FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:熵解码(Entropy Decoding)部分
=====================================================
H.264源代码分析文章列表:
【编码 - x264】
x264源代码简单分析:概述
x264源代码简单分析:x264命令行工具(x264.exe)
x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-1
x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-2
x264源代码简单分析:x264_slice_write()
x264源代码简单分析:滤波(Filter)部分
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块编码(Encode)部分
x264源代码简单分析:熵编码(Entropy Encoding)部分
FFmpeg与libx264接口源代码简单分析
【解码 - libavcodec H.264 解码器】
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:概述
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解析器(Parser)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解码器主干部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:熵解码(EntropyDecoding)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:环路滤波(Loop Filter)部分
=====================================================
本文分析FFmpeg的H.264解码器的熵解码(Entropy Decoding)部分的源代码。FFmpeg的H.264解码器调用decode_slice()函数完成了解码工作。这些解码工作可以大体上分为3个步骤:熵解码,宏块解码以及环路滤波。本文分析这3个步骤中的第1个步骤。
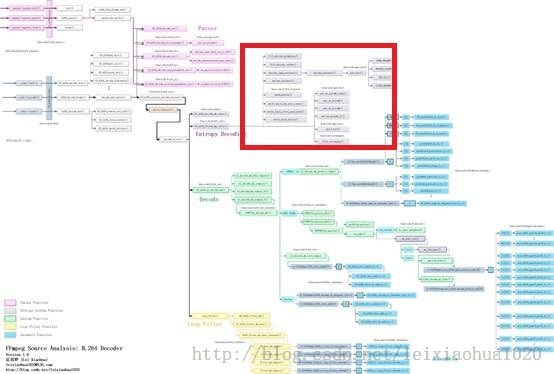
函数调用关系图
熵解码(Entropy Decoding)部分的源代码在整个H.264解码器中的位置如下图所示。ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()调用了很多的读取指数哥伦布编码数据的函数,例如get_ue_golomb_long(),get_ue_golomb(),get_se_golomb(),get_ue_golomb_31()等。此外在解码残差数据的时候,调用了decode_residual()函数,而decode_residual()会调用get_vlc2()函数读取CAVLC编码数据。
总而言之,“熵解码”部分的作用就是按照H.264语法和语义的规定,读取数据(宏块类型、运动矢量、参考帧、残差等)并且赋值到FFmpeg H.264解码器中相应的变量上。需要注意的是,“熵解码”部分并不使用这些变量还原视频数据。还原视频数据的功能在下一步“宏块解码”步骤中完成。
在开始看ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()之前先回顾一下decode_slice()函数。
decode_slice()
decode_slice()用于解码H.264的Slice。该函数完成了“熵解码”、“宏块解码”、“环路滤波”的功能。它的定义位于libavcodec\h264_slice.c,如下所示。//解码slice
//三个主要步骤:
//1.熵解码(CAVLC/CABAC)
//2.宏块解码
//3.环路滤波
//此外还包含了错误隐藏代码
static int decode_slice(struct AVCodecContext *avctx, void *arg)
{
H264Context *h = *(void **)arg;
int lf_x_start = h->mb_x;
h->mb_skip_run = -1;
av_assert0(h->block_offset[15] == (4 * ((scan8[15] - scan8[0]) & 7) << h->pixel_shift) + 4 * h->linesize * ((scan8[15] - scan8[0]) >> 3));
h->is_complex = FRAME_MBAFF(h) || h->picture_structure != PICT_FRAME ||
avctx->codec_id != AV_CODEC_ID_H264 ||
(CONFIG_GRAY && (h->flags & CODEC_FLAG_GRAY));
if (!(h->avctx->active_thread_type & FF_THREAD_SLICE) && h->picture_structure == PICT_FRAME && h->er.error_status_table) {
const int start_i = av_clip(h->resync_mb_x + h->resync_mb_y * h->mb_width, 0, h->mb_num - 1);
if (start_i) {
int prev_status = h->er.error_status_table[h->er.mb_index2xy[start_i - 1]];
prev_status &= ~ VP_START;
if (prev_status != (ER_MV_END | ER_DC_END | ER_AC_END))
h->er.error_occurred = 1;
}
}
//CABAC情况
if (h->pps.cabac) {
/* realign */
align_get_bits(&h->gb);
/* init cabac */
//初始化CABAC解码器
ff_init_cabac_decoder(&h->cabac,
h->gb.buffer + get_bits_count(&h->gb) / 8,
(get_bits_left(&h->gb) + 7) / 8);
ff_h264_init_cabac_states(h);
//循环处理每个宏块
for (;;) {
// START_TIMER
//解码CABAC数据
int ret = ff_h264_decode_mb_cabac(h);
int eos;
// STOP_TIMER("decode_mb_cabac")
//解码宏块
if (ret >= 0)
ff_h264_hl_decode_mb(h);
// FIXME optimal? or let mb_decode decode 16x32 ?
//宏块级帧场自适应。很少接触
if (ret >= 0 && FRAME_MBAFF(h)) {
h->mb_y++;
ret = ff_h264_decode_mb_cabac(h);
//解码宏块
if (ret >= 0)
ff_h264_hl_decode_mb(h);
h->mb_y--;
}
eos = get_cabac_terminate(&h->cabac);
if ((h->workaround_bugs & FF_BUG_TRUNCATED) &&
h->cabac.bytestream > h->cabac.bytestream_end + 2) {
//错误隐藏
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y, h->mb_x - 1,
h->mb_y, ER_MB_END);
if (h->mb_x >= lf_x_start)
loop_filter(h, lf_x_start, h->mb_x + 1);
return 0;
}
if (h->cabac.bytestream > h->cabac.bytestream_end + 2 )
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "bytestream overread %"PTRDIFF_SPECIFIER"\n", h->cabac.bytestream_end - h->cabac.bytestream);
if (ret < 0 || h->cabac.bytestream > h->cabac.bytestream_end + 4) {
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"error while decoding MB %d %d, bytestream %"PTRDIFF_SPECIFIER"\n",
h->mb_x, h->mb_y,
h->cabac.bytestream_end - h->cabac.bytestream);
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y, h->mb_x,
h->mb_y, ER_MB_ERROR);
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
//mb_x自增
//如果自增后超过了一行的mb个数
if (++h->mb_x >= h->mb_width) {
//环路滤波
loop_filter(h, lf_x_start, h->mb_x);
h->mb_x = lf_x_start = 0;
decode_finish_row(h);
//mb_y自增(处理下一行)
++h->mb_y;
//宏块级帧场自适应,暂不考虑
if (FIELD_OR_MBAFF_PICTURE(h)) {
++h->mb_y;
if (FRAME_MBAFF(h) && h->mb_y < h->mb_height)
predict_field_decoding_flag(h);
}
}
//如果mb_y超过了mb的行数
if (eos || h->mb_y >= h->mb_height) {
tprintf(h->avctx, "slice end %d %d\n",
get_bits_count(&h->gb), h->gb.size_in_bits);
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y, h->mb_x - 1,
h->mb_y, ER_MB_END);
if (h->mb_x > lf_x_start)
loop_filter(h, lf_x_start, h->mb_x);
return 0;
}
}
} else {
//CAVLC情况
//循环处理每个宏块
for (;;) {
//解码宏块的CAVLC
int ret = ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc(h);
//解码宏块
if (ret >= 0)
ff_h264_hl_decode_mb(h);
// FIXME optimal? or let mb_decode decode 16x32 ?
