Objective-C的对象模型和runtime机制
内容列表
- 对象模型(结构定义,类对象、元类和实例对象的关系)
- 消息传递和转发机制
- runtime系统功能理解
对象模型
结构定义
对象(Object): OC中基本构造单元 (building block),用于存储和传递数据。
可以在objc.h的文件中查找到对象结构的定义,如下所示即对象结构为Class类型的isa,而Class是 objc_class结构类型指针。objc_class即我们理解的类对象结构,其也包含一个isa类对象结构指针。
类和对象的最终实现都是一种数据结构,(subclass is an instance of superclass)
- 对象结构
/// Represents an instance of a class.
struct objc_object {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
};- id类型定义
/// A pointer to an instance of a class.
typedef struct objc_object *id;- Class类型定义
/// An opaque type that represents an Objective-C class.
typedef struct objc_class *Class;- 类(对象)结构
struct objc_class {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
#if !__OBJC2__
Class super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
const char *name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_ivar_list *ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_method_list **methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_cache *cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_protocol_list *protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;类(类对象)、元类(元类对象)和实例对象的关系
一个完整的类应该包括类方法、实例方法和成员变量(实例变量), 每个对象都包括一个isa(is a class)指针指向类对象(运行时方法发送给对象消息,才确定类别并调用相应的方法实现),类对象结构中记载了类的所有信息。
类对象的isa指向元类对象(meta class),类对象中的方法列表是实例方法(-, instance methods), 元类对象中的方法列表是类方法(+, class methods)
- 可以这么理解:
类包括类对象和元类对象,它们通过类对象结构定义,构成类的所有信息。在定义实例对象的时候,并不会进行任何存储空间(堆)分配,直到调用类方法alloc函数和实例方法init函数实现实例对象在堆中的结构存储分配,并将isa指向其类对象,父类成员变量和对应类对象成员变量初始化为0或nil
上述理解可以通过下面代码和对象变量结构分析来进行确认。
- 测试代码
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@interface AClass : NSObject
{
int a;
char cA;
}
- (void)printA;
@end
@implementation AClass
- (void)printA
{
NSLog(@"I am class A~");
}
@end
@interface BClass : AClass
{
int b;
char cB;
}
- (void)printB;
@end
@implementation BClass
- (void)printB
{
NSLog(@"I am class B~");
}
@end
// ---------- main ----------
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
// ******对象模型初探******
AClass *a = [[AClass alloc] init];
BClass *b = [[BClass alloc] init];
BClass *b1;
[a printA];
[b printB];
}
return 0;
}- 查看对象变量结构(通过设置断点进入Debug模式查看)
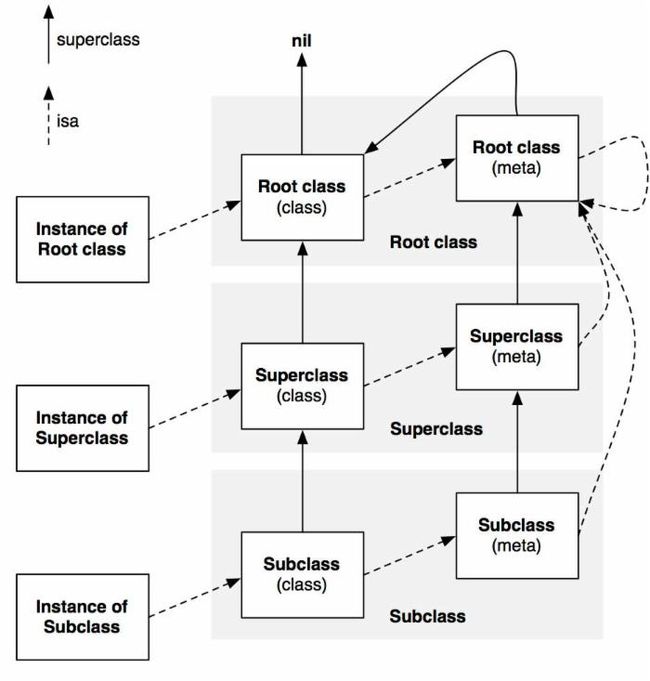
- 类对象、元类和实例对象的isa指针调用图示(subclass is a instance of superclass)
(1) Root class 是NSObject, NSObject没有超类,superclass -> nil
(2) 每个类对象都有一个isa指向唯一的Meta class
(3) 每个元类对象的 isa指针都指向 NSObject的元类对象
消息传递和转发机制
消息传递(Messaging): 在对象之间传递数据并执行任务的过程
Objective-C基于C语言加入了面向对象特性和消息转发机制的动态语言,除编译器外还需要用Runtime系统来动态创建类和对象进行消息发送和转发。
不同语言有不同函数传递方法,C语言 - 函数指针,C++ - 函数调用(引用)类成员函数在编译时候就确定了其所属类别, Objective-C 通过选择器和block。
Objective-C强调消息传递而非方法调用。可以向一个对象传递消息,且不需要再编译期声明这些消息的处理方法。这些方法在运行时才确定。运行时(runtime)具体功能将在下面介绍。
[receiver message];
并不会马上执行 receiver 对象的 message方法的代码,而是向receiver发送一条message消息,该句话被编译器转化为:
id obj_msgSend(id self, SEL op, …);
PS: 消息调用函数还存在特殊情况,如其他函数
objc_msgSend_stret //待发送消息返回结构体
objc_msgSend_fpret //返回浮点数
objc_msgSendSuper //给超类发消息
SEL 表示方法选择器,结构如下: typedef struct objc_selector*SEL;, 可通过关键字@selector()获得
id 数据结构在第一部分:对象模型中已经有定义。
obj_msgSend 发消息流程:
- 根据receiver 对象的isa类对象指针获取对应的class(类对象);
