kruskal算法
克鲁斯卡尔算法(Kruskal's algorithm)是两个经典的最小生成树算法的较为简单理解的一个。这里面充分体现了贪心算法的精髓。大致的流程可以用一个图来表示。这里的图的选择借用了Wikipedia上的那个。非常清晰且直观。
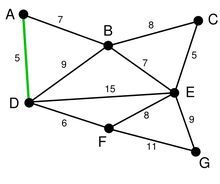
首先第一步,我们有一张图,有若干点和边。
第一步我们要做的事情就是将所有的边的长度排序,用排序的结果作为我们选择边的依据。这里再次体现了贪心算法的思想。资源排序,对局部最优的资源进行选择。
排序完成后,我们率先选择了边AD。这样我们的图就变成了
.
.
.
.
.
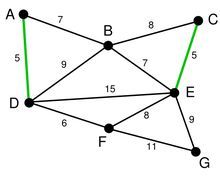
第二步,在剩下的边中寻找。我们找到了CE。这里边的权重也是5
.
.
.
.
.
依次类推我们找到了6,7,7。完成之后,图变成了这个样子。
.
.
.
.
.
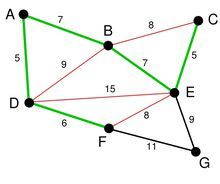
下一步就是关键了。下面选择那条边呢? BC或者EF吗?都不是,尽管现在长度为8的边是最小的未选择的边。但是他们已经连通了(对于BC可以通过CE,EB来连接,类似的EF可以通过EB,BA,AD,DF来接连)。所以我们不需要选择他们。类似的BD也已经连通了(这里上图的连通线用红色表示了)。
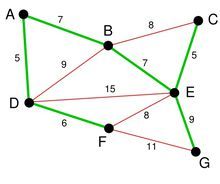
最后就剩下EG和FG了。当然我们选择了EG。最后成功的图就是下图:
.
.
.
.
.
到这里所有的边点都已经连通了,一个最小生成树构建完成。
Kruskal算法的时间复杂度由排序算法决定,若采用快排则时间复杂度为O(N log N)。
大致的算法流程:
1.初始时所有的节点属于各自的集合。
2.按照边权递增顺序遍历所有的边,若遍历到的边两个顶点任分属于不同的集合则确定该边为最小生成树上的一条边,并将这两个顶点分属顶点集合合并。
3.遍历完所有边后,原图上的所有节点属于同一个集合则被选取的边与原来图重的所有的节点构成最小生成树。否则不存在。
- 题目描述:
-
某省调查乡村交通状况,得到的统计表中列出了任意两村庄间的距离。省政府“畅通工程”的目标是使全省任何两个村庄间都可以实现公路交通(但不一定有直接的公路相连,只要能间接通过公路可达即可),并要求铺设的公路总长度为最小。请计算最小的公路总长度。
- 输入:
-
测试输入包含若干测试用例。每个测试用例的第1行给出村庄数目N ( < 100 );随后的N(N-1)/2行对应村庄间的距离,每行给出一对正整数,分别是两个村庄的编号,以及此两村庄间的距离。为简单起见,村庄从1到N编号。
当N为0时,输入结束,该用例不被处理。
- 输出:
-
对每个测试用例,在1行里输出最小的公路总长度。
- 样例输入:
-
3 1 2 1 1 3 2 2 3 4 4 1 2 1 1 3 4 1 4 1 2 3 3 2 4 2 3 4 5 0
- 样例输出:
-
3 5
- 来源:
- 2006年浙江大学计算机及软件工程研究生机试真题
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define N 101
int Tree[N];
int findRoot(int x)
{
if(Tree[x]==-1) return x;
else
{
int temp=findRoot(Tree[x]);
Tree[x]=temp;
return temp;
}
}
struct Edge{
int a,b;
int cost;
bool operator<(const Edge &A) const{
return cost<A.cost;
}
}edge[6000];
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF&&n!=0)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n*(n-1)/2;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&edge[i].a,&edge[i].b,&edge[i].cost);
}
sort(edge+1,edge+1+n*(n-1)/2);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) Tree[i]=-1;
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n*(n-1)/2;i++)
{
int a = findRoot(edge[i].a);
int b=findRoot(edge[i].b);
if(a!=b){
Tree[a]=b;
ans+=edge[i].cost;
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}