MediaProvider源码分析
--------------START------------
MediaProvider包括五个类:
com.android.providers.media.MediaProvider
com.android.providers.media.MediaScannerCursor
com.android.providers.media.MediaScannerReceiver
com.android.providers.media.MediaScannerService
com.android.providers.media.MediaThumbRequest
1.MediaProvider
此类继承ContentProvider,实现一个内容提供者。主要用于创建媒体库的数据库表。有自己创建过ContentProvider的同学相信都比较清楚的。
特别说明一下在MediaProvider中有个广播接收者,代码如下:
1: private BroadcastReceiver mUnmountReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
2: @Override
3: public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
4: if (intent.getAction().equals(Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_EJECT)) {
5: // Remove the external volume and then notify all cursors backed by
6: // data on that volume
7: detachVolume(Uri.parse("content://media/external"));
8: sFolderArtMap.clear();
9: MiniThumbFile.reset();
10: }
11: }
12: };
此接收者是用来接收Sdcard卸载的广播。当Sdcard从手机中分离出来的时候,Sdcard中的媒体文件相对应的数据库将无法操作。
1: private void detachVolume(Uri uri) {
2: //判断是否是同一个进程
3: if (Process.supportsProcesses() && Binder.getCallingPid() != Process.myPid()) {
4: throw new SecurityException(
5: "Opening and closing databases not allowed.");
6: }
7: //此方法只是操作Sdcard的媒体数据库,不支持手机内存的媒体数据库
8: String volume = uri.getPathSegments().get(0);
9: if (INTERNAL_VOLUME.equals(volume)) {
10: throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
11: "Deleting the internal volume is not allowed");
12: } else if (!EXTERNAL_VOLUME.equals(volume)) {
13: throw new IllegalArgumentException(
14: "There is no volume named " + volume);
15: }
16:
17: synchronized (mDatabases) {
18: DatabaseHelper database = mDatabases.get(volume);
19: if (database == null) return;
20:
21: try {
22: // touch the database file to show it is most recently used
23: File file = new File(database.getReadableDatabase().getPath());
24: file.setLastModified(System.currentTimeMillis());
25: } catch (SQLException e) {
26: Log.e(TAG, "Can't touch database file", e);
27: }
28: //移除数据库
29: mDatabases.remove(volume);
30: database.close();
31: }
32:
33: getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null);
34: if (LOCAL_LOGV) Log.v(TAG, "Detached volume: " + volume);
35: }
注意移除数据库并非删除数据库文件(*.db),mDatabases是一个HashMap<String,DatabaseHelper>,移除的含义是暂时无法操作,也可以说说是查询返回的数据都是空的。
2.MediaScannerCursor
一个自定义游标,用来查询媒体文件的扫描状态。主要有一个volume字段,用来区分是内置媒体数据库还是Sdcard的媒体数据库。
3.MediaScannerReceiver
此类实现广播接收者。接收到广播的时候对手机的媒体文件进行扫描。
1: public class MediaScannerReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver
2: {
3: private final static String TAG = "MediaScannerReceiver";
4:
5: @Override
6: public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
7: String action = intent.getAction();
8: Uri uri = intent.getData();
9: String externalStoragePath = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getPath();
10: //系统启动完毕
11: if (action.equals(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED)) {
12: // scan internal storage
13: scan(context, MediaProvider.INTERNAL_VOLUME);
14: } else {
15: if (uri.getScheme().equals("file")) {
16: // handle intents related to external storage
17: String path = uri.getPath();
18: if (action.equals(Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_MOUNTED/*Sdcard挂载广播*/) &&
19: externalStoragePath.equals(path)) {
20: scan(context, MediaProvider.EXTERNAL_VOLUME);
21: } else if (action.equals(Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_SCANNER_SCAN_FILE/*单个文件扫描广播*/) &&
22: path != null && path.startsWith(externalStoragePath + "/")) {
23: scanFile(context, path);
24: }
25: }
26: }
27: }
扫描分为两种三种情况:
a,启动完毕扫面手机内存中的媒体文件
b.sdcard挂载完毕扫描扩展卡的媒体文件
c,扫描单个文件
应用实例:我们可以发送不同的广播让系统去扫描媒体文件。当需要扫描单个文件的时候需要设置一些参数,如下:
1: /**
2: * 扫描文件
3: *
4: * @param filePath 文件路径
5: * @author http://t.sina.com.cn/halzhang
6: */
7: public void scanOneFile(final String filePath) {
8: Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_SCANNER_SCAN_FILE);
9: Uri uri = Uri.parse("file://" + filePath);
10: intent.setData(uri);
