Hibernate第四章知识点总结——第四章--高级映射
Hibernate第四章知识点总结——第四章--高级映射
关联映射回顾
一对一关联
唯一外键/共享主键
cascade/outer-join
一对多关联
单向/双向
inverse/lazy
多对多关联
中间表
目标
掌握并应用组件映射
掌握并应用继承映射
理解不同继承映射策略优劣势
掌握并应用集合映射
知识点预览
组件映射
继承映射
集合映射
组件映射
1. 组件映射
a) 在hibernate中,我们将某个实体对象中的一个逻辑组成称为组件;
b) 组件并没有身份标识,因此一个持久化的组件并不需要标识符属性或者标识符映射。
2. 组件映射样例—数据模型
3. 组件映射样例—POJO代码片段
public class Person {
private Integer Id;
private String sex;
private Date birthday;
private Addr addr;
private Name name;
public Addr getAddr() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(Addr addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
public Name getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(Name name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Addr {
private String street;
private String city;
private String zip;
……
}
public class Name {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String initial;
……
}
4. 组件映射样例—XML配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.oracle.entity.Person" table="T_PERSON"> <id name="Id"> <generator class="native" /> </id> <property name="sex"></property> <property name="birthday"></property> <!– 没有单独的配置文件 --> <component name="name" class="com.oracle.entity.Name"> <property name="firstName"></property> <property name="lastName"></property> <property name="initial" column="ini"></property> </component> <component name="addr" class="com.oracle.entity.Addr"> <property name="street"></property> <property name="city"></property> <property name="zip"></property> </component> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
5. 组件映射样例—持久化代码片段
package com.oracle.test;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestOnetoOne {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Addr addr=new Addr();
addr.setCity("beijing");
addr.setStreet("nanjing road");
addr.setZip("021");
Name name=new Name();
name.setFirstName("zhang");
name.setLastName("william");
name.setInitial("z");
Person p=new Person();
p.setSex("m");
p.setBirthday(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-mm-dd").parse("1985-02-22"));
p.setAddr(addr);
p.setName(name);
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sf = null;
Session s = null;
Transaction tran = null;
try {
sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
s = sf.openSession();
tran = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(p);
tran.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
tran.rollback();
}finally{
if(s!=null){s.close();}if(sf!=null){sf.close();}
}
}
}
继承映射
1. Hibernate支持三种基本的继承映射策略
a) 每一张表一个类层次(Table per class hierarchy):只有一张表,表与类形成一对多关系。
b) 每一张表一个子类(Table per subclass):每个子类对应一张表,并与主类共享主表。
c) 每个类一张表(Table per concrete class):表与实现类之间形成独立的一对一关系。
2. 每一张表一个类层次
a) 一张表映射到整个类层次上面,这张表的列和类层次中的所有属性相对应。具体的子类代表的行有标识列来决定。
b) 这种映射策略在性能和简易性上都是优秀的。同时它也是表示多态的最好方法,不论是多态查询还是非多态查询都能工作的很好。
c) 问题:
表示属性的列必须是可以为null。
子类属性过多,造成存储空间的浪费。
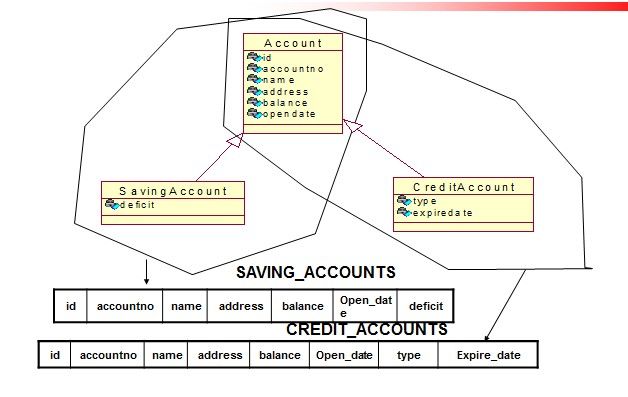
d) 每一张表一个类层次样例—数据模型
e) 每一张表一个类层次样例—注解代码片段
public class Account {
private Integer id;
private String accountInfo;
private String name;
private String address;
private double balance;
private Date openDate;
}
public class SavingAccount extends Account {
private double deficit;
//子类中无id信息
public double getDeficit() {
return deficit;
}
public void setDeficit(double deficit) {
this.deficit = deficit;
}
}
public class CreditAccount extends Account {
private String type;
private Date expireDate;
}
f) 每一张表一个类层次样例—配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.oracle.entity.Account" table="T_ACCT" discriminator-value="SA"> <id name="Id" > <generator class="native" /> </id> <discriminator column="dtype" type="string"></discriminator> <!– 紧挨着id--> <property name="accountInfo" ></property> <property name="name" ></property> <property name="address" ></property> <property name="balance" ></property> <property name="openDate" ></property> <subclass name="com.oracle.entity.SavingAccount" discriminator-value="SA"> <property name="deficit"></property> </subclass> <subclass name="com.oracle.entity.CreditAccount" discriminator-value="CA"> <property name="type"></property> <property name="expireDate"></property> </subclass> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
g) 每张表一个类层次—持久化代码片段
package com.oracle.test;
public class TestExtends {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
SavingAccount sa=new SavingAccount();
sa.setBalance(1200);
sa.setDeficit(205);
sa.setName("savingAccount");
CreditAccount ca=new CreditAccount();
ca.setBalance(20000);
ca.setType("gold");
ca.setName("creditAccount");
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sf = null;
Session s = null;
Transaction tran = null;
try {
sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
s = sf.openSession();
tran = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(sa);
s.save(ca);
tran.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
tran.rollback();
}finally{
if(s!=null){s.close();}if(sf!=null){sf.close();}
}
}
}
3. 一张表一个子类
a) 第二种做法就是使用继承关系来表示外键关系类型。每一个子类都声明持久化属性-甚至包括抽象类和接口,都有自己的表。
b) 与每张表一个具体的类不同,这里表中的列对那些非继承过来的属性有效,主键也是父类对应的表的外键
c) 采用最多
d) 问题:
子类过多,DB维护过多的表,增加性能开销
e) 每一张表一个子类样例—数据库模型
f) 每一张表一个子类样例—POJO代码片段
public class Account {
private Integer id;
private String accountInfo;
private String name;
private String address;
private double balance;
private Date openDate;
}
public class SavingAccount extends Account {
private double deficit;
public double getDeficit() {
return deficit;
}
public void setDeficit(double deficit) {
this.deficit = deficit;
}
}
public class CreditAccount extends Account {
private String type;
private Date expireDate;
}
g) 每一张表一个子类样例—配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.oracle.entity.Account" table="T_ACCT“ > <id name="Id" > <generator class="native" /> </id> <property name="accountInfo" ></property> <property name="name" ></property> <property name="address" ></property> <property name="balance" ></property> <property name="openDate" ></property> <joined-subclass name="com.oracle.entity.SavingAccount" table="T_SA"> <key column="acct_id"></key> <property name="deficit"></property> </joined-subclass> <joined-subclass name="com.oracle.entity.CreditAccount" table="T_CA"> <key column="acct_id"></key> <property name="type"></property> <property name="expireDate"></property> </joined-subclass> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
h) 每张表一个子类—持久化代码片段
package com.oracle.test;
public class TestExtends {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
SavingAccount sa=new SavingAccount();
sa.setBalance(1200);
sa.setDeficit(205);
sa.setName("savingAccount");
CreditAccount ca=new CreditAccount();
ca.setBalance(20000);
ca.setType("gold");
ca.setName("creditAccount");
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sf = null;
Session s = null;
Transaction tran = null;
try {
sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
s = sf.openSession();
tran = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(sa);
s.save(ca);
tran.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
tran.rollback();
}finally{
if(s!=null){s.close();}if(sf!=null){sf.close();}
}
}
}
4. 每个类一张表
a) 最简单的方法: 每一张表对应一个子类,类当中的所有属性,包括继承的属性,都会映射到表中的列。
b) 问题:
不能很好的支持多态的关联。
c) 每个类一张表—数据库模型
d) 每个类一张表—POJO代码片段
public class Account {
private Integer id;
