Android Binder机制学习总结(二)-Driver部分
git clone https://android.googlesource.com/kernel/goldfish.gitBinder Driver 指令
Binder支持如下指令:
#define BINDER_WRITE_READ _IOWR('b', 1, struct binder_write_read) //最常用的指令
#define BINDER_SET_IDLE_TIMEOUT _IOW('b', 3, int64_t)
#define BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS _IOW('b', 5, size_t) //设定最大处理线程,一般供Service使用
#define BINDER_SET_IDLE_PRIORITY _IOW('b', 6, int)
#define BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR _IOW('b', 7, int) //设定ServiceManager,仅限ServiceManager使用
#define BINDER_THREAD_EXIT _IOW('b', 8, int)
#define BINDER_VERSION _IOWR('b', 9, struct binder_version) 其中,BINDER_WRITE_READ是最常用的指令,数据写入和读取都通过这个指令执行。BINDER_WRITE_READ指令,限定数据格式为binder_write_read(这个struct后面会介绍),binder_write_read结构体的write_buffer/read_buffer缓冲用于保存需要写入/读出的协议和数据。
具体来说,BINDER_WRITE_READ写入协议如下:
enum BinderDriverCommandProtocol {//按照字面翻译的话,应该是命令协议
BC_TRANSACTION = _IOW('c', 0, struct binder_transaction_data),//数据发送
BC_REPLY = _IOW('c', 1, struct binder_transaction_data),//数据答复
/*
* binder_transaction_data: the sent command.
*/
BC_ACQUIRE_RESULT = _IOW('c', 2, int),
/*
* not currently supported
* int: 0 if the last BR_ATTEMPT_ACQUIRE was not successful.
* Else you have acquired a primary reference on the object.
*/
BC_FREE_BUFFER = _IOW('c', 3, int),//buffer释放
/*
* void *: ptr to transaction data received on a read
*/
// binder_ref 引用计数控制指令
BC_INCREFS = _IOW('c', 4, int),
BC_ACQUIRE = _IOW('c', 5, int),
BC_RELEASE = _IOW('c', 6, int),
BC_DECREFS = _IOW('c', 7, int),
/*
* int: descriptor
*/
BC_INCREFS_DONE = _IOW('c', 8, struct binder_ptr_cookie),
BC_ACQUIRE_DONE = _IOW('c', 9, struct binder_ptr_cookie),
/*
* void *: ptr to binder
* void *: cookie for binder
*/
BC_ATTEMPT_ACQUIRE = _IOW('c', 10, struct binder_pri_desc),
/*
* not currently supported
* int: priority
* int: descriptor
*/
BC_REGISTER_LOOPER = _IO('c', 11),
/*
* No parameters.
* Register a spawned looper thread with the device.
*/
// 线程进入/退出循环指令
BC_ENTER_LOOPER = _IO('c', 12),
BC_EXIT_LOOPER = _IO('c', 13),
/*
* No parameters.
* These two commands are sent as an application-level thread
* enters and exits the binder loop, respectively. They are
* used so the binder can have an accurate count of the number
* of looping threads it has available.
*/
// 注册死亡通知
BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION = _IOW('c', 14, struct binder_ptr_cookie),
/*
* void *: ptr to binder
* void *: cookie
*/
// 注销死亡通知
BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION = _IOW('c', 15, struct binder_ptr_cookie),
/*
* void *: ptr to binder
* void *: cookie
*/
BC_DEAD_BINDER_DONE = _IOW('c', 16, void *),
/*
* void *: cookie
*/
}; BINDER_WRITE_READ读出协议如下:
enum BinderDriverReturnProtocol { //字面翻译的话,应该是返回协议
BR_ERROR = _IOR('r', 0, int), //操作失败
/*
* int: error code
*/
BR_OK = _IO('r', 1),//操作成功
/* No parameters! */
BR_TRANSACTION = _IOR('r', 2, struct binder_transaction_data), // 读取到数据
BR_REPLY = _IOR('r', 3, struct binder_transaction_data), // 读取到答复
/*
* binder_transaction_data: the received command.
*/
BR_ACQUIRE_RESULT = _IOR('r', 4, int),
/*
* not currently supported
* int: 0 if the last bcATTEMPT_ACQUIRE was not successful.
* Else the remote object has acquired a primary reference.
*/
BR_DEAD_REPLY = _IO('r', 5),
/*
* The target of the last transaction (either a bcTRANSACTION or
* a bcATTEMPT_ACQUIRE) is no longer with us. No parameters.
*/
BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE = _IO('r', 6), // 数据发送完成
/*
* No parameters... always refers to the last transaction requested
* (including replies). Note that this will be sent even for
* asynchronous transactions.
*/
BR_INCREFS = _IOR('r', 7, struct binder_ptr_cookie),
BR_ACQUIRE = _IOR('r', 8, struct binder_ptr_cookie),
BR_RELEASE = _IOR('r', 9, struct binder_ptr_cookie),
BR_DECREFS = _IOR('r', 10, struct binder_ptr_cookie),
/*
* void *: ptr to binder
* void *: cookie for binder
*/
BR_ATTEMPT_ACQUIRE = _IOR('r', 11, struct binder_pri_ptr_cookie),
/*
* not currently supported
* int: priority
* void *: ptr to binder
* void *: cookie for binder
*/
BR_NOOP = _IO('r', 12), // 空操作指令,无需处理
/*
* No parameters. Do nothing and examine the next command. It exists
* primarily so that we can replace it with a BR_SPAWN_LOOPER command.
*/
BR_SPAWN_LOOPER = _IO('r', 13), // 新线程创建指令
/*
* No parameters. The driver has determined that a process has no
* threads waiting to service incomming transactions. When a process
* receives this command, it must spawn a new service thread and
* register it via bcENTER_LOOPER.
*/
BR_FINISHED = _IO('r', 14),
/*
* not currently supported
* stop threadpool thread
*/
BR_DEAD_BINDER = _IOR('r', 15, void *),
/*
* void *: cookie
*/
BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE = _IOR('r', 16, void *),
/*
* void *: cookie
*/
BR_FAILED_REPLY = _IO('r', 17),
/*
* The the last transaction (either a bcTRANSACTION or
* a bcATTEMPT_ACQUIRE) failed (e.g. out of memory). No parameters.
*/
};
Binder Driver中的Struct
先把主要的Struct介绍一下,方便理解后面的内容,看不太懂或者没耐心看的,也可以直接跳过本节,后面用到了再回来联系起来看,比较好理解。
binder_proc
简单的说,binder_pro代表了使用binder driver的process,保存了process的相关信息。binder driver会为每一个调用过open函数打开“dev/binder”文件的进程创建一个binder_proc.
struct binder_proc {
struct hlist_node proc_node; //全局binder_proc列表,双向列表
struct rb_root threads; //binder_thread红黑树,process内使用binder driver的线程都会被保存在这颗红黑树中
struct rb_root nodes; //binder_node(binder实体)红黑树,process所持有的binder_node都保存在这颗红黑树中
struct rb_root refs_by_desc;//binder_ref(binder引用)红黑树,process所持有的biner_refs都会保存在颗红黑树中,红黑树以binder_ref.desc排序
struct rb_root refs_by_node;//同refs_by_desc,不过以binder_ref.node排序
int pid;//进程号
struct vm_area_struct *vma;//进程虚地址分配表
struct task_struct *tsk;//进程描述符
struct files_struct *files;//文件描述符列表
struct hlist_node deferred_work_node;
int deferred_work;
void *buffer;//binder缓冲区在内核态的地址
ptrdiff_t user_buffer_offset;//binder缓冲区在内核态地址与用户态地址的偏移量
struct list_head buffers;//binder_buffer列表
struct rb_root free_buffers;//空闲binder_buffer红黑树
struct rb_root allocated_buffers;//已分配binder_buffer红黑树
size_t free_async_space;
struct page **pages;//内存分配页表
size_t buffer_size;//binder缓冲区到大小
uint32_t buffer_free;//空闲的binder缓冲区
struct list_head todo;//binder_work列表,等待被处理的binder_work
wait_queue_head_t wait;//linux内核等待队列,参考函数wait_event&wake_up
struct binder_stats stats;
struct list_head delivered_death;
int max_threads;//最大线程数量
int requested_threads;
int requested_threads_started;
int ready_threads;
long default_priority;
}; 针对特定的key,Linux内核提供的红黑树实现可以提供O(log2N)的搜索效率(关于linux kernel红黑树并不是本文的主题,所以不做讲解,有兴趣的请自行Google)。为了提高对于binder_ref的搜索性能, refs_by_desc和refs_by_node存储了相同的内容,但分别以不同的key进行排序,这样,binder driver使用这两种key进行搜索时,都可以获得较高的效率。
binder_thread
binder_thread代表了binder_proc内的线程,保存了线程相关信息。binder driver会为每一个调用过ioctl函数操作“dev/binder”文件的线程创建binder_thread.
struct binder_thread {
struct binder_proc *proc;//线程所属进程的binder_proc
struct rb_node rb_node;//binder_thread通过rb_node链入到binder_proc的threads成员指向的红黑树中
int pid;//线程号,为什么线程号也叫pid呢?
int looper;
struct binder_transaction *transaction_stack;//暂存binder_transaction
struct list_head todo;//binder_work列表,等待被处理的binder_work
uint32_t return_error; /* Write failed, return error code in read buf */
uint32_t return_error2; /* Write failed, return error code in read */
/* buffer. Used when sending a reply to a dead process that */
/* we are also waiting on */
wait_queue_head_t wait;//linux内核等待队列,参考函数wait_event&wake_up
struct binder_stats stats;
};
binder_node
binder_node代表一个内核态的binder实体,每一个binder_node都关联到用户态的BBinder对象。
struct binder_node {
int debug_id;
struct binder_work work;//work.type=BINDER_WORK_NODE
union {
struct rb_node rb_node;//binder_node通过本节点,链入到binder_proc的nodes成员所指向的红黑树中
struct hlist_node dead_node;
};
struct binder_proc *proc;//binder_node所属进程的binder_proc
struct hlist_head refs;//binder_ref列表,储存了所有引用本binder_node的binder_ref
int internal_strong_refs;//指向本binder_node的强binder_ref计数
int local_weak_refs;//本地弱引用计数
int local_strong_refs;//本地强引用计数
void __user *ptr;//指向用户态Binder实例的指针,通常指向BBinder的弱引用
void __user *cookie;//自定义数据,通常为指向BBinder的指针
unsigned has_strong_ref : 1;
unsigned pending_strong_ref : 1;
unsigned has_weak_ref : 1;
unsigned pending_weak_ref : 1;
unsigned has_async_transaction : 1;
unsigned accept_fds : 1;
int min_priority : 8;//最低优先级
struct list_head async_todo;//异步binder
};
binder_ref
binder_ref代表内核态的binder引用,用户态每一个有效的BpBinder都关联到特定的binder_ref。同时binder_ref总是关联到一个binder_node
struct binder_ref {
/* Lookups needed: */
/* node + proc => ref (transaction) */
/* desc + proc => ref (transaction, inc/dec ref) */
/* node => refs + procs (proc exit) */
int debug_id;
struct rb_node rb_node_desc;//binder_ref通过本节点,链入到binder_proc的refs_by_desc所指向的红黑树中
struct rb_node rb_node_node;//同上,链入到binder_proc的refs_by_node所指向的红黑树中
struct hlist_node node_entry;//binder_ref通过本节点,链入到binder_node的refs成员所指向的双向链表中
struct binder_proc *proc;//所属的binder_proc
struct binder_node *node;//所指向的binder_node
uint32_t desc;//序号,等于BpBinder.mhandle
int strong;//强引用计数
int weak;//弱引用计数
struct binder_ref_death *death;//Binder死亡通知
};
binder_work
binder_work代表一个未完成的Binder工作项,可以被保存在todo队列中。
struct binder_work {
struct list_head entry;//binder_worker通过本节点链入到binder_proc或者binder_thread的todo成员指向的列表中
enum {
BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION = 1, // binder_work的owner是binder_transaction
BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE, // 发送binder_transaction数据成功
BINDER_WORK_NODE, // binder_work的owner为binder_node
BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER, // binder_work的owner为binder_ref_deatch,通知Client,Service已经死亡
BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR, //在BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER的基础上,再执行BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION
BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION, // binder_work的owner为binder_ref_deatch,通知Client,binder死亡通知已经清除
} type;//binder工作项类型
};
大部分情况下,binder_work总是作为binder_transaction的成员使用,除此以外,它还是binder_node的成员。
binder_write_read
binder_write_read为BINDER_WRITE_READ指定的数据类型,它的定义如下:
struct binder_write_read {
signed long write_size; /* bytes to write */
signed long write_consumed; /* bytes consumed by driver */
unsigned long write_buffer;
signed long read_size; /* bytes to read */
signed long read_consumed; /* bytes consumed by driver */
unsigned long read_buffer;
};
binder_transaction_data
binder_transaction_data为写入协议BC_TRANSACTION、BC_REPLY以及读出协议BR_TRANSACTION、BR_REPLY所指定的数据类型,Binder驱动的使用者(e.i. Client、Service、Service Manager)通过binder_transaction_data和Binder driver进行数据交换。
struct binder_transaction_data {
/* The first two are only used for bcTRANSACTION and brTRANSACTION,
* identifying the target and contents of the transaction.
*/
union {
size_t handle; /* target descriptor of command transaction */
void *ptr; /* target descriptor of return transaction */
} target;
void *cookie; /* target object cookie */
unsigned int code; /* transaction command */ //Service自定义的指令码,以SeviceManager的addService为函数例的话,code=ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION
/* General information about the transaction. */
unsigned int flags; //TF_ACCEPT_FDS TF_ONE_WAY
pid_t sender_pid; //发送方进程id
uid_t sender_euid; //发送方用户id
size_t data_size; /* number of bytes of data */
size_t offsets_size; /* number of bytes of offsets */
/* If this transaction is inline, the data immediately
* follows here; otherwise, it ends with a pointer to
* the data buffer.
*/
union {
struct {
/* transaction data */
const void *buffer;
/* offsets from buffer to flat_binder_object structs */
const void *offsets;
} ptr;
uint8_t buf[8];
} data;
}; 首先,就像注释中说明的那样,target成员和cookie成员仅在BC_TRANSACTION和BR_TRANSACTION协议中使用。通常,Client使用BC_TRANSACTION协议写入数据时,需要通过target.handle指定数据接收方。而Service读取到BR_TRANSACTION的binder_transaction_data.ptr成员保存了用户空间binder实体的地址(实际上,BBinder的弱引用地址),而cookie成员保存了用户数据(实际上,cookie才真正保存了BBinder的地址)。而使用BC_REPLY写入时,Binder driver忽略这两个参数,而读取到BR_REPLY的 binder_transaction_data的target和cookie成员则恒为空。
其次,flag的含义与下面的常量相关。常用的标记为TF_ONE_WAY和TF_ACCEPT_FDS。
enum transaction_flags {
TF_ONE_WAY = 0x01, /* this is a one-way call: async, no return */
TF_ROOT_OBJECT = 0x04, /* contents are the component's root object */
TF_STATUS_CODE = 0x08, /* contents are a 32-bit status code */
TF_ACCEPT_FDS = 0x10, /* allow replies with file descriptors */
};
最后,也是对于理解binder_transaction_data最重要的一点,binder_transaction_data结构体,并不包含传输的数据,而是通过其ptr.buffer成员保存了数据的内存地址。而ptr.offsets成员则保存了Binder对象(或者说flat_binder_object)在ptr.buffer的偏移量数组的首地址。data_size成员则记录了数据的长度,offsets_size则是编译量数组的长度(以字节为单位,所以,编译量数组实际的长度是offsets_size/4)。
举个例子来说(这个例子的内容,后面的文章中还会讲到,不明白没关系,这里只是为了帮助理解这几个成员的含义),当Client调用ServiceManager的getService接口请求MediaPlayerService的Binder时,Client端会调用BpServiceManager的checkService函数:
virtual sp<IBinder> checkService( const String16& name) const
{
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor());//IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor()="android.os.IServiceManager"
data.writeString16(name); //name=“media.player”
remote()->transact(CHECK_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, &reply);//这个函数内部最终会调用ioctl操作dev/binder文件写入数据,并获得返回数据
return reply.readStrongBinder();
} 下面是Parcel writeInterfaceToken的实现:
// Write RPC headers. (previously just the interface token)
status_t Parcel::writeInterfaceToken(const String16& interface)
{
writeInt32(IPCThreadState::self()->getStrictModePolicy() |
STRICT_MODE_PENALTY_GATHER);
// currently the interface identification token is just its name as a string
return writeString16(interface);
} 可以看到,实际上就是写入一个int和一个string。所以加上前面的Service name,总共是写入一个int32和两个string。另外,writeString函数执行时,会在字符串内容前先写入一个int32以表示字符串的长度,所以,最后内存上的数据可能是这样的(假设buffer地址从0x10000开始):
- 这种情况下,未向binder driver写入binder数据(即写入数据中不包含flat_binder_object结构体),所以未创建offsets对应的缓冲区。
- buffer占用内存0x10000~0x1005B,总计92个字节
- Strict Mode Policy为一个int32,占用了0x10000~0x10003这四个字节。
- interface token总计占用0x10004~0x1003D,总计58个字节,其中:
- 字符串长度为int32,占用0x10004~0x10007,4个字节
- "android.os.IServiceManager"总计26个字符,加上末尾的空字符,还有宽字符集的关系,总计需要(26+1)*2=54个字节,占用0x10008~0x1003D
- service name总计占用0x1003E~0x1005B,总计30个字节,其中:
- 字符串长度为int32,占用0x1003E~0x10041,总计4字节
- “media.player”总计12个字符,加上末尾空字符,总计需要(12+1)*2=26字节,占用0x10042~0x1005B
所以,binder_transaction_data应该是这样的:
binder_transaction_data tr; tr.data_size=92; tr.offsets_size=0; tr.ptr.buffer=0x10000; tr.ptr.offsets=NULL;Service Manager接收到请求以后,会发送MediaPlayService的Binder给Client 。这时候,ServiceManager发送的数据为一个flat_binder_object结构体,Service Manager的数据缓存是这样子的(假设数据缓存从0x10000地址开始):
- offset占用0x10000~0x1003,总计4字节,内容为0(即flat_binder_object结构体在buffer中的偏移量为0).
- buffer占用0x10010~0x1002B,总计16个字节(sizeof(flat_binder_object)=16)
所以,binder_transaction_data应该是这样子的:
binder_transaction_data tr; tr.data_size=16; tr.offsets_size=4; tr.ptr.buffer=0x10010; tr.ptr.offsets=0x10000;是不是看得有点乱了?简单总结一下:
- tr.ptr.buffer指定了数据开始地址
- tr.data_size指定了数据的长度
- tr.offsets_size的值是数组中flat_binder_object数量的4倍,因为偏移量是用int32表示的,而offsets_size则以字节为单位
- tr.ptr.offsets则是偏移量数组的首地址,其中偏移量的个数=offsets_size/4
flat_binder_object
flat_binder_object结构体用于表示在binder中传输的binder。
struct flat_binder_object {
/* 8 bytes for large_flat_header. */
unsigned long type; // binder类型
unsigned long flags; // flags
/* 8 bytes of data. */
union {
void *binder; /* local object */ //指向BBinder
signed long handle; /* remote object */ //Bpbinder.handle
};
/* extra data associated with local object */
void *cookie; //自定义数据
}; 其中,type成员可选的值如下:
#define B_PACK_CHARS(c1, c2, c3, c4) \
((((c1)<<24)) | (((c2)<<16)) | (((c3)<<8)) | (c4))
#define B_TYPE_LARGE 0x85
enum {
BINDER_TYPE_BINDER = B_PACK_CHARS('s', 'b', '*', B_TYPE_LARGE),
BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER = B_PACK_CHARS('w', 'b', '*', B_TYPE_LARGE),
BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE = B_PACK_CHARS('s', 'h', '*', B_TYPE_LARGE),
BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE = B_PACK_CHARS('w', 'h', '*', B_TYPE_LARGE),
BINDER_TYPE_FD = B_PACK_CHARS('f', 'd', '*', B_TYPE_LARGE),
}; 忽略强弱引用的差异,type可以分为三类BINDER、HANDLE、FD。
- type为BINDER类型时,flat_binder_object代表binder_node,flat_binder_object.binder等于相应binder_node.ptr,指向Service用户空间的BBinder。
- type为HANDLE类型时,flat_binder_object代表binder_ref,flat_binder_object.handle等于相应binder_refs.desc,也就是等于Client用户空间BpBinder.handle。
- type为FD类型时,flat_binder_object代表文件Binder,flat_binder_object.handle是文件在进程内的文件号。本文不讨论文件Binder,有兴趣的可以参考《Android设计与实现 设计篇》的5.2.1章节
另外,flat_binder_object的cookies和flag成员仅当type为BINDER类型,并且Binder driver还未创建相应的binder_node时起效。这时,Binder driver会创建新的binder_node,并根据flag值来设定binder_node.min_priority和binder_node.accept_fds,并保存cookies到binder_node.cookies中。其他情况下,忽略这两个成员。
flag成员可取的值如下:
enum {
FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_PRIORITY_MASK = 0xff,//binder_node.min_priority = flat_binder_object.flags & FLAT_BIDNER_FLAG_PRIORITY_MASK
FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS = 0x100,//binder_node.accept_fds = flat_binder_object.flags & FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPT_FDS
}; Binder driver在进程间传递flat_binder_object时,需要对flat_binder_object做处理。以Client向ServiceManager请求MedialPlayerService的Binder为例,ServiceManager向Client发送的flat_binder_object.type=BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE,flat_binder_object.handle=ServiceManager进程内MediaPlayerService的binder_ref.desc。如果Binder Driver不做任何处理,就把数据发送给Client,Client的确可以根据flat_binder_object.handle构造BpBinder,但是Client使用BpBinder与MediaPlayerService通信的时候,根据BpBinder的handle值却找不到对应的binder_ref或者找错了binder_ref,而通信失败。
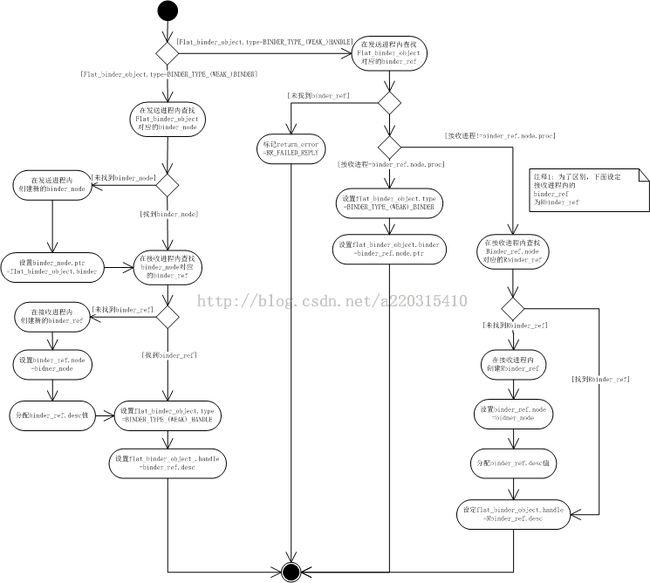
处理的逻辑简单描述如下:
如果发送的flat_binder_object.type=BINDER,
- 在发送进程内查找flat_binder_object.binder对应的binder_node
- 如果找到则执行步骤4,否则执行步骤3
- 在发送进程内创建新的binder_node,binder_node.ptr=flat_binder_object.binder
- 在接收进程内查找binder_node对应的binder_ref,如果找到则执行步骤6,否则执行步骤5
- 在接收进程内创建新的binder_ref,binder_ref.node=binder_node,分配binder_ref.desc值
- 修改flat_binder_object.type=HANDLE(BINDER_TYPE_BINDER->BINER_TYPE_HANDLE;BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER->BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE).
- 修改flat_binder_object.handle=binder_refs.desc
如果发送的flat_binder_object.type=HANDLE,
- 在发送进程内查找flat_binder_object.handle对应的binder_ref,如果找到,执行步骤3,否则执行步骤2
- 设置error为BR_FAILED_REPLY,执行步骤11(这里的设计,防止了Client通过蒙猜的方式进行非法通信
- binder_ref.node.proc是否为接收进程,如果是,则执行步骤4,否则执行步骤7
- 设置flat_binder_obecjt.type=BINDER(BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE->BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE->BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER)
- 设置flat_binder_object.binder=binder_ref.node.binder.
- 设置flat_binder_object.cookies=binder_ref.node.cookies,执行步骤11
- 在接收进程内超找对应的binder_ref,如果未找到,执行步骤8,否则执行步骤10
- 在接收进程内创建新的binder_ref
- 设置binder_ref(接收进程).node=binder_ref(发送进程).node,并分配binder_refs(接收进程).desc
- 设置flat_binder_object.handle=binder_ref(接收进程).desc
- 结束
binder_transaction
如果说binder_transaction_data是binder driver与binder 使用者之间的数据通信的工具的话,binder_transaction则是binder_driver内部,进程间交换数据的“载体”。
struct binder_transaction {
int debug_id;
struct binder_work work;//通过本节点链入到binder_proc或者binder_thread的todo队列中
struct binder_thread *from;//数据发送方
struct binder_transaction *from_parent;
struct binder_proc *to_proc;//目标进程
struct binder_thread *to_thread;//目标线程
struct binder_transaction *to_parent;
unsigned need_reply : 1; //code = BC_TRANSACTION, 并且binder_transaction_data.flags&TF_ONE_WAY= NULL时,need_reply=1
/*unsigned is_dead : 1;*/ /* not used at the moment */
struct binder_buffer *buffer; // binder_buffer,数据缓冲区
unsigned int code; //同binder_transaction_data.code
unsigned int flags; //同binder_transaction_data.flags
long priority; // 数据发送方的线程优先级线程优先级
long saved_priority; // 数据接收方的线程优先级
uid_t sender_euid; // 发送方用户id
};
binder_ref_death
在理想情况下,通过对于binder_node强/弱引用的管理,可以保证在Client请求期间,biner_node实体以及Service内的BBinder不会被回收。但是Binder机制毕竟属于跨进程的实现,当遇到exception,kill指令,LMK等情况下,Service进程可能会退出,导致binder_node实体被回收。所以,Binder Driver为Client提供了死亡通知功能。而binder_ref_death正是服务于死亡通知功能。
struct binder_ref_death {
struct binder_work work; //用以链入到todo队列,其中binder_work.type的可选值为:BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER、
// BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR、
// BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION
void __user *cookie;
};
Binder Dirver中的Methods
Linux内核启动时,会调用下面的代码来注册Binder驱动:
static const struct file_operations binder_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.poll = binder_poll,// poll的类型为函数指针,定义为unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
// 把binder_poll的地址赋值给poll成员,系统就可以通过poll来调用binder_poll函数
// 以下的成员也同理
.unlocked_ioctl = binder_ioctl,
.mmap = binder_mmap,
.open = binder_open,
.flush = binder_flush,
.release = binder_release,
};
static struct miscdevice binder_miscdev = {
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, //自动生成次设备号
.name = "binder", //设备文件名
.fops = &binder_fops
};
static int __init binder_init(void)
{
int ret;
...... //在/sys/kernel/debug/目录下创建binder目录
ret = misc_register(&binder_miscdev);//注册驱动
...... //在/sys/kernel/debug/binder目录下继续创建proc目录,
return ret;
}
......
device_initcall(binder_init); //声明驱动启动函数
misc_register函数为杂项设备注册函数,执行这个函数以后,我们就可在dev/文件夹下看到binder文件了。而misc设备为字符设备,所以binder也属于字符设备。然后,binder_miscdev.fops即binder_fops指定了Binner驱动提供了那些系统调用。
一般,Binder使用者通过下面的步骤使用Binder机制:
- 调用open函数打开dev/binder,获得文件描述符fd
- 调用mmap函数映射fd
- 调用ioctl函数操作fd,进行写入和读取
- 进程主动调用close关闭fd,或者当进程退出时由系统调用close关闭fd
下面,逐个解释这些函数的实现方式。
binder_open
当Binder使用者在用户态执行
int fd = open("/dev/binder", O_RDWR); 时,进程就会转入核心态,系统会调用binder_open函数:
static int binder_open(struct inode *nodp, struct file *filp)
{
struct binder_proc *proc;
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_OPEN_CLOSE, "binder_open: %d:%d\n",
current->group_leader->pid, current->pid);
proc = kzalloc(sizeof(*proc), GFP_KERNEL);//kzalloc函数:分配内存,并把分配的内存空间的内容设置成NULL
if (proc == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
get_task_struct(current);//增加进程信息块的引用计数
proc->tsk = current;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&proc->todo); //初始化进程的todo队列,相当于 java中new一个容器
init_waitqueue_head(&proc->wait); //初始化等待队列
proc->default_priority = task_nice(current); // 保存当前优先级
binder_lock(__func__);// 进入互斥区, __func__ 返回当前函数名
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_PROC);
hlist_add_head(&proc->proc_node, &binder_procs); //把proc链入到全局的binder_procs中
proc->pid = current->group_leader->pid; //当前进程号
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&proc->delivered_death); //初始化proc_delivered_death
filp->private_data = proc; //保存proc到filp中,所以,后面binder_mmap, binder_ioctl函数可以获取到proc
binder_unlock(__func__);//退出互斥区
if (binder_debugfs_dir_entry_proc) { //调试相关,可以忽略
char strbuf[11];
snprintf(strbuf, sizeof(strbuf), "%u", proc->pid);
proc->debugfs_entry = debugfs_create_file(strbuf, S_IRUGO,
binder_debugfs_dir_entry_proc, proc, &binder_proc_fops);
}
return 0;
}
从代码还是比较简单易懂的,创建一个binder_proc实例,初始化binder_proc实例,然后保存到file结构体filp中。
binder_mmap
当进程在用户态调用:
mVMStart = mmap(0, BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD, 0); //时,进程就会转入内核态,执行binder_mmap
static int binder_mmap(struct file *filp, struct vm_area_struct *vma)
{
int ret;
struct vm_struct *area;
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data; //获取在binder_open函数中创建的binder_proc
const char *failure_string;
struct binder_buffer *buffer;
if ((vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start) > SZ_4M) // binder 缓冲区最大为4MB
vma->vm_end = vma->vm_start + SZ_4M;
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_OPEN_CLOSE,
"binder_mmap: %d %lx-%lx (%ld K) vma %lx pagep %lx\n",
proc->pid, vma->vm_start, vma->vm_end,
(vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start) / SZ_1K, vma->vm_flags,
(unsigned long)pgprot_val(vma->vm_page_prot));
if (vma->vm_flags & FORBIDDEN_MMAP_FLAGS) {
ret = -EPERM;
failure_string = "bad vm_flags";
goto err_bad_arg;
}
vma->vm_flags = (vma->vm_flags | VM_DONTCOPY) & ~VM_MAYWRITE;
mutex_lock(&binder_mmap_lock);
if (proc->buffer) {
ret = -EBUSY;
failure_string = "already mapped";
goto err_already_mapped;
}
area = get_vm_area(vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start, VM_IOREMAP); //在kernel space虚地址空间分配配;vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start大小的空间
if (area == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
failure_string = "get_vm_area";
goto err_get_vm_area_failed;
}
proc->buffer = area->addr;
proc->user_buffer_offset = vma->vm_start - (uintptr_t)proc->buffer; // 计算用户区虚地址和内核态虚地址的地址偏移量, 这个很重要!
mutex_unlock(&binder_mmap_lock);
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_CACHE_VIPT
if (cache_is_vipt_aliasing()) {
while (CACHE_COLOUR((vma->vm_start ^ (uint32_t)proc->buffer))) {
printk(KERN_INFO "binder_mmap: %d %lx-%lx maps %p bad alignment\n", proc->pid, vma->vm_start, vma->vm_end, proc->buffer);
vma->vm_start += PAGE_SIZE;
}
}
#endif
proc->pages = kzalloc(sizeof(proc->pages[0]) * ((vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start) / PAGE_SIZE), GFP_KERNEL); //分配页表空间
if (proc->pages == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
failure_string = "alloc page array";
goto err_alloc_pages_failed;
}
proc->buffer_size = vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start;
vma->vm_ops = &binder_vm_ops; //设定虚地址操作函数
vma->vm_private_data = proc;
if (binder_update_page_range(proc, 1, proc->buffer, proc->buffer + PAGE_SIZE, vma)) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
failure_string = "alloc small buf";
goto err_alloc_small_buf_failed;
}
buffer = proc->buffer;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&proc->buffers); //初始化buffer list
list_add(&buffer->entry, &proc->buffers); //保存刚刚分配的buffer
buffer->free = 1;
binder_insert_free_buffer(proc, buffer); //保存到未分配的buffer列表中
proc->free_async_space = proc->buffer_size / 2;
barrier();
proc->files = get_files_struct(proc->tsk);
proc->vma = vma;
proc->vma_vm_mm = vma->vm_mm;
/*printk(KERN_INFO "binder_mmap: %d %lx-%lx maps %p\n",
proc->pid, vma->vm_start, vma->vm_end, proc->buffer);*/
return 0;
err_alloc_small_buf_failed:
kfree(proc->pages);
proc->pages = NULL;
err_alloc_pages_failed:
mutex_lock(&binder_mmap_lock);
vfree(proc->buffer);
proc->buffer = NULL;
err_get_vm_area_failed:
err_already_mapped:
mutex_unlock(&binder_mmap_lock);
err_bad_arg:
printk(KERN_ERR "binder_mmap: %d %lx-%lx %s failed %d\n",
proc->pid, vma->vm_start, vma->vm_end, failure_string, ret);
return ret;
}
binder_mmap函数,主要完成了两个操作,首先,在内核态分配与用户态的内存空间同等大小的虚地址空间。并保存两个虚地址起始地址的偏移量。
area = get_vm_area(vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start, VM_IOREMAP); //在kernel space虚地址空间内分配 vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start大小的空间
if (area == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
failure_string = "get_vm_area";
goto err_get_vm_area_failed;
}
proc->buffer = area->addr;
proc->user_buffer_offset = vma->vm_start - (uintptr_t)proc->buffer; // 计算用户区虚地址和内核态虚地址的地址偏移量, 这个很重要! 上面的代码中,vma是linux的进程虚地址管理单元,表示mmap函数在用户态分配的虚地址空间。然后,通过get_vm_area函数,在内核态分配了同一大小的虚地址空间。最后,计算了两个虚地址之间的偏移量(vma->vm_start - proc->buffer),并保存。
其次,通过binder_update_page_range为刚刚分配的虚地址空间分配第一个物理内存页面,并保存到proc->buffers和proc->free_buffers中:
if (binder_update_page_range(proc, 1, proc->buffer, proc->buffer + PAGE_SIZE, vma)) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
failure_string = "alloc small buf";
goto err_alloc_small_buf_failed;
}
buffer = proc->buffer;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&proc->buffers); //初始化buffer list
list_add(&buffer->entry, &proc->buffers); //保存刚刚分配的buffer
buffer->free = 1;
binder_insert_free_buffer(proc, buffer); //保存到未分配的buffer列表中
binder_update_page_range
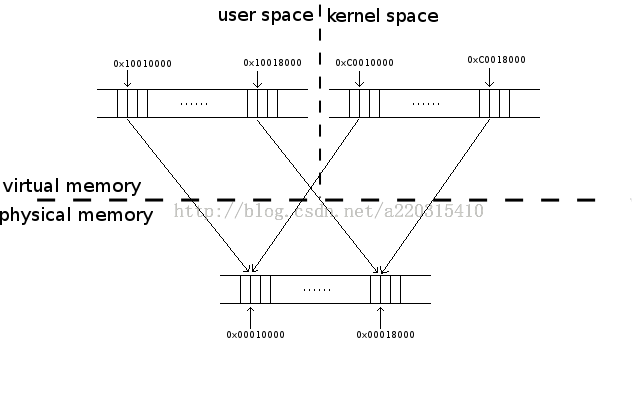
在开始介绍binder_update_page_range函数前,有必要先解释下Binder驱动中,用户态和核心态共享同一段物理内存的设计。
为了提高数据传输速度,Binder通信时,数据接收端和Binder驱动会使用两个不同的虚地址共享同一段物理内存,这样,数据从数据发送端copy到Binder driver时,相当于已经拷贝到数据接收端。减少了一次从binder driver向数据接收端的拷贝。这里提到的两个不同的虚地址,即为binder_open函数中vma代表的用户态序地址和proc->buffer指向的核心态虚地址。
假设binder使用者map了一个128KB的binder缓存,那么mmap函数执行完以后,可能是这样的(假设这时已经为全部缓存分配物理内存):
这时,binder使用者在用户态的缓冲区的虚地址为0x10010000~0x10018000,即vma->vm_start=0x10010000, vma->vm_end=0x10018000.
而binder driver在内核态为binder用户创建的缓冲区虚地址为0xC0010000~0xC0018000,即proc.buffer=0xC0010000,proc.buffer_size=0x8000.
此时,proc.user_buffer_offset=0xB0000000.
这种情况下,我们再假设binder driver在地址0xC0010010上保存了一个int值1,即*((int*)0xC0010010)=1。
那么,binder使用者在地址0x10010010(0xC0010010-0xB0000000)读取一个int值也等于1.因为两者访问的是同一段物理内存,所以其中的内容也是一致的。
binder_update_page_range函数提供物理内存的分配和释放功能。这里,我们主要关注分配物理内存,并把同一个物理内存页映射到两段不同的虚拟地址的实现.
static int binder_update_page_range(struct binder_proc *proc, int allocate, // proc 分配虚地址的进程; allocate==1 则分配内存,反之,释放内存
void *start, void *end, //start 开始虚地址; end 结束虚地址
struct vm_area_struct *vma) //vma 用户空间虚地址
{
void *page_addr;
unsigned long user_page_addr;
struct vm_struct tmp_area;
struct page **page;
struct mm_struct *mm;
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_BUFFER_ALLOC,
"binder: %d: %s pages %p-%p\n", proc->pid,
allocate ? "allocate" : "free", start, end);
if (end <= start)
return 0;
trace_binder_update_page_range(proc, allocate, start, end);
if (vma)
mm = NULL;
else
mm = get_task_mm(proc->tsk);
if (mm) {
down_write(&mm->mmap_sem);
vma = proc->vma;
if (vma && mm != proc->vma_vm_mm) {
pr_err("binder: %d: vma mm and task mm mismatch\n",
proc->pid);
vma = NULL;
}
}
if (allocate == 0)
goto free_range;
if (vma == NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: %d: binder_alloc_buf failed to "
"map pages in userspace, no vma\n", proc->pid);
goto err_no_vma;
}
for (page_addr = start; page_addr < end; page_addr += PAGE_SIZE) {
int ret;
struct page **page_array_ptr;
page = &proc->pages[(page_addr - proc->buffer) / PAGE_SIZE]; //根据开始地址,从proc的页表中找到对应的内存页
//proc的页表(proc->pages)在binder_mmap中初始化
BUG_ON(*page);
*page = alloc_page(GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_ZERO); //分配物理内存页
if (*page == NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: %d: binder_alloc_buf failed "
"for page at %p\n", proc->pid, page_addr);
goto err_alloc_page_failed;
}
tmp_area.addr = page_addr;
tmp_area.size = PAGE_SIZE + PAGE_SIZE /* guard page? */; // vm_structde.size=实际大小+PAGE_SIZE,这个是linux内核设计的
// 可能和用于侦测越界访问的页面保护设计有关
page_array_ptr = page;
ret = map_vm_area(&tmp_area, PAGE_KERNEL, &page_array_ptr); //把page_array_ptr指定的物理内存页分配给tmp_area指定的虚地址
// page_array_ptr是一个内存页的列表,当前仅有一个元素
if (ret) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: %d: binder_alloc_buf failed "
"to map page at %p in kernel\n",
proc->pid, page_addr);
goto err_map_kernel_failed;
}
user_page_addr =
(uintptr_t)page_addr + proc->user_buffer_offset;
ret = vm_insert_page(vma, user_page_addr, page[0]);//把page[0]指定的内存页分配给vma中user_page_add指定的虚地址
if (ret) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: %d: binder_alloc_buf failed "
"to map page at %lx in userspace\n",
proc->pid, user_page_addr);
goto err_vm_insert_page_failed;
}
/* vm_insert_page does not seem to increment the refcount */
}
if (mm) { //看不懂的,就忽略了吧...
up_write(&mm->mmap_sem);
mmput(mm);
}
return 0;
free_range:
for (page_addr = end - PAGE_SIZE; page_addr >= start;
page_addr -= PAGE_SIZE) {
page = &proc->pages[(page_addr - proc->buffer) / PAGE_SIZE];
if (vma)
zap_page_range(vma, (uintptr_t)page_addr +
proc->user_buffer_offset, PAGE_SIZE, NULL);
err_vm_insert_page_failed:
unmap_kernel_range((unsigned long)page_addr, PAGE_SIZE);
err_map_kernel_failed:
__free_page(*page);
*page = NULL;
err_alloc_page_failed:
;
}
err_no_vma:
if (mm) {
up_write(&mm->mmap_sem);
mmput(mm);
}
return -ENOMEM;
} 最主要的代码是上面第44行开始的for循环。每次循环需要执行3个操作:
- 调用alloc_page分配一个物理页表
- 调用map_vm_area把内核态虚地址和物理页表关联起来
- 调用vm_insert_page把内核态虚地址和物理页表关联起来
binder_ioctl
当binder使用者在用户态调用
ioctl(mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr)时,进程即转入核心态,调用binder_ioctl函数:
static long binder_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int ret;
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data; //获取binder_open函数保存的binder_proc
struct binder_thread *thread;
unsigned int size = _IOC_SIZE(cmd);//获取cmd对应的data size
void __user *ubuf = (void __user *)arg;
/*printk(KERN_INFO "binder_ioctl: %d:%d %x %lx\n", proc->pid, current->pid, cmd, arg);*/
trace_binder_ioctl(cmd, arg);
ret = wait_event_interruptible(binder_user_error_wait, binder_stop_on_user_error < 2); //如果binder_stop_on_user_error>=2,会进入等待
if (ret)
goto err_unlocked;
binder_lock(__func__);
thread = binder_get_thread(proc);//获取当前线程的binder_thread
if (thread == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err;
}
switch (cmd) {
case BINDER_WRITE_READ: {
struct binder_write_read bwr;
if (size != sizeof(struct binder_write_read)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
if (copy_from_user(&bwr, ubuf, sizeof(bwr))) {
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_READ_WRITE,
"binder: %d:%d write %ld at %08lx, read %ld at %08lx\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, bwr.write_size, bwr.write_buffer,
bwr.read_size, bwr.read_buffer);
if (bwr.write_size > 0) {
ret = binder_thread_write(proc, thread, (void __user *)bwr.write_buffer, bwr.write_size, &bwr.write_consumed);
trace_binder_write_done(ret);
if (ret < 0) {
bwr.read_consumed = 0;
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr)))
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
}
if (bwr.read_size > 0) {
ret = binder_thread_read(proc, thread, (void __user *)bwr.read_buffer, bwr.read_size, &bwr.read_consumed, filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK);
trace_binder_read_done(ret);
if (!list_empty(&proc->todo))
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
if (ret < 0) {
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr)))
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
}
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_READ_WRITE,
"binder: %d:%d wrote %ld of %ld, read return %ld of %ld\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, bwr.write_consumed, bwr.write_size,
bwr.read_consumed, bwr.read_size);
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr))) {
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
break;
}
case BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS:
if (copy_from_user(&proc->max_threads, ubuf, sizeof(proc->max_threads))) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
break;
case BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR:
if (binder_context_mgr_node != NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR already set\n");
ret = -EBUSY;
goto err;
}
ret = security_binder_set_context_mgr(proc->tsk);
if (ret < 0)
goto err;
if (binder_context_mgr_uid != -1) {
if (binder_context_mgr_uid != current->cred->euid) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: BINDER_SET_"
"CONTEXT_MGR bad uid %d != %d\n",
current->cred->euid,
binder_context_mgr_uid);
ret = -EPERM;
goto err;
}
} else
binder_context_mgr_uid = current->cred->euid;
binder_context_mgr_node = binder_new_node(proc, NULL, NULL);
if (binder_context_mgr_node == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err;
}
binder_context_mgr_node->local_weak_refs++;
binder_context_mgr_node->local_strong_refs++;
binder_context_mgr_node->has_strong_ref = 1;
binder_context_mgr_node->has_weak_ref = 1;
break;
case BINDER_THREAD_EXIT:
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS, "binder: %d:%d exit\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
binder_free_thread(proc, thread);
thread = NULL;
break;
case BINDER_VERSION:
if (size != sizeof(struct binder_version)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
if (put_user(BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION, &((struct binder_version *)ubuf)->protocol_version)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
break;
default:
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
ret = 0;
err:
if (thread)
thread->looper &= ~BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_NEED_RETURN;
binder_unlock(__func__);
wait_event_interruptible(binder_user_error_wait, binder_stop_on_user_error < 2);
if (ret && ret != -ERESTARTSYS)
printk(KERN_INFO "binder: %d:%d ioctl %x %lx returned %d\n", proc->pid, current->pid, cmd, arg, ret);
err_unlocked:
trace_binder_ioctl_done(ret);
return ret;
}
首先,binder driver确定当前进程信息(binder_proc)和线程信息(binder_thread)。binder_proc可以从参数的file结构体中获得,而binder_thread则通过binder_get_thread函数从binder_proc对象中获取。
接着开始处理cmd,我们根据cmd的类型逐个分析:
BINDER_WRITE_READ
case BINDER_WRITE_READ: {
struct binder_write_read bwr;
if (size != sizeof(struct binder_write_read)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
if (copy_from_user(&bwr, ubuf, sizeof(bwr))) {//从user space拷贝binder_write_read
//还记得binder_write_read长什么样么?去上个章节看看就知道了
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_READ_WRITE,
"binder: %d:%d write %ld at %08lx, read %ld at %08lx\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, bwr.write_size, bwr.write_buffer,
bwr.read_size, bwr.read_buffer);
if (bwr.write_size > 0){ //如果write_size大于0,则进行写入/发送操作
ret = binder_thread_write(proc, thread, (void __user *)bwr.write_buffer, bwr.write_size, &bwr.write_consumed);
trace_binder_write_done(ret);
if (ret < 0) {
bwr.read_consumed = 0;
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr)))
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
}
if (bwr.read_size > 0) {//如果read_size大于0,则进行读取/接收操作
ret = binder_thread_read(proc, thread, (void __user *)bwr.read_buffer, bwr.read_size, &bwr.read_consumed, filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK);
trace_binder_read_done(ret);
if (!list_empty(&proc->todo))
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
if (ret < 0) {
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr)))
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
}
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_READ_WRITE,
"binder: %d:%d wrote %ld of %ld, read return %ld of %ld\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, bwr.write_consumed, bwr.write_size,
bwr.read_consumed, bwr.read_size);
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr))) {//把读取到的数据,写回到user space
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
break;
} 可以看到,对于BINDER_READ_WRITE指令,ioctl通过调用binder_thread_write&binder_thread_read进行处理。
BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS
case BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS:
if (copy_from_user(&proc->max_threads, ubuf, sizeof(proc->max_threads))) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
break; BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS指令,供Service使用。Service可以通过该指令设定自身的最大线程数。当binder driver发现Service的所有线程都处于繁忙中,并且Service的线程树<proc->max_threads,就会向Service发送BR_SPAWN_LOOPER。Serivce接收到BR_SPAWN_LOOPER以后,会开启新的线程,以处理更多的请求。
BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR
case BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR:
if (binder_context_mgr_node != NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR already set\n");
ret = -EBUSY;
goto err;
}
ret = security_binder_set_context_mgr(proc->tsk); //基于Permission的安全检查
if (ret < 0)
goto err;
if (binder_context_mgr_uid != -1) {
if (binder_context_mgr_uid != current->cred->euid) { //如果已经设置过context manager,则前后用户id必须一致
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: BINDER_SET_"
"CONTEXT_MGR bad uid %d != %d\n",
current->cred->euid,
binder_context_mgr_uid);
ret = -EPERM;
goto err;
}
} else
binder_context_mgr_uid = current->cred->euid;
binder_context_mgr_node = binder_new_node(proc, NULL, NULL); //创建新的binder_node, ptr=null, cookie=null
if (binder_context_mgr_node == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err;
}
binder_context_mgr_node->local_weak_refs++;
binder_context_mgr_node->local_strong_refs++;
binder_context_mgr_node->has_strong_ref = 1;
binder_context_mgr_node->has_weak_ref = 1;
break; 通常,仅ServiceManager会使用BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR指令。鉴于在正规厂商的rom中,不会有别的Binder使用者早于ServiceManager启动,所以,BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR指令应该还是比较安全的。
BINDER_THREAD_EXIT
case BINDER_THREAD_EXIT: binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS, "binder: %d:%d exit\n", proc->pid, thread->pid); binder_free_thread(proc, thread);//释放binder_thread对象 thread = NULL; break;Serivice端处理线程退出时,会使用该指令。
BINDER_VERSION
case BINDER_VERSION:
if (size != sizeof(struct binder_version)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
if (put_user(BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION, &((struct binder_version *)ubuf)->protocol_version)) { //BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION = 7
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
break;
binder_thread_write
binder_thread_write函数由binder_ioctl函数调用,提供了对于BC_XXXX系列(BinderDriverCommandProtocol)命令的支持:
int binder_thread_write(struct binder_proc *proc, struct binder_thread *thread,
void __user *buffer, int size, signed long *consumed)
{
uint32_t cmd;
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;
void __user *end = buffer + size;
while (ptr < end && thread->return_error == BR_OK) { // BINDER_WRITE_READ指令允许一次写入多条BC_XXXX指令
if (get_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr)) // 读取BC_XXXX
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
trace_binder_command(cmd);
if (_IOC_NR(cmd) < ARRAY_SIZE(binder_stats.bc)) {
binder_stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]++;
proc->stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]++;
thread->stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]++;
}
switch (cmd) {
case BC_INCREFS:
case BC_ACQUIRE:
case BC_RELEASE:
case BC_DECREFS: {
uint32_t target;
struct binder_ref *ref;
const char *debug_string;
if (get_user(target, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
if (target == 0 && binder_context_mgr_node &&
(cmd == BC_INCREFS || cmd == BC_ACQUIRE)) {
ref = binder_get_ref_for_node(proc,
binder_context_mgr_node);
if (ref->desc != target) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:"
"%d tried to acquire "
"reference to desc 0, "
"got %d instead\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
ref->desc);
}
} else
ref = binder_get_ref(proc, target);
if (ref == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d refcou"
"nt change on invalid ref %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, target);
break;
}
switch (cmd) {
case BC_INCREFS:
debug_string = "IncRefs";
binder_inc_ref(ref, 0, NULL);
break;
case BC_ACQUIRE:
debug_string = "Acquire";
binder_inc_ref(ref, 1, NULL);
break;
case BC_RELEASE:
debug_string = "Release";
binder_dec_ref(ref, 1);
break;
case BC_DECREFS:
default:
debug_string = "DecRefs";
binder_dec_ref(ref, 0);
break;
}
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_USER_REFS,
"binder: %d:%d %s ref %d desc %d s %d w %d for node %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, debug_string, ref->debug_id,
ref->desc, ref->strong, ref->weak, ref->node->debug_id);
break;
}
case BC_INCREFS_DONE:
case BC_ACQUIRE_DONE: {
void __user *node_ptr;
void *cookie;
struct binder_node *node;
if (get_user(node_ptr, (void * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
if (get_user(cookie, (void * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
node = binder_get_node(proc, node_ptr);
if (node == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d "
"%s u%p no match\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
cmd == BC_INCREFS_DONE ?
"BC_INCREFS_DONE" :
"BC_ACQUIRE_DONE",
node_ptr);
break;
}
if (cookie != node->cookie) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d %s u%p node %d"
" cookie mismatch %p != %p\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
cmd == BC_INCREFS_DONE ?
"BC_INCREFS_DONE" : "BC_ACQUIRE_DONE",
node_ptr, node->debug_id,
cookie, node->cookie);
break;
}
if (cmd == BC_ACQUIRE_DONE) {
if (node->pending_strong_ref == 0) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d "
"BC_ACQUIRE_DONE node %d has "
"no pending acquire request\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
node->debug_id);
break;
}
node->pending_strong_ref = 0;
} else {
if (node->pending_weak_ref == 0) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d "
"BC_INCREFS_DONE node %d has "
"no pending increfs request\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
node->debug_id);
break;
}
node->pending_weak_ref = 0;
}
binder_dec_node(node, cmd == BC_ACQUIRE_DONE, 0);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_USER_REFS,
"binder: %d:%d %s node %d ls %d lw %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
cmd == BC_INCREFS_DONE ? "BC_INCREFS_DONE" : "BC_ACQUIRE_DONE",
node->debug_id, node->local_strong_refs, node->local_weak_refs);
break;
}
case BC_ATTEMPT_ACQUIRE:
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: BC_ATTEMPT_ACQUIRE not supported\n");
return -EINVAL;
case BC_ACQUIRE_RESULT:
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: BC_ACQUIRE_RESULT not supported\n");
return -EINVAL;
case BC_FREE_BUFFER: {
void __user *data_ptr;
struct binder_buffer *buffer;
if (get_user(data_ptr, (void * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
buffer = binder_buffer_lookup(proc, data_ptr);
if (buffer == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d "
"BC_FREE_BUFFER u%p no match\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, data_ptr);
break;
}
if (!buffer->allow_user_free) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d "
"BC_FREE_BUFFER u%p matched "
"unreturned buffer\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, data_ptr);
break;
}
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_FREE_BUFFER,
"binder: %d:%d BC_FREE_BUFFER u%p found buffer %d for %s transaction\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, data_ptr, buffer->debug_id,
buffer->transaction ? "active" : "finished");
if (buffer->transaction) {
buffer->transaction->buffer = NULL;
buffer->transaction = NULL;
}
if (buffer->async_transaction && buffer->target_node) {
BUG_ON(!buffer->target_node->has_async_transaction);
if (list_empty(&buffer->target_node->async_todo))
buffer->target_node->has_async_transaction = 0;
else
list_move_tail(buffer->target_node->async_todo.next, &thread->todo);
}
trace_binder_transaction_buffer_release(buffer);
binder_transaction_buffer_release(proc, buffer, NULL);
binder_free_buf(proc, buffer);
break;
}
case BC_TRANSACTION:
case BC_REPLY: {
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
if (copy_from_user(&tr, ptr, sizeof(tr)))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(tr);
binder_transaction(proc, thread, &tr, cmd == BC_REPLY);
break;
}
case BC_REGISTER_LOOPER:
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS,
"binder: %d:%d BC_REGISTER_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
if (thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED) {
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_INVALID;
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d ERROR:"
" BC_REGISTER_LOOPER called "
"after BC_ENTER_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
} else if (proc->requested_threads == 0) {
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_INVALID;
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d ERROR:"
" BC_REGISTER_LOOPER called "
"without request\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
} else {
proc->requested_threads--;
proc->requested_threads_started++;
}
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED;
break;
case BC_ENTER_LOOPER:
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS,
"binder: %d:%d BC_ENTER_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
if (thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED) {
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_INVALID;
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d ERROR:"
" BC_ENTER_LOOPER called after "
"BC_REGISTER_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
}
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED;
break;
case BC_EXIT_LOOPER:
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS,
"binder: %d:%d BC_EXIT_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_EXITED;
break;
case BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION:
case BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION: {
uint32_t target;
void __user *cookie;
struct binder_ref *ref;
struct binder_ref_death *death;
if (get_user(target, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
if (get_user(cookie, (void __user * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
ref = binder_get_ref(proc, target);
if (ref == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d %s "
"invalid ref %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
cmd == BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION ?
"BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION" :
"BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION",
target);
break;
}
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_DEATH_NOTIFICATION,
"binder: %d:%d %s %p ref %d desc %d s %d w %d for node %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
cmd == BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION ?
"BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION" :
"BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION",
cookie, ref->debug_id, ref->desc,
ref->strong, ref->weak, ref->node->debug_id);
if (cmd == BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION) {
if (ref->death) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%"
"d BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTI"
"FICATION death notific"
"ation already set\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
break;
}
death = kzalloc(sizeof(*death), GFP_KERNEL);
if (death == NULL) {
thread->return_error = BR_ERROR;
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_FAILED_TRANSACTION,
"binder: %d:%d "
"BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION failed\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
break;
}
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_DEATH);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&death->work.entry);
death->cookie = cookie;
ref->death = death;
if (ref->node->proc == NULL) {
ref->death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER;
if (thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED | BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) {
list_add_tail(&ref->death->work.entry, &thread->todo);
} else {
list_add_tail(&ref->death->work.entry, &proc->todo);
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
}
}
} else {
if (ref->death == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%"
"d BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFI"
"CATION death notificat"
"ion not active\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
break;
}
death = ref->death;
if (death->cookie != cookie) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%"
"d BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFI"
"CATION death notificat"
"ion cookie mismatch "
"%p != %p\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
death->cookie, cookie);
break;
}
ref->death = NULL;
if (list_empty(&death->work.entry)) {
death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION;
if (thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED | BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) {
list_add_tail(&death->work.entry, &thread->todo);
} else {
list_add_tail(&death->work.entry, &proc->todo);
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
}
} else {
BUG_ON(death->work.type != BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER);
death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR;
}
}
} break;
case BC_DEAD_BINDER_DONE: {
struct binder_work *w;
void __user *cookie;
struct binder_ref_death *death = NULL;
if (get_user(cookie, (void __user * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
list_for_each_entry(w, &proc->delivered_death, entry) {
struct binder_ref_death *tmp_death = container_of(w, struct binder_ref_death, work);
if (tmp_death->cookie == cookie) {
death = tmp_death;
break;
}
}
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_DEAD_BINDER,
"binder: %d:%d BC_DEAD_BINDER_DONE %p found %p\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, cookie, death);
if (death == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d BC_DEAD"
"_BINDER_DONE %p not found\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, cookie);
break;
}
list_del_init(&death->work.entry);
if (death->work.type == BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR) {
death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION;
if (thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED | BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) {
list_add_tail(&death->work.entry, &thread->todo);
} else {
list_add_tail(&death->work.entry, &proc->todo);
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
}
}
} break;
default:
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: %d:%d unknown command %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, cmd);
return -EINVAL;
}
*consumed = ptr - buffer;
}
return 0;
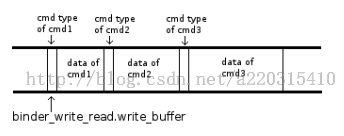
} 因为BINDER_WRITE_READ允许调用者在一次ioctl调用中写入多条指令,所以,binder_write_read.write_buffer指向的内存地址可能是下面这样的(图中假设binder_write_read.write_consumed = 0):
如果所示,
- 第一条指令从地址binder_write_reader.write_buffer+binder_write_consumed开始,其他指令逐个跟随其后。
- 每条指令由cmd(图中以cmd type表示)和data两部分组成,data跟随cmd之后。
因为上面的设计,所以binder_thread_write的实现为一个循环:
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;
void __user *end = buffer + size;
while (ptr < end && thread->return_error == BR_OK) { //退出循环的条件是,处理完所有指令,或者执行出错 循环开始的第一步,读取指令的cmd:
if (get_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr)) return -EFAULT; ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);接下来,就是根据指令的类型,执行不同的处理。
BC_INCREFS、BC_ACQUIRE、BC_RELEASE、BC_DECREFS
这四条指令用于处理binder ref的引用计数:
| 指令触发时间 | binder driver对应的操作 | |
| BC_INCREFS | BpBinder构造时 | binder_ref的弱引用计数+1 |
| BC_ACQUIRE | BpBinder获得第一个sp (strong pointer) |
binder_ref的强引用计数+1 |
| BC_RELEASE | BpBinder释放最后一个sp | binder_ref的强引用计数-1 |
| BC_DECREFS | BpBinder析构 | binder_ref的弱引用计数-1 |
首先,需要确定BpBinder对应的binder_ref:
if (get_user(target, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))//读取BpBinder.mHandle
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
if (target == 0 && binder_context_mgr_node &&
(cmd == BC_INCREFS || cmd == BC_ACQUIRE)) {
ref = binder_get_ref_for_node(proc,
binder_context_mgr_node);
if (ref->desc != target) { //个人认为这个if永远不可能为true,可能是为了鲁棒性的考虑
binder_user_error("binder: %d:"
"%d tried to acquire "
"reference to desc 0, "
"got %d instead\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
ref->desc);
}
} else
ref = binder_get_ref(proc, target);
if (ref == NULL) {//找不到binder_ref,出错
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d refcou"
"nt change on invalid ref %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, target);
break;
} 然后,根据cmd,调用binder_inc_ref函数来处理binder_ref的引用计数:
switch (cmd) {
case BC_INCREFS:
debug_string = "IncRefs";
binder_inc_ref(ref, 0, NULL);
break;
case BC_ACQUIRE:
debug_string = "Acquire";
binder_inc_ref(ref, 1, NULL);
break;
case BC_RELEASE:
debug_string = "Release";
binder_dec_ref(ref, 1);
break;
case BC_DECREFS:
default:
debug_string = "DecRefs";
binder_dec_ref(ref, 0);
break;
}
BC_INCREFS_DONE、BC_ACQUIRE_DONE
和前面的四个指令相似,区别在于,这两个指令用于管理binder_node的引用计数:
| 指令触发时间 | binder driver对应的操作 | |
| BC_INCREFS_DONE | BBinder接收到BR_INCREFS后 进行BBinder的弱引用计数+1, 操作完成后,向binder driver发送 BC_INCREFS_DONE |
node->pending_strong_ref = 0; node->local_weak_refs - 1 |
| BC_ACQUIRE_NODE | BBinder接收到BR_ACQUIRE后 |
node->pending_weak_ref = 0; node-local_string_refs - 1 |
if (get_user(node_ptr, (void * __user *)ptr)) // binder_node.ptr return -EFAULT; ptr += sizeof(void *); if (get_user(cookie, (void * __user *)ptr)) // binder_node.cookies return -EFAULT; ptr += sizeof(void *); node = binder_get_node(proc, node_ptr); // 查找binder_node然后,设置binder_node->pending_strong_ref & binder_node->pending_weak_ref:
if (cmd == BC_ACQUIRE_DONE) {
if (node->pending_strong_ref == 0) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d "
"BC_ACQUIRE_DONE node %d has "
"no pending acquire request\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
node->debug_id);
break;
}
node->pending_strong_ref = 0;
} else {
if (node->pending_weak_ref == 0) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d "
"BC_INCREFS_DONE node %d has "
"no pending increfs request\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
node->debug_id);
break;
}
node->pending_weak_ref = 0;
} 最后调用
binder_dec_node(node, cmd == BC_ACQUIRE_DONE, 0);来减少node->local_strong_refs&node->local_weak_refs。
至于为什么要减少node->local_strong_refs&node->local_weak_refs,这个是因为binder driver处理BINDER_WORK_NODE时,增加过它们,所以,现在这里要把它们再减回来。
BC_FREE_BUFFER
因为binder driver内binder缓冲区(binder_buffer)和数据接收者的用户态数据缓冲区共享同一段物理内存,所以binder driver不会主动去释放缓冲区,否则数据接受者会无法访问自己的用户态数据缓区。而数据接收者在处理完数据以后,需要向binder driver发送BC_FREE_BUFFER指令,“命令”binder driver释放binder_buffer.
首先,确定需要释放的binder_buffer:
if (get_user(data_ptr, (void * __user *)ptr))//获取binder_buffer的data在用户空间的地址 return -EFAULT; ptr += sizeof(void *); buffer = binder_buffer_lookup(proc, data_ptr);//在proc->allocated_buffers内寻找binder_buffer然后,把两个指针置零:
if (buffer->transaction) { //通常buffer->transaction != null
buffer->transaction->buffer = NULL;
buffer->transaction = NULL;
} 接着,当binder_buffer属于一个异步binder请求时,还需要做特殊处理:
if (buffer->async_transaction && buffer->target_node) {
BUG_ON(!buffer->target_node->has_async_transaction);
if (list_empty(&buffer->target_node->async_todo))
buffer->target_node->has_async_transaction = 0;
else
list_move_tail(buffer->target_node->async_todo.next, &thread->todo);
} 说到这里,有必要交代一下同步Binder和异步binder之间的差别:
- 异步binder请求不允许回复请求
- 这意味着如果Client想知道异步Binder请求是否被处理完,处理结果时,需要在发送同步binder请求来查询
- 这意味着如果Client想知道异步Binder请求是否被处理完,处理结果时,需要在发送同步binder请求来查询
- todo队列中,同一时间最多仅允许有一个异步binder请求。如果Serivce线程todo队列中已经有一个异步binder请求,或者正在处理这个异步binder请求,那么后续接收到的异步binder_请求都会被保存到target_node->async_todo队列中。而同步请求则不受此限制。
- 因为同步请求意味着client会等待Service的处理结果,而异步请求说明client对于处理时间是有“心理准备”的,所以同步Binder请求的优先级高于异步Binder请求。
- 因为同步请求意味着client会等待Service的处理结果,而异步请求说明client对于处理时间是有“心理准备”的,所以同步Binder请求的优先级高于异步Binder请求。
- 当Service处理完一个异步请求后,下一个异步binder请求才允许被放入到todo队列中。
最后,释放binder_buffer并把它重新标记为可用状态。
binder_transaction_buffer_release(proc, buffer, NULL);//释放binder_buffer内的所有flat_binder_object binder_free_buf(proc, buffer);//释放buffer占用的物理内存,并且标记binder_buffer为空闲
BC_ENTER_LOOPER
当Service端主线程(准确来说,第一个线程)进入处理循环前,该线程会向binder driver发送BC_ENTER_LOOPER,这时binder driver需要标记binder_thread的状态:
if (thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED) { //如果线程已经发送过BC_REGISTER_LOOPER,则出错
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_INVALID;
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d ERROR:"
" BC_ENTER_LOOPER called after "
"BC_REGISTER_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
}
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED;
BC_REGISTER_LOOPER
当Driver向Serivce发送BR_SPAWN_LOOPER指令时,Serivce应该开启新的线程,进入处理循环。在新线程进入处理循环前,它会向binderdriver发送指令BC_REGISTER_LOOPER指令。
if (thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED) { //如果线程已经发送过BC_ENTER_LOOPER,则出错
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_INVALID;
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d ERROR:"
" BC_REGISTER_LOOPER called "
"after BC_ENTER_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
} else if (proc->requested_threads == 0) { //如果proc->request_threads==0,说明binder driver未发出BR_SPAWN_LOOPER指令
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_INVALID;
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d ERROR:"
" BC_REGISTER_LOOPER called "
"without request\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
} else { //处理计数
proc->requested_threads--;
proc->requested_threads_started++;
}
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED; //标记线程状态
break; 从代码上我们可以看到BC_REGISTER_LOOPER和BC_ENTER_LOOPER指令其实是很相似的,它们之间的区别在于:
当处理线程是Service主动开启时,它进入循环前应该发送BC_ENTER_LOOPER给binder driver。当Service的线程开启是BR_SPAWN_LOOPER指令触发时,线程进入循环前应该发送BC_REGISTER_LOOPER给binder driver。
BC_EXIT_LOOPER
既然线程进入处理循环前会发送指令来使binder driver标记自己的状态,那么它退出处理循环后,当然也需要发送指令来修改自己的状态:
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS, "binder: %d:%d BC_EXIT_LOOPER\n", proc->pid, thread->pid); thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_EXITED;无论线程进入循环时发送的指令是BC_REGISTER_LOOPER还是BC_ENTER_LOOPER,退出循环时,发送的指令都是BC_EXIT_LOOPER。
BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION、BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION
前面已经介绍过binder driver通过binder_ref_death结构体来实现死亡通知机制。而Client可以通过BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION指令来注册指定的binder_node的死亡通知,也可以通过BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION指令来清除死亡通知。
第一步,binder driver读取目标binder_ref的desc和cookie:
if (get_user(target, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))//读取BpBinder.mHandle,即binder_ref.desc return -EFAULT; ptr += sizeof(uint32_t); if (get_user(cookie, (void __user * __user *)ptr))//读取cookie return -EFAULT;这里的cookie,不是之前binder_node.cookie。不过,两个cookie的作用比较类似,指令发送者可以用cookie保存自己想要保存的任何值。通常Client会用cookie保存BpBinder对象的地址,用于在死亡通知触发后,区别是哪个BpBinder接收到了死亡通知。
第二步,根据desc,确定binder_ref:
ref = binder_get_ref(proc, target);
if (ref == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d %s "
"invalid ref %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
cmd == BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION ?
"BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION" :
"BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION",
target);
break;
} 第三步,处理BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION:
if (cmd == BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION) {
if (ref->death) { //已经注册了死亡通知,
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%"
"d BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTI"
"FICATION death notific"
"ation already set\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
break;
}
death = kzalloc(sizeof(*death), GFP_KERNEL); //分配binder_ref_death的内存空间
if (death == NULL) {
thread->return_error = BR_ERROR;
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_FAILED_TRANSACTION,
"binder: %d:%d "
"BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION failed\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
break;
}
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_DEATH);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&death->work.entry);
death->cookie = cookie;//保存cookie
ref->death = death;//保存binder_ref_deatch
if (ref->node->proc == NULL) {//如果binder_ref对应的binder_node已经死亡,则需要立即发送死亡通知
ref->death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER;
if (thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED | BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) { //通常这个if总是true
list_add_tail(&ref->death->work.entry, &thread->todo);
} else {
list_add_tail(&ref->death->work.entry, &proc->todo);
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
}
}
} 第四步,处理BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION:
else {
if (ref->death == NULL) {//没有注册过死亡通知
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%"
"d BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFI"
"CATION death notificat"
"ion not active\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
break;
}
death = ref->death;
if (death->cookie != cookie) { //当时注册的cookie和现在的cookie不同
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%"
"d BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFI"
"CATION death notificat"
"ion cookie mismatch "
"%p != %p\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
death->cookie, cookie);
break;
}
ref->death = NULL; // 注销死亡通知
if (list_empty(&death->work.entry)) { //binder_ref对应的binder_node未死亡
death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION;
if (thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED | BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) {
list_add_tail(&death->work.entry, &thread->todo);//向当前线程发送BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE
} else {
list_add_tail(&death->work.entry, &proc->todo);
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
}
} else {//binder_ref对应的binder_node已经死亡
BUG_ON(death->work.type != BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER);
death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR; //binder driver已经先向Client发送BR_DEAD_BINDER,当client返回BC_DEAD_BINDER_DONE之后,再想向client发送BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE
}
}
BC_DEAD_BINDER_DONE
当binder_node死亡以后,binder driver会向client发送BR_DEAD_BINDER指令,而client处理完该指令后,应该向binder driver发送指令BC_DEAD_BINDER_DONE指令。
第一步,读取cookie:
if (get_user(cookie, (void __user * __user *)ptr)) return -EFAULT;第二步,遍历查找cookie对应的binder_ref:
list_for_each_entry(w, &proc->delivered_death, entry) {//遍历proc->delivered_death列表,把数据放到w中
struct binder_ref_death *tmp_death = container_of(w, struct binder_ref_death, work);//把list_head转换成binder_ref_death
if (tmp_death->cookie == cookie) {
death = tmp_death;
break;
}
} 第三步,从proc->delevered_death列表中删除binder_ref_death:
list_del_init(&death->work.entry);第四步, 如果death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR,则继续发送BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE:
if (death->work.type == BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR) {
death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION; //说明之前Client有发送过BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION指令
if (thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED | BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) {
list_add_tail(&death->work.entry, &thread->todo);
} else {
list_add_tail(&death->work.entry, &proc->todo);
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
}
}
BC_TRANSACTION、BC_REPLY
通常,Client通过BC_TRANSACTION指令发送请求给Service,然后,Service通过BC_REPLY指令答复请求。作为传输数据的指令,BC_TRANSACTION和BC_REPLY指令的实现基本相同:
首先,读取发送者提供的binder_transaction_data结构体:
struct binder_transaction_data tr; if (copy_from_user(&tr, ptr, sizeof(tr))) return -EFAULT; ptr += sizeof(tr);然后,调用
binder_transaction(proc, thread, &tr, cmd == BC_REPLY);把数据发送到接收者的todo队列。
binder_transaction
前面我们已经看到,binder_transaction函数由binder_thread_write函数在处理BC_TRANSACTION或BC_REPLY指令时调用:
static void binder_transaction(struct binder_proc *proc, //发送方进程
struct binder_thread *thread, //发送方线程
struct binder_transaction_data *tr, int reply) //如果binder_transaction由BC_REPLY指令触发,reply = 1,否则为0
{
struct binder_transaction *t;
struct binder_work *tcomplete;
size_t *offp, *off_end;
struct binder_proc *target_proc;
struct binder_thread *target_thread = NULL;
struct binder_node *target_node = NULL;
struct list_head *target_list;
wait_queue_head_t *target_wait;
struct binder_transaction *in_reply_to = NULL;
struct binder_transaction_log_entry *e;
uint32_t return_error;
e = binder_transaction_log_add(&binder_transaction_log);
e->call_type = reply ? 2 : !!(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY);
e->from_proc = proc->pid;
e->from_thread = thread->pid;
e->target_handle = tr->target.handle;
e->data_size = tr->data_size;
e->offsets_size = tr->offsets_size;
if (reply) {
in_reply_to = thread->transaction_stack;
if (in_reply_to == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got reply transaction "
"with no transaction stack\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_empty_call_stack;
}
binder_set_nice(in_reply_to->saved_priority);
if (in_reply_to->to_thread != thread) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got reply transaction "
"with bad transaction stack,"
" transaction %d has target %d:%d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, in_reply_to->debug_id,
in_reply_to->to_proc ?
in_reply_to->to_proc->pid : 0,
in_reply_to->to_thread ?
in_reply_to->to_thread->pid : 0);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
in_reply_to = NULL;
goto err_bad_call_stack;
}
thread->transaction_stack = in_reply_to->to_parent;
target_thread = in_reply_to->from;
if (target_thread == NULL) {
return_error = BR_DEAD_REPLY;
goto err_dead_binder;
}
if (target_thread->transaction_stack != in_reply_to) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got reply transaction "
"with bad target transaction stack %d, "
"expected %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
target_thread->transaction_stack ?
target_thread->transaction_stack->debug_id : 0,
in_reply_to->debug_id);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
in_reply_to = NULL;
target_thread = NULL;
goto err_dead_binder;
}
target_proc = target_thread->proc;
} else {
if (tr->target.handle) {
struct binder_ref *ref;
ref = binder_get_ref(proc, tr->target.handle);
if (ref == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got "
"transaction to invalid handle\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_invalid_target_handle;
}
target_node = ref->node;
} else {
target_node = binder_context_mgr_node;
if (target_node == NULL) {
return_error = BR_DEAD_REPLY;
goto err_no_context_mgr_node;
}
}
e->to_node = target_node->debug_id;
target_proc = target_node->proc;
if (target_proc == NULL) {
return_error = BR_DEAD_REPLY;
goto err_dead_binder;
}
if (security_binder_transaction(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk) < 0) {//基于Permission的安全检查机制,暂且忽略,因为正常情况下,安全检查都会通过
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_invalid_target_handle;
}
if (!(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY) && thread->transaction_stack) {
struct binder_transaction *tmp;
tmp = thread->transaction_stack;
if (tmp->to_thread != thread) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got new "
"transaction with bad transaction stack"
", transaction %d has target %d:%d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, tmp->debug_id,
tmp->to_proc ? tmp->to_proc->pid : 0,
tmp->to_thread ?
tmp->to_thread->pid : 0);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_bad_call_stack;
}
while (tmp) {
if (tmp->from && tmp->from->proc == target_proc)
target_thread = tmp->from;
tmp = tmp->from_parent;
}
}
}
if (target_thread) {
e->to_thread = target_thread->pid;
target_list = &target_thread->todo;
target_wait = &target_thread->wait;
} else {
target_list = &target_proc->todo;
target_wait = &target_proc->wait;
}
e->to_proc = target_proc->pid;
/* TODO: reuse incoming transaction for reply */
t = kzalloc(sizeof(*t), GFP_KERNEL);
if (t == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_alloc_t_failed;
}
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION);
tcomplete = kzalloc(sizeof(*tcomplete), GFP_KERNEL);
if (tcomplete == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_alloc_tcomplete_failed;
}
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE);
t->debug_id = ++binder_last_id;
e->debug_id = t->debug_id;
if (reply)
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION,
"binder: %d:%d BC_REPLY %d -> %d:%d, "
"data %p-%p size %zd-%zd\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, t->debug_id,
target_proc->pid, target_thread->pid,
tr->data.ptr.buffer, tr->data.ptr.offsets,
tr->data_size, tr->offsets_size);
else
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION,
"binder: %d:%d BC_TRANSACTION %d -> "
"%d - node %d, data %p-%p size %zd-%zd\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, t->debug_id,
target_proc->pid, target_node->debug_id,
tr->data.ptr.buffer, tr->data.ptr.offsets,
tr->data_size, tr->offsets_size);
if (!reply && !(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY))
t->from = thread;
else
t->from = NULL;
t->sender_euid = proc->tsk->cred->euid;
t->to_proc = target_proc;
t->to_thread = target_thread;
t->code = tr->code;
t->flags = tr->flags;
t->priority = task_nice(current);
trace_binder_transaction(reply, t, target_node);
t->buffer = binder_alloc_buf(target_proc, tr->data_size,
tr->offsets_size, !reply && (t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY));
if (t->buffer == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_alloc_buf_failed;
}
t->buffer->allow_user_free = 0;
t->buffer->debug_id = t->debug_id;
t->buffer->transaction = t;
t->buffer->target_node = target_node;
trace_binder_transaction_alloc_buf(t->buffer);
if (target_node)
binder_inc_node(target_node, 1, 0, NULL);
offp = (size_t *)(t->buffer->data + ALIGN(tr->data_size, sizeof(void *)));
if (copy_from_user(t->buffer->data, tr->data.ptr.buffer, tr->data_size)) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with invalid "
"data ptr\n", proc->pid, thread->pid);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_copy_data_failed;
}
if (copy_from_user(offp, tr->data.ptr.offsets, tr->offsets_size)) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with invalid "
"offsets ptr\n", proc->pid, thread->pid);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_copy_data_failed;
}
if (!IS_ALIGNED(tr->offsets_size, sizeof(size_t))) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with "
"invalid offsets size, %zd\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, tr->offsets_size);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_bad_offset;
}
off_end = (void *)offp + tr->offsets_size;
for (; offp < off_end; offp++) {
struct flat_binder_object *fp;
if (*offp > t->buffer->data_size - sizeof(*fp) ||
t->buffer->data_size < sizeof(*fp) ||
!IS_ALIGNED(*offp, sizeof(void *))) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with "
"invalid offset, %zd\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, *offp);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_bad_offset;
}
fp = (struct flat_binder_object *)(t->buffer->data + *offp);
switch (fp->type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER:
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER: {
struct binder_ref *ref;
struct binder_node *node = binder_get_node(proc, fp->binder);
if (node == NULL) {
node = binder_new_node(proc, fp->binder, fp->cookie);
if (node == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_new_node_failed;
}
node->min_priority = fp->flags & FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_PRIORITY_MASK;
node->accept_fds = !!(fp->flags & FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS);
}
if (fp->cookie != node->cookie) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d sending u%p "
"node %d, cookie mismatch %p != %p\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
fp->binder, node->debug_id,
fp->cookie, node->cookie);
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
if (security_binder_transfer_binder(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk)) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
ref = binder_get_ref_for_node(target_proc, node);
if (ref == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
if (fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_BINDER)
fp->type = BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE;
else
fp->type = BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE;
fp->handle = ref->desc;
binder_inc_ref(ref, fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE,
&thread->todo);
trace_binder_transaction_node_to_ref(t, node, ref);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION,
" node %d u%p -> ref %d desc %d\n",
node->debug_id, node->ptr, ref->debug_id,
ref->desc);
} break;
case BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE:
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE: {
struct binder_ref *ref = binder_get_ref(proc, fp->handle);
if (ref == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got "
"transaction with invalid "
"handle, %ld\n", proc->pid,
thread->pid, fp->handle);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_failed;
}
if (security_binder_transfer_binder(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk)) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_failed;
}
if (ref->node->proc == target_proc) {
if (fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE)
fp->type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
else
fp->type = BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER;
fp->binder = ref->node->ptr;
fp->cookie = ref->node->cookie;
binder_inc_node(ref->node, fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_BINDER, 0, NULL);
trace_binder_transaction_ref_to_node(t, ref);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION,
" ref %d desc %d -> node %d u%p\n",
ref->debug_id, ref->desc, ref->node->debug_id,
ref->node->ptr);
} else {
struct binder_ref *new_ref;
new_ref = binder_get_ref_for_node(target_proc, ref->node);
if (new_ref == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
fp->handle = new_ref->desc;
binder_inc_ref(new_ref, fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE, NULL);
trace_binder_transaction_ref_to_ref(t, ref,
new_ref);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION,
" ref %d desc %d -> ref %d desc %d (node %d)\n",
ref->debug_id, ref->desc, new_ref->debug_id,
new_ref->desc, ref->node->debug_id);
}
} break;
case BINDER_TYPE_FD: {
int target_fd;
struct file *file;
if (reply) {
if (!(in_reply_to->flags & TF_ACCEPT_FDS)) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got reply with fd, %ld, but target does not allow fds\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, fp->handle);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_fd_not_allowed;
}
} else if (!target_node->accept_fds) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with fd, %ld, but target does not allow fds\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, fp->handle);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_fd_not_allowed;
}
file = fget(fp->handle);
if (file == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with invalid fd, %ld\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, fp->handle);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_fget_failed;
}
if (security_binder_transfer_file(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk, file) < 0) {
fput(file);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_get_unused_fd_failed;
}
target_fd = task_get_unused_fd_flags(target_proc, O_CLOEXEC);
if (target_fd < 0) {
fput(file);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_get_unused_fd_failed;
}
task_fd_install(target_proc, target_fd, file);
trace_binder_transaction_fd(t, fp->handle, target_fd);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION,
" fd %ld -> %d\n", fp->handle, target_fd);
/* TODO: fput? */
fp->handle = target_fd;
} break;
default:
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transactio"
"n with invalid object type, %lx\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, fp->type);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_bad_object_type;
}
}
if (reply) {
BUG_ON(t->buffer->async_transaction != 0);
binder_pop_transaction(target_thread, in_reply_to);
} else if (!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) {
BUG_ON(t->buffer->async_transaction != 0);
t->need_reply = 1;
t->from_parent = thread->transaction_stack;
thread->transaction_stack = t;
} else {
BUG_ON(target_node == NULL);
BUG_ON(t->buffer->async_transaction != 1);
if (target_node->has_async_transaction) {
target_list = &target_node->async_todo;
target_wait = NULL;
} else
target_node->has_async_transaction = 1;
}
t->work.type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION;
list_add_tail(&t->work.entry, target_list);
tcomplete->type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE;
list_add_tail(&tcomplete->entry, &thread->todo);
if (target_wait)
wake_up_interruptible(target_wait);
return;
err_get_unused_fd_failed:
err_fget_failed:
err_fd_not_allowed:
err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed:
err_binder_get_ref_failed:
err_binder_new_node_failed:
err_bad_object_type:
err_bad_offset:
err_copy_data_failed:
trace_binder_transaction_failed_buffer_release(t->buffer);
binder_transaction_buffer_release(target_proc, t->buffer, offp);
t->buffer->transaction = NULL;
binder_free_buf(target_proc, t->buffer);
err_binder_alloc_buf_failed:
kfree(tcomplete);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE);
err_alloc_tcomplete_failed:
kfree(t);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION);
err_alloc_t_failed:
err_bad_call_stack:
err_empty_call_stack:
err_dead_binder:
err_invalid_target_handle:
err_no_context_mgr_node:
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_FAILED_TRANSACTION,
"binder: %d:%d transaction failed %d, size %zd-%zd\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, return_error,
tr->data_size, tr->offsets_size);
{
struct binder_transaction_log_entry *fe;
fe = binder_transaction_log_add(&binder_transaction_log_failed);
*fe = *e;
}
BUG_ON(thread->return_error != BR_OK);
if (in_reply_to) {
thread->return_error = BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE;
binder_send_failed_reply(in_reply_to, return_error);
} else
thread->return_error = return_error;
} binder_transaction函数主要到操作是把发送方提供的binder_transaction_data转换成binder driver专用的binder_transaction对象,并保存到接收者进程/线程的todo队列中。
这里,我们分BC_TRANSACTION和BC_REPLY两个情境来分析binder_transaction函数的实现。
BC_TRANSACTION(reply = 0)
第一步,确定target_node:
if (tr->target.handle) { // target.handle != 0
struct binder_ref *ref;
ref = binder_get_ref(proc, tr->target.handle);//根据desc确定binder_ref
if (ref == NULL) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got "
"transaction to invalid handle\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_invalid_target_handle;
}
target_node = ref->node; //根据binder_ref确定binder_node就很简单了
} else { // target.handle = 0时,特殊处理。因为binder driver从来创建指向binder_context_mgr_node的binder_ref
// 作为代替,binder driver对于mHandle=0的BpBinder做特殊处理
target_node = binder_context_mgr_node;
if (target_node == NULL) {
return_error = BR_DEAD_REPLY;
goto err_no_context_mgr_node;
}
} 第二步,确定target_proc和target_thread:
确定target_proc很简单:
target_proc = target_node->proc;//根据target_node确定target_proc通常情况下,Client并不在乎由Service的哪个线程来处理请求,即target_thread = null。但是,考虑一个特殊的复杂情况(这个情况我,我称呼为循环请求):
- 进程A是一个Service,它提供了多个线程A1,A2,A3等多个线程来服务Client
- 进程B是一个Client,它向A发送了请求(即binder_transaction)T1。
- A1接收到了来自B的请求T1。
- A1处理T1的过程中,发现为了处理T1的请求,需要Serivce C协助。
- A1向C发送了请求,并等待C回复请求T2
- C的C1线程接收到请求,但是,处理T2的过程中,发现也需要A协助
- C1向A发送请求T3
这种情况下,因为A1处于等待状态,比起A2和A3来,由A1来处理T3请求会是一个提高性能的解决方案。也就是说,我们希望target_thread=A1。但是,通过什么样的逻辑来实现呢?
首先,明确当前的情况:
thread = C1; target_porc = A; T3->from = C1; T3->from_parent = T2; // 关于from_parent大致,可以理解为,T3是由T2的处理触发的 C1->transaction_stack = T2; T2->from = A1; T2->from_parent=T1; A1->proc=A;
所以,通过当前thread的transaction_stack以及binder_transaction->from_parent可以找到A1。现在可以理解下面的代码了:
if (!(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY) && thread->transaction_stack) {
struct binder_transaction *tmp;
tmp = thread->transaction_stack;
if (tmp->to_thread != thread) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got new "
"transaction with bad transaction stack"
", transaction %d has target %d:%d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, tmp->debug_id,
tmp->to_proc ? tmp->to_proc->pid : 0,
tmp->to_thread ?
tmp->to_thread->pid : 0);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_bad_call_stack;
}
while (tmp) {
if (tmp->from && tmp->from->proc == target_proc)
target_thread = tmp->from;
tmp = tmp->from_parent;
}
} 第四步,根据target_proc和target_thread确定target_todo 和 target_wait:
if (target_thread) {
e->to_thread = target_thread->pid;
target_list = &target_thread->todo;
target_wait = &target_thread->wait;
} else {
target_list = &target_proc->todo;
target_wait = &target_proc->wait;
} 第五步,构造并初始化bind_transaction结构体:
t = kzalloc(sizeof(*t), GFP_KERNEL);//t 发送给target_todo,把请求发送给目标进程/目标线程 ....... tcomplete = kzalloc(sizeof(*tcomplete), GFP_KERNEL); // tcomplete则发送给当前线程的todo队列,向发送者返回BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE ...... if (!reply && !(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) t->from = thread; else t->from = NULL; t->sender_euid = proc->tsk->cred->euid; //记录发送者的有效用户id,是Binder机制安全保障的一环 t->to_proc = target_proc; t->to_thread = target_thread; t->code = tr->code; // 见binder_transaction_data.code t->flags = tr->flags; // 见binder_transaction_data.flags t->priority = task_nice(current); //记录请求线程的优先级,Service端处理线程的优先级需要高于请求线程的优先级 //同时,linux系统对于优先级的定义是,数字越小,优先级越高 //结果来说,处理线程的nice<=请求线程的nice第六步,构造并初始化binder_buffer结构体:
t->buffer = binder_alloc_buf(target_proc, tr->data_size, tr->offsets_size, !reply && (t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY));//binder_alloc_buf函数用于分配binder_buffer //binder_buffer.data_size=tr->data_size //binder_buffer.offset_size=tr->data_size ...... t->buffer->allow_user_free = 0;//在数据被读取之前,不允许释放binder_buffer t->buffer->debug_id = t->debug_id; t->buffer->transaction = t; t->buffer->target_node = target_node; if (target_node) binder_inc_node(target_node, 1, 0, NULL);//增加binder_node的local强引用计数第七步,copy数据:
offp = (size_t *)(t->buffer->data + ALIGN(tr->data_size, sizeof(void *)));//binder_buffer中偏移量数组的首地址
if (copy_from_user(t->buffer->data, tr->data.ptr.buffer, tr->data_size)) { //copy数据
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with invalid "
"data ptr\n", proc->pid, thread->pid);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_copy_data_failed;
}
if (copy_from_user(offp, tr->data.ptr.offsets, tr->offsets_size)) { //copy偏移量数组
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with invalid "
"offsets ptr\n", proc->pid, thread->pid);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_copy_data_failed;
} 值得注意的是,虽然我们之前已经多次看到copy_from_user函数,但是之前copy的都是Binder指令,或者结构体(binder_transaction_data),而binder_transaction_data.ptr.buffer&binder_transaction_data.ptr.offsets也仅仅是保存了数据和偏移量数组在user space的首地址,而非数据本身。所以,这里才是真正的数据copy,而Binder通信中唯一一次数据copy指的这里。
第八步,处理flat_binder_object结构体.
这是一个循环,循环处理偏移量数组中的每一个偏移量:
off_end = (void *)offp + tr->offsets_size;
for (; offp < off_end; offp++) {
......
} 接下来,对于flat_binder_object.type的类型不同,以不同的方式处理(前面介绍flat_binder_object结构体的时候,已经有介绍过处理逻辑,所以,这里就不在具体介绍)。
BIDNER_TYPE(_WEAK)_BINDER:
fp = (struct flat_binder_object *)(t->buffer->data + *offp);
switch (fp->type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER:
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER: {
struct binder_ref *ref;
struct binder_node *node = binder_get_node(proc, fp->binder);//根据binder_node.ptr查找binder_node
if (node == NULL) {
node = binder_new_node(proc, fp->binder, fp->cookie);//第一次在Binder通信中传输Binder,所以为BBinder创建binder_nod
if (node == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_new_node_failed;
}
node->min_priority = fp->flags & FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_PRIORITY_MASK; //记录Service处理线程的最小优先级
node->accept_fds = !!(fp->flags & FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS);
}
if (fp->cookie != node->cookie) {//如果通过native的标准实现IPCThreadState类进行Binder通信的话,这个if永远不会为true
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d sending u%p "
"node %d, cookie mismatch %p != %p\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
fp->binder, node->debug_id,
fp->cookie, node->cookie);
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
if (security_binder_transfer_binder(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk)) { //基于Permission的安全检查
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
ref = binder_get_ref_for_node(target_proc, node); //在目标进程内找到binder_node对应的binder_ref
//如果未找到,则在目标进程内创建binder_ref,并返回
if (ref == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
if (fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_BINDER) //更改fp->type
fp->type = BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE;
else
fp->type = BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE;
fp->handle = ref->desc; //设置fp->handle为ref.desc
binder_inc_ref(ref, fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE,
&thread->todo);//增加ref的引用计数
......
