转载和积累系列 - HTTP application/x-www-form-urlencode和multipart/form-data
application/x-www-form-urlencode
我们在提交表单的时候,form表单参数中会有一个enctype的参数。enctype指定了HTTP请求的Content-Type。
默认情况下,HTML的form表单的enctype=application/x-www-form-urlencoded。
application/x-www-form-urlencoded是指表单的提交,并且将提交的数据进行urlencode。默认情况下,我们所有的表单提交都是通过这种默认的方式实现的。
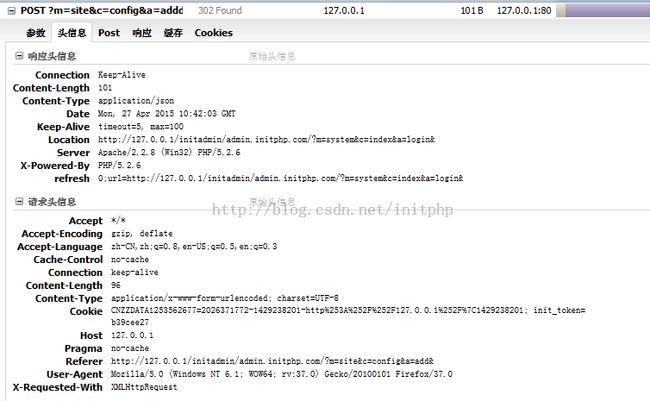
在火狐浏览器下,我们可以看一下提交数据的过程:
我们可以看到Content-type:
Content-Type application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8
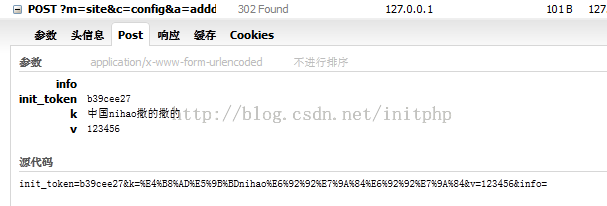
然后继续看一下原始请求数据,原始的请求数据被urlencode了。
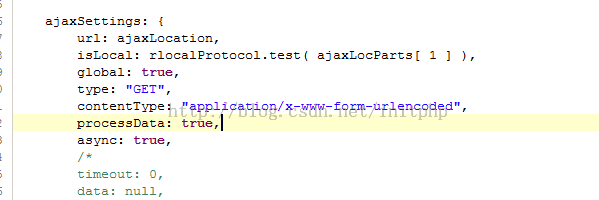
Ajax默认也是通过HTTP application/x-www-form-urlencoded提交数据。可以看下Jquery的源码:
multipart/form-data
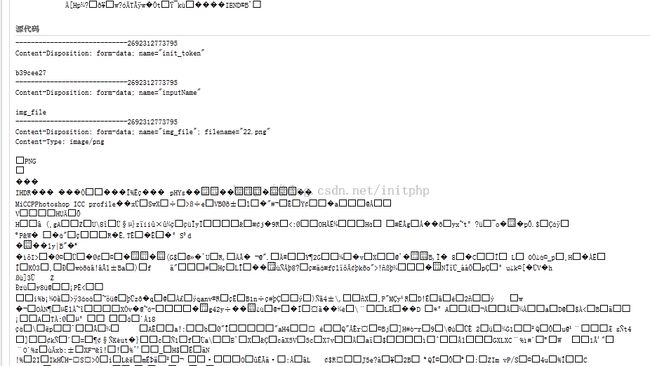
一般情况下,我们如果要在表单中上传文件,一般会将form的enctype参数设置为multipart/form-data。这种方式只支持POST的请求方式。
Contype-Type=multipart/form-data情况的时候,都会通过一个特殊的字符串来将原始POST数据进行分割。
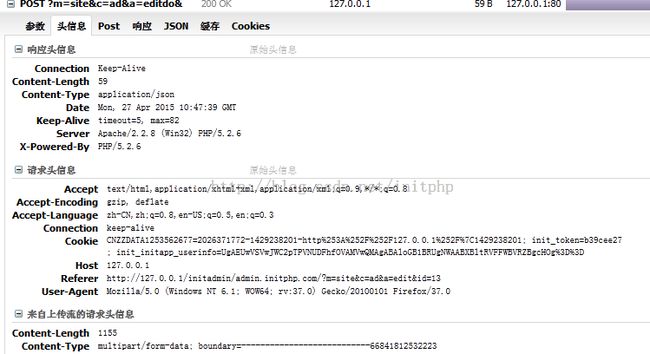
我们可以看到下面的请求中Content-type的类型:
Content-Type multipart/form-data; boundary=---------------------------66841812532223
其中boundary=---------------------------66841812532223,为分割符号。
其中数据块开始的分隔符 =={boundary} 会在前面加上“==”
数据块结束的分隔符 =={boundary}== 会在后面加上“==”
继续看下原始数据,我们可以清晰的看到,各种请求数据被boundary值进行了分割。
虽然这些知识点很早就知道了,但是知其然知其所以然可以让我们深入每一个技术细节。
application/json
有些时候,我们会直接提交Content-type是json数据格式的请求。
例如:
var data = {'title':'test', 'sub' : [1,2,3]};
$http.post(url, data).success(function(result) {
...
});请求:
POST http://www.example.com HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8
{"title":"test","sub":[1,2,3]}
这种情况下,请求的Content-Type是Json的数据格式,http body中的内容就是请求的json数据。
如果是php的话,需要通过 php://input来接收POST中的原始数据信息。
如果是Java,则需要下面的方式来读取HTTP 请求BODY中的数据
protected void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
try {
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
int size = request.getContentLength();
System.out.println(size);
InputStream is = request.getInputStream();
byte[] reqBodyBytes = readBytes(is, size);
String res = new String(reqBodyBytes);
System.out.println(res);
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.getOutputStream().write(res.getBytes("utf-8"));
response.flushBuffer();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
public static final byte[] readBytes(InputStream is, int contentLen) {
if (contentLen > 0) {
int readLen = 0;
int readLengthThisTime = 0;
byte[] message = new byte[contentLen];
try {
while (readLen != contentLen) {
readLengthThisTime = is.read(message, readLen, contentLen
- readLen);
if (readLengthThisTime == -1) {// Should not happen.
break;
}
readLen += readLengthThisTime;
}
return message;
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
// e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return new byte[] {};
}