private String accountInfo;
private String name;
private String address;
private double balance;
private Date openDate;
}
public class SavingAccount extends Account {
private double deficit;
public double getDeficit() {
return deficit;
}
public void setDeficit(double deficit) {
this.deficit = deficit;
}
}
public class CreditAccount extends Account {
private String type;
private Date expireDate;
}
e) 每个类一张表—配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name=“com.oracle.entity.Account” > <!– 无table信息--> <id name="Id" > <generator class="native" /> </id> <property name="accountInfo" ></property> <property name="name" ></property> <property name="address" ></property> <property name="balance" ></property> <property name="openDate" ></property> <union-subclass name="com.oracle.entity.SavingAccount" table="T_SA"> <property name="deficit"></property> </ union-subclass > < union-subclass name="com.oracle.entity.CreditAccount" table="T_CA"> <property name="type"></property> <property name="expireDate"></property> </ union-subclass > </class> </hibernate-mapping>
f) 每个类一张表—持久化代码片
package com.oracle.test;
public class TestExtends {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
SavingAccount sa=new SavingAccount();
sa.setBalance(1200);
sa.setDeficit(205);
sa.setName("savingAccount");
CreditAccount ca=new CreditAccount();
ca.setBalance(20000);
ca.setType("gold");
ca.setName("creditAccount");
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sf = null;
Session s = null;
Transaction tran = null;
try {
sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
s = sf.openSession();
tran = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(sa);
s.save(ca);
tran.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
tran.rollback();
}finally{
if(s!=null){s.close();}if(sf!=null){sf.close();}
}
}
}
5. 选择一种策略
a) 如果不进行多态连接和查询,那么使用每张表对应一个类的策略。
b) 而如果需要进行多态链接和查询,且子类的属性相对较少的情况下,那么使用每张表对应一个类层次的策略。
c) 如果需要进行多态链接和查询,并且子类的属性很多那么使用每张表一个子类的方法。
值类型集合映射
1. 集合映射
a) Hibernate支持包含值类型的实例:
b) Set: 无序且无法包含重复元素
c) Bag: 无序且允许包含重复元素
d) List: 有序且允许包含重复元素
e) Map: 包含键和值
f) 有序:是针对Hibernate数据持久化中,是否保存数据集合中的记录排列顺序加以区分的。
g) 被定义成有序的数据集合,会按照集合元素排列的先后顺序同时固化到数据库中(以某个特定字段存储顺序号),下次读取时,也会返回具备同样排列顺序的数据集合。
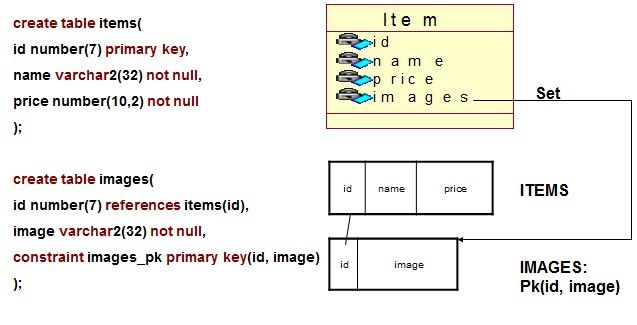
2. Set值类型集合映射样例—数据库模型
3. Set值类型集合映射样例—POJO类片段
package com.oracle.collection;
public class Item {
private Integer Id;
private String name;
private Double price;
private Set images;
public Set getImages() {
return images;
}
public void setImages(Set images) {
this.images = images;
}
}
4. Set值类型集合映射样例—XML映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.oracle.collection.Item" table="T_ITEM"> <id name="Id" > <generator class="native" /> </id> <property name="name" ></property> <property name="price" ></property> <set name="images" table="T_IMAGE"> <key column="id"></key> <element type="string" column="path"></element> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
5. Set值类型集合映射样例—持久化代码片段
package com.oracle.test;
import com.oracle.collection.Item;
public class TestSet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
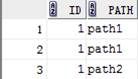
Set images=new HashSet();
images.add("path1");
images.add("path1");
images.add("path2");
Item item=new Item();
item.setName("item1");
item.setPrice(12.3);
item.setImages(images);
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sf = null;
Session s = null;
Transaction tran = null;
try {
sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
s = sf.openSession();
tran = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(item);//存储2个图片路径 Set 无序不重复