if (ret >= 0 && FRAME_MBAFF(h)) {
h->mb_y++;
ret = ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc(h);
if (ret >= 0)
ff_h264_hl_decode_mb(h);
h->mb_y--;
}
if (ret < 0) {
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"error while decoding MB %d %d\n", h->mb_x, h->mb_y);
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y, h->mb_x,
h->mb_y, ER_MB_ERROR);
return ret;
}
if (++h->mb_x >= h->mb_width) {
//环路滤波
loop_filter(h, lf_x_start, h->mb_x);
h->mb_x = lf_x_start = 0;
decode_finish_row(h);
++h->mb_y;
if (FIELD_OR_MBAFF_PICTURE(h)) {
++h->mb_y;
if (FRAME_MBAFF(h) && h->mb_y < h->mb_height)
predict_field_decoding_flag(h);
}
if (h->mb_y >= h->mb_height) {
tprintf(h->avctx, "slice end %d %d\n",
get_bits_count(&h->gb), h->gb.size_in_bits);
if ( get_bits_left(&h->gb) == 0
|| get_bits_left(&h->gb) > 0 && !(h->avctx->err_recognition & AV_EF_AGGRESSIVE)) {
//错误隐藏
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y,
h->mb_x - 1, h->mb_y, ER_MB_END);
return 0;
} else {
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y,
h->mb_x, h->mb_y, ER_MB_END);
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
}
}
if (get_bits_left(&h->gb) <= 0 && h->mb_skip_run <= 0) {
tprintf(h->avctx, "slice end %d %d\n",
get_bits_count(&h->gb), h->gb.size_in_bits);
if (get_bits_left(&h->gb) == 0) {
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y,
h->mb_x - 1, h->mb_y, ER_MB_END);
if (h->mb_x > lf_x_start)
loop_filter(h, lf_x_start, h->mb_x);
return 0;
} else {
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y, h->mb_x,
h->mb_y, ER_MB_ERROR);
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
}
}
}
}
可以看出decode_slice()的的流程如下:
(1)判断H.264码流是CABAC编码还是CAVLC编码,进入不同的处理循环。
(2)如果是CABAC编码,首先调用ff_init_cabac_decoder()初始化CABAC解码器。然后进入一个循环,依次对每个宏块进行以下处理:
a)调用ff_h264_decode_mb_cabac()进行CABAC熵解码
b)调用ff_h264_hl_decode_mb()进行宏块解码
c)解码一行宏块之后调用loop_filter()进行环路滤波
d)此外还有可能调用er_add_slice()进行错误隐藏处理
(3)如果是CABAC编码,直接进入一个循环,依次对每个宏块进行以下处理:
a)调用ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()进行CAVLC熵解码
b)调用ff_h264_hl_decode_mb()进行宏块解码
c)解码一行宏块之后调用loop_filter()进行环路滤波
d)此外还有可能调用er_add_slice()进行错误隐藏处理
可以看出,出了熵解码以外,宏块解码和环路滤波的函数是一样的。下面详细看一下CAVLC熵解码函数ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()。
ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()
ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()完成了FFmpeg H.264解码器中“熵解码”的功能。“熵解码”部分的作用就是按照H.264语法和语义的规定,读取数据(宏块类型、运动矢量、参考帧、残差等)并且赋值到FFmpeg H.264解码器中相应的变量上。具体说来就是完成了解析H.264码流中Slice Data的功能。该函数比较复杂,它的定义位于libavcodec\h264_cavlc.c,如下所示。/*
* 注释:雷霄骅
* leixiaohua1020@126.com
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
*
* 解码宏块的CAVLC数据
* 解码Slice Data(注意不包含Slice Header)
*
*/
int ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc(H264Context *h){
int mb_xy;
int partition_count;
unsigned int mb_type, cbp;
int dct8x8_allowed= h->pps.transform_8x8_mode;
//如果是YUV420或者YUV422,需要处理色度(YUV444中的UV直接当亮度处理)
int decode_chroma = h->sps.chroma_format_idc == 1 || h->sps.chroma_format_idc == 2;
const int pixel_shift = h->pixel_shift;
unsigned local_ref_count[2];
//mb_xy的计算方法
mb_xy = h->mb_xy = h->mb_x + h->mb_y*h->mb_stride;
tprintf(h->avctx, "pic:%d mb:%d/%d\n", h->frame_num, h->mb_x, h->mb_y);
cbp = 0; /* avoid warning. FIXME: find a solution without slowing
down the code */
//slice_type_nos意思是SI/SP 被映射为 I/P (即没有SI/SP这种帧)
//处理Skip宏块-不携带任何数据
//解码器通过周围已重建的宏块的数据来恢复skip块
if(h->slice_type_nos != AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I){
//熵编码为CAVLC时候特有的字段
if(h->mb_skip_run==-1)
h->mb_skip_run= get_ue_golomb_long(&h->gb);
if (h->mb_skip_run--) {
if(FRAME_MBAFF(h) && (h->mb_y&1) == 0){
if(h->mb_skip_run==0)
h->mb_mbaff = h->mb_field_decoding_flag = get_bits1(&h->gb);
}
decode_mb_skip(h);
return 0;
}
}
if (FRAME_MBAFF(h)) {
if( (h->mb_y&1) == 0 )
h->mb_mbaff = h->mb_field_decoding_flag = get_bits1(&h->gb);
}
h->prev_mb_skipped= 0;
//获取宏块类型(I,B,P)
//I片中只允许出现I宏块
//P片中即可以出现P宏块也可以出现I宏块
//B片中即可以出现B宏块也可以出现I宏块
//这个语义含义比较复杂,需要查表
mb_type= get_ue_golomb(&h->gb);
//B
if(h->slice_type_nos == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B){
//b_mb_type_info存储了B宏块的类型
//type代表宏块类型
//partition_count代表宏块分区数目
if(mb_type < 23){
partition_count= b_mb_type_info[mb_type].partition_count;
mb_type= b_mb_type_info[mb_type].type;
}else{
mb_type -= 23;
goto decode_intra_mb;
}
//P
}else if(h->slice_type_nos == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_P){
//p_mb_type_info存储了P宏块的类型
//type代表宏块类型
//partition_count代表宏块分区数目(一般为1,2,4)
if(mb_type < 5){
partition_count= p_mb_type_info[mb_type].partition_count;
mb_type= p_mb_type_info[mb_type].type;
}else{
mb_type -= 5;
goto decode_intra_mb;
}
}else{
//i_mb_type_info存储了I宏块的类型
//注意i_mb_type_info和p_mb_type_info、b_mb_type_info是不一样的:
//type:宏块类型。只有MB_TYPE_INTRA4x4,MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16(基本上都是这种),MB_TYPE_INTRA_PCM三种
//pred_mode:帧内预测方式(四种:DC,Horizontal,Vertical,Plane)。
//cbp:指亮度和色度分量的各小块的残差的编码方案,所谓编码方案有以下几种:
// 0) 所有残差(包括 DC、AC)都不编码。
// 1) 只对 DC 系数编码。
// 2) 所有残差(包括 DC、AC)都编码。
av_assert2(h->slice_type_nos == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I);
if(h->slice_type == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_SI && mb_type)
mb_type--;
decode_intra_mb:
if(mb_type > 25){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "mb_type %d in %c slice too large at %d %d\n", mb_type, av_get_picture_type_char(h->slice_type), h->mb_x, h->mb_y);
return -1;
}
partition_count=0;
cbp= i_mb_type_info[mb_type].cbp;
h->intra16x16_pred_mode= i_mb_type_info[mb_type].pred_mode;
mb_type= i_mb_type_info[mb_type].type;
}
//隔行
if(MB_FIELD(h))
mb_type |= MB_TYPE_INTERLACED;
h->slice_table[ mb_xy ]= h->slice_num;
//I_PCM不常见
if(IS_INTRA_PCM(mb_type)){
const int mb_size = ff_h264_mb_sizes[h->sps.chroma_format_idc] *
h->sps.bit_depth_luma;
// We assume these blocks are very rare so we do not optimize it.
h->intra_pcm_ptr = align_get_bits(&h->gb);
if (get_bits_left(&h->gb) < mb_size) {
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Not enough data for an intra PCM block.\n");
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
skip_bits_long(&h->gb, mb_size);
// In deblocking, the quantizer is 0
h->cur_pic.qscale_table[mb_xy] = 0;
// All coeffs are present
memset(h->non_zero_count[mb_xy], 16, 48);
//赋值
h->cur_pic.mb_type[mb_xy] = mb_type;
return 0;
}
//
local_ref_count[0] = h->ref_count[0] << MB_MBAFF(h);
local_ref_count[1] = h->ref_count[1] << MB_MBAFF(h);
/* 设置上左,上,上右,左宏块的索引值和宏块类型
* 这4个宏块在解码过程中会用到
* 位置如下图所示
*
* +----+----+----+
* | UL | U | UR |
* +----+----+----+
* | L | |
* +----+----+
*/
fill_decode_neighbors(h, mb_type);
//填充Cache
fill_decode_caches(h, mb_type);
/*
*
* 关于多次出现的scan8
*
* scan8[]是一个表格。表格中存储了一整个宏块的信息,每一个元素代表了一个“4x4块”(H.264中最小的处理单位)。
* scan8[]中的“8”,意思应该是按照8x8为单元来扫描?
* 因此可以理解为“按照8x8为单元来扫描4x4的块”?
*
* scan8中按照顺序分别存储了Y,U,V的索引值。具体的存储还是在相应的cache中。
*
* PS:“4x4”貌似是H.264解码器中最小的“块”单位
*
* cache中首先存储Y,然后存储U和V。cache中的存储方式如下所示。
* 其中数字代表了scan8[]中元素的索引值
* scan8[]中元素的值则代表了其代表的变量在cache中的索引值
* +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
* | | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
* +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
* | 0 | 48| | | | y| y| y| y|
* | 1 | | | | y| 0| 1| 4| 5|
* | 2 | | | | y| 2| 3| 6| 7|
* | 3 | | | | y| 8| 9| 12| 13|
* | 4 | | | | y| 10| 11| 14| 15|
* | 5 | 49| | | | u| u| u| u|
* | 6 | | | | u| 16| 17| 20| 21|
* | 7 | | | | u| 18| 19| 22| 23|
* | 8 | | | | u| 24| 25| 28| 29|
* | 9 | | | | u| 26| 27| 30| 31|
* |10 | 50| | | | v| v| v| v|
* |11 | | | | v| 32| 33| 36| 37|
* |12 | | | | v| 34| 35| 38| 39|
* |13 | | | | v| 40| 41| 44| 45|
* |14 | | | | v| 42| 43| 46| 47|
* |---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
* | |
*
*/
//mb_pred
//分成3种情况进行预测工作:
//1.帧内预测
//2.划分为4个块(此时每个8x8的块可以再次划分为4种类型)
//3.其他类型(包括16x16,16x8,8x16,这些划分不可再次划分)
if(IS_INTRA(mb_type)){
//情况1:帧内宏块
int pred_mode;
// init_top_left_availability(h);
//如果是帧内4x4,帧内预测方式需要特殊处理(9种)
if(IS_INTRA4x4(mb_type)){
int i;
int di = 1;
//先不考虑这种相对特殊情况,认为di=1
if(dct8x8_allowed && get_bits1(&h->gb)){
mb_type |= MB_TYPE_8x8DCT;
di = 4;
}
// fill_intra4x4_pred_table(h);
//对于一个宏块(16x16)来说,包含了4*4=16个4x4帧内预测的块
//所以循环16次
/*
* 帧内预测:16x16 宏块被划分为16个4x4子块
*
* +----+----+----+----+
* | | | | |
* +----+----+----+----+
* | | | | |
* +----+----+----+----+
* | | | | |
* +----+----+----+----+
* | | | | |
* +----+----+----+----+
*
*/
for(i=0; i<16; i+=di){
//获得对Intra4x4的预测模式的预测值(挺绕口,确实是这样)
//这个预测模式由左边和上边块的预测模式(取最小值)推导主来
int mode= pred_intra_mode(h, i);
//这1bit是dcPredModePredictedFlag,如果为1,则直接使用推导出来的预测模式
if(!get_bits1(&h->gb)){
//否则就使用读取出来的预测模式
const int rem_mode= get_bits(&h->gb, 3);
mode = rem_mode + (rem_mode >= mode);
}
if(di==4)
fill_rectangle( &h->intra4x4_pred_mode_cache[ scan8[i] ], 2, 2, 8, mode, 1 );
else
h->intra4x4_pred_mode_cache[ scan8[i] ] = mode;//赋值
/*
* 将mode填充至intra4x4_pred_mode_cache
*
* 用简单图形表示intra4x4_pred_mode_cache如下。数字代表填充顺序(一共填充16次)
* |
* --+-------------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 1 2 5 6
* | 0 0 0 0 3 4 7 8
* | 0 0 0 0 9 10 13 14
* | 0 0 0 0 11 12 15 16
*
*/
}
//将宏块的Cache中的intra4x4_pred_mode拷贝至整张图片的intra4x4_pred_mode变量中
write_back_intra_pred_mode(h);
if( ff_h264_check_intra4x4_pred_mode(h) < 0)
return -1;
}else{
//帧内16x16的检测:检查宏块上方和左边的数据是否可用
h->intra16x16_pred_mode= ff_h264_check_intra_pred_mode(h, h->intra16x16_pred_mode, 0);
if(h->intra16x16_pred_mode < 0)
return -1;
}
if(decode_chroma){
//色度帧内预测的检测,和亮度一样
pred_mode= ff_h264_check_intra_pred_mode(h, get_ue_golomb_31(&h->gb), 1);
if(pred_mode < 0)
return -1;
h->chroma_pred_mode= pred_mode;
} else {
h->chroma_pred_mode = DC_128_PRED8x8;
}
}else if(partition_count==4){
//情况2:宏块划分为4
//为什么宏块划分为4的时候要单独处理?因为宏块划分为4的时候,每个8x8的子宏块还可以进一步划分为2个4x8,2个8x4(4x8),或者4个4x4。
//而其他方式的宏块划分(例如16x16,16x8,8x16等)是不可以这样再次划分的
/*
* 16x16 宏块被划分为4个8x8子块
*
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | 0 | 1 |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | 2 | 3 |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
int i, j, sub_partition_count[4], list, ref[2][4];
//获得8x8子块的宏块类型
//后续的很多代码都是循环处理4个8x8子块
//所以很多for()循环的次数都是为4
if(h->slice_type_nos == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B){
//B宏块
//4个子块
for(i=0; i<4; i++){
//子宏块的预测类型
h->sub_mb_type[i]= get_ue_golomb_31(&h->gb);
if(h->sub_mb_type[i] >=13){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "B sub_mb_type %u out of range at %d %d\n", h->sub_mb_type[i], h->mb_x, h->mb_y);
return -1;
}
sub_partition_count[i]= b_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].partition_count;
h->sub_mb_type[i]= b_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].type;
}
if( IS_DIRECT(h->sub_mb_type[0]|h->sub_mb_type[1]|h->sub_mb_type[2]|h->sub_mb_type[3])) {
ff_h264_pred_direct_motion(h, &mb_type);
h->ref_cache[0][scan8[4]] =
h->ref_cache[1][scan8[4]] =
h->ref_cache[0][scan8[12]] =
h->ref_cache[1][scan8[12]] = PART_NOT_AVAILABLE;
}
}else{
av_assert2(h->slice_type_nos == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_P); //FIXME SP correct ?
