RecyclerView与CardView的使用
对于博文标题的两个View,其并没有引入默认的SDK中,需要自己手动导入使用,下面将介绍导入的方式与使用的细节问题。
1.将RecyclerView与CardView导入Android Studio
对于Android Studio导入比较简单,在build.gradle(Module:app)中添加如下代码:
dependencies {
compile fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:23.0.1'
compile 'com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:21.0.0'
compile 'com.android.support:cardview-v7:21.0.0'
}
红色标记为添加的代码,添加好后,我们就可以使用其控件。
2.单独使用RecyclerView
布局文件中导入其控件:
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView android:id="@+id/lyj_recycler" android:scrollbars="vertical" android:layout_below="@+id/activity_main_toolbar" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:padding="5dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
都是一些基本的属性,与ListView并无不同。
因为谷歌实现RecyclerView是扩展ListView功能,使其功能更加的丰富,所以,使用RecylerView也需要一个适配器Adapter,RecyclerView适配器为RecyclerView.Adapter,代码基本格式如下:
public class LYJAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<LYJAdapter.ViewHolder> { @Override public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) { return null; } @Override public void onBindViewHolder(ViewHolder holder, int position) { } @Override public int getItemCount() { return 0; } class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { public ViewHolder(View view){ super(view); } } }
其适配器强制我们使用ViewHolder模式优化ListView。当然优点就应该强制使用。其使用方式与BaseAdapter大同小异。
下面我们来实现自身的适配器,代码如下:
public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyAdapter.ViewHolder> { private List<MusicItem> data; public MyAdapter(List<MusicItem> data) { this.data = data; } @Override public MyAdapter.ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup viewGroup, int i) { //绑定布局 View itemLayoutView = LayoutInflater.from(viewGroup.getContext()).inflate(R.layout.cv_main, null); //创建ViewHolder ViewHolder viewHolder = new ViewHolder(itemLayoutView); return viewHolder; } @Override public void onBindViewHolder(MyAdapter.ViewHolder viewHolder, int i) { viewHolder.info.setText(data.get(i).getTitle()); viewHolder.image.setImageResource(data.get(i).getResId()); } @Override public int getItemCount() { return data.size(); } public static class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { public TextView info; public ImageView image; public ViewHolder(View itemLayoutView) { super(itemLayoutView); info = (TextView) itemLayoutView.findViewById(R.id.lyj_txt); image=(ImageView)itemLayoutView.findViewById(R.id.lyj_image); } } }
布局cv_main代码如下:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_margin="5dp"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/lyj_image" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:layout_marginRight="5dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/lyj_txt" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/lyj_image" android:layout_gravity="center" /> </RelativeLayout>
RecyclerView的实体类如下:
public class MusicItem { private String title; private int resId; public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } public int getResId() { return resId; } public void setResId(int resId) { this.resId = resId; } }
其实RecyclerView的优点就是将ListView的items布局分离出来,好让我们实现如下三种效果。
㈠GridLayoutManager(网格布局)
下面的代码我们将Activity界面初始化分离出来:
public void initView() { initActionBar(); String[] strTitle = {"慵懒慢时光,爵士中文", "【华语】曾经的你已杳无音信", "粤语歌中的华语镜像", "凡走过必留下痕迹", "摇滚Live也可以温柔到骨子里", "人生中的舍得与难舍"}; int[] resId={R.drawable.one,R.drawable.two,R.drawable.three,R.drawable.four,R.drawable.five,R.drawable.six}; for(int i=0;i<6;i++){ MusicItem item=new MusicItem(); item.setTitle(strTitle[i]); item.setResId(resId[i]); musicItems.add(item); } recyclerView = (RecyclerView) findViewById(R.id.lyj_recycler); RecyclerView.LayoutManager layout = new GridLayoutManager(this,3);//网格布局,每行为3 recyclerView.setLayoutManager(layout); recyclerView.setHasFixedSize(true);//适配器内容改变,不会改变RecyclerView的大小 adapter = new MyAdapter(musicItems); recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter); }
对于设置ListView的适配器代码不需要过多解释,其他的代码都有注释。运行后界面如下(是不是有网易云音乐首首页选项列表的感觉):
㈡LinearLayoutManager(垂直布局、水平布局)
只需要更改上面代码中网格布局的那行代码,如下:
RecyclerView.LayoutManager layout=new LinearLayoutManager(this,LinearLayoutManager.HORIZONTAL,false);
参数1:上下文
参数2:水平还是垂直
参数3:为false表示数据按输入的顺序显示,为true表示数据逆向显示。
运行程序当得到如下界面:
当你将参数2更改成垂直,那么运行后的界面就如listView一样了。这里就不截图了。
㈢StaggeredGridLayoutManager(瀑布流布局)
如2(二)所示,也只需要更改一条代码即可:
StaggeredGridLayoutManager layout=new StaggeredGridLayoutManager(2,StaggeredGridLayoutManager.VERTICAL);
参数1:为每行几个元素。
参数2:为垂直瀑布还是水平瀑布
运行后界面如下:
这里不好看的原因是没有结合CardView一起使用,下面将介绍如何整合RecyclerView与CardView。
3.当RecyclerView遇上CardView
CardView继承自Framelayout,所以FrameLayout所有属性CardView均可以直接拿来用,不过CardView还有自己独有的属性。下面我们将item布局的父标签换成CardView。并且用RelativeLayout包裹两个子控件。代码如下:
<android.support.v7.widget.CardView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_margin="5dp"> <RelativeLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/lyj_image" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:layout_marginRight="5dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/lyj_txt" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/lyj_image" android:layout_marginTop="40dp" /> </RelativeLayout> </android.support.v7.widget.CardView>
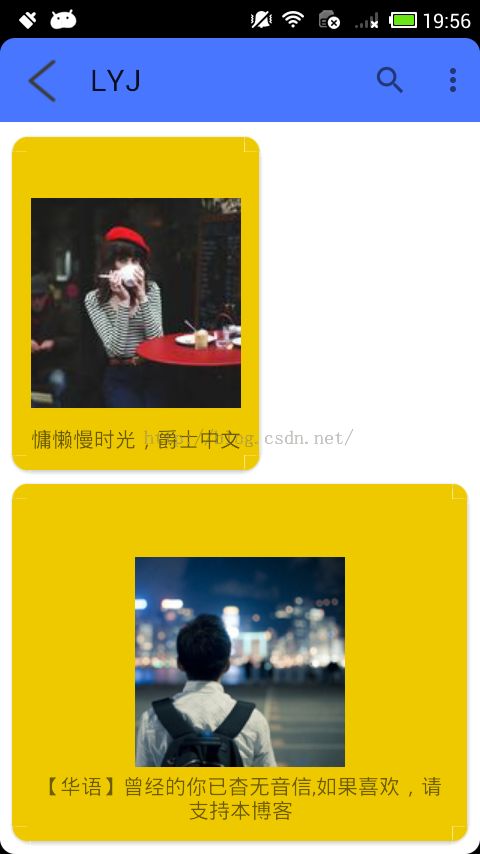
运行效果图如下:
其每个item变成了一个卡片的样式,如果色彩搭配的好,那么界面将如上线的APP一样酷炫。
下面来介绍CardView独有的属性:
app:cardElevation 阴影的大小
app:cardMaxElevation 阴影最大高度
app:cardBackgroundColor 卡片的背景色
app:cardCornerRadius 卡片的圆角大小
app:contentPadding 卡片内容于边距的间隔◦card_view:contentPaddingBottom
app:contentPaddingTop
app:contentPaddingLeft
app:contentPaddingRight
app:contentPaddingStart
app:contentPaddingEnd
app:cardUseCompatPadding 设置内边距,V21+的版本和之前的版本仍旧具有一样的计算方式
app:cardPreventConrerOverlap 在V20和之前的版本中添加内边距,这个属性为了防止内容和边角的重叠
下面简单设置几个属性:
app:cardBackgroundColor="#EEC900":卡片背景为黄色。
app:cardCornerRadius="10dp":卡片圆角半径为10dp。
app:cardPreventCornerOverlap="true":防止内容与边角重叠
app:cardUseCompatPadding="true":设置边距
app:contentPadding="10dp":边距的间隔大小为10dp
运行一下效果图如下所示: