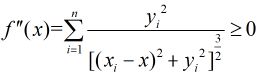最小距离和
题目:在一个平面坐标系中给定![]() (
(![]() )个点,坐标为范围的绝对值均在
)个点,坐标为范围的绝对值均在![]() 范围内,在
范围内,在![]() 轴上找一点
轴上找一点
使得这点到所有点的距离之和最短。
分析:本题方法是三分,我们知道三分满足的条件是这个对象必须是单峰函数。题目要求找到最小值,那么也就是说
这个距离之和是一个下凸函数,现在来开始证明。
设要找的点的坐标为![]() ,那么设距离之和的函数为
,那么设距离之和的函数为![]() ,那么得到
,那么得到
在高数中我们学过下面的定理:
定理:设![]() 在区间
在区间![]() 上有二阶导数,如果
上有二阶导数,如果![]() ,则为
,则为![]() 上的下凸函数,否则如果
上的下凸函数,否则如果![]() ,
,
则![]() 为
为![]() 上的上凸函数。
上的上凸函数。
那么得到
也就是说![]() 为凸函数,也就是单峰函数,那么对于凸函数求最值我们利用三分即可。
为凸函数,也就是单峰函数,那么对于凸函数求最值我们利用三分即可。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
const double eps = 1e-8;
struct Point
{
double x,y;
};
Point p[N];
double dist(Point A,Point B)
{
return sqrt((A.x-B.x)*(A.x-B.x)+(A.y-B.y)*(A.y-B.y));
}
double sum(Point p[],int n,double x)
{
Point t;
t.x = x;
t.y = 0;
double ans = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
ans += dist(p[i],t);
return ans;
}
double Search(Point p[],int n)
{
double l = -1e6;
double r = 1e6;
while(r - l > eps)
{
double ll = (2 * l + r) / 3;
double rr = (l + 2 * r) / 3;
double ans1 = sum(p,n,ll);
double ans2 = sum(p,n,rr);
if(ans1 > ans2) l = ll;
else r = rr;
}
return l;
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y);
printf("%.6lf\n",Search(p,n));
}
return 0;
}