//P宏块
//4个子块
for(i=0; i<4; i++){
h->sub_mb_type[i]= get_ue_golomb_31(&h->gb);
if(h->sub_mb_type[i] >=4){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "P sub_mb_type %u out of range at %d %d\n", h->sub_mb_type[i], h->mb_x, h->mb_y);
return -1;
}
//p_sub_mb_type_info存储了P子宏块的类型,和前面的p_mb_type_info类似
//type代表宏块类型
//partition_count代表宏块分区数目
sub_partition_count[i]= p_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].partition_count;
h->sub_mb_type[i]= p_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].type;
}
}
//8x8块的子宏块的参考帧序号
for(list=0; list<h->list_count; list++){
int ref_count = IS_REF0(mb_type) ? 1 : local_ref_count[list];
//4个子块
for(i=0; i<4; i++){
if(IS_DIRECT(h->sub_mb_type[i])) continue;
if(IS_DIR(h->sub_mb_type[i], 0, list)){
unsigned int tmp;
if(ref_count == 1){
tmp= 0;
}else if(ref_count == 2){
tmp= get_bits1(&h->gb)^1;
}else{
//参考帧序号
tmp= get_ue_golomb_31(&h->gb);
if(tmp>=ref_count){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "ref %u overflow\n", tmp);
return -1;
}
}
//存储
ref[list][i]= tmp;
}else{
//FIXME
ref[list][i] = -1;
}
}
}
if(dct8x8_allowed)
dct8x8_allowed = get_dct8x8_allowed(h);
//8x8块的子宏块的运动矢量
//依次处理L0和L1
for(list=0; list<h->list_count; list++){
//4个子块
for(i=0; i<4; i++){
if(IS_DIRECT(h->sub_mb_type[i])) {
h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i] ] = h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i]+1 ];
continue;
}
h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i] ]=h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i]+1 ]=
h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i]+8 ]=h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i]+9 ]= ref[list][i];
if(IS_DIR(h->sub_mb_type[i], 0, list)){
const int sub_mb_type= h->sub_mb_type[i];
const int block_width= (sub_mb_type & (MB_TYPE_16x16|MB_TYPE_16x8)) ? 2 : 1;
//8x8块的子块(可能是8x8,8x4,4x8,4x4)的运动矢量
//依次处理,数量为sub_partition_count
for(j=0; j<sub_partition_count[i]; j++){
int mx, my;
//scan8索引
const int index= 4*i + block_width*j;
int16_t (* mv_cache)[2]= &h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[index] ];
//先获取“预测MV”(取中值),结果存入mx,my
pred_motion(h, index, block_width, list, h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[index] ], &mx, &my);
//获取MVD并且累加至“预测MV”
//MV=预测MV+MVD
mx += get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
my += get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
tprintf(h->avctx, "final mv:%d %d\n", mx, my);
if(IS_SUB_8X8(sub_mb_type)){
//8x8子宏块的宏块划分方式为8x8(等同于没划分)
//则把mv_cache中的4个块对应的值都赋值成一样的
//即:[0],[1],[0+8],[1+8]
//PS:stride(代表一行元素个数)为8(即“+8”代表是下一行)
/*
* +----+----+
* | |
* + + +
* | |
* +----+----+
*
*/
mv_cache[ 1 ][0]=
mv_cache[ 8 ][0]= mv_cache[ 9 ][0]= mx;
mv_cache[ 1 ][1]=
mv_cache[ 8 ][1]= mv_cache[ 9 ][1]= my;
}else if(IS_SUB_8X4(sub_mb_type)){
//如果是8x4子宏块
//则把mv_cache中的横向的2个块对应的值都赋值成一样的
//即:[0],[1]
/*
* +----+----+
* | |
* +----+----+
* | |
* +----+----+
*
*/
mv_cache[ 1 ][0]= mx;
mv_cache[ 1 ][1]= my;
}else if(IS_SUB_4X8(sub_mb_type)){
//如果是4x8子宏块
//则把mv_cache中纵向的2个块对应的值都赋值成一样的
//即:[0],[0+8]
/*
* +----+----+
* | | |
* + + +
* | | |
* +----+----+
*
*/
mv_cache[ 8 ][0]= mx;
mv_cache[ 8 ][1]= my;
}
//赋值
//PS:如果是4x4子宏块划分的话,则不会触发上面的if else语句,即分别得到4个4x4块的运动矢量
mv_cache[ 0 ][0]= mx;
mv_cache[ 0 ][1]= my;
/*
* mv_cache赋值方式如下
* scan8[0]代表了cache里面亮度Y的起始点,取值12
* 如果全部都是4x4划分的话,mv_cache填充顺序即按照scan8中元素中的顺序:
* scan8[0],scan8[1],scan8[2],scan8[3],scan8[4],scan8[5]......
* 即:
* 4 + 1 * 8, 5 + 1 * 8, 4 + 2 * 8, 5 + 2 * 8,
* 6 + 1 * 8, 7 + 1 * 8, 6 + 2 * 8, 7 + 2 * 8,
* 4 + 3 * 8, 5 + 3 * 8, 4 + 4 * 8, 5 + 4 * 8,......
* 用简单图形表示mv_cache如下。数字代表填充顺序(一共填充16次)
* |
* --+-------------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 1 2 5 6
* | 0 0 0 0 3 4 7 8
* | 0 0 0 0 9 10 13 14
* | 0 0 0 0 11 12 15 16
*
* 如果全部是8x8划分的话,mv_cache填充顺序即按照scan8中元素中的顺序:
* scan8[0],scan8[4],scan8[8],scan8[16]......
* 填充后赋值3个元素
* 用简单图形表示mv_cache如下。数字代表填充顺序(一共填充4次)
* |
* --+-------------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 3 3 4 4
* | 0 0 0 0 3 3 4 4
*
* 如果全部是8x4划分的话,mv_cache填充顺序即按照scan8中元素中的顺序:
* scan8[0],scan8[2],scan8[4],scan8[6]......
* 填充后赋值右边1个元素
* 用简单图形表示mv_cache如下。数字代表填充顺序(一共填充8次)
* |
* --+-------------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 3 3
* | 0 0 0 0 2 2 4 4
* | 0 0 0 0 5 5 7 7
* | 0 0 0 0 6 6 8 8
*
* 如果全部是4x8划分的话,mv_cache填充顺序即按照scan8中元素中的顺序:
* scan8[0],scan8[1],scan8[4],scan8[5],scan8[8],scan8[9]......
