LeetCode—Binary Tree Postorder Traversal 解题报告
转载请注明:http://blog.csdn.net/ict2014/article/details/17471257
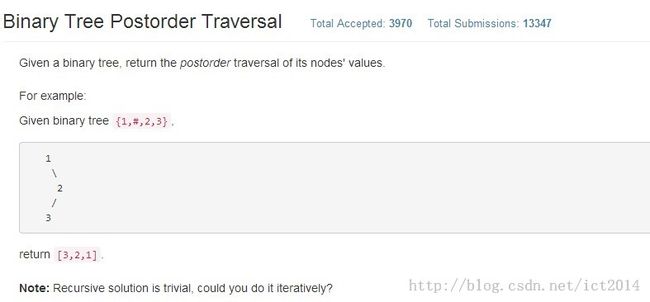
原题如下:
题目解析:
此题是“二叉树的后序遍历”,一般最经典的模式就是递归方式,也是非常容易实现的一种。但是函数递归会耗费大量的栈空间,有可能会产生栈溢出错误。我的经验是,能用“循环”解决的事情,尽量不要用递归。对于这道题目,我会采用两种方法进行写代码。
第一种就是:递归模式。先访问左子树,在访问右子树,然后访问根节点,程序的思路和这个是一样的,很方便实现。
第二种就是:循环模式。这种方法比较难实现。由于必须先访问左子树,在访问右子树,才能访问根节点,因此,我们必须使用了一个堆栈进行保存数据。当访问到一个结点的时候,站在这个3叉路口的时候,我们有3种选择:进入左子树,进入右子树,从栈中抛出这个节点。我们应该如何做三种决定呢?也就是程序如何做三种决定呢?我们可以把“前一个删除的节点”保存起来,
(一)做第一种决定可以如下实现:
左子树不为空、 左子树不等于“前一个删除的节点”、右子树不等于“前一个删除的节点”
(二)做第二种决定可以如下实现:
第一种决定不满足、右子树不为空、右子树不等于“前一个删除的节点”
(三)做第三种决定可以如下实现:
第一种决定不满足、第二种决定不满足
程序代码:
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> post_order;
if(root == NULL){
return post_order;
}
PostorderVisitIterative(root, post_order);
return post_order;
}
//recursive solution
void PostorderVisitRecursive(TreeNode* root,
vector<int>& result){
if(root == NULL){
return;
}
//visit left child tree
PostorderVisitRecursive(root->left, result);
//visit right child tree
PostorderVisitRecursive(root->right, result);
//visit the root
result.push_back(root->val);
}
//iterative solution
void PostorderVisitIterative(TreeNode* root,
vector<int>& result){
//stack used for keeping the nodes
stack<TreeNode*> datas;
datas.push(root);
TreeNode* top, *pre = root;
while(!datas.empty()){
top = datas.top();
//the first condition
//whether or not enter the left child tree
if(top->left != NULL &&
top->left != pre &&
top->right != pre){
datas.push(top->left);
}else{
//the second condition
//whether or not enter the right child tree
if(top->right != NULL &&
top->right != pre){
datas.push(top->right);
}else{
//the third condition
//pop the current node
result.push_back(top->val);
pre = top;
datas.pop();
}
}
}
}
};