11: sendBroadcast(intent);
12: }
接着看一下scan和scenFile两个方法:
1: private void scan(Context context, String volume/*内置卡或者外置卡*/) {
2: Bundle args = new Bundle();
3: args.putString("volume", volume);
4: context.startService(
5: new Intent(context, MediaScannerService.class).putExtras(args));
6: }
7:
8: private void scanFile(Context context, String path/*文件路径*/) {
9: Bundle args = new Bundle();
10: args.putString("filepath", path);
11: context.startService(
12: new Intent(context, MediaScannerService.class).putExtras(args));
13: }
两个方法都是启动MediaScannerService去扫描媒体文件的。
关于MediaScannerSerive且听下回分解。
-------------------END--------------
----------------------START---------------------------
在 上一篇文章中说到系统当接收到扫描请求广播的时候就会调用scan或者scanFile去扫描手机(手机内存和sdcard)中的媒体文件。这两个方法都 是启动MediaScannerService这个服务来完成扫描任务的。接下来我们来看看MediaScannerService是怎么工作的……
4.MediaScannerService(MSS)
MSS实现了Runnable,所以必然的需要实现run方法了,代码如下:
1: public void run()
2: {
3: // reduce priority below other background threads to avoid interfering
4: // with other services at boot time.
5: Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND +
6: Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_LESS_FAVORABLE);
7: Looper.prepare();
8:
9: mServiceLooper = Looper.myLooper();
10: mServiceHandler = new ServiceHandler();
11:
12: Looper.loop();
13: }
在run方法中设置了线程的优先级,优先级比较低,主要为了避免跟其他服务抢夺资源。还有就是利用looper对ServiceHandler的消息进行循环控制。
接着看一下ServiceHandler的实现代码:
1: private final class ServiceHandler extends Handler
2: {
3: @Override
4: public void handleMessage(Message msg)
5: {
6: Bundle arguments = (Bundle) msg.obj;
7: //获取文件路径
8: String filePath = arguments.getString("filepath");
9:
10: try {
11: if (filePath != null) {
12: //文件路径不为空,则调用扫面当个文件的方法
13: IBinder binder = arguments.getIBinder("listener");
14: IMediaScannerListener listener =
15: (binder == null ? null : IMediaScannerListener.Stub.asInterface(binder));
16: Uri uri = scanFile(filePath, arguments.getString("mimetype"));//扫描单个文件
17: if (listener != null) {
18: //执行扫描完成方法
19: listener.scanCompleted(filePath, uri);
20: }
21: } else {
22: //如果文件路径为空,则获取扫面手机内存或者sdcard
23: String volume = arguments.getString("volume");
24: String[] directories = null;
25: //内置卡
26: if (MediaProvider.INTERNAL_VOLUME.equals(volume)) {
27: // scan internal media storage
28: directories = new String[] {
29: Environment.getRootDirectory() + "/media",
30: };
31: }//外置卡
32: else if (MediaProvider.EXTERNAL_VOLUME.equals(volume)) {
33: // scan external storage
34: directories = new String[] {
35: Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getPath(),
36: };
37: }
38:
39: if (directories != null) {
40: if (Config.LOGD) Log.d(TAG, "start scanning volume " + volume);
41: //扫描
42: scan(directories, volume);
43: if (Config.LOGD) Log.d(TAG, "done scanning volume " + volume);
44: }
45: }
46: } catch (Exception e) {
47: Log.e(TAG, "Exception in handleMessage", e);
48: }
49:
50: stopSelf(msg.arg1);
51: }
52: };
在ServiceHandler中主要根据相关参数来调用不同的扫描方法。![]()
那是在哪里调用ServiceHandler发送消息的呢?请看如下代码:
1: @Override
2: public void onCreate() {
3: PowerManager pm = (PowerManager) getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
4: mWakeLock = pm.newWakeLock(PowerManager.PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, TAG);
5: //启用新线程,这样就可以避免阻塞,执行run,初始化成员变量loop和handler
6: Thread thr = new Thread(null, this, "MediaScannerService");
7: thr.start();
8: }
9:
10: @Override
11: public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
12: while (mServiceHandler == null) {
13: synchronized (this) {
14: try {
15: wait(100);
16: } catch (InterruptedException e) {
17: }
18: }
19: }
20:
21: if (intent == null) {
22: Log.e(TAG, "Intent is null in onStartCommand: ", new NullPointerException());
23: return Service.START_NOT_STICKY;
24: }
25:
26: Message msg = mServiceHandler.obtainMessage();
27: msg.arg1 = startId;
28: msg.obj = intent.getExtras();
29: //ServiceHandler发送消息
30: mServiceHandler.sendMessage(msg);
31:
32: // Try again later if we are killed before we can finish scanning.
33: return Service.START_REDELIVER_INTENT;
34: }
35:
36: @Override
37: public void onDestroy() {
38: // Make sure thread has started before telling it to quit.
39: while (mServiceLooper == null) {
40: synchronized (this) {
41: try {
42: wait(100);
43: } catch (InterruptedException e) {
44: }
45: }
46: }
47: mServiceLooper.quit();
48: }
以上三个方法是属于Service的生命周期的。当我们调用startService的时候,如果对应的Service还未创建就会调用onCreate方法===方法。每次startService的时候就调用onStartCommand,所以ServiceHandler就在此发送 消息了。
最后,稍微看一下MSS里面扫描方面。主要是调用MediaScanner对媒体文件进行扫描分析的。至于MediaScanner的实现以后在分析。
1: private void openDatabase(String volumeName) {
2: try {
3: ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
4: values.put("name", volumeName);
5: getContentResolver().insert(Uri.parse("content://media/"), values);
6: } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
7: Log.w(TAG, "failed to open media database");
8: }
9: }
10:
11: private void closeDatabase(String volumeName) {
12: try {
13: getContentResolver().delete(
14: Uri.parse("content://media/" + volumeName), null, null);
15: } catch (Exception e) {
16: Log.w(TAG, "failed to close media database " + volumeName + " exception: " + e);
17: }
18: }
19: //创建扫描器
20: private MediaScanner createMediaScanner() {
21: MediaScanner scanner = new MediaScanner(this);
22: Locale locale = getResources().getConfiguration().locale;
23: if (locale != null) {
24: String language = locale.getLanguage();
25: String country = locale.getCountry();
26: String localeString = null;
27: if (language != null) {
28: if (country != null) {
29: scanner.setLocale(language + "_" + country);
30: } else {
31: scanner.setLocale(language);
32: }
33: }
34: }
35:
36: return scanner;
37: }
38: //扫描目录
39: private void scan(String[] directories, String volumeName) {
40: // don't sleep while scanning
41: mWakeLock.acquire();
42:
43: ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
44: values.put(MediaStore.MEDIA_SCANNER_VOLUME, volumeName);
45: Uri scanUri = getContentResolver().insert(MediaStore.getMediaScannerUri(), values);
46:
47: Uri uri = Uri.parse("file://" + directories[0]);
48: sendBroadcast(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_SCANNER_STARTED, uri));
49:
50: try {
51: if (volumeName.equals(MediaProvider.EXTERNAL_VOLUME)) {
52: openDatabase(volumeName);
53: }
54:
55: MediaScanner scanner = createMediaScanner();
56: scanner.scanDirectories(directories, volumeName);
57: } catch (Exception e) {
58: Log.e(TAG, "exception in MediaScanner.scan()", e);
59: }
60:
61: getContentResolver().delete(scanUri, null, null);
62:
63: sendBroadcast(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MEDIA_SCANNER_FINISHED, uri));
64: mWakeLock.release();
65: }
66: //扫描文件
67: private Uri scanFile(String path, String mimeType) {
68: String volumeName = MediaProvider.INTERNAL_VOLUME;
69: String externalStoragePath = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getPath();
70:
71: if (path.startsWith(externalStoragePath)) {
72: volumeName = MediaProvider.EXTERNAL_VOLUME;
73: openDatabase(volumeName);
74: }
75: MediaScanner scanner = createMediaScanner();
76: //扫描单个文件
77: return scanner.scanSingleFile(path, volumeName, mimeType);
78: }
在MediaProvider中还有一个类:MediaThumbRequest,用来创建预览图的,比如视频的预览图,图片的预览图,音频的专辑图片…这些图片的信息也是保存在数据库的,有兴趣的同学可以自己打开数据库看看里面的表。如下图:
啰哩啰唆的写了两篇文章,希望对大家有所帮助。
其中应该有不少是错误的观点,望大家指正。
----------------------END------------------------------
神马是MediaScanner呢?在Android的SDK里面是看不到这个类的,因为被google隐藏了。通过Android的源码我们可以看到MediaScanner的类注解多了一个@hide的标注。所以对于一般应用开发者,此文意义不是很大,大家可以绕道。
在 前两篇文章中,最后我们都了解了Android的媒体文件的扫描是在MediaScannerService中调用MediaScanner的scanDirectories或者scanSingleFile完成最终的扫描的。那么MediaScanner是如何工作的呢?
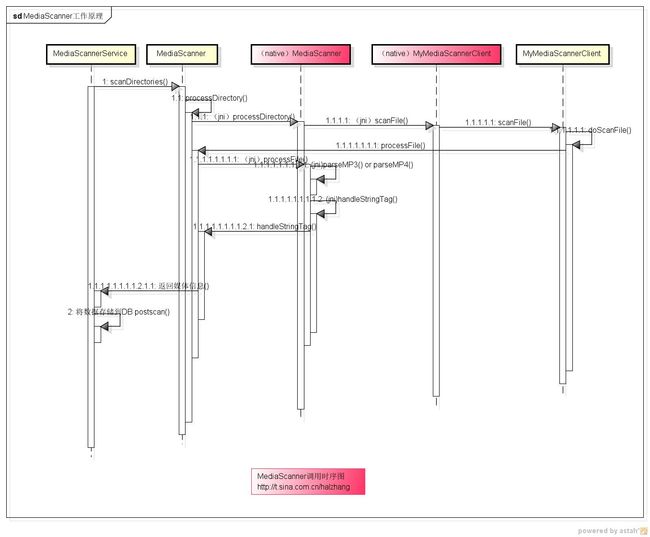
google对MediaScanner写了一大堆的类注释,如下:
1: /* In summary:
2: * Java MediaScannerService calls
3: * Java MediaScanner scanDirectories, which calls
4: * Java MediaScanner processDirectory (native method), which calls
5: * native MediaScanner processDirectory, which calls
6: * native MyMediaScannerClient scanFile, which calls
7: * Java MyMediaScannerClient scanFile, which calls
8: * Java MediaScannerClient doScanFile, which calls
9: * Java MediaScanner processFile (native method), which calls
10: * native MediaScanner processFile, which calls
11: * native parseMP3, parseMP4, parseMidi, parseOgg or parseWMA, which calls
12: * native MyMediaScanner handleStringTag, which calls
13: * Java MyMediaScanner handleStringTag.
14: * Once MediaScanner processFile returns, an entry is inserted in to the database.
15: *
16: * {@hide}
17: */
下面为调用时序图,如下:
这时序图好像不是很规范!点击看大图!请见谅。![]() 开始看代码把……
开始看代码把……
1,scanDirectories。
初始化数据并调用processDirectory处理扫描。
1: public void scanDirectories(String[] directories, String volumeName) {
2: try {
3: long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
4: //初始化
5: initialize(volumeName);
6: //将数据库中的数据缓存到mFileCache
7: /*
8: * mFileCache.put(key, new FileCacheEntry(uri, rowId, path, lastModified));
9: */
10: prescan(null);
11: long prescan = System.currentTimeMillis();
12:
13: for (int i = 0; i < directories.length; i++) {
14: //扫描处理
15: processDirectory(directories[i], MediaFile.sFileExtensions, mClient);
16: }
17: long scan = System.currentTimeMillis();
18: //处理后续数据
19: postscan(directories);
20: long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
2,processDirectory
这是一个native方法,所以我们直接转向jni,代码如下:
1: static void
2: android_media_MediaScanner_processDirectory(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring path, jstring extensions, jobject client)
3: { //获取MediaScanner
4: MediaScanner *mp = (MediaScanner *)env->GetIntField(thiz, fields.context);
5: //参数判断,并抛出异常
6: if (path == NULL) {
7: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException", NULL);
8: return;
9: }
10: if (extensions == NULL) {
11: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException", NULL);
12: return;
13: }
14:
15: const char *pathStr = env->GetStringUTFChars(path, NULL);
16: if (pathStr == NULL) { // Out of memory
17: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/RuntimeException", "Out of memory");
18: return;
19: }
20: const char *extensionsStr = env->GetStringUTFChars(extensions, NULL);
21: if (extensionsStr == NULL) { // Out of memory
22: env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, pathStr);
23: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/RuntimeException", "Out of memory");
24: return;
25: }
26: //初始化client实例
27: MyMediaScannerClient myClient(env, client);
28: //mp调用processDirectory
29: mp->processDirectory(pathStr, extensionsStr, myClient, ExceptionCheck, env);
30: //gc
31: env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, pathStr);
32: env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(extensions, extensionsStr);
33: }
3,mp->processDirectory(pathStr, extensionsStr, myClient, ExceptionCheck, env);
1: status_t MediaScanner::processDirectory(const char *path, const char* extensions,
2: MediaScannerClient& client, ExceptionCheck exceptionCheck, void* exceptionEnv)
3: {//这方法不知道干吗的,估计跟线程有关
4: InitializeForThread();
5:
6: int pathLength = strlen(path);
7: if (pathLength >= PATH_MAX) {
8: return PVMFFailure;
9: }
10: char* pathBuffer = (char *)malloc(PATH_MAX + 1);
11: if (!pathBuffer) {
12: return PVMFFailure;
13: }
14:
15: int pathRemaining = PATH_MAX - pathLength;
16: strcpy(pathBuffer, path);
17: if (pathBuffer[pathLength - 1] != '/') {
18: pathBuffer[pathLength] = '/';
19: pathBuffer[pathLength + 1] = 0;
20: --pathRemaining;
21: }
22:
23: client.setLocale(mLocale);
24: //有是一个关键点
25: status_t result = doProcessDirectory(pathBuffer, pathRemaining, extensions, client, exceptionCheck, exceptionEnv);
26: //释放内存
27: free(pathBuffer);
28: return result;
29: }
4,doProcessDirectory
1: status_t MediaScanner::doProcessDirectory(char *path, int pathRemaining, const char* extensions,
2: MediaScannerClient& client, ExceptionCheck exceptionCheck, void* exceptionEnv)
3: {
4: ……
5: ……
6: if (type == DT_REG || type == DT_DIR) {
7: int nameLength = strlen(name);
8: bool isDirectory = (type == DT_DIR);
9:
10: if (nameLength > pathRemaining || (isDirectory && nameLength + 1 > pathRemaining)) {
11: // path too long!
12: continue;
13: }
14:
15: strcpy(fileSpot, name);
16: if (isDirectory) {
17: // ignore directories with a name that starts with '.'
18: // for example, the Mac ".Trashes" directory
19: if (name[0] == '.') continue;
20:
21: strcat(fileSpot, "/");
22: //文件夹,递归调用
23: int err = doProcessDirectory(path, pathRemaining - nameLength - 1, extensions, client, exceptionCheck, exceptionEnv);
24: if (err) {
25: // pass exceptions up - ignore other errors
26: if (exceptionCheck && exceptionCheck(exceptionEnv)) goto failure;
27: LOGE("Error processing '%s' - skipping\n", path);
28: continue;
29: }
30: } else if (fileMatchesExtension(path, extensions)) {
31: //文件,扩展名符合
32: struct stat statbuf;
33: stat(path, &statbuf);
34: if (statbuf.st_size > 0) {
35: //调用client的scanFile方法
36: client.scanFile(path, statbuf.st_mtime, statbuf.st_size);
37: }
38: if (exceptionCheck && exceptionCheck(exceptionEnv)) goto failure;
39: }
40: }
41: ……
42: ……
5,client.scanFile
1: // returns true if it succeeded, false if an exception occured in the Java code
2: virtual bool scanFile(const char* path, long long lastModified, long long fileSize)
3: {
4: jstring pathStr;
5: if ((pathStr = mEnv->NewStringUTF(path)) == NULL) return false;
6: //有点反射的感觉,调用java里面mClient中的scanFile方法
7: mEnv->CallVoidMethod(mClient, mScanFileMethodID, pathStr, lastModified, fileSize);
8:
9: mEnv->DeleteLocalRef(pathStr);
10: return (!mEnv->ExceptionCheck());
11: }
6,mEnv->CallVoidMethod(mClient, mScanFileMethodID, pathStr, lastModified, fileSize); 让我们回到Java![]()
在android.media.MediaScanner.MyMediaScannerClient中的scanFile方法是直接调用doScanFile的,来看看doScanFile
1:
2: public Uri doScanFile(String path, String mimeType, long lastModified, long fileSize,
3: boolean scanAlways) {
4: Uri result = null;
5: // long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
6: try {
7: FileCacheEntry entry = beginFile(path, mimeType, lastModified, fileSize);
8: // rescan for metadata if file was modified since last scan
9: if (entry != null && (entry.mLastModifiedChanged || scanAlways)) {
10: String lowpath = path.toLowerCase();
11: boolean ringtones = (lowpath.indexOf(RINGTONES_DIR) > 0);
12: boolean notifications = (lowpath.indexOf(NOTIFICATIONS_DIR) > 0);
13: boolean alarms = (lowpath.indexOf(ALARMS_DIR) > 0);
14: boolean podcasts = (lowpath.indexOf(PODCAST_DIR) > 0);
15: boolean music = (lowpath.indexOf(MUSIC_DIR) > 0)
16: || (!ringtones && !notifications && !alarms && !podcasts);
17:
18: if (isMetadataSupported(mFileType)) {
19: // 调用jni方法
20: processFile(path, mimeType, this);
21: } else if (MediaFile.isImageFileType(mFileType)) {
22: // we used to compute the width and height but it's not
23: // worth it
24: }
25:
26: result = endFile(entry, ringtones, notifications, alarms, music, podcasts);
27: }
28: } catch (RemoteException e) {
29: Log.e(TAG, "RemoteException in MediaScanner.scanFile()", e);
30: }
31: // long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
32: // Log.v(TAG, "scanFile: " + path + " took " + (t2-t1));
33: return result;
34: }
补充:result = endFile(entry, ringtones, notifications, alarms, music, podcasts);就是在这里将媒体数据信息存放到数据库的
7,接着是native的 processFile
1: static void
2: android_media_MediaScanner_processFile(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring path, jstring mimeType, jobject client)
3: {
4: MediaScanner *mp = (MediaScanner *)env->GetIntField(thiz, fields.context);
5:
6: if (path == NULL) {
7: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException", NULL);
8: return;
9: }
10:
11: const char *pathStr = env->GetStringUTFChars(path, NULL);
12: if (pathStr == NULL) { // Out of memory
13: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/RuntimeException", "Out of memory");
14: return;
15: }
16: const char *mimeTypeStr = (mimeType ? env->GetStringUTFChars(mimeType, NULL) : NULL);
17: if (mimeType && mimeTypeStr == NULL) { // Out of memory
18: env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, pathStr);
19: jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/RuntimeException", "Out of memory");
20: return;
21: }
22:
23: MyMediaScannerClient myClient(env, client);
24: //调用MediaScanner的processFile
25: mp->processFile(pathStr, mimeTypeStr, myClient);
26: env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, pathStr);
27: if (mimeType) {
28: env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(mimeType, mimeTypeStr);
29: }
30: }
8,mp->processFile(pathStr, mimeTypeStr, myClient);
在此方法中根据不同的文件扩展名调用更加底层的解析方法,我想主要是ID3信息解析
1: status_t MediaScanner::processFile(const char *path, const char* mimeType, MediaScannerClient& client)
2: {
3: status_t result;
4: InitializeForThread();
5: //初始化client
6: client.setLocale(mLocale);
7: client.beginFile();
8:
9: //LOGD("processFile %s mimeType: %s\n", path, mimeType);
10: const char* extension = strrchr(path, '.');
11: //根据扩展名调用不同的解析方法
12: if (extension && strcasecmp(extension, ".mp3") == 0) {
13: result = parseMP3(path, client);
14: } else if (extension &&
15: (strcasecmp(extension, ".mp4") == 0 || strcasecmp(extension, ".m4a") == 0 ||
16: strcasecmp(extension, ".3gp") == 0 || strcasecmp(extension, ".3gpp") == 0 ||
17: strcasecmp(extension, ".3g2") == 0 || strcasecmp(extension, ".3gpp2") == 0)) {
18: result = parseMP4(path, client);
19: } else if (extension && strcasecmp(extension, ".ogg") == 0) {
20: result = parseOgg(path, client);
21: } else if (extension &&
22: ( strcasecmp(extension, ".mid") == 0 || strcasecmp(extension, ".smf") == 0
23: || strcasecmp(extension, ".imy") == 0)) {
24: result = parseMidi(path, client);
25: } else if (extension &&
26: (strcasecmp(extension, ".wma") == 0 || strcasecmp(extension, ".aac") == 0)) {
27: //TODO: parseWMA needs to be renamed to reflect what it is really doing,
28: //ie. using OpenCORE frame metadata utility(FMU) to retrieve metadata.
29: result = parseWMA(path, client);
30: } else {
31: result = PVMFFailure;
32: }
33: //调用client
34: client.endFile();
35:
36: return result;
37: }
9,client.endFile()
1: void MediaScannerClient::endFile()
2: {
3: if (mLocaleEncoding != kEncodingNone) {
4: int size = mNames->size();
5: uint32_t encoding = kEncodingAll;
6:
7: // compute a bit mask containing all possible encodings
8: for (int i = 0; i < mNames->size(); i++)
9: encoding &= possibleEncodings(mValues->getEntry(i));
10:
11: // if the locale encoding matches, then assume we have a native encoding.
12: if (encoding & mLocaleEncoding)
13: convertValues(mLocaleEncoding);
14:
15: // finally, push all name/value pairs to the client
16: for (int i = 0; i < mNames->size(); i++) {
17: //在handleStringTag中是通过类反射的方法调用java中的handleStringTag
18: if (!handleStringTag(mNames->getEntry(i), mValues->getEntry(i)))
19: break;
20: }
21: }
22: // else addStringTag() has done all the work so we have nothing to do
23:
24: delete mNames;
25: delete mValues;
26: mNames = NULL;
27: mValues = NULL;
28: }
10,java中的handleStringTag,这个方法主要处理那些在底层解析后的数据返回到java层
1: public void handleStringTag(String name, String value) {
2: if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("title") || name.startsWith("title;")) {
3: // Don't trim() here, to preserve the special \001 character
4: // used to force sorting. The media provider will trim() before
5: // inserting the title in to the database.
6: mTitle = value;
7: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("artist") || name.startsWith("artist;")) {
8: mArtist = value.trim();
9: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("albumartist") || name.startsWith("albumartist;")) {
10: mAlbumArtist = value.trim();
11: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("album") || name.startsWith("album;")) {
12: mAlbum = value.trim();
13: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("composer") || name.startsWith("composer;")) {
14: mComposer = value.trim();
15: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("genre") || name.startsWith("genre;")) {
16: // handle numeric genres, which PV sometimes encodes like "(20)"
17: if (value.length() > 0) {
18: int genreCode = -1;
19: char ch = value.charAt(0);
20: if (ch == '(') {
21: genreCode = parseSubstring(value, 1, -1);
22: } else if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
23: genreCode = parseSubstring(value, 0, -1);
24: }
25: if (genreCode >= 0 && genreCode < ID3_GENRES.length) {
26: value = ID3_GENRES[genreCode];
27: }
28: }
29: mGenre = value;
30: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("year") || name.startsWith("year;")) {
31: mYear = parseSubstring(value, 0, 0);
32: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("tracknumber") || name.startsWith("tracknumber;")) {
33: // track number might be of the form "2/12"
34: // we just read the number before the slash
35: int num = parseSubstring(value, 0, 0);
36: mTrack = (mTrack / 1000) * 1000 + num;
37: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("discnumber") ||
38: name.equals("set") || name.startsWith("set;")) {
39: // set number might be of the form "1/3"
40: // we just read the number before the slash
41: int num = parseSubstring(value, 0, 0);
42: mTrack = (num * 1000) + (mTrack % 1000);
43: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("duration")) {
44: mDuration = parseSubstring(value, 0, 0);
45: } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("writer") || name.startsWith("writer;")) {
46: mWriter = value.trim();
47: }
48: }
此致,此文结束,累。![]()
三篇有关MediaScanner的文章,希望对大家有所帮助。
对C/C++不是很熟悉,如发现分析有误,请告知。
--------END-------
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/tanlon/archive/2011/03/11/1981804.html