poj 2318 TOYS
http://blog.csdn.net/qinmusiyan/article/details/8041576
TOYS
| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 7904 | Accepted: 3736 |
Description
Calculate the number of toys that land in each bin of a partitioned toy box.
Mom and dad have a problem - their child John never puts his toys away when he is finished playing with them. They gave John a rectangular box to put his toys in, but John is rebellious and obeys his parents by simply throwing his toys into the box. All the toys get mixed up, and it is impossible for John to find his favorite toys.
John's parents came up with the following idea. They put cardboard partitions into the box. Even if John keeps throwing his toys into the box, at least toys that get thrown into different bins stay separated. The following diagram shows a top view of an example toy box.
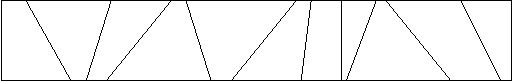
For this problem, you are asked to determine how many toys fall into each partition as John throws them into the toy box.
Mom and dad have a problem - their child John never puts his toys away when he is finished playing with them. They gave John a rectangular box to put his toys in, but John is rebellious and obeys his parents by simply throwing his toys into the box. All the toys get mixed up, and it is impossible for John to find his favorite toys.
John's parents came up with the following idea. They put cardboard partitions into the box. Even if John keeps throwing his toys into the box, at least toys that get thrown into different bins stay separated. The following diagram shows a top view of an example toy box.

For this problem, you are asked to determine how many toys fall into each partition as John throws them into the toy box.
Input
The input file contains one or more problems. The first line of a problem consists of six integers, n m x1 y1 x2 y2. The number of cardboard partitions is n (0 < n <= 5000) and the number of toys is m (0 < m <= 5000). The coordinates of the upper-left corner and the lower-right corner of the box are (x1,y1) and (x2,y2), respectively. The following n lines contain two integers per line, Ui Li, indicating that the ends of the i-th cardboard partition is at the coordinates (Ui,y1) and (Li,y2). You may assume that the cardboard partitions do not intersect each other and that they are specified in sorted order from left to right. The next m lines contain two integers per line, Xj Yj specifying where the j-th toy has landed in the box. The order of the toy locations is random. You may assume that no toy will land exactly on a cardboard partition or outside the boundary of the box. The input is terminated by a line consisting of a single 0.
Output
The output for each problem will be one line for each separate bin in the toy box. For each bin, print its bin number, followed by a colon and one space, followed by the number of toys thrown into that bin. Bins are numbered from 0 (the leftmost bin) to n (the rightmost bin). Separate the output of different problems by a single blank line.
Sample Input
5 6 0 10 60 0 3 1 4 3 6 8 10 10 15 30 1 5 2 1 2 8 5 5 40 10 7 9 4 10 0 10 100 0 20 20 40 40 60 60 80 80 5 10 15 10 25 10 35 10 45 10 55 10 65 10 75 10 85 10 95 10 0
Sample Output
0: 2 1: 1 2: 1 3: 1 4: 0 5: 1 0: 2 1: 2 2: 2 3: 2 4: 2
Hint
As the example illustrates, toys that fall on the boundary of the box are "in" the box.
Source
Rocky Mountain 2003
思路:判断点落在哪个区域
设直线方程 y=k*x+b ; 点P(x0,y0) ;
1) 当k
不存在(这里我将它的值设为0) 只要x0在直线的左边既满足
2) 当k<0 时,点P落在直线左边的条件是 y0<k*x0+b;
3) 当k>0 时, 点P落在直线的左边的条件是 y0>k*x0+b;
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<iostream>
- #include<algorithm>
- using namespace std;
- struct node
- {
- int x,y;
- double k,b;
- }box[5005];
- int sum[5005];
- int n,m,x1,y1,x2,y2,x,y;
- bool cmp(node a,node b)
- {
- return a.x<b.x;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int i,j;
- while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF&&n)
- {
- scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&m,&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
- for(i=0;i<n;i++)
- {
- scanf("%d%d",&box[i].x,&box[i].y);
- box[i].k=(y2-y1)*1.0/(box[i].y-box[i].x);
- box[i].b=y1-box[i].k*box[i].x;
- if(box[i].x==box[i].y) box[i].k=box[i].b=0;
- }
- memset(sum,0,sizeof(sum));
- sort(box,box+n,cmp);
- box[n].x=x2;box[n].y=y1;
- box[i].k=box[i].b=0;
- for(i=0;i<m;i++)
- {
- scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
- for(j=0;j<=n;j++)
- {
- if(box[j].k==0)
- {
- if(x<box[j].x) {sum[j]++;break;}
- }
- else
- {
- if(box[j].k<0) {if(y<box[j].k*x+box[j].b) { sum[j]++;break;}}
- else {if(y>box[j].k*x+box[j].b) {sum[j]++;break;}}
- }
- }
- }
- for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
- {
- printf("%d: %d\n",i,sum[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- return 0;
- }
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
struct Point
{
int x,y;
};
Point a[5010],b[5010];
int ans[5010];//存放每个区域内含有点的个数
int xmulti(Point p0,Point p1,Point p2)
{
return (p1.x - p0.x) * (p2.y - p0.y) - (p2.x - p0.x) * (p1.y - p0.y);
}
int main ()
{
int n,m;
Point p0;
while(scanf("%d",&n)&&n)
{
memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));
scanf("%d",&m);
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a[0].x,&a[0].y,&b[n+1].x,&b[n+1].y);
b[0].x = a[0].x;
b[0].y = b[n+1].y;
a[n+1].x = b[n+1].x;
a[n+1].y = a[0].y;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&b[i].x);
a[i].y = a[0].y;
b[i].y = b[0].y;
}
for(int i = 0;i < m;++i)
{
scanf("%d%d",&p0.x,&p0.y);
int l = 0,r = n + 1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = (l+r)/2;
if (xmulti(b[mid],p0,a[mid]) > 0)
l = mid+1;
else
r = mid;
// cout<<l<<' '<<r<<' '<<mid<<endl;
// getchar();
}
ans[l]++;
//cout<<l<<endl;
}
for(int i = 0;i <= n;++i)
printf("%d: %d\n",i,ans[i+1]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
http://blog.163.com/archer_nzy/blog/static/133382582201121410243778/
简单题,二分查找
#include
<
iostream
>
#include
<
cstdio
>
#include
<
cstdlib
>
#include
<
cstring
>
#include
<
algorithm
>
using
namespace
std;
#define
maxn 5005
struct
Line
{
int
u, d;
} line[maxn];
int
n, m, x1, x2, y1, y2;
int
toy[maxn];
bool
left(
int
x,
int
y, Line a)
{
if
(x
<
a.d
+
(y
-
y2)
*
(a.u
-
a.d)
*
1.0
/
(y1
-
y2))
return
true
;
return
false
;
}
int
binarysearch(
int
x,
int
y)
{
int
l
=
0
, r
=
n;
int
mid;
while
(l
<
r)
{
mid
=
(l
+
r)
/
2
;
if
(left(x, y, line[mid]))
r
=
mid;
else
l
=
mid
+
1
;
}
return
l;
}
int
main()
{
//
freopen("t.txt", "r", stdin);
while
(scanf(
"
%d
"
,
&
n), n
!=
0
)
{
memset(toy,
0
,
sizeof
(toy));
scanf(
"
%d%d%d%d%d
"
,
&
m,
&
x1,
&
y1,
&
x2,
&
y2);
for
(
int
i
=
0
; i
<
n; i
++
)
scanf(
"
%d%d
"
,
&
line[i].u,
&
line[i].d);
for
(
int
i
=
0
; i
<
m; i
++
)
{
int
x, y;
scanf(
"
%d%d
"
,
&
x,
&
y);
toy[binarysearch(x, y)]
++
;
}
for
(
int
i
=
0
; i
<=
n; i
++
)
printf(
"
%d: %d\n
"
, i, toy[i]);
printf(
"
\n
"
);
}
return
0
;
}
下面给出我仿写的代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#define maxn 5005
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int u,l;
}line[maxn];
int n,m,x1,x2,y1,y2;
int toy[maxn];
inline bool isLeft(int x,int y, node a)
{
if(x<a.l+(y-y2)*(a.u-a.l)*1.0/(y1-y2))
return true;
else
return false;
}
inline int binarySearch(int x,int y)
{
int l = 0 ,r = n;
int mid;
while(l<r)
{
mid = (l+r)/2;
if(isLeft(x,y,line[mid]))
r = mid;
else
l = mid+1;
}
return l;
}
int main()
{
int i,x,y;
while(scanf("%d",&n)==1)
{
memset(toy, 0, sizeof(toy));
if(n==0) break;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&m,&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&line[i].u,&line[i].l);
line[n].u = x2,line[n].l = x2;
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
toy[binarySearch(x,y)]++;
}
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d: %d\n",i,toy[i]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
172ms poj 上跑过
二分区间查找 其实最后的line【n】的数据有没有是无所谓的
另外这个二分查找属于区间查找的方法 另外不可能出现在边界上的原因 所以一旦小于mid r=mid 大于mid 的话 l =mid+1
另外其实这些线的代表是这样的 第0条线代表第一块区域 。。。。。。。。。
下面是我仿写的第一个人写的代码,不过进行了优化,进行了二分查找 然后将时间从近550ms缩短到 150ms
这个程序在书写的过程中应该注意的地方是斜率k还有截距要用double
在这个地方挂了很久 数学类问题 就是这样精度误差是十分可怕的
其实细细看来这两种算法的思想是一样的 ,都是通过判断这个点是否在中间值的左边进行二分查找。
然后最后找到点所在的区域
代码如下
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#define maxn 5005
using namespace std;
struct node
{
double k,b;
}line[maxn];
int toy[maxn];
int n,m,x1,x2,y1,y2,u,l,x,y;
bool isLeft(int x,int y,node a)
{
if(a.k==0)
{
if(x<a.b) return true;
else return false;
}
else if(a.k>0)
{
if(y>x*a.k+a.b) return true;
else return false;
}
else
{
if(y<x*a.k+a.b) return true;
else return false;
}
}
int binarySearch(int x,int y)
{
int l = 0,r = n;
int mid;
while(l<r)
{
mid = (l+r)/2;
if(isLeft(x,y,line[mid]))
r = mid;
else
l = mid+1;
}
return r;
}
int main()
{
//freopen("1.txt","r",stdin);
int i;
while(scanf("%d",&n)==1)
{
if(n==0) break;
memset(toy,0,sizeof(toy));
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&m,&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&u,&l);
if(u!=l)
line[i].k = (y1-y2)*1.0/(u-l),line[i].b = y1 - line[i].k*u;
else
line[i].b = u,line[i].k = 0;
}
//line[i].b =x2; line[i].k = 0;
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
toy[binarySearch(x,y)]++;
}
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d: %d\n",i,toy[i]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}