tran.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
tran.rollback();
}finally{
if(s!=null){s.close();}if(sf!=null){sf.close();}
}
}
}
6. 使用Bag
a) Java集合API没有提供包接口,但Hibernate支持在用List模拟包的行为。
b) 注意,尽管约定一个列表是一个有序集合,但Hibernate 定义为一个持久化的包时,不能维持集合中元素固有的顺序。
c) Bag值类型集合映射样例—数据库模型
d) Bag值类型集合映射样例—POJO类片段
package com.oracle.collection;
public class Item {
private Integer Id;
private String name;
private Double price;
private List images;
public List getImages() {
return images;
}
public void setImages(List images) {
this.images = images;
}
}
e) Bag值类型集合映射样例—XML映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.oracle.collection.Item" table="T_ITEM"> <id name="Id" > <generator class="native" /> </id> <property name="name" ></property> <property name="price" ></property> <bag name="images" table="T_IMAGE"> <key column="id"></key> <element type="string" column="path"></element> </bag> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
f) Bag值类型集合映射样例—持久化代码片段
package com.oracle.test;
import com.oracle.collection.Item;
public class TestSet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
List images=new ArrayList();
images.add("path1");
images.add("path1");
images.add("path2");
Item item=new Item();
item.setName("item1");
item.setPrice(12.3);
item.setImages(images);
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sf = null;
Session s = null;
Transaction tran = null;
try {
sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
s = sf.openSession();
tran = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(item);
tran.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
tran.rollback();
}finally{
if(s!=null){s.close();}if(sf!=null){sf.close();}
}
}
7. 使用idbag
a) Idbag映射添加了一个代理键到集合表。
b) idBag值类型集合映射样例—模型
c) idBag值类型集合映射样例—POJO类片段
package com.oracle.collection;
import java.util.List;
public class Item {
private Integer Id;
private String name;
private Double price;
private List images;
public List getImages() {
return images;
}
public void setImages(List images) {
this.images = images;
}
}
d) idBag值类型集合映射样例—XML映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.oracle.collection.Item" table="T_ITEM"> <id name="Id" > <generator class="native" /> </id> <property name="name" ></property> <property name="price" ></property> <idbag name="images" table="T_IMAGE"> <collection-id type="integer" column="img_id"> <generator class="native"></generator> </collection-id> <key column="id"></key> <element type="string" column="path"></element> </idbag> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
e) idBag值类型集合映射样例—持久化代码片段
package com.oracle.test;
import com.oracle.collection.Item;
public class TestSet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
List images=new ArrayList();
images.add("path1");
images.add("path1");
images.add("path2");
Item item=new Item();
item.setName("item1");
item.setPrice(12.3);
item.setImages(images);
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sf = null;
Session s = null;
Transaction tran = null;
try {
sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
s = sf.openSession();
tran = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(item);
tran.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
tran.rollback();
}finally{
if(s!=null){s.close();}if(sf!=null){sf.close();}
}
}
}
8. 使用list
a) 一个List映射需要把一个索引列新增到数据库表;
b) 索引列定义元素在集合中的位置。
c) 有序可重复较常用
d) List值类型集合映射样例—数据库模型
e) List值类型集合映射样例—POJO类片段
package com.oracle.collection;
import java.util.List;
public class Item {
private Integer Id;
private String name;
private Double price;
private List images;
public List getImages() {
return images;
}
public void setImages(List images) {
this.images = images;
}
}
f) List值类型集合映射样例—XML映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.oracle.collection.Item" table="T_ITEM"> <id name="Id" > <generator class="native" /> </id> <property name="name" ></property> <property name="price" ></property> <list name="images" table="T_IMAGE"> <key column="id"></key> <index column="pos"></index> <element type="string" column="path"></element> </list> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
g) List值类型集合映射样例—持久化代码片段
package com.oracle.test;
import com.oracle.collection.Item;
public class TestSet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
List images=new ArrayList();
images.add("path1");
images.add("path1");
images.add("path2");
Item item=new Item();
item.setName("item1");
item.setPrice(12.3);
item.setImages(images);
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sf = null;
Session s = null;
Transaction tran = null;
try {
sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
s = sf.openSession();
tran = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(item);
tran.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
tran.rollback();
}finally{
if(s!=null){s.close();}if(sf!=null){sf.close();}
}
}
}
9. 使用map
a) 假如我们的字典里除了这些词还有描述。
b) 在java中我们使用Map,记作为键,描述为值。
c) 键值对
d) Map值类型集合映射样例—数据库模型
e) Map值类型集合映射样例—POJO类代码片段
package com.oracle.collection;
import java.util.Map;
public class Dictionary {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String publisher;
private Map words;
public Map getWords() {
return words;
}
public void setWords(Map words) {
this.words = words;
}
}
f) Map值类型集合映射样例—XML映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.oracle.collection.Dictionary" table="T_DICTIONARY"> <id name="Id" > <generator class="native" /> </id> <property name="name" ></property> <property name="publisher" ></property> <map name="words" table="T_WORDS"> <key column="dic_id"></key> <map-key type="string" column="word"></map-key> <element type="string" column="description"></element> </map> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
g) Map值类型集合映射样例—持久化代码片段
package com.oracle.test;
import com.oracle.collection.Dictionary;
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
Map words=new HashMap();
words.put("hello", "你好");
words.put("ok", "是");
Dictionary dic=new Dictionary();
dic.setName("eng");
dic.setPublisher("william");
dic.setWords(words);
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sf = null;
Session s = null;
Transaction tran = null;
try {
sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
s = sf.openSession();
tran = s.beginTransaction();
s.save(dic);
tran.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
tran.rollback();
}finally{
if(s!=null){s.close();}if(sf!=null){sf.close();}
}
}
}
结果集排序—排序集合和有序集合
1. 排序集合是用一个Java比较器在内存中进行排序;
2. 有序集合是用包含order by子句的SQL查询在数据中排序。
3. Map排序集合样例—XML映射
<map name="words" table="WORDS" sort=“natural"> <key column="dic_id"></key> <map-key type="string" column="word"></map-key> <element type="string" column="description"></element> </map>
通过指定sort=“natural”,指定Hibernate使用 SortedMap,调用java.lang.String的compareTo()方法对图片名称进行排序。
如果需要其它排序算法,如按字母反向排序,可以在sort属性中指定实现java.util.Comparator的类名。
4. 有序集合
a) 可以选择使用有序映射,在数据库端而不是在内存中排序。
b) Hibernate使用LinkedHashSet和LinkedHashMap实现排序集合或映射,所以只支持JDK1.4或以上版本。
c) 配置
<map name="words" table="WORDS" order-by=“word"> <key column="dic_id"></key> <map-key type="string" column="word"></map-key> <element type="string" column="description"></element> </map>
总结
组件映射
继承映射
每张表一个类层次、每张表一个子类、每个类一张表
值类型集合映射
Set/Bag/idBag/List/Map
sort/order-by
问题
完成课堂样例demo
三种类继承映射策略
值集合映射类型及特点