- 优先在类对象的cache(fast map)查找message方法,Not find ->再到methodLists(类中的调度表,用于映射方法和实际内存地址,同时类中还包括指向父类的指针)查找;
- 如果没有在class象里找到,再到super_class查找;
- 如果找到message这个方法,执行它的实现IMP
- 如果找不到消息,则执行消息转发(message forwarding)
Method数据结构 runtime.h头文件中定义:
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
struct objc_method { SEL method_name; // 特殊的字符串,描述方法名, 可以通过关键字 @selector( ) 获取 char *method_types; IMP method_imp; }PS:消息转发分为两大阶段即动态添加方法解析(dynamic method resolution)和完整的消息转发机制(full forward mechanism)
runtime系统功能理解
runtime : 程序运行后,提供相关支持的代码叫做OC运行期环境(OC runtime),它提供了对象间传递消息的重要函数(比如objc_msgSend),并且包含创建类实例所用的全部逻辑(即创建实例对象的存储结构和空间,包括isa指向“类对象”的指针)
runtime系统是一个用C语言编写动态链接库,核心是消息分发。Runtime机制包括对象模型,消息传递和转发,方法实现机制和其他运行时方法,可以实现动态创建修改类对象和对象等功能,消息传递和转发,方法动态实现,Method Swizzling等功能。
##Objective-C程序生成目标文件中的运行时信息如何获取?
对于一个OC的.m程序文件,在Terminal输入命令:
gcc -framework Foundation main.m -o p1
当然,执行命令即: ./p1
然后,通过 otool 工具获取目标文件(包含头部、加载指令、各个segment)中运行时信息(有专门的segment保存)
otool -o p1
PS 我们可以通过获取运行时信息了解对象模型中元类对象和类对象结构等信息,如下所示,可以清晰看到类对象列表和元类映射关系,结构信息
p1:
Contents of (__DATA,__objc_classlist) section
0000000100001098 0x100001310
isa 0x1000012e8
superclass 0x0
cache 0x0
vtable 0x0
data 0x100001160 (struct class_ro_t *)
flags 0x0
instanceStart 8
instanceSize 13
reserved 0x0
ivarLayout 0x0
name 0x100000f60 AClass
baseMethods 0x1000010f8 (struct method_list_t *)
entsize 24
count 1
name 0x100000f6e printA
types 0x100000f91 v16@0:8
imp 0x100000d90
baseProtocols 0x0
ivars 0x100001118
entsize 32
count 2
offset 0x1000012c8 8
name 0x100000f75 a
type 0x100000f99 i
alignment 2
size 4
offset 0x1000012d0 12
name 0x100000f77 cA
type 0x100000f9b c
alignment 0
size 1
weakIvarLayout 0x0
baseProperties 0x0
Meta Class
isa 0x0
superclass 0x0
cache 0x0
vtable 0x0
data 0x1000010b0 (struct class_ro_t *)
flags 0x1 RO_META
instanceStart 40
instanceSize 40
reserved 0x0
ivarLayout 0x0
name 0x100000f60 AClass
baseMethods 0x0 (struct method_list_t *)
baseProtocols 0x0
ivars 0x0
weakIvarLayout 0x0
baseProperties 0x0
00000001000010a0 0x100001360
isa 0x100001338
superclass 0x100001310
cache 0x0
vtable 0x0
data 0x100001258 (struct class_ro_t *)
flags 0x0
instanceStart 16
instanceSize 21
reserved 0x0
ivarLayout 0x0
name 0x100000f67 BClass
baseMethods 0x1000011f0 (struct method_list_t *)
entsize 24
count 1
name 0x100000f7a printB
types 0x100000f91 v16@0:8
imp 0x100000dc0
baseProtocols 0x0
ivars 0x100001210
entsize 32
count 2
offset 0x1000012d8 16
name 0x100000f81 b
type 0x100000f99 i
alignment 2
size 4
offset 0x1000012e0 20
name 0x100000f83 cB
type 0x100000f9b c
alignment 0
size 1
weakIvarLayout 0x0
baseProperties 0x0
Meta Class
isa 0x0
superclass 0x1000012e8
cache 0x0
vtable 0x0
data 0x1000011a8 (struct class_ro_t *)
flags 0x1 RO_META
instanceStart 40
instanceSize 40
reserved 0x0
ivarLayout 0x0
name 0x100000f67 BClass
baseMethods 0x0 (struct method_list_t *)
baseProtocols 0x0
ivars 0x0
weakIvarLayout 0x0
baseProperties 0x0
Contents of (__DATA,__objc_classrefs) section
00000001000012b8 0x100001310
00000001000012c0 0x100001360
Contents of (__DATA,__objc_imageinfo) section
version 0
flags 0x0参考资源
Effective Objective-C 2.0
Objective-C的对象模型与运行时
深入理解Objective-C的Runtime机制
Objective-C的动态特性