* 填充后赋值下边1个元素
* 用简单图形表示mv_cache如下。数字代表填充顺序(一共填充8次)
* |
* --+-------------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 4
* | 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 4
* | 0 0 0 0 5 6 7 8
* | 0 0 0 0 5 6 7 8
*
* 其他划分的不同组合,可以参考上面的填充顺序
*/
}
}else{
uint32_t *p= (uint32_t *)&h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[4*i] ][0];
p[0] = p[1]=
p[8] = p[9]= 0;
}
}
}
}else if(IS_DIRECT(mb_type)){
//Direct模式
ff_h264_pred_direct_motion(h, &mb_type);
dct8x8_allowed &= h->sps.direct_8x8_inference_flag;
}else{
//情况3:既不是帧内宏块(情况1),宏块划分数目也不为4(情况2)
//这种情况下不存在8x8的子宏块再次划分这样的事情
int list, mx, my, i;
//FIXME we should set ref_idx_l? to 0 if we use that later ...
if(IS_16X16(mb_type)){
/*
* 16x16 宏块
*
* +--------+--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* + + +
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
//运动矢量对应的参考帧
//L0和L1
for(list=0; list<h->list_count; list++){
unsigned int val;
if(IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, list)){
if(local_ref_count[list]==1){
val= 0;
} else if(local_ref_count[list]==2){
val= get_bits1(&h->gb)^1;
}else{
//参考帧图像序号
val= get_ue_golomb_31(&h->gb);
if (val >= local_ref_count[list]){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "ref %u overflow\n", val);
return -1;
}
}
//填充ref_cache
//fill_rectangle(数据起始点,宽,高,一行数据个数,数据值,每个数据占用的byte)
//scan8[0]代表了cache里面亮度Y的起始点
/*
* 在这里相当于在ref_cache[list]填充了这样的一份数据(val=v):
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
*/
fill_rectangle(&h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] ], 4, 4, 8, val, 1);
}
}
//运动矢量
for(list=0; list<h->list_count; list++){
if(IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, list)){
//预测MV(取中值)
pred_motion(h, 0, 4, list, h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] ], &mx, &my);
//MVD从码流中获取
//MV=预测MV+MVD
mx += get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
my += get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
tprintf(h->avctx, "final mv:%d %d\n", mx, my);
//填充mv_cache
//fill_rectangle(数据起始点,宽,高,一行数据个数,数据值,每个数据占用的byte)
//scan8[0]代表了cache里面亮度Y的起始点
/*
* 在这里相当于在mv_cache[list]填充了这样的一份数据(val=v):
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
*/
fill_rectangle(h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[0] ], 4, 4, 8, pack16to32(mx,my), 4);
}
}
}
else if(IS_16X8(mb_type)){ //16x8
/*
* 16x8 宏块划分
*
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | | |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
//运动矢量对应的参考帧
for(list=0; list<h->list_count; list++){
//横着的2个
for(i=0; i<2; i++){
//存储在val
unsigned int val;
if(IS_DIR(mb_type, i, list)){
if(local_ref_count[list] == 1) {
val= 0;
} else if(local_ref_count[list] == 2) {
val= get_bits1(&h->gb)^1;
}else{
val= get_ue_golomb_31(&h->gb);
if (val >= local_ref_count[list]){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "ref %u overflow\n", val);
return -1;
}
}
}else
val= LIST_NOT_USED&0xFF;
//填充ref_cache
//fill_rectangle(数据起始点,宽,高,一行数据个数,数据值,每个数据占用的byte)
//scan8[0]代表了cache里面亮度Y的起始点
/*
* 在这里相当于在ref_cache[list]填充了这样的一份数据(第一次循环val=1,第二次循环val=2):
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
* | 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 2
*/
fill_rectangle(&h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] + 16*i ], 4, 2, 8, val, 1);
}
}
//运动矢量
for(list=0; list<h->list_count; list++){
//2个
for(i=0; i<2; i++){
//存储在val
unsigned int val;
if(IS_DIR(mb_type, i, list)){
//预测MV
pred_16x8_motion(h, 8*i, list, h->ref_cache[list][scan8[0] + 16*i], &mx, &my);
//MV=预测MV+MVD
mx += get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
my += get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
tprintf(h->avctx, "final mv:%d %d\n", mx, my);
//打包?
val= pack16to32(mx,my);
}else
val=0;
//填充mv_cache
//fill_rectangle(数据起始点,宽,高,一行数据个数,数据值,每个数据占用的byte)
//scan8[0]代表了cache里面亮度Y的起始点
/*
* 在这里相当于在ref_cache[list]填充了这样的一份数据(第一次循环val=1,第二次循环val=2):
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
* | 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 2
*/
fill_rectangle(h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[0] + 16*i ], 4, 2, 8, val, 4);
}
}
}else{ //8x16?
/*
* 8x16 宏块划分
*
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
*
*/
av_assert2(IS_8X16(mb_type));
for(list=0; list<h->list_count; list++){
//竖着的2个
for(i=0; i<2; i++){
unsigned int val;
if(IS_DIR(mb_type, i, list)){ //FIXME optimize
if(local_ref_count[list]==1){
val= 0;
} else if(local_ref_count[list]==2){
val= get_bits1(&h->gb)^1;
}else{
val= get_ue_golomb_31(&h->gb);
if (val >= local_ref_count[list]){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "ref %u overflow\n", val);
return -1;
}
}
}else
val= LIST_NOT_USED&0xFF;
//填充ref_cache
//fill_rectangle(数据起始点,宽,高,一行数据个数,数据值,每个数据占用的byte)
//scan8[0]代表了cache里面亮度Y的起始点
/*
* 在这里相当于在ref_cache[list]填充了这样的一份数据(第一次循环val=1,第二次循环val=2):
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
*/
fill_rectangle(&h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] + 2*i ], 2, 4, 8, val, 1);
}
}
for(list=0; list<h->list_count; list++){
for(i=0; i<2; i++){
unsigned int val;
if(IS_DIR(mb_type, i, list)){
//预测MV
pred_8x16_motion(h, i*4, list, h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] + 2*i ], &mx, &my);
//MV=预测MV+MVD
mx += get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
my += get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
tprintf(h->avctx, "final mv:%d %d\n", mx, my);
val= pack16to32(mx,my);
}else
val=0;
//填充mv_cache
//fill_rectangle(数据起始点,宽,高,一行数据个数,数据值,每个数据占用的byte)
//scan8[0]代表了cache里面亮度Y的起始点
/*
* 在这里相当于在mv_cache[list]填充了这样的一份数据(第一次循环val=1,第二次循环val=2):
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
*/
fill_rectangle(h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[0] + 2*i ], 2, 4, 8, val, 4);
}
}
}
}
//将宏块的Cache中的MV拷贝至整张图片的motion_val变量中
if(IS_INTER(mb_type))
write_back_motion(h, mb_type);
//Intra16x16的CBP位于mb_type中,其他类型的宏块的CBP需要单独读取
if(!IS_INTRA16x16(mb_type)){
//获取CBP
cbp= get_ue_golomb(&h->gb);
if(decode_chroma){
//YUV420,YUV422的情况
if(cbp > 47){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "cbp too large (%u) at %d %d\n", cbp, h->mb_x, h->mb_y);
return -1;
}
//获取CBP
if(IS_INTRA4x4(mb_type)) cbp= golomb_to_intra4x4_cbp[cbp];
else cbp= golomb_to_inter_cbp [cbp];
}else{
if(cbp > 15){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "cbp too large (%u) at %d %d\n", cbp, h->mb_x, h->mb_y);
return -1;
}
if(IS_INTRA4x4(mb_type)) cbp= golomb_to_intra4x4_cbp_gray[cbp];
else cbp= golomb_to_inter_cbp_gray[cbp];
}
} else {
if (!decode_chroma && cbp>15) {
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "gray chroma\n");
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
}
if(dct8x8_allowed && (cbp&15) && !IS_INTRA(mb_type)){
mb_type |= MB_TYPE_8x8DCT*get_bits1(&h->gb);
}
//赋值CBP
h->cbp=
h->cbp_table[mb_xy]= cbp;
//赋值mb_type
h->cur_pic.mb_type[mb_xy] = mb_type;
/*
* 亮度cbp取值(只有低4位有意义):
* 变量的最低位比特从最低位开始,每1位对应1个子宏块,该位等于1时表明对应子宏块残差系数被传送;
* 该位等于0时表明对应子宏块残差全部不被传送
* 色度cbp取值:
* 0,代表所有残差都不被传送
* 1,只传送DC
* 2,传送DC+AC
*/
//cbp不为0,才有残差信息
if(cbp || IS_INTRA16x16(mb_type)){
int i4x4, i8x8, chroma_idx;
int dquant;
int ret;
GetBitContext *gb= IS_INTRA(mb_type) ? h->intra_gb_ptr : h->inter_gb_ptr;
const uint8_t *scan, *scan8x8;
const int max_qp = 51 + 6*(h->sps.bit_depth_luma-8);
if(IS_INTERLACED(mb_type)){
scan8x8= h->qscale ? h->field_scan8x8_cavlc : h->field_scan8x8_cavlc_q0;
scan= h->qscale ? h->field_scan : h->field_scan_q0;
}else{