} break;BINDER_TYPE(_WEAK)_HANDLE:
fp = (struct flat_binder_object *)(t->buffer->data + *offp);
......
case BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE:
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE: {
struct binder_ref *ref = binder_get_ref(proc, fp->handle); //根据binder_ref.desc确定binder_ref
if (ref == NULL) { //如果使用蒙猜法,ref就会为null,通信就会终止
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got "
"transaction with invalid "
"handle, %ld\n", proc->pid,
thread->pid, fp->handle);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_failed;
}
if (security_binder_transfer_binder(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk)) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_failed;
}
if (ref->node->proc == target_proc) { // 如果target_proc即binder_node的宿主进程
if (fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE) //设置fp->type
fp->type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
else
fp->type = BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER;
fp->binder = ref->node->ptr;
fp->cookie = ref->node->cookie;
binder_inc_node(ref->node, fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_BINDER, 0, NULL); //增加binder_node的本地强引用计数
......
} else {
struct binder_ref *new_ref;
new_ref = binder_get_ref_for_node(target_proc, ref->node);//查找ref->node对应的binder_ref,找不到就新建
if (new_ref == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
fp->handle = new_ref->desc;//修改desc
binder_inc_ref(new_ref, fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE, NULL); //增加ref引用计数
......
}
} break;BINDER_TYPE_FD:
暂不讨论,总觉得文件Binder并不是一个"纯种"的binder。
第九步, 发送binder_transaction到target_todo:
else if (!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) { //同步Binder
BUG_ON(t->buffer->async_transaction != 0);
t->need_reply = 1; //标记为同步binder
t->from_parent = thread->transaction_stack; //可能请求线程有未处理的binder_transaction,通过from_parent保存起来
thread->transaction_stack = t; //保存t到请求线程的transaction_stack中
} else { // 异步Binder,因为未保存t到thread->transaction,所以异步binder是不允许回复的
BUG_ON(target_node == NULL);
BUG_ON(t->buffer->async_transaction != 1);
if (target_node->has_async_transaction) { //已经有异步binder存在
target_list = &target_node->async_todo; //保存到target_node->async_todo中
target_wait = NULL; //无需唤醒,
//当上一个异步Binder请求被处理完,释放binder_buffer时,
//会自动从binder_node.async_todo中,移动binder_transaction到binder_proc->todo中
} else //尚无异步binder
target_node->has_async_transaction = 1;//仍旧把transaction放入到target_todo中,但标记has_async_transaction = 1
}
t->work.type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION;
list_add_tail(&t->work.entry, target_list);//把t放入到target_todo队列,或者更准确的说是,把t->work放进todo队列中
//todo队列,到binder_thread_read函数再解释
tcomplete->type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE;
list_add_tail(&tcomplete->entry, &thread->todo);//把tcomplete放入到请求线程的doto队列
if (target_wait) //如果target_proc或者target_thread在阻塞状态,则唤醒
wake_up_interruptible(target_wait);
BC_REPLY(reply=1)
前面已经说过BC_TRANSACTION和BC_REPLY的处理比较相似,所以,BC_REPLY需要说明的也就是和BC_TRANSACTION有区别的第一步和第九步。
第一步,确定target_node:
in_reply_to = thread->transaction_stack;//in_reply_to即Binder请求, //一会我们可以在binder_thread_read的实现中,看到 //Service线程在读取binder请求时,会把binder_transaction保存到处理线程的transaction_stack中 //所以,我们现在可以从thread->transaction_stack中获取这个binder_stransaction ...... binder_set_nice(in_reply_to->saved_priority); //恢复处理线程的优先级 ...... thread->transaction_stack = in_reply_to->to_parent; //恢复thread->transaction_stack, //大部分情况下(即不考虑循环请求的情况),in_reply_to->to_parent=null target_thread = in_reply_to->from; //回忆一下,上面的第五步,in_reply_to被发送到当前线程的时候,from对象是不是保存了请求线程 //当时的请求线程,到了现在就是目标线程 ...... target_proc = target_thread->proc;
第九步,发送binder_transaction到target_node:
BUG_ON(t->buffer->async_transaction != 0);
binder_pop_transaction(target_thread, in_reply_to);//target_thread,即请求线程的transaction_stack
......
t->work.type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION; //从这里开始,就和BC_TRANSACTION的第九步一样了
list_add_tail(&t->work.entry, target_list);
tcomplete->type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE;
list_add_tail(&tcomplete->entry, &thread->todo);
if (target_wait)
wake_up_interruptible(target_wait);
binder_thread_read
前面已经解释过biner_transaction函数,主要是把binder_transaction.work放入到接收端的todo队列。而binder_thread_read函数主要是处理todo队列中的binder_work对象:
static int binder_thread_read(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
void __user *buffer, int size,
signed long *consumed, int non_block)
{
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;//buffer为用户接收缓存区首地址,consumed通常为0
void __user *end = buffer + size; //size为接收缓存区的大小
int ret = 0;
int wait_for_proc_work;
if (*consumed == 0) { //先返回一个BR_NOOP
if (put_user(BR_NOOP, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
}
retry:
wait_for_proc_work = thread->transaction_stack == NULL &&
list_empty(&thread->todo);
if (thread->return_error != BR_OK && ptr < end) {
if (thread->return_error2 != BR_OK) {
if (put_user(thread->return_error2, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, thread->return_error2);
if (ptr == end)
goto done;
thread->return_error2 = BR_OK;
}
if (put_user(thread->return_error, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, thread->return_error);
thread->return_error = BR_OK;
goto done;
}
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads++;
binder_unlock(__func__);
trace_binder_wait_for_work(wait_for_proc_work,
!!thread->transaction_stack,
!list_empty(&thread->todo));
if (wait_for_proc_work) {
if (!(thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED |
BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED))) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d ERROR: Thread waiting "
"for process work before calling BC_REGISTER_"
"LOOPER or BC_ENTER_LOOPER (state %x)\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, thread->looper);
wait_event_interruptible(binder_user_error_wait,
binder_stop_on_user_error < 2);
}
binder_set_nice(proc->default_priority);
if (non_block) {
if (!binder_has_proc_work(proc, thread))
ret = -EAGAIN;
} else
ret = wait_event_interruptible_exclusive(proc->wait, binder_has_proc_work(proc, thread));
} else {
if (non_block) {
if (!binder_has_thread_work(thread))
ret = -EAGAIN;
} else
ret = wait_event_interruptible(thread->wait, binder_has_thread_work(thread));
}
binder_lock(__func__);
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads--;
thread->looper &= ~BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
if (ret)
return ret;
while (1) {
uint32_t cmd;
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
struct binder_work *w;
struct binder_transaction *t = NULL;
if (!list_empty(&thread->todo))
w = list_first_entry(&thread->todo, struct binder_work, entry);
else if (!list_empty(&proc->todo) && wait_for_proc_work)
w = list_first_entry(&proc->todo, struct binder_work, entry);
else {
if (ptr - buffer == 4 && !(thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_NEED_RETURN)) /* no data added */
goto retry;
break;
}
if (end - ptr < sizeof(tr) + 4)
break;
switch (w->type) {
case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION: {
t = container_of(w, struct binder_transaction, work);
} break;
case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE: {
cmd = BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE;
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, cmd);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE,
"binder: %d:%d BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
list_del(&w->entry);
kfree(w);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE);
} break;
case BINDER_WORK_NODE: {
struct binder_node *node = container_of(w, struct binder_node, work);
uint32_t cmd = BR_NOOP;
const char *cmd_name;
int strong = node->internal_strong_refs || node->local_strong_refs;
int weak = !hlist_empty(&node->refs) || node->local_weak_refs || strong;
if (weak && !node->has_weak_ref) {
cmd = BR_INCREFS;
cmd_name = "BR_INCREFS";
node->has_weak_ref = 1;
node->pending_weak_ref = 1;
node->local_weak_refs++;
} else if (strong && !node->has_strong_ref) {
cmd = BR_ACQUIRE;
cmd_name = "BR_ACQUIRE";
node->has_strong_ref = 1;
node->pending_strong_ref = 1;
node->local_strong_refs++;
} else if (!strong && node->has_strong_ref) {
cmd = BR_RELEASE;
cmd_name = "BR_RELEASE";
node->has_strong_ref = 0;
} else if (!weak && node->has_weak_ref) {
cmd = BR_DECREFS;
cmd_name = "BR_DECREFS";
node->has_weak_ref = 0;
}
if (cmd != BR_NOOP) {
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
if (put_user(node->ptr, (void * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
if (put_user(node->cookie, (void * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, cmd);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_USER_REFS,
"binder: %d:%d %s %d u%p c%p\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, cmd_name, node->debug_id, node->ptr, node->cookie);
} else {
list_del_init(&w->entry);
if (!weak && !strong) {
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_INTERNAL_REFS,
"binder: %d:%d node %d u%p c%p deleted\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, node->debug_id,
node->ptr, node->cookie);
rb_erase(&node->rb_node, &proc->nodes);
kfree(node);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_NODE);
} else {
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_INTERNAL_REFS,
"binder: %d:%d node %d u%p c%p state unchanged\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, node->debug_id, node->ptr,
node->cookie);
}
}
} break;
case BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER:
case BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR:
case BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION: {
struct binder_ref_death *death;
uint32_t cmd;
death = container_of(w, struct binder_ref_death, work);
if (w->type == BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION)
cmd = BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE;
else
cmd = BR_DEAD_BINDER;
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
if (put_user(death->cookie, (void * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, cmd);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_DEATH_NOTIFICATION,
"binder: %d:%d %s %p\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
cmd == BR_DEAD_BINDER ?
"BR_DEAD_BINDER" :
"BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE",
death->cookie);
if (w->type == BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION) {
list_del(&w->entry);
kfree(death);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_DEATH);
} else
list_move(&w->entry, &proc->delivered_death);
if (cmd == BR_DEAD_BINDER)
goto done; /* DEAD_BINDER notifications can cause transactions */
} break;
}
if (!t)
continue;
BUG_ON(t->buffer == NULL);
if (t->buffer->target_node) {
struct binder_node *target_node = t->buffer->target_node;
tr.target.ptr = target_node->ptr;
tr.cookie = target_node->cookie;
t->saved_priority = task_nice(current);
if (t->priority < target_node->min_priority &&
!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY))
binder_set_nice(t->priority);
else if (!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY) ||
t->saved_priority > target_node->min_priority)
binder_set_nice(target_node->min_priority);
cmd = BR_TRANSACTION;
} else {
tr.target.ptr = NULL;
tr.cookie = NULL;
cmd = BR_REPLY;
}
tr.code = t->code;
tr.flags = t->flags;
tr.sender_euid = t->sender_euid;
if (t->from) {
struct task_struct *sender = t->from->proc->tsk;
tr.sender_pid = task_tgid_nr_ns(sender,
current->nsproxy->pid_ns);
} else {
tr.sender_pid = 0;
}
tr.data_size = t->buffer->data_size;
tr.offsets_size = t->buffer->offsets_size;
tr.data.ptr.buffer = (void *)t->buffer->data +
proc->user_buffer_offset;
tr.data.ptr.offsets = tr.data.ptr.buffer +
ALIGN(t->buffer->data_size,
sizeof(void *));
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
if (copy_to_user(ptr, &tr, sizeof(tr)))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(tr);
trace_binder_transaction_received(t);
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, cmd);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION,
"binder: %d:%d %s %d %d:%d, cmd %d"
"size %zd-%zd ptr %p-%p\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
(cmd == BR_TRANSACTION) ? "BR_TRANSACTION" :
"BR_REPLY",
t->debug_id, t->from ? t->from->proc->pid : 0,
t->from ? t->from->pid : 0, cmd,
t->buffer->data_size, t->buffer->offsets_size,
tr.data.ptr.buffer, tr.data.ptr.offsets);
list_del(&t->work.entry);
t->buffer->allow_user_free = 1;
if (cmd == BR_TRANSACTION && !(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) {
t->to_parent = thread->transaction_stack;
t->to_thread = thread;
thread->transaction_stack = t;
} else {
t->buffer->transaction = NULL;
kfree(t);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION);
}
break;
}
done:
*consumed = ptr - buffer;
if (proc->requested_threads + proc->ready_threads == 0 &&
proc->requested_threads_started < proc->max_threads &&
(thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED |
BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) /* the user-space code fails to */
/*spawn a new thread if we leave this out */) {
proc->requested_threads++;
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS,
"binder: %d:%d BR_SPAWN_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
if (put_user(BR_SPAWN_LOOPER, (uint32_t __user *)buffer))
return -EFAULT;
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, BR_SPAWN_LOOPER);
}
return 0;
} 第一步,binder_driver首先确定当前线程是否有未处理完成的工作,如果没有,那么就让本线程去处理发给进程的工作(即不限定由那个线程完成的工作):
wait_for_proc_work = thread->transaction_stack == NULL && //thread->transaction_stack!=null说明当前线程曾发送同步请求,而未得到回复 list_empty(&thread->todo); //thread->todo非空,说明有binder_work等待本线程处理第二步,开始等待binder_work:
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING; //标记线程进入等待
if (wait_for_proc_work) //线程处于空闲状态,所以它开始处理本进程的工作
proc->ready_threads++; //空闲线程数加1
binder_unlock(__func__);
if (wait_for_proc_work) {//等待进程的工作项
......
binder_set_nice(proc->default_priority);
if (non_block) {
if (!binder_has_proc_work(proc, thread))
ret = -EAGAIN; //返回EAGAIN,示意调用者再次调用ioctl
} else
ret = wait_event_interruptible_exclusive(proc->wait, binder_has_proc_work(proc, thread));//如果binder_has_proc_work(proc, thread)=true,则不会进入等待
} else {//等待线程的工作项
if (non_block) {
if (!binder_has_thread_work(thread))
ret = -EAGAIN;
} else
ret = wait_event_interruptible(thread->wait, binder_has_thread_work(thread));//如果binder_has_thread_work(thread)=true,则不会进入等待
}
binder_lock(__func__);
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads--; //现在线程不空闲了
thread->looper &= ~BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;//清除等待标记
第三步,循环处理binder_work,下面把第三步拆分成若干小节分析。
第一小节,确定binder_work,即代码中的w。
while (1) {//binder_thread_read执行一次,允许执行多个binder_work
uint32_t cmd;
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
struct binder_work *w;
struct binder_transaction *t = NULL;
if (!list_empty(&thread->todo)) //线程自己的工作项,总是优先处理
w = list_first_entry(&thread->todo, struct binder_work, entry);
else if (!list_empty(&proc->todo) && wait_for_proc_work)
w = list_first_entry(&proc->todo, struct binder_work, entry);
else {
if (ptr - buffer == 4 && !(thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_NEED_RETURN)) /* no data added */
// ptr - buffer == 4 意为着 binder driver仅向用户态接收缓冲区写入了一个BR_NOOP,即当前还未处理过binder_work
// !(thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_NEED_RETURN) 意为着当前线程并不急着返回,可以继续工作
goto retry; //继续等待下一个binder_work
break;
}
if (end - ptr < sizeof(tr) + 4) //用户接收缓存区快被写满了,返回,等待下次调用ioctl
break;
第二小节,处理binder_work.因为根据binder_work.type的类型不同处理方式不同,所以按照BINDER_WORK_XXXX进行分析:
BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION
BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION说明收到了一个来自其他进程的binder_transaction,而如何根据w确定binder_transaction呢?
t = container_of(w, struct binder_transaction, work);先回忆一下,binder_transaction函数中,对target_todo做了些什么:
t->work.type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION;
list_add_tail(&t->work.entry, target_list) 它把transaction->work保存到了todo队列中。
再来看看container_of的实现:
/**
* container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure
* @ptr: the pointer to the member.
* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the member within the struct.
