar)
源码如下:
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.5"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<!-- 配置spring核心servlet -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<!-- 可以自定义servlet.xml配置文件的位置和名称,默认为WEB-INF目录下,名称为[<servlet-name>]-servlet.xml,如springmvc-servlet.xml-->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/hib-config.xml,/WEB-INF/springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!-- url-pattern配置为/,不带文件后缀,会造成其它静态文件(js,css等)不能访问。如配为*.do,则不影响静态文件的访问 -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
springmvc-servlet.xml
springmvc-servlet这个名字是因为上面web.xml中<servlet-name>标签配的值为springmvc(<servlet-name> springmvc </servlet-name>),再加上“-servlet”后缀而形成的springmvc-servlet.xml文件名,如果改为spring,对应的文件名则为spring-servlet.xml。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.0.xsd">
<!-- 对web包中的所有类进行扫描,以完成Bean创建和自动依赖注入的功能 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.tgb.web"/>
<!-- 支持spring3.0新的mvc注解 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<!-- 启动Spring MVC的注解功能,完成请求和注解POJO的映射 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter"/>
<!--对模型视图名称的解析,即在模型视图名称添加前后缀 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"
p:prefix="/WEB-INF/jsp/" p:suffix=".jsp">
<!-- 如果使用jstl的话,配置下面的属性 -->
<property name="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView" />
</bean>
</beans>
hib-config.xml(配置了spring集成hibernate)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
">
<!-- 启动包扫描功能,以便注册带有@Controller、@Service、@repository、@Component等注解的类成为spring的bean -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.tgb"/>
<!-- 支持aop注解 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName"
value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">
</property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myhib"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource" />
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<!-- key的名字前面都要加hibernate. -->
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</prop>
</props>
</property>
<property name="packagesToScan">
<value>com.tgb.po</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="hibernateTemplate" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate" >
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置一个JdbcTemplate实例-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理 -->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager" >
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager" />
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(public * com.tgb.service.impl.*.*(..))" id="businessService"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="businessService" />
</aop:config>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager" >
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true" propagation="NOT_SUPPORTED" />
<!-- get开头的方法不需要在事务中运行 。 有些情况是没有必要使用事务的,比如获取数据。开启事务本身对性能是有一定的影响的-->
<tx:method name="*"/> <!-- 其他方法在实务中运行 -->
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
</beans>
index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>**********${params.uname}</h1>
<h1>**********${requestScope.u}</h1>
<h1>**********${requestScope.user}</h1>
</body>
</html>
User.java
package com.tgb.po;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
private String uname;
private String pwd;
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUname() {
return uname;
}
public void setUname(String uname) {
this.uname = uname;
}
}
UserDao.java
package com.tgb.dao;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.tgb.po.User;
@Repository("userDao")
public class UserDao {
@Resource
private HibernateTemplate hibernateTemplate;
public void add(User u) {
System.out.println("UserDao.add()");
hibernateTemplate.save(u);
}
public HibernateTemplate getHibernateTemplate() {
return hibernateTemplate;
}
public void setHibernateTemplate(HibernateTemplate hibernateTemplate) {
this.hibernateTemplate = hibernateTemplate;
}
}
UserService.java
package com.tgb.service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.tgb.dao.UserDao;
import com.tgb.po.User;
@Service("userService")
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao;
public void add(String uname){
System.out.println("UserService.add()");
User u = new User();
u.setUname(uname);
userDao.add(u);
}
public UserDao getUserDao() {
return userDao;
}
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}
UserController.java
package com.tgb.web;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.SessionAttributes;
import com.tgb.po.User;
import com.tgb.service.UserService;
@Controller("userController")
@RequestMapping("/user.do")
public class UserController {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(params="method=reg")
public String reg(String uname) {
System.out.println("HelloController.handleRequest()");
userService.add(uname);
return "index";
}
public UserService getUserService() {
return userService;
}
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
}
运行测试:
http://localhost:8080/ SpringMVCTest /user.do?method=reg&uname=kobe
则会调用userController的reg方法,从而将数据内容插入到数据库中。
5. 总结
现在主流的Web MVC框架除了Struts这个主力外,其次就是Spring MVC了,因此这也是作为一名程序员需要掌握的主流框架,框架选择多了,应对多变的需求和业务时,可实行的方案自然就多了。不过要想灵活运用Spring MVC来应对大多数的Web开发,就必须要掌握它的配置及原理。
Spring MVC与Struts从原理上很相似(都是基于MVC架构),都有一个控制页面请求的Servlet,处理完后跳转页面。