scan8x8= h->qscale ? h->zigzag_scan8x8_cavlc : h->zigzag_scan8x8_cavlc_q0;
scan= h->qscale ? h->zigzag_scan : h->zigzag_scan_q0;
}
//QP量化参数的偏移值
dquant= get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
//由前一个宏块的量化参数累加得到本宏块的QP
h->qscale += dquant;
//注:slice中第1个宏块的计算方法(不存在前一个宏块了):
//QP = 26 + pic_init_qp_minus26 + slice_qp_delta
if(((unsigned)h->qscale) > max_qp){
if(h->qscale<0) h->qscale+= max_qp+1;
else h->qscale-= max_qp+1;
if(((unsigned)h->qscale) > max_qp){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "dquant out of range (%d) at %d %d\n", dquant, h->mb_x, h->mb_y);
return -1;
}
}
h->chroma_qp[0]= get_chroma_qp(h, 0, h->qscale);
h->chroma_qp[1]= get_chroma_qp(h, 1, h->qscale);
//解码残差-亮度
if( (ret = decode_luma_residual(h, gb, scan, scan8x8, pixel_shift, mb_type, cbp, 0)) < 0 ){
return -1;
}
h->cbp_table[mb_xy] |= ret << 12;
if (CHROMA444(h)) {
//YUV444,把U,V都当成亮度处理
if( decode_luma_residual(h, gb, scan, scan8x8, pixel_shift, mb_type, cbp, 1) < 0 ){
return -1;
}
if( decode_luma_residual(h, gb, scan, scan8x8, pixel_shift, mb_type, cbp, 2) < 0 ){
return -1;
}
} else {
//解码残差-色度
const int num_c8x8 = h->sps.chroma_format_idc;
//色度CBP位于高4位
//0:不传
//1:只传DC
//2:DC+AC
if(cbp&0x30){
//如果传了的话
//就要解码残差数据
//2个分量
for(chroma_idx=0; chroma_idx<2; chroma_idx++)
if (decode_residual(h, gb, h->mb + ((256 + 16*16*chroma_idx) << pixel_shift),
CHROMA_DC_BLOCK_INDEX+chroma_idx,
CHROMA422(h) ? chroma422_dc_scan : chroma_dc_scan,
NULL, 4*num_c8x8) < 0) {
return -1;
}
}
//如果传递了AC系数
if(cbp&0x20){
//2个分量
for(chroma_idx=0; chroma_idx<2; chroma_idx++){
const uint32_t *qmul = h->dequant4_coeff[chroma_idx+1+(IS_INTRA( mb_type ) ? 0:3)][h->chroma_qp[chroma_idx]];
int16_t *mb = h->mb + (16*(16 + 16*chroma_idx) << pixel_shift);
for (i8x8 = 0; i8x8<num_c8x8; i8x8++) {
for (i4x4 = 0; i4x4 < 4; i4x4++) {
const int index = 16 + 16*chroma_idx + 8*i8x8 + i4x4;
if (decode_residual(h, gb, mb, index, scan + 1, qmul, 15) < 0)
return -1;
mb += 16 << pixel_shift;
}
}
}
}else{
/*
* non_zero_count_cache:
* 每个4x4块的非0系数个数的缓存
*
* 在这里把U,V都填充为0
* non_zero_count_cache[]内容如下所示
* 图中v=0,上面的块代表Y,中间的块代表U,下面的块代表V
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 x x x x
* | 0 0 0 0 x x x x
* | 0 0 0 0 x x x x
* | 0 0 0 0 x x x x
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
*/
fill_rectangle(&h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[16]], 4, 4, 8, 0, 1);
fill_rectangle(&h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[32]], 4, 4, 8, 0, 1);
}
}
}else{
/*
* non_zero_count_cache:
* 每个4x4块的非0系数个数的缓存
*
* cbp为0时,既不传DC,也不传AC,即全部赋值为0
*
* non_zero_count_cache[]内容如下所示
* 图中v=0,上面的块代表Y,中间的块代表U,下面的块代表V
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
*
*/
fill_rectangle(&h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[ 0]], 4, 4, 8, 0, 1);
fill_rectangle(&h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[16]], 4, 4, 8, 0, 1);
fill_rectangle(&h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[32]], 4, 4, 8, 0, 1);
}
//赋值QP
h->cur_pic.qscale_table[mb_xy] = h->qscale;
//将宏块的non_zero_count_cache拷贝至整张图片的non_zero_count变量中
write_back_non_zero_count(h);
return 0;
}
ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()的定义有将近1000行代码,算是一个比较复杂的函数了。我在其中写了不少注释,因此不再对源代码进行详细的分析。下面先简单梳理一下它的流程:
(1)解析Skip类型宏块
(2)获取mb_type
(3)填充当前宏块左边和上边宏块的信息(后面的预测中会用到)
(4)根据mb_type的不同,分成三种情况进行预测工作:
a)宏块是帧内预测
i.如果宏块是Intra4x4类型,则需要单独解析帧内预测模式。
ii.如果宏块是Intra16x16类型,则不再做过多处理。
b)宏块划分为4个块(此时每个8x8的块可以再次划分为4种类型)
这个时候每个8x8的块可以再次划分为8x8、8x4、4x8、4x4几种子块。需要分别处理这些小的子块:
i.解析子块的参考帧序号
ii.解析子块的运动矢量
c)其它类型(包括16x16,16x8,8x16几种划分,这些划分不可再次划分)
这个时候需要判断宏块的类型为16x16,16x8还是8x16,然后作如下处理:
i.解析子宏块的参考帧序号
ii.解析子宏块的运动矢量
(5)解码残差信息
(6)将宏块的各种信息输出到整个图片相应的变量中
下面简单总结一下ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()中涉及到的一些知识点。
mb_type
mb_type是宏块的类型的索引。FFmpeg H.264解码器中使用i_mb_type_info[]存储了I宏块的类型信息;使用p_mb_type_info[]存储了P宏块的类型信息;使用b_mb_type_info[]存储了B宏块的类型信息。使用“X_mb_type_info[mb_type]”的方式(“X”可以取“i”、“p”、“b”)可以获得该类型宏块的信息。例如获得B宏块的分块数可以使用下面这句代码。int partition_count= b_mb_type_info[mb_type].partition_count;下面看一下这几个数组的定义。
i_mb_type_info[]
i_mb_type_info[]存储了I宏块的类型。其中的元素为IMbInfo类型的结构体。IMbInfo类型结构体的定义如下所示。typedef struct IMbInfo {
uint16_t type;
uint8_t pred_mode;//帧内预测模式
uint8_t cbp;// Coded Block Pattern,高4位为色度,低4位为亮度
} IMbInfo;i_mb_type_info[]的定义如下。
//I宏块的mb_type
/*
* 规律:
* pred_mode总是Vertical->Horizontal->DC->Plane(记住帧内预测中Vertical排在第0个)
* cbp:传送数据量越来越大(前半部分不传亮度残差)
* 按照数据量排序
*
* 只有Intra_16x16宏块类型,CBP的值不是由句法元素给出,而是通过mb_type得到。
*
* CBP(Coded Block Pattern)
* 色度CBP含义:
* 0:不传残差
* 1:只传DC
* 2:传送DC+AC
* 亮度CBP(只有最低4位有定义)含义:
* 变量的最低位比特从最低位开始,每一位对应一个子宏块,该位等于1时表明对应子宏块残差系数被传送;该位等于0
* 时表明对应子宏块残差全部不被传送,解码器把这些残差系数赋为0。
*/
static const IMbInfo i_mb_type_info[26] = {
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA4x4, -1, -1 },//pred_mode还需要单独获取
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 2, 0 },//cbp:0000+0
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 1, 0 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 0, 0 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 3, 0 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 2, 16 },//cbp:0000+1<<4
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 1, 16 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 0, 16 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 3, 16 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 2, 32 },//cbp:0000+2<<4
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 1, 32 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 0, 32 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 3, 32 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 2, 15 + 0 },//cbp:1111+0<<4
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 1, 15 + 0 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 0, 15 + 0 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 3, 15 + 0 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 2, 15 + 16 },//cbp:1111+1<<4
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 1, 15 + 16 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 0, 15 + 16 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 3, 15 + 16 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 2, 15 + 32 },//cbp:1111+2<<4
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 1, 15 + 32 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 0, 15 + 32 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16, 3, 15 + 32 },
{ MB_TYPE_INTRA_PCM, -1, -1 },//特殊
};
p_mb_type_info[]
p_mb_type_info[]存储了P宏块的类型。其中的元素为PMbInfo类型的结构体。PMbInfo类型结构体的定义如下所示。typedef struct PMbInfo {
uint16_t type;//宏块类型
uint8_t partition_count;//分块数量
} PMbInfo;p_mb_type_info[]的定义如下。
//P宏块的mb_type
/*
* 规律:
* 宏块划分尺寸从大到小(子宏块数量逐渐增多)
* 先是“胖”(16x8)的,再是“瘦”(8x16)的
* MB_TYPE_PXL0中的“X”代表宏块的第几个分区,只能取0或者1
* MB_TYPE_P0LX中的“X”代表宏块参考的哪个List。P宏块只能参考list0
*
*/
static const PMbInfo p_mb_type_info[5] = {
{ MB_TYPE_16x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L0, 1 },//没有“P1”
{ MB_TYPE_16x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L0, 2 },
{ MB_TYPE_8x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L0, 2 },
{ MB_TYPE_8x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L0, 4 },
{ MB_TYPE_8x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L0 | MB_TYPE_REF0, 4 },
};
b_mb_type_info[]
b_mb_type_info[]存储了B宏块的类型。其中的元素为PMbInfo类型的结构体。在这里需要注意,p_mb_type_info[]和b_mb_type_info[]中的元素的类型是一样的,都是PMbInfo类型的结构体。b_mb_type_info[]的定义如下。
//B宏块的mb_type
/*
* 规律:
* 宏块划分尺寸从大到小(子宏块数量逐渐增多)
* 先是“胖”(16x8)的,再是“瘦”(8x16)的