*
*/
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof(((type *)0)->member) * __mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)((char *)__mptr - offsetof(type, member)); }) 说实话,这种方式对于本人这种JAVA程序员来说挺难理解的,大致可以用下面的理解方式理解:
- binder_transaction结构体包含一个work成员
- w记录了work成员的地址
- offsetof(binder_transaction,work)即binder_transaction的地址和其work成员的地址的偏移量
- w-offsetof(binder_transaction,work)即包含了w的binder_transaction的地址
- 把w-offsetof(binder_transaction,work)强转为binder_transaction类型的指针
虽然理解的有些绕,但的确是一个高效率且节约内存的存储方式,Linux内核中的容器(e.g. rb_tree、list、 hlist)很多使用了这样的实现方式。
接下来,逐步处理binder_transaction。
首先,根据binder_transaction(即代码中的t)t初始化binder_transaction_data(即代码中的tr):
if (t->buffer->target_node) {//t是由BC_TRANSACTION发送过来的,当前线程为Serivce的处理线程
struct binder_node *target_node = t->buffer->target_node;
tr.target.ptr = target_node->ptr;
tr.cookie = target_node->cookie;
t->saved_priority = task_nice(current); //保存处理线程当前的优先级
if (t->priority < target_node->min_priority &&
!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) //t->priority为请求线程的优先级
//同步Binder的情况下,设置处理线程的优先级为请求线程的优先级和处理线程最低优先级较高者
//即nice较小者
binder_set_nice(t->priority);
else if (!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY) ||
t->saved_priority > target_node->min_priority)
binder_set_nice(target_node->min_priority);
cmd = BR_TRANSACTION;
} else { //t是由BC_REPLY指令发送过来的,当前线程为Client的请求线程
tr.target.ptr = NULL;
tr.cookie = NULL;
cmd = BR_REPLY;
}
tr.code = t->code;
tr.flags = t->flags;
tr.sender_euid = t->sender_euid;
if (t->from) { //cmd=BR_REPLY
struct task_struct *sender = t->from->proc->tsk;
tr.sender_pid = task_tgid_nr_ns(sender,
current->nsproxy->pid_ns);
} else {
tr.sender_pid = 0;//因为读取回复不需要安全验证,安全验证总是在通过BC_TRANSACTION发送请求时进行
}
//这里不需要copy数据实体到用户态,因为内核态和用户态已经共享物理内存
//所以,这里只需要在tr中返回数据在内核态的起始地址和偏移量数组在内核态的首地址
tr.data_size = t->buffer->data_size;
tr.offsets_size = t->buffer->offsets_size;
tr.data.ptr.buffer = (void *)t->buffer->data +
proc->user_buffer_offset;//计算用户态地址,需要加上内核态地址和用户态地址的偏移量
tr.data.ptr.offsets = tr.data.ptr.buffer +
ALIGN(t->buffer->data_size,
sizeof(void *));
然后,向Client返回cmd和tr:
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr)) return -EFAULT; ptr += sizeof(uint32_t); if (copy_to_user(ptr, &tr, sizeof(tr))) return -EFAULT; ptr += sizeof(tr);最后,收尾:
list_del(&t->work.entry);//从todo队列中移除w
t->buffer->allow_user_free = 1;//数据已经被读取,所以允许通过BC_FREE_BUFFER指令来释放这个binder_buffer
if (cmd == BR_TRANSACTION && !(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) { //当前线程为Service的处理线程,把t保存到thread->transaction_stack
//处理完成以后,回复请求时,会用到它
t->to_parent = thread->transaction_stack;
t->to_thread = thread;
thread->transaction_stack = t;
} else {//回复,或者异步Binder时,因为不需要回复,所以,也不必保存t,可以直接释放
t->buffer->transaction = NULL;
kfree(t);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION);
}
BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE
BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE说明当前thread刚刚成功的执行binder_transaction(通过BC_TRANSACTION或者BC_REPLY),这时,需要向用户缓冲区写入BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE指令,即向用户态返回BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE指令。
case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE: { //w.type=BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE时,w没有宿主
cmd = BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE;
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))//向用户态缓冲区写入BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, cmd);
list_del(&w->entry);//从todo队列中移除w,
kfree(w);//释放binder_work
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE);
} break;
BINDER_WORK_NODE
BINDER_WORK_NODE说明指定的binder_node需要更新引用计数。
case BINDER_WORK_NODE: {//w的宿主为binder_node
struct binder_node *node = container_of(w, struct binder_node, work);
uint32_t cmd = BR_NOOP;//该指令无需用户态处理,所以BR_NOOP
const char *cmd_name;
int strong = node->internal_strong_refs || node->local_strong_refs;
int weak = !hlist_empty(&node->refs) || node->local_weak_refs || strong;
if (weak && !node->has_weak_ref) {//无弱引用的状态->有弱引用的状态
cmd = BR_INCREFS;//请求Service增加BBinder的弱引用
cmd_name = "BR_INCREFS";
node->has_weak_ref = 1;
node->pending_weak_ref = 1;
node->local_weak_refs++;
} else if (strong && !node->has_strong_ref) {//无强引用的状态->有强引用的状态
cmd = BR_ACQUIRE;//请求Service增加BBinder的强引用
cmd_name = "BR_ACQUIRE";
node->has_strong_ref = 1;
node->pending_strong_ref = 1;
node->local_strong_refs++;
} else if (!strong && node->has_strong_ref) {//有强引用的状态->无强引用的状态
cmd = BR_RELEASE;//提示Service可以减少BBinder的强引用
cmd_name = "BR_RELEASE";
node->has_strong_ref = 0;
} else if (!weak && node->has_weak_ref) {//有弱引用的状态->无弱引用的状态
cmd = BR_DECREFS;//提示Service可以减少BBinder的弱引用
cmd_name = "BR_DECREFS";
node->has_weak_ref = 0;
}
if (cmd != BR_NOOP) {//向Serice返回指令
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
if (put_user(node->ptr, (void * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
if (put_user(node->cookie, (void * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
......
} else {//状态无变化
list_del_init(&w->entry);
if (!weak && !strong) {
......
rb_erase(&node->rb_node, &proc->nodes);//从proc->nodes中移除node
kfree(node);//无引用了,可以释放binder_node
......
} else {
......
}
}
} break;
BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER、BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR、BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION
这三个BINDER_WORK_XXXX都和死亡通知有关,w的宿主都是binder_ref_death。
- BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER:binder_node死亡时,触发
- BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR:Client通过BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION指令清除死亡通知时,发现binder_node已经死亡时,触发
- BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION:binder driver处理完BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION时,触发
death = container_of(w, struct binder_ref_death, work);//获得binder_ref_death
if (w->type == BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION)
cmd = BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE;//通知Client已经清除死亡通知
else
cmd = BR_DEAD_BINDER;//向Client发送死亡通知
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr)) //开始写回数据
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
if (put_user(death->cookie, (void * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
if (w->type == BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION) {
list_del(&w->entry);//从todo队列中移除w
kfree(death);//释放death
} else
list_move(&w->entry, &proc->delivered_death);//把w从todo队列移动到proc->delivered_death队列中
//等Client处理BR_DEAD_BINDER指令后,返回BC_DEAD_BINDER_DONE时,再继续处理
if (cmd == BR_DEAD_BINDER)
goto done; /* DEAD_BINDER notifications can cause transactions */
第四步,准备返回biner_ioctl,进而返回到用户态:
*consumed = ptr - buffer;//consumed记录了binder driver向调用者返回的数据长度
if (proc->requested_threads + proc->ready_threads == 0 && //binder driver尚未发送过BR_SPAWN_LOOPER,且当前没有线程处于空闲状态
proc->requested_threads_started < proc->max_threads && //当前binder driver开启的处理线程小于Service设置的max_threads
(thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED |
BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) /* the user-space code fails to */
/*spawn a new thread if we leave this out */) {//通常,Client线程并不会进入处理循环,也不会把thread->looper设置为BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED或者BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED,所以binder driver不会向client发送BR_SPWN_LOOPER指令
proc->requested_threads++;
if (put_user(BR_SPAWN_LOOPER, (uint32_t __user *)buffer))//把第一步中写入的BR_NOOP覆盖为BR_SPAWN_LOOPER,促使Service开启新的处理线程
return -EFAULT;
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, BR_SPAWN_LOOPER);
}
binder_new_node
binder_new_node用于创建新的binder_node:
static struct binder_node *binder_new_node(struct binder_proc *proc,
void __user *ptr,
void __user *cookie)
{
struct rb_node **p = &proc->nodes.rb_node; //proc->nodes红黑树以用户态BBbinder的地址(即binder_node->ptr)排序
struct rb_node *parent = NULL;
struct binder_node *node;
while (*p) { //确定新的binder_node在proc->nodes中的位置
parent = *p;
node = rb_entry(parent, struct binder_node, rb_node);
if (ptr < node->ptr)
p = &(*p)->rb_left;
else if (ptr > node->ptr)
p = &(*p)->rb_right;
else
return NULL;//已经为该BBinder创建过binder_node
}
node = kzalloc(sizeof(*node), GFP_KERNEL);//分配内存
if (node == NULL)
return NULL;
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_NODE);
rb_link_node(&node->rb_node, parent, p);//保存到proc->nodes中
rb_insert_color(&node->rb_node, &proc->nodes);//调整红黑树
node->debug_id = ++binder_last_id;
//初始化node成员
node->proc = proc;
node->ptr = ptr;
node->cookie = cookie;
node->work.type = BINDER_WORK_NODE;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&node->work.entry);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&node->async_todo);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_INTERNAL_REFS,
"binder: %d:%d node %d u%p c%p created\n",
proc->pid, current->pid, node->debug_id,
node->ptr, node->cookie);
return node;
}
binder_inc_node
binder_inc_node函数用于增加binder_node的引用计数器:
static int binder_inc_node(struct binder_node *node, int strong, int internal,
struct list_head *target_list)
{
if (strong) {//强引用
if (internal) {//远端引用
if (target_list == NULL &&
node->internal_strong_refs == 0 &&
!(node == binder_context_mgr_node &&
node->has_strong_ref)) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: invalid inc strong "
"node for %d\n", node->debug_id);
return -EINVAL;
}
node->internal_strong_refs++;
} else //本地引用
node->local_strong_refs++;
if (!node->has_strong_ref && target_list) { // 请求发送BR_ACQUIRE,以增加BBinder的强引用
list_del_init(&node->work.entry);
list_add_tail(&node->work.entry, target_list);
}
} else {
if (!internal)//binder_node没有远端弱引用计数器(即无internal_weak_refs),实际上internal_weak_refs=lengthof(node_refs)
//所以,strong=0,internal=1时,无操作。
node->local_weak_refs++;
if (!node->has_weak_ref && list_empty(&node->work.entry)) {
if (target_list == NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: invalid inc weak node "
"for %d\n", node->debug_id);
return -EINVAL;
}
list_add_tail(&node->work.entry, target_list);// 请求发送BR_INCREFS,以增加BBinder的弱引用
}
}
return 0;
}
关于binder_node的本地引用和远端引用,我是这样理解的:
- 凡是来自binder_ref的引用全部属于远端引用:每一个指向binder_node的binder_ref构成一个远端弱引用,其中,每一个存在强引用的binder_ref对binder_node构成一个远端强引用。
- 本地引用的来源有两个:binder_transaction,每一个发送到binder_node的binder_transaction构成一个本地强引用。当binder_stransaction被释放的时候,本地强引用须要减1;每一个类型为BINDER_TYPE_BINDER的flat_binder_object构成一个本地强引用,每一个类型为BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER的flat_binder_object构成一个本地弱引用,释放flat_binder_object的时候,本地强/弱引用需要减1.
binder_dec_node
binder_dec_node用于减少binder_node的引用计数器:
static int binder_dec_node(struct binder_node *node, int strong, int internal)
{
if (strong) { //强引用
if (internal) //远端引用
node->internal_strong_refs--;
else
node->local_strong_refs--;
if (node->local_strong_refs || node->internal_strong_refs)
return 0;
} else {
if (!internal)
node->local_weak_refs--;
if (node->local_weak_refs || !hlist_empty(&node->refs))
return 0;
}
if (node->proc && (node->has_strong_ref || node->has_weak_ref)) {
if (list_empty(&node->work.entry)) { //未把node.work添加到todo队列
list_add_tail(&node->work.entry, &node->proc->todo);
wake_up_interruptible(&node->proc->wait);//
}
} else {
if (hlist_empty(&node->refs) && !node->local_strong_refs &&
!node->local_weak_refs) {//binder_node已经没有使用者了,所以可以释放它
list_del_init(&node->work.entry);//从todo队列中,移除node
if (node->proc) {//Service进程未退出
rb_erase(&node->rb_node, &node->proc->nodes);//从node->proc中移除binder_node
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_INTERNAL_REFS,
"binder: refless node %d deleted\n",
node->debug_id);
} else {
hlist_del(&node->dead_node);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_INTERNAL_REFS,
"binder: dead node %d deleted\n",
node->debug_id);
}
kfree(node);//释放node
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_NODE);
}
}
return 0;
}
binder_get_ref
binder_ger_ref用于从proc->refs_by_desc红黑树中,根据desc查找binder_ref:
static struct binder_ref *binder_get_ref(struct binder_proc *proc,
uint32_t desc)
{
struct rb_node *n = proc->refs_by_desc.rb_node;//refs_by_desc以desc排序
struct binder_ref *ref;
while (n) {
ref = rb_entry(n, struct binder_ref, rb_node_desc);
if (desc < ref->desc)
n = n->rb_left;
else if (desc > ref->desc)
n = n->rb_right;
else
return ref;
}
return NULL; //未找到,则返回NULL
}
binder_get_ref_for_node
binder_get_ref_for_node函数和binder_get_ref相似,从binder_proc.refs_by_node红黑树中搜索binder_ref。但是,在未找到binder_ref的情况下,会创建新的binder_ref,所以,基本不会返回NULL:
static struct binder_ref *binder_get_ref_for_node(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_node *node)
{
struct rb_node *n;
struct rb_node **p = &proc->refs_by_node.rb_node;//refs_by_node,以node地址排序
struct rb_node *parent = NULL;
struct binder_ref *ref, *new_ref;
while (*p) { //查找binder_ref
parent = *p;
ref = rb_entry(parent, struct binder_ref, rb_node_node);
if (node < ref->node)
p = &(*p)->rb_left;
else if (node > ref->node)
p = &(*p)->rb_right;
else
return ref;
}
//未找到binder_ref则创建
new_ref = kzalloc(sizeof(*ref), GFP_KERNEL);
if (new_ref == NULL)
return NULL;
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_REF);
//初始化new_ref的成员
new_ref->debug_id = ++binder_last_id;
new_ref->proc = proc;
new_ref->node = node;
rb_link_node(&new_ref->rb_node_node, parent, p);//保存到refs_by_node中
rb_insert_color(&new_ref->rb_node_node, &proc->refs_by_node);
new_ref->desc = (node == binder_context_mgr_node) ? 0 : 1;
for (n = rb_first(&proc->refs_by_desc); n != NULL; n = rb_next(n)) {//分配desc值, 基本逻辑为从小到大,查找未分配到最小int值
ref = rb_entry(n, struct binder_ref, rb_node_desc);
if (ref->desc > new_ref->desc)
break;
new_ref->desc = ref->desc + 1;
}
p = &proc->refs_by_desc.rb_node;
while (*p) {//确定new_ref在refs_by_desc中到位置
parent = *p;
ref = rb_entry(parent, struct binder_ref, rb_node_desc);
if (new_ref->desc < ref->desc)
p = &(*p)->rb_left;
else if (new_ref->desc > ref->desc)
p = &(*p)->rb_right;
else
BUG();
}
rb_link_node(&new_ref->rb_node_desc, parent, p); //保存到refs_by_desc中
rb_insert_color(&new_ref->rb_node_desc, &proc->refs_by_desc);
if (node) {
hlist_add_head(&new_ref->node_entry, &node->refs);//保存new_ref到node->refs中
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_INTERNAL_REFS,
"binder: %d new ref %d desc %d for "
"node %d\n", proc->pid, new_ref->debug_id,
new_ref->desc, node->debug_id);
} else {
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_INTERNAL_REFS,
"binder: %d new ref %d desc %d for "
"dead node\n", proc->pid, new_ref->debug_id,
new_ref->desc);
}
return new_ref;
}
binder_inc_ref
binder_inc_ref用于增加binder_ref的引用计数:
static int binder_inc_ref(struct binder_ref *ref, int strong,
struct list_head *target_list)
{
int ret;
if (strong) {
if (ref->strong == 0) {//ref->strong从0增加到1,需要增加对应binder_node的引用计数,防止BBinder被
ret = binder_inc_node(ref->node, 1, 1, target_list);
if (ret)
return ret;
}
ref->strong++;
} else {
if (ref->weak == 0) {
ret = binder_inc_node(ref->node, 0, 1, target_list);
if (ret)
return ret;
}
ref->weak++;
}
return 0;
}
binder_dec_ref
binder_dec_ref用于减少binder_ref的引用计数:
static int binder_dec_ref(struct binder_ref *ref, int strong)
{
if (strong) {
if (ref->strong == 0) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d invalid dec strong, "
"ref %d desc %d s %d w %d\n",
ref->proc->pid, ref->debug_id,
ref->desc, ref->strong, ref->weak);
return -EINVAL;
}
ref->strong--;
if (ref->strong == 0) {
int ret;
ret = binder_dec_node(ref->node, strong, 1);//释放由binder_ref构成到远端强引用
if (ret)
return ret;
}
} else {
if (ref->weak == 0) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d invalid dec weak, "
"ref %d desc %d s %d w %d\n",
ref->proc->pid, ref->debug_id,
ref->desc, ref->strong, ref->weak);
return -EINVAL;
}
ref->weak--;
}
if (ref->strong == 0 && ref->weak == 0)
binder_delete_ref(ref);//释放binder_ref
return 0;
}
binder_delete_ref
binder_delete_ref用于释放binder_ref:
static void binder_delete_ref(struct binder_ref *ref)
{
......
//从当前binder_proc中删除binder_ref
rb_erase(&ref->rb_node_desc, &ref->proc->refs_by_desc);
rb_erase(&ref->rb_node_node, &ref->proc->refs_by_node);
if (ref->strong) //强引用计数不为0
binder_dec_node(ref->node, 1, 1);
hlist_del(&ref->node_entry);//从binder_node->refs中移除ref
binder_dec_node(ref->node, 0, 1);//减少node的远端弱引用
if (ref->death) {//释放死亡通知
......
list_del(&ref->death->work.entry);
kfree(ref->death);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_DEATH);
}
kfree(ref);//释放ref
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_REF);
}
binder_get_thread
binder_get_thread用于从当前binder_proc中获取当前binder_thread,如果找不到,则创建新的binder_thread:
static struct binder_thread *binder_get_thread(struct binder_proc *proc)
{
struct binder_thread *thread = NULL;
struct rb_node *parent = NULL;
struct rb_node **p = &proc->threads.rb_node;//proc->threads中,binder_thread以pid为key排序
while (*p) {
parent = *p;
thread = rb_entry(parent, struct binder_thread, rb_node);
if (current->pid < thread->pid)
p = &(*p)->rb_left;
else if (current->pid > thread->pid)
p = &(*p)->rb_right;
else
break;
}
if (*p == NULL) { //未找到thread,则创建binder_thread的新实例
thread = kzalloc(sizeof(*thread), GFP_KERNEL);
if (thread == NULL)
return NULL;
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_THREAD);
thread->proc = proc;
thread->pid = current->pid;
init_waitqueue_head(&thread->wait);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&thread->todo);
rb_link_node(&thread->rb_node, parent, p);
rb_insert_color(&thread->rb_node, &proc->threads);
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_NEED_RETURN;
thread->return_error = BR_OK;
thread->return_error2 = BR_OK;
}
return thread;
} 关于thread.pid,可能大家存在和我当初一样的困惑,进程内所有线程的pid不是都一样的么?因为他们属于同一个进程,当然应该有相同的pid?
好吧,windows程序员有这样的理解并没有错。因为多线程技术是windows系统先引入的,所以windows系统对于多线程的支持比较好。而Linux系统上对于多线程的实现有些“神似而行非”:
- 后台线程其实也是一个进程,但是,他不太“独立”,他和前台线程共享虚地址,共享寄存器等资源,有些书上也称呼为轻量级进程
- 轻量级进程和UI进程间可以共享内存等资源,所以,他们逻辑上可以组成一个”进程“,在Linux系统中,把这个”进程“称为一个任务组
- 任务组的组id为UI进程的pid,也就是我们常说的进程号
- UI进程的pid,相当于"UI线程"的线程id;轻量级进程的pid,相当于”后台线程“的线程id
所以,这里到pid,就是我们常说的线程id。
binder_free_thread
binder_freee_thread用于释放binder_thread:
static int binder_free_thread(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread)
{
struct binder_transaction *t;
struct binder_transaction *send_reply = NULL;
int active_transactions = 0;
rb_erase(&thread->rb_node, &proc->threads);//从proc中移除thread
t = thread->transaction_stack;
if (t && t->to_thread == thread)//thread还有未回复的请求
send_reply = t;
while (t) {
active_transactions++;
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_DEAD_TRANSACTION,
"binder: release %d:%d transaction %d "
"%s, still active\n", proc->pid, thread->pid,
t->debug_id,
(t->to_thread == thread) ? "in" : "out");
if (t->to_thread == thread) {
t->to_proc = NULL;
t->to_thread = NULL;
if (t->buffer) {
t->buffer->transaction = NULL;
t->buffer = NULL;
}
t = t->to_parent;
} else if (t->from == thread) {
t->from = NULL;
t = t->from_parent;
} else
BUG();
}
if (send_reply)
binder_send_failed_reply(send_reply, BR_DEAD_REPLY);//设置请求线程的error_code=BR_DEAD_REPLY
binder_release_work(&thread->todo);//释放未处理的binder_work
kfree(thread);//释放thread
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_THREAD);
return active_transactions;
}
binder_alloc_buf
binder_alloc_buf用于分配binder_buffer以保存数据实体:
static struct binder_buffer *binder_alloc_buf(struct binder_proc *proc,
size_t data_size,
size_t offsets_size, int is_async)
{
struct rb_node *n = proc->free_buffers.rb_node;
struct binder_buffer *buffer;
size_t buffer_size;
struct rb_node *best_fit = NULL;
void *has_page_addr;
void *end_page_addr;
size_t size;
if (proc->vma == NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: %d: binder_alloc_buf, no vma\n",
proc->pid);
return NULL;
}
size = ALIGN(data_size, sizeof(void *)) +
ALIGN(offsets_size, sizeof(void *)); //binder_buffer的size至少要能够放下数据和偏移量数组,并且4字节对齐
if (size < data_size || size < offsets_size) {//发生溢出
binder_user_error("binder: %d: got transaction with invalid "
"size %zd-%zd\n", proc->pid, data_size, offsets_size);
return NULL;
}
if (is_async &&
proc->free_async_space < size + sizeof(struct binder_buffer)) {
......
return NULL;
}
while (n) {//用最佳匹配算法选择一个binder_buffer
buffer = rb_entry(n, struct binder_buffer, rb_node);
BUG_ON(!buffer->free);
buffer_size = binder_buffer_size(proc, buffer);//计算buffer的大小
if (size < buffer_size) {
best_fit = n;
n = n->rb_left;
} else if (size > buffer_size)
n = n->rb_right;
else {
best_fit = n;
break;
}
}
if (best_fit == NULL) {
......
return NULL;
}
if (n == NULL) {
buffer = rb_entry(best_fit, struct binder_buffer, rb_node);
buffer_size = binder_buffer_size(proc, buffer);
}
......
has_page_addr =
(void *)(((uintptr_t)buffer->data + buffer_size) & PAGE_MASK);//因为下一个binder_buffer结构体必然已经分配了物理页,
//所以需要去计算页起点对应的内存地址
if (n == NULL) {
if (size + sizeof(struct binder_buffer) + 4 >= buffer_size)//buffer_size - size已经不足已再创建一个binder_buffer
buffer_size = size; /* no room for other buffers */
else //可以在剩余的空间内再创建一个binder_buffer,所以分配物理页时,需要考虑binder_buffer结构体需要的空间
buffer_size = size + sizeof(struct binder_buffer);
}
end_page_addr =
(void *)PAGE_ALIGN((uintptr_t)buffer->data + buffer_size);//计算终点的下界
if (end_page_addr > has_page_addr) //下界其实已经分配了物理内存
end_page_addr = has_page_addr;
if (binder_update_page_range(proc, 1,
(void *)PAGE_ALIGN((uintptr_t)buffer->data), end_page_addr, NULL))//为指定的虚地址分配物理页,并同时映射到用户空间内存
return NULL;
rb_erase(best_fit, &proc->free_buffers);//buffer已经被分配,所以从空闲buffer中中移除
buffer->free = 0;
binder_insert_allocated_buffer(proc, buffer);//插入到已分配buffer列表中
if (buffer_size != size) {//空余空间分配出来的新的binder_buffer
struct binder_buffer *new_buffer = (void *)buffer->data + size;
list_add(&new_buffer->entry, &buffer->entry); //保存到proc->buffers
new_buffer->free = 1;
binder_insert_free_buffer(proc, new_buffer);//保存到proc->free_buffers列表中
}
......
buffer->data_size = data_size;
buffer->offsets_size = offsets_size;
buffer->async_transaction = is_async;
if (is_async) {
proc->free_async_space -= size + sizeof(struct binder_buffer);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_BUFFER_ALLOC_ASYNC,
"binder: %d: binder_alloc_buf size %zd "
"async free %zd\n", proc->pid, size,
proc->free_async_space);
}
return buffer;
}
关于最佳匹配算法,用一句话描述就是:从proc->free_buffers中寻找size>=需求大小,并size尽可能小的buffer,而proc->free_buffers是保存了proc内所有空闲的binder_buffer,并以size大小排序。
当匹配到的最佳binder_buffer的buffer_size>size(需求大小)+sizeof(binder_buffer) + 4,为了尽可能利用内存资源,需要把buffer_size-size的部分利用起来,分配一个新的binder_buffer.所以也需要为新的binder_buffer结构体分配物理内存,所以,我们可以看到下面的代码:
buffer_size = size + sizeof(struct binder_buffer);
binder_insert_allocated_buffer
binder_insert_allocated_buffer用于将binder_buffer保存到proc->allocated_buffers中:
static void binder_insert_allocated_buffer(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_buffer *new_buffer)
{
struct rb_node **p = &proc->allocated_buffers.rb_node;
struct rb_node *parent = NULL;
struct binder_buffer *buffer;
BUG_ON(new_buffer->free);
while (*p) {//根据buffer的地址,确定合适的插入位置
parent = *p;
buffer = rb_entry(parent, struct binder_buffer, rb_node);
BUG_ON(buffer->free);
if (new_buffer < buffer)
p = &parent->rb_left;
else if (new_buffer > buffer)
p = &parent->rb_right;
else
BUG();
}
rb_link_node(&new_buffer->rb_node, parent, p);
rb_insert_color(&new_buffer->rb_node, &proc->allocated_buffers);
}
binder_insert_free_buffer
binder_insert_free_buffer用于把binder_buffer保存到proc->free_buffers中,不同于proc->allocated_buffers的是,proc->free_buffer是基于binder_buffer的size排序的,以提高binder_alloc_buf函数中,搜索最佳匹配buffer的性能:
static void binder_insert_free_buffer(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_buffer *new_buffer)
{
struct rb_node **p = &proc->free_buffers.rb_node;
struct rb_node *parent = NULL;
struct binder_buffer *buffer;
size_t buffer_size;
size_t new_buffer_size;
BUG_ON(!new_buffer->free);
new_buffer_size = binder_buffer_size(proc, new_buffer);//计算buffer的大小
......
while (*p) {//寻找插入位置
parent = *p;
buffer = rb_entry(parent, struct binder_buffer, rb_node);
BUG_ON(!buffer->free);
buffer_size = binder_buffer_size(proc, buffer);
if (new_buffer_size < buffer_size)
p = &parent->rb_left;
else
p = &parent->rb_right;
}
rb_link_node(&new_buffer->rb_node, parent, p);//插入
rb_insert_color(&new_buffer->rb_node, &proc->free_buffers);
}
binder_buffer_size
binder_buffer_size用于计算binder_buffer的size,binder_buffer的size为binder_buffer->data到下一个binder_buffer的地址起点之间的大小:
static size_t binder_buffer_size(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_buffer *buffer)
{
if (list_is_last(&buffer->entry, &proc->buffers))
return proc->buffer + proc->buffer_size - (void *)buffer->data;
else
return (size_t)list_entry(buffer->entry.next,
struct binder_buffer, entry) - (size_t)buffer->data;
}
binder_release
当调用close关闭dev/binder的文件描述符时,进程会进入内核态,执行binder_release:
static int binder_release(struct inode *nodp, struct file *filp)
{
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
debugfs_remove(proc->debugfs_entry);
binder_defer_work(proc, BINDER_DEFERRED_RELEASE);
return 0;
}
binder_defer_work
上面,我们看到了binder_release会调用binder_defer_work:
static void
binder_defer_work(struct binder_proc *proc, enum binder_deferred_state defer)
{
mutex_lock(&binder_deferred_lock);
proc->deferred_work |= defer;
if (hlist_unhashed(&proc->deferred_work_node)) {
hlist_add_head(&proc->deferred_work_node,
&binder_deferred_list);
queue_work(binder_deferred_workqueue, &binder_deferred_work);//主要是这行
}
mutex_unlock(&binder_deferred_lock);
}
queue_work为linux工作队列函数,具体的本人也不清楚,但是,我们可以先看看binder_deferred_work:
static DECLARE_WORK(binder_deferred_work, binder_deferred_func);所以,queue_work最终会调用函数binder_deferred_func
binder_deferred_func
static void binder_deferred_func(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct binder_proc *proc;
struct files_struct *files;
int defer;
do {
binder_lock(__func__);
mutex_lock(&binder_deferred_lock);
if (!hlist_empty(&binder_deferred_list)) {
proc = hlist_entry(binder_deferred_list.first,
struct binder_proc, deferred_work_node);
hlist_del_init(&proc->deferred_work_node);
defer = proc->deferred_work;
proc->deferred_work = 0;
} else {
proc = NULL;
defer = 0;
}
mutex_unlock(&binder_deferred_lock);
files = NULL;
if (defer & BINDER_DEFERRED_PUT_FILES) {
files = proc->files;
if (files)
proc->files = NULL;
}
if (defer & BINDER_DEFERRED_FLUSH)
binder_deferred_flush(proc);//binder_flush最终会执行这行
if (defer & BINDER_DEFERRED_RELEASE)
binder_deferred_release(proc); /* frees proc *///binder_release最终会执行这行
binder_unlock(__func__);
if (files)
put_files_struct(files);
} while (proc);
}
binder_deferred_release
binder_release函数最终会调用binder_deferred_release函数完成工作,那他做了些什么呢?它如何释放资源?如何触发死亡通知?
static void binder_deferred_release(struct binder_proc *proc)
{
struct hlist_node *pos;
struct binder_transaction *t;
struct rb_node *n;
int threads, nodes, incoming_refs, outgoing_refs, buffers, active_transactions, page_count;
BUG_ON(proc->vma);
BUG_ON(proc->files);
hlist_del(&proc->proc_node);
if (binder_context_mgr_node && binder_context_mgr_node->proc == proc) {
......
binder_context_mgr_node = NULL;
}
threads = 0;
active_transactions = 0;
while ((n = rb_first(&proc->threads))) { //循环释放proc内的thread
struct binder_thread *thread = rb_entry(n, struct binder_thread, rb_node);
threads++;
active_transactions += binder_free_thread(proc, thread);//释放thread
}
nodes = 0;
incoming_refs = 0;
while ((n = rb_first(&proc->nodes))) {//发送死亡通知,告知node已死亡
struct binder_node *node = rb_entry(n, struct binder_node, rb_node);
nodes++;
rb_erase(&node->rb_node, &proc->nodes);//从proc->nodes中移除node
list_del_init(&node->work.entry);//从todo队列中移除binder_work,如果node->work未添加到todo队列中,相当与空操作
if (hlist_empty(&node->refs)) {//没有refs,则直接释放node
kfree(node);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_NODE);
} else {//有binder_ref指向node,则发送死亡通知,等client端收到通知并释放BpBinder后,调用BC_RELEASE释放binder_ref,然后才释放node
struct binder_ref *ref;
int death = 0;
node->proc = NULL;
node->local_strong_refs = 0;
node->local_weak_refs = 0;
hlist_add_head(&node->dead_node, &binder_dead_nodes);//添加到全局死亡队列
//触发死亡通知
hlist_for_each_entry(ref, pos, &node->refs, node_entry) {
incoming_refs++;
if (ref->death) {//已注册死亡通知
death++;
if (list_empty(&ref->death->work.entry)) {//未发送死亡通知
ref->death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER;
list_add_tail(&ref->death->work.entry, &ref->proc->todo);//添加到todo队列
wake_up_interruptible(&ref->proc->wait);
} else //死亡通知已发送
BUG();
}
}
......
}
}
outgoing_refs = 0;
while ((n = rb_first(&proc->refs_by_desc))) {//循环释放binder_ref
struct binder_ref *ref = rb_entry(n, struct binder_ref,
rb_node_desc);
outgoing_refs++;
binder_delete_ref(ref);//释放binder_ref
}
binder_release_work(&proc->todo);//释放等待队列
buffers = 0;
while ((n = rb_first(&proc->allocated_buffers))) {//释放已分配的binder_buffer
struct binder_buffer *buffer = rb_entry(n, struct binder_buffer,
rb_node);
t = buffer->transaction;
if (t) {
t->buffer = NULL;
buffer->transaction = NULL;
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: release proc %d, "
"transaction %d, not freed\n",
proc->pid, t->debug_id);
/*BUG();*/
}
binder_free_buf(proc, buffer);//释放单个binder_buffer
buffers++;
}
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_PROC);
page_count = 0;
if (proc->pages) {//释放物理页表
int i;
for (i = 0; i < proc->buffer_size / PAGE_SIZE; i++) {
if (proc->pages[i]) {
void *page_addr = proc->buffer + i * PAGE_SIZE;
......
unmap_kernel_range((unsigned long)page_addr,
PAGE_SIZE);
__free_page(proc->pages[i]);
page_count++;
}
}
kfree(proc->pages);
vfree(proc->buffer);
}
put_task_struct(proc->tsk);//进程计数器减1
......
kfree(proc);
} 代码看起来路略长,但是胜在逻辑比较清晰,不难理解。期间调用了不少内部函数,在此不再解释。对于了解Binder driver的设计和工作过程,上面的代码已经足够。更加具体的实现,有兴趣的读者可以自己去读源码。
binder_flush
当进程调用flush函数操作“dev/binder”的文件描述符时,进程会转入内核态,调用函数binder_flush:
static int binder_flush(struct file *filp, fl_owner_t id)
{
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
binder_defer_work(proc, BINDER_DEFERRED_FLUSH);
return 0;
} binder_defer_work前面已经解释过,直接看binder_deferred_flush。
binder_deferred_flush
从代码来看,binder_flush就是让等待事件的线程返回:
static void binder_deferred_flush(struct binder_proc *proc)
{
struct rb_node *n;
int wake_count = 0;
for (n = rb_first(&proc->threads); n != NULL; n = rb_next(n)) {
struct binder_thread *thread = rb_entry(n, struct binder_thread, rb_node);
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_NEED_RETURN;
if (thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING) {
wake_up_interruptible(&thread->wait);
wake_count++;
}
}
wake_up_interruptible_all(&proc->wait);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_OPEN_CLOSE,
"binder_flush: %d woke %d threads\n", proc->pid,
wake_count);
}
binder_poll
和binder_flush相反,binder_poll则是等待可读取的数据:
static unsigned int binder_poll(struct file *filp,
struct poll_table_struct *wait)
{
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
struct binder_thread *thread = NULL;
int wait_for_proc_work;
binder_lock(__func__);
thread = binder_get_thread(proc);
wait_for_proc_work = thread->transaction_stack == NULL &&
list_empty(&thread->todo) && thread->return_error == BR_OK;//等待线程的todo队列,还是进程的todo队列?
binder_unlock(__func__);
if (wait_for_proc_work) {
if (binder_has_proc_work(proc, thread))
return POLLIN;
poll_wait(filp, &proc->wait, wait);
if (binder_has_proc_work(proc, thread))
return POLLIN;
} else {
if (binder_has_thread_work(thread))
return POLLIN;
poll_wait(filp, &thread->wait, wait);
if (binder_has_thread_work(thread))
return POLLIN;
}
return 0;
}
个人总结
对Binder机制来说,ServiceManager和binder_context_mgr_node都是特殊的存在。
Binder机制的设计存在一个鸡生蛋、蛋生鸡的问题:
- Binder通信的前提是内核空间必须存在binder_ref和binder_node。
- binder_ref和binder_node在Binder通信的过程中创建,在Service第一次通过flat_binder_object向Client发送自己的binder时,binder driver创建了binder_node;在Client第一次从flat_binder_object中获取到Service的binder时,binder driver创建了binder_ref。
- 换言之,没有binder_ref和binder_node就无法进行binder通信;无法进行binder通信就无法创建binder_nodehe和binder_ref
- 那么第一个binder_ref和binder_node从何而来?
所以,Binder机制约定,所有mHandle=0的BpBinder都“指向”binder_context_mgr_node.而binder_context_mgr_node节点并不是由Binder通信的过程中创建,而是由SerivceManager通过BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR指令创建,而且,ServiceManager必须早于Service和Client启动(实际上,可以观察到ServiceManager的进程号小于Zygote进程,所以ServiceManager的启动早于Android系统).
Binder driver内核态缓冲区和接收者的用户态缓冲区共享物理内存的设计,在提升数据传输性能的同时,也有一个缺陷:
因为Binder driver缓冲区的释放需要由接收者通过BC_FREE_BUFFER来触发,一方面,提高了通信的复杂度,二来也造成了一个隐患:如果开发者并没有通过IPCThreadState类来进行Binder通信,而是直接调用ioctl,那么如果开发者忘了在接收消息后发送BC_FREE_BUFFER,那么binder缓冲区很快被用尽(buffer缓冲区最大才4MB),后续的通信会因为缓冲区不足而失败。
最后,在不考虑循环请求和异步Binder的情况下,Binder通信的使用者必须遵循“请求->答复”的工作模型,否则会导致通信失败;即使考虑循环请求的情况,Binder通信的使用者还是在逻辑上遵守“请求->答复”的工作模型,具体实现上,需要满足Binder读、写间隔进行的规则,不允许连续读取两次或者联系写入两次,否则通信失败;异步Binder是最自由的,但是不允许答复异步请求。