* 每个分区参考的list越来越多(意见越来越不一致了)
*
* MB_TYPE_PXL0中的“X”代表宏块的第几个分区,只能取0或者1
* MB_TYPE_P0LX中的“X”代表宏块参考的哪个List。B宏块参考list0和list1
*
*/
static const PMbInfo b_mb_type_info[23] = {
{ MB_TYPE_DIRECT2 | MB_TYPE_L0L1, 1, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L0, 1, },//没有“P1”
{ MB_TYPE_16x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L1, 1, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P0L1, 1, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L0, 2, },//两个分区(每个分区两个参考帧)都参考list0
{ MB_TYPE_8x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L0, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },//两个分区(每个分区两个参考帧)都参考list1
{ MB_TYPE_8x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },//0分区(两个参考帧)参考list0,1分区(两个参考帧)参考list1
{ MB_TYPE_8x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L0, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_8x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L0, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_8x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_8x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L0, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_8x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L0, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_8x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_16x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_8x16 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 2, },
{ MB_TYPE_8x8 | MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L1, 4, },
};
填充当前宏块左边和上边宏块的信息
在宏块预测的时候需要用到当前宏块左边、上左、上边,上右位置的宏块有关的信息。因此在预测前需要先填充这些信息。H.264解码器中调用了fill_decode_neighbors()和fill_decode_caches()两个函数填充这些信息。fill_decode_caches()函数我目前还没有仔细看,在这里简单分析一下fill_decode_neighbors()函数fill_decode_neighbors()
fill_decode_neighbors()用于设置当前宏块左边、上左、上边,上右位置的宏块的索引值和宏块类型,定义位于libavcodec\h264_mvpred.h,如下所示。/* 设置上左,上,上右,左宏块的索引值和宏块类型
* 这4个宏块在解码过程中会用到
* 位置如下图所示
*
* +----+----+----+
* | UL | U | UR |
* +----+----+----+
* | L | |
* +----+----+
*/
static void fill_decode_neighbors(H264Context *h, int mb_type)
{
const int mb_xy = h->mb_xy;
int topleft_xy, top_xy, topright_xy, left_xy[LEFT_MBS];
static const uint8_t left_block_options[4][32] = {
{ 0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 10, 8, 11, 3 + 0 * 4, 3 + 1 * 4, 3 + 2 * 4, 3 + 3 * 4, 1 + 4 * 4, 1 + 8 * 4, 1 + 5 * 4, 1 + 9 * 4 },
{ 2, 2, 3, 3, 8, 11, 8, 11, 3 + 2 * 4, 3 + 2 * 4, 3 + 3 * 4, 3 + 3 * 4, 1 + 5 * 4, 1 + 9 * 4, 1 + 5 * 4, 1 + 9 * 4 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 1, 7, 10, 7, 10, 3 + 0 * 4, 3 + 0 * 4, 3 + 1 * 4, 3 + 1 * 4, 1 + 4 * 4, 1 + 8 * 4, 1 + 4 * 4, 1 + 8 * 4 },
{ 0, 2, 0, 2, 7, 10, 7, 10, 3 + 0 * 4, 3 + 2 * 4, 3 + 0 * 4, 3 + 2 * 4, 1 + 4 * 4, 1 + 8 * 4, 1 + 4 * 4, 1 + 8 * 4 }
};
h->topleft_partition = -1;
//上方宏块。当前宏块减去一行
//top_xy=mb_xy-mb_stride
top_xy = mb_xy - (h->mb_stride << MB_FIELD(h));
/* Wow, what a mess, why didn't they simplify the interlacing & intra
* stuff, I can't imagine that these complex rules are worth it. */
//上左宏块。上方宏块减1
topleft_xy = top_xy - 1;
//上右宏块。上方宏块加1
topright_xy = top_xy + 1;
//左边宏块。当前宏块减1
left_xy[LBOT] = left_xy[LTOP] = mb_xy - 1;
h->left_block = left_block_options[0];
if (FRAME_MBAFF(h)) {
const int left_mb_field_flag = IS_INTERLACED(h->cur_pic.mb_type[mb_xy - 1]);
const int curr_mb_field_flag = IS_INTERLACED(mb_type);
if (h->mb_y & 1) {
if (left_mb_field_flag != curr_mb_field_flag) {
left_xy[LBOT] = left_xy[LTOP] = mb_xy - h->mb_stride - 1;
if (curr_mb_field_flag) {
left_xy[LBOT] += h->mb_stride;
h->left_block = left_block_options[3];
} else {
topleft_xy += h->mb_stride;
/* take top left mv from the middle of the mb, as opposed
* to all other modes which use the bottom right partition */
h->topleft_partition = 0;
h->left_block = left_block_options[1];
}
}
} else {
if (curr_mb_field_flag) {
topleft_xy += h->mb_stride & (((h->cur_pic.mb_type[top_xy - 1] >> 7) & 1) - 1);
topright_xy += h->mb_stride & (((h->cur_pic.mb_type[top_xy + 1] >> 7) & 1) - 1);
top_xy += h->mb_stride & (((h->cur_pic.mb_type[top_xy] >> 7) & 1) - 1);
}
if (left_mb_field_flag != curr_mb_field_flag) {
if (curr_mb_field_flag) {
left_xy[LBOT] += h->mb_stride;
h->left_block = left_block_options[3];
} else {
h->left_block = left_block_options[2];
}
}
}
}
//宏块索引值
//上左
h->topleft_mb_xy = topleft_xy;
//上
h->top_mb_xy = top_xy;
//上右
h->topright_mb_xy = topright_xy;
//左。逐行扫描时候left_xy[LTOP]==left_xy[LBOT]
h->left_mb_xy[LTOP] = left_xy[LTOP];
h->left_mb_xy[LBOT] = left_xy[LBOT];
//FIXME do we need all in the context?
//宏块类型
h->topleft_type = h->cur_pic.mb_type[topleft_xy];
h->top_type = h->cur_pic.mb_type[top_xy];
h->topright_type = h->cur_pic.mb_type[topright_xy];
h->left_type[LTOP] = h->cur_pic.mb_type[left_xy[LTOP]];
h->left_type[LBOT] = h->cur_pic.mb_type[left_xy[LBOT]];
if (FMO) {
if (h->slice_table[topleft_xy] != h->slice_num)
h->topleft_type = 0;
if (h->slice_table[top_xy] != h->slice_num)
h->top_type = 0;
if (h->slice_table[left_xy[LTOP]] != h->slice_num)
h->left_type[LTOP] = h->left_type[LBOT] = 0;
} else {
if (h->slice_table[topleft_xy] != h->slice_num) {
h->topleft_type = 0;
if (h->slice_table[top_xy] != h->slice_num)
h->top_type = 0;
if (h->slice_table[left_xy[LTOP]] != h->slice_num)
h->left_type[LTOP] = h->left_type[LBOT] = 0;
}
}
if (h->slice_table[topright_xy] != h->slice_num)
h->topright_type = 0;
}
从源代码中可以看出,fill_decode_neighbors()设置了下面几个索引值:
topleft_mb_xy,top_mb_xy,topright_mb_xy,left_mb_xy[LTOP]和left_mb_xy[LBOT]
设置了下面几个宏块的类型:
topleft_type,top_type,topright_type,left_type[LTOP],left_type[LBOT]
需要注意的是,在逐行扫面的情况下left_xy[LTOP]和left_xy[LBOT]是相等的。
各种Cache(缓存)
在H.264解码器中包含了各种各样的Cache(缓存)。例如:intra4x4_pred_mode_cache:Intra4x4帧内预测模式的缓存
non_zero_count_cache:每个4x4块的非0系数个数的缓存
mv_cache:运动矢量缓存
ref_cache:运动矢量参考帧的缓存
这几个Cache的定义如下所示。
/**
* Intra4x4帧内预测模式的缓存
* 结构如下所示
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
*/
int8_t intra4x4_pred_mode_cache[5 * 8];
/**
* non zero coeff count cache.
* is 64 if not available.
* 每个4x4块的非0系数个数的缓存
*/
uint8_t __attribute__ ((aligned (8))) non_zero_count_cache[15 * 8];
/**
* Motion vector cache.
* 运动矢量缓存[list][data][x,y]
* list:L0或者L1
* data:共5x8个元素(注意是int16_t类型)
* 结构如下所示
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* x,y:运动矢量的横坐标和纵坐标
*/
int16_t __attribute__ ((aligned (16))) mv_cache[2][5 * 8][2];
/**
* 运动矢量参考帧的缓存,与mv_cache配合使用(注意数据是int8_t类型)
* 结构如下所示
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
*/
int8_t __attribute__ ((aligned (8))) ref_cache [2][5 * 8];
通过观察上面的定义,我们会发现Cache都是一个包含x*8个元素的一维数组(x取15或者5)。按照我自己的理解,我觉得Cache使用一维数组比较形象的存储了二维图像的信息。从上面的代码可以看出Cache中存储有效数据的地方是一个位于右下角的“方形区域”,这一部分实际上对应一维数组中第12-15,20-23,28-31,36-39的元素。这个“方形区域”代表了一个宏块的亮度相关的信息,其中一共包含16个元素。由于1个宏块的亮度数据是1个16x16的块,所以这个“方形区域”里面1个元素实际上代表了一个4x4的块的信息(“4x4”的亮度块应该也是H.264压缩编码中最小的处理单元)。
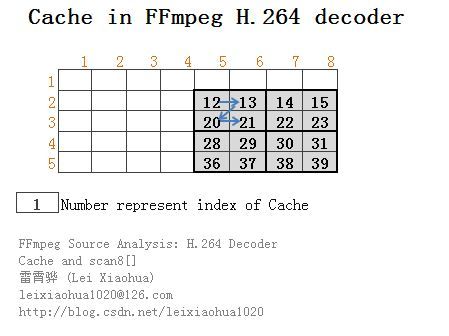
如果我们使用12-15,20-23,28-31,36-39这些范围内的下标引用Cache中的元素,实在是不太方便。由此也引出了FFmpeg H.264解码器中另一个关键的变量——scan8[]数组。
scan8[]
scan8[]存储的是缓存的序号值,它一般情况下是与前面提到的Cache配合使用的。scan8[]的定义位于libavcodec\h264.h,如下所示。/*
* 扫描方式:
* o-o o-o
* / / /
* o-o o-o
* ,---'
* o-o o-o
* / / /
* o-o o-o
*/
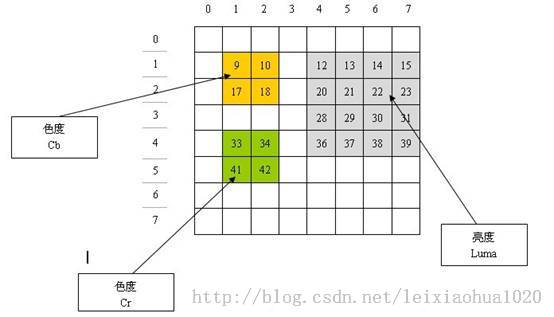
/* Scan8 organization:
* 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
* 0 DY y y y y y
* 1 y Y Y Y Y
* 2 y Y Y Y Y
* 3 y Y Y Y Y
* 4 y Y Y Y Y
* 5 DU u u u u u
* 6 u U U U U
* 7 u U U U U
* 8 u U U U U
* 9 u U U U U
* 10 DV v v v v v
* 11 v V V V V
* 12 v V V V V
* 13 v V V V V
* 14 v V V V V
* DY/DU/DV are for luma/chroma DC.
*/
// This table must be here because scan8[constant] must be known at compiletime
//scan8[]通常与各种cache配合使用(mv_cache,ref_cache等)
static const uint8_t scan8[16 * 3 + 3] = {
4 + 1 * 8, 5 + 1 * 8, 4 + 2 * 8, 5 + 2 * 8,
6 + 1 * 8, 7 + 1 * 8, 6 + 2 * 8, 7 + 2 * 8,
4 + 3 * 8, 5 + 3 * 8, 4 + 4 * 8, 5 + 4 * 8,
6 + 3 * 8, 7 + 3 * 8, 6 + 4 * 8, 7 + 4 * 8,
4 + 6 * 8, 5 + 6 * 8, 4 + 7 * 8, 5 + 7 * 8,
6 + 6 * 8, 7 + 6 * 8, 6 + 7 * 8, 7 + 7 * 8,
4 + 8 * 8, 5 + 8 * 8, 4 + 9 * 8, 5 + 9 * 8,
6 + 8 * 8, 7 + 8 * 8, 6 + 9 * 8, 7 + 9 * 8,
4 + 11 * 8, 5 + 11 * 8, 4 + 12 * 8, 5 + 12 * 8,
6 + 11 * 8, 7 + 11 * 8, 6 + 12 * 8, 7 + 12 * 8,
4 + 13 * 8, 5 + 13 * 8, 4 + 14 * 8, 5 + 14 * 8,
6 + 13 * 8, 7 + 13 * 8, 6 + 14 * 8, 7 + 14 * 8,
0 + 0 * 8, 0 + 5 * 8, 0 + 10 * 8
};
可以看出scan8[]数组中元素的值都是以“a+b*8”的形式写的,我们不妨计算一下前面16个元素的值:
scan8[0]=12
scan8[1]= 13
scan8[2]= 20
scan8[3]= 21
scan8[4]= 14
scan8[5]= 15
scan8[6]= 22
scan8[7]= 23
scan8[8]= 28
scan8[9]= 29
scan8[10]= 36
scan8[11]= 37
scan8[12]= 30
scan8[13]= 31
scan8[14]= 38
scan8[15]= 39
如果把scan8[]数组这些元素的值,作为Cache(例如mv_cache,ref_cache等)的序号,会发现他们的在Cache中代表的元素的位置如下图所示。
图中每个元素代表了一个4x4的块的信息,每个由16个元素组成的“大方块”代表了1个宏块的1个分量的信息。灰色背景的“大方块”存储的是宏块中亮度Y相关的信息,蓝色背景的“大方块”存储的是宏块中色度U相关的信息,粉红背景的“大方块”存储的是宏块中色度U相关的信息。
PS:有关scan8[]数组在网上能查到一点资料。但是经过源代码比对之后,我发现网上的资料已经过时了。旧版本scan8[]代表的Cache的存储方式如下所示。
可以看出旧版本的scan8[]中U、V是存储在Y的左边的区域,而且每个分量只有4个元素,而新版本的scan8[]中U、V是存储在Y的下边的区域,而且每个分量有16个元素。
推测Intra4x4帧内预测模式
在Intra4x4帧内编码的宏块中,每个4x4的子块都有自己的帧内预测方式。H.264码流中并不是直接保存了每个子块的帧内预测方式(不利于压缩)。而是优先通过有周围块的信息推测当前块的帧内预测模式。具体的方法就是获取到左边块和上边块的预测模式,然后取它们的最小值作为当前块的预测模式。H.264解码器中有关这部分功能的实现代码位于pred_intra_mode()函数中,如下所示。/**
* Get the predicted intra4x4 prediction mode.
*/
//获得对Intra4x4的预测模式的预测值(挺绕口,确实是这样)
//这个预测模式由左边和上边块的预测模式(取最小值)推导主来
static av_always_inline int pred_intra_mode(H264Context *h, int n)
{
const int index8 = scan8[n];
//左边块的预测方式
const int left = h->intra4x4_pred_mode_cache[index8 - 1];
//上边块的预测方式
const int top = h->intra4x4_pred_mode_cache[index8 - 8];
//获得左边和上边的最小值
const int min = FFMIN(left, top);
tprintf(h->avctx, "mode:%d %d min:%d\n", left, top, min);
//返回
if (min < 0)
return DC_PRED;
else
return min;
}
参考帧序号和运动矢量的获取
无论处理哪种类型的宏块,H.264解码器都是首先获得宏块的参考帧序号,然后获得宏块的运动矢量。获取参考帧序号和运动矢量的代码占用了ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()最大的篇幅。在这里我们看一段最简单的例子——帧间16x16宏块参考帧序号和运动矢量获取。该部分的代码如下所示。if(IS_16X16(mb_type)){
/*
* 16x16 宏块
*
* +--------+--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* + + +
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
//运动矢量对应的参考帧
//L0和L1
for(list=0; list<h->list_count; list++){
unsigned int val;
if(IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, list)){
if(local_ref_count[list]==1){
val= 0;
} else if(local_ref_count[list]==2){
val= get_bits1(&h->gb)^1;
}else{
//参考帧图像序号
val= get_ue_golomb_31(&h->gb);
if (val >= local_ref_count[list]){
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "ref %u overflow\n", val);
return -1;
}
}
//填充ref_cache
//fill_rectangle(数据起始点,宽,高,一行数据个数,数据值,每个数据占用的byte)
//scan8[0]代表了cache里面亮度Y的起始点
/*
* 在这里相当于在ref_cache[list]填充了这样的一份数据(val=v):
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
*/
fill_rectangle(&h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] ], 4, 4, 8, val, 1);
}
}
//运动矢量
for(list=0; list<h->list_count; list++){
if(IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, list)){
//预测MV(取中值)
pred_motion(h, 0, 4, list, h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] ], &mx, &my);
//MVD从码流中获取
//MV=预测MV+MVD
mx += get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
my += get_se_golomb(&h->gb);
tprintf(h->avctx, "final mv:%d %d\n", mx, my);
//填充mv_cache
//fill_rectangle(数据起始点,宽,高,一行数据个数,数据值,每个数据占用的byte)
//scan8[0]代表了cache里面亮度Y的起始点
/*
* 在这里相当于在mv_cache[list]填充了这样的一份数据(val=v):
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
* | 0 0 0 0 v v v v
*/
fill_rectangle(h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[0] ], 4, 4, 8, pack16to32(mx,my), 4);
}
}
}
从代码中可以看出,H.264解码器首先读取了参考帧图像序号(val变量)并且存入了ref_cache缓存中,然后读取了运动矢量(mx,my变量)并且存入了mv_cache缓存中。在读取运动矢量的时候,有一点需要注意:运动矢量信息在H.264中是以MVD(运动矢量差值)的方式存储的。因此一个宏块真正的运动矢量应该使用下式计算:
在FFmpeg H.264解码器中,运动矢量预测部分的代码在pred_motion()函数中实现。该函数定义位于libavcodec\h264_mvpred.h,如下所示。
/**
* Get the predicted MV.
* @param n the block index
* @param part_width the width of the partition (4, 8,16) -> (1, 2, 4)
* @param mx the x component of the predicted motion vector
* @param my the y component of the predicted motion vector
*/
//获取预测MV(取中值),结果存入mx,my
static av_always_inline void pred_motion(H264Context *const h, int n,
int part_width, int list, int ref,
int *const mx, int *const my)
{
const int index8 = scan8[n];
const int top_ref = h->ref_cache[list][index8 - 8];
const int left_ref = h->ref_cache[list][index8 - 1];
//左侧MV
const int16_t *const A = h->mv_cache[list][index8 - 1];
//上方MV
const int16_t *const B = h->mv_cache[list][index8 - 8];
//右上MV?
const int16_t *C;
int diagonal_ref, match_count;
av_assert2(part_width == 1 || part_width == 2 || part_width == 4);
/* mv_cache
* B . . A T T T T
* U . . L . . , .
* U . . L . . . .
* U . . L . . , .
* . . . L . . . .
*/
diagonal_ref = fetch_diagonal_mv(h, &C, index8, list, part_width);
match_count = (diagonal_ref == ref) + (top_ref == ref) + (left_ref == ref);
tprintf(h->avctx, "pred_motion match_count=%d\n", match_count);
if (match_count > 1) { //most common
//取A,B,C中值
*mx = mid_pred(A[0], B[0], C[0]);
*my = mid_pred(A[1], B[1], C[1]);
} else if (match_count == 1) {
//只取其中的一个值
if (left_ref == ref) {
*mx = A[0];
*my = A[1];
} else if (top_ref == ref) {
*mx = B[0];
*my = B[1];
} else {
*mx = C[0];
*my = C[1];
}
} else {
if (top_ref == PART_NOT_AVAILABLE &&
diagonal_ref == PART_NOT_AVAILABLE &&
left_ref != PART_NOT_AVAILABLE) {
*mx = A[0];
*my = A[1];
} else {
*mx = mid_pred(A[0], B[0], C[0]);
*my = mid_pred(A[1], B[1], C[1]);
}
}
tprintf(h->avctx,
"pred_motion (%2d %2d %2d) (%2d %2d %2d) (%2d %2d %2d) -> (%2d %2d %2d) at %2d %2d %d list %d\n",
top_ref, B[0], B[1], diagonal_ref, C[0], C[1], left_ref,
A[0], A[1], ref, *mx, *my, h->mb_x, h->mb_y, n, list);
}
解码残差
H.264解码器首先判断CBP是否为0。如果CBP不为0,则解码CAVLC编码的残差数据;如果CBP为0,则直接将non_zero_count_cache[]全部赋值为0。CBP
CBP全称为Coded Block Pattern,指亮度和色度分量的各小块的残差的编码方案。H.264解码器中cbp变量(一个uint8_t类型变量)高4位存储了色度CBP,低4位存储了亮度CBP。色度CBP和亮度CBP的含义是不一样的:亮度CBP数据从最低位开始,每1位对应1个子宏块,该位等于1时表明对应子宏块残差系数被传送。(因此亮度CBP数据通常需要当成二进制数据来看)
色度CBP包含3种取值:
0:代表所有残差都不被传送
1:只传送DC系数
2:传送DC系数以及AC系数
(因此色度CBP数据通常可以当成十进制数据来看)
decode_luma_residual()
当CBP不为0的时候,会调用decode_luma_residual()解码亮度残差数据。此外如果包含色度残差的话,还会调用decode_residual()解码色度残差数据。decode_luma_residual()的定义如下所示。//解码残差-亮度
static av_always_inline int decode_luma_residual(H264Context *h, GetBitContext *gb, const uint8_t *scan, const uint8_t *scan8x8, int pixel_shift, int mb_type, int cbp, int p){
int i4x4, i8x8;
int qscale = p == 0 ? h->qscale : h->chroma_qp[p-1];
if(IS_INTRA16x16(mb_type)){
//Intra16x16类型
AV_ZERO128(h->mb_luma_dc[p]+0);
AV_ZERO128(h->mb_luma_dc[p]+8);
AV_ZERO128(h->mb_luma_dc[p]+16);
AV_ZERO128(h->mb_luma_dc[p]+24);
//解码残差
//在这里是解码Hadamard变换后的系数?
if( decode_residual(h, h->intra_gb_ptr, h->mb_luma_dc[p], LUMA_DC_BLOCK_INDEX+p, scan, NULL, 16) < 0){
return -1; //FIXME continue if partitioned and other return -1 too
}
av_assert2((cbp&15) == 0 || (cbp&15) == 15);
//cbp=15=1111
if(cbp&15){
//如果子宏块亮度残差全都编码了
for(i8x8=0; i8x8<4; i8x8++){
for(i4x4=0; i4x4<4; i4x4++){
//循环16次
const int index= i4x4 + 4*i8x8 + p*16;
if( decode_residual(h, h->intra_gb_ptr, h->mb + (16*index << pixel_shift),
index, scan + 1, h->dequant4_coeff[p][qscale], 15) < 0 ){
return -1;
}
}
}
return 0xf;
}else{
//如果子宏块亮度残差没有编码
//就把non_zero_count_cache亮度部分全部填上0
fill_rectangle(&h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[p*16]], 4, 4, 8, 0, 1);
return 0;
}
}else{
int cqm = (IS_INTRA( mb_type ) ? 0:3)+p;
/* For CAVLC 4:4:4, we need to keep track of the luma 8x8 CBP for deblocking nnz purposes. */
int new_cbp = 0;
for(i8x8=0; i8x8<4; i8x8++){
if(cbp & (1<<i8x8)){
if(IS_8x8DCT(mb_type)){
int16_t *buf = &h->mb[64*i8x8+256*p << pixel_shift];
uint8_t *nnz;
for(i4x4=0; i4x4<4; i4x4++){
const int index= i4x4 + 4*i8x8 + p*16;
if( decode_residual(h, gb, buf, index, scan8x8+16*i4x4,
h->dequant8_coeff[cqm][qscale], 16) < 0 )
return -1;
}
nnz= &h->non_zero_count_cache[ scan8[4*i8x8+p*16] ];
nnz[0] += nnz[1] + nnz[8] + nnz[9];
new_cbp |= !!nnz[0] << i8x8;
}else{
for(i4x4=0; i4x4<4; i4x4++){
const int index= i4x4 + 4*i8x8 + p*16;
//解码残差
if( decode_residual(h, gb, h->mb + (16*index << pixel_shift), index,
scan, h->dequant4_coeff[cqm][qscale], 16) < 0 ){
return -1;
}
new_cbp |= h->non_zero_count_cache[ scan8[index] ] << i8x8;
}
}
}else{
uint8_t * const nnz= &h->non_zero_count_cache[ scan8[4*i8x8+p*16] ];
nnz[0] = nnz[1] = nnz[8] = nnz[9] = 0;
}
}
return new_cbp;
}
}
从源代码可以看出,decode_luma_residual()内部实际上也是调用了decode_residual()解码残差数据。decode_residual()内部则调用了get_vlc2()解析CAVLC数据。由于decode_residual()内部还没有仔细看,所以暂时不进行详细分析。
宏块的各种信息输出到整个图片相应的内存中
ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()中包含了很多名称为write_back_{XXX}()的函数。这些函数用于将Cache中当前宏块的信息拷贝至整张图片的相应的变量中。例如如下几个函数:write_back_intra_pred_mode():将intra4x4_pred_mode_cache中的数据拷贝至intra4x4_pred_mode。
write_back_motion():将mv_cache中的数据拷贝至cur_pic结构体中的motion_val;然后将ref_cache中的数据拷贝至cur_pic结构体中的ref_index。
write_back_non_zero_count():将non_zero_count_cache中的数据拷贝至non_zero_count。
在这里我们选择write_back_motion()看看它的源代码。
write_back_motion()
write_back_motion()可以将宏块的Cache中的MV拷贝至整张图片的motion_val变量中。//将宏块的Cache中的MV拷贝至整张图片的motion_val变量中
static av_always_inline void write_back_motion(H264Context *h, int mb_type)
{
const int b_stride = h->b_stride;
const int b_xy = 4 * h->mb_x + 4 * h->mb_y * h->b_stride; // try mb2b(8)_xy
const int b8_xy = 4 * h->mb_xy;
//L0:将宏块的Cache中的MV拷贝至整张图片的motion_val变量中
if (USES_LIST(mb_type, 0)) {
write_back_motion_list(h, b_stride, b_xy, b8_xy, mb_type, 0);
} else {
fill_rectangle(&h->cur_pic.ref_index[0][b8_xy],
2, 2, 2, (uint8_t)LIST_NOT_USED, 1);
}
//L1:将宏块的Cache中的MV拷贝至整张图片的motion_val变量中(最后一个参数不同)
if (USES_LIST(mb_type, 1))
write_back_motion_list(h, b_stride, b_xy, b8_xy, mb_type, 1);
if (h->slice_type_nos == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B && CABAC(h)) {
if (IS_8X8(mb_type)) {
uint8_t *direct_table = &h->direct_table[4 * h->mb_xy];
direct_table[1] = h->sub_mb_type[1] >> 1;
direct_table[2] = h->sub_mb_type[2] >> 1;
direct_table[3] = h->sub_mb_type[3] >> 1;
}
}
}
从源代码可以看出,如果使用了List0,会调用一次write_back_motion_list()函数(注意最后一个参数为“0”);如果使用了List1(双向预测),又会调用一次write_back_motion_list()函数(注意最后一个参数为“1”)。下面再看一下write_back_motion_list()函数。
write_back_motion_list()
write_back_motion_list()是将宏块的Cache中的MV拷贝至整张图片的motion_val变量中的执行函数。该函数定义如下所示。//将宏块的Cache中的MV拷贝至整张图片的motion_val变量中-这是具体的执行函数
static av_always_inline void write_back_motion_list(H264Context *h,
int b_stride,
int b_xy, int b8_xy,
int mb_type, int list)
{
//目的:整张图片的motion_val
int16_t(*mv_dst)[2] = &h->cur_pic.motion_val[list][b_xy];
//源:宏块的Cache,从scan8[0]开始
int16_t(*mv_src)[2] = &h->mv_cache[list][scan8[0]];
//一个运动矢量的坐标(x或者y)占用一个int16_t
//一个宏块一行有4个运动矢量
//每个运动矢量包含2个坐标(x和y)
//一个宏块一行运动矢量的数据量=16*4*2=128
//因此这里拷贝128bit
AV_COPY128(mv_dst + 0 * b_stride, mv_src + 8 * 0);
//每个宏块有4行4列的运动矢量(总计16个)
//因此要分别拷贝4行
//b_stride代表了1行图像中运动矢量的个数
AV_COPY128(mv_dst + 1 * b_stride, mv_src + 8 * 1);
AV_COPY128(mv_dst + 2 * b_stride, mv_src + 8 * 2);
AV_COPY128(mv_dst + 3 * b_stride, mv_src + 8 * 3);
if (CABAC(h)) {
uint8_t (*mvd_dst)[2] = &h->mvd_table[list][FMO ? 8 * h->mb_xy
: h->mb2br_xy[h->mb_xy]];
uint8_t(*mvd_src)[2] = &h->mvd_cache[list][scan8[0]];
if (IS_SKIP(mb_type)) {
AV_ZERO128(mvd_dst);
} else {
AV_COPY64(mvd_dst, mvd_src + 8 * 3);
AV_COPY16(mvd_dst + 3 + 3, mvd_src + 3 + 8 * 0);
AV_COPY16(mvd_dst + 3 + 2, mvd_src + 3 + 8 * 1);
AV_COPY16(mvd_dst + 3 + 1, mvd_src + 3 + 8 * 2);
}
}
{
//拷贝参考帧序号
//目的:整张图片的ref_index
int8_t *ref_index = &h->cur_pic.ref_index[list][b8_xy];
//源:宏块的Cache,从scan8[0]开始
int8_t *ref_cache = h->ref_cache[list];
ref_index[0 + 0 * 2] = ref_cache[scan8[0]];
ref_index[1 + 0 * 2] = ref_cache[scan8[4]];
ref_index[0 + 1 * 2] = ref_cache[scan8[8]];
ref_index[1 + 1 * 2] = ref_cache[scan8[12]];
}
}
由于源代码中作了比较详细的注释,这里就不在过多解释了。从源代码中可以得知write_back_motion_list()首先将mv_cache中的运动矢量信息拷贝至cur_pic(H264Picture类型)的motion_val中(motion_val中存储了整张图片的运动矢量信息);然后将ref_cache中的参考帧序号信息拷贝至cur_pic(H264Picture类型)的ref_index中(ref_index中存储了整张图片的参考帧信息)。
至此FFmpeg H.264解码器的熵解码部分就基本上分析完毕了。
雷霄骅
leixiaohua1020@126.com
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020