算法之美——排序算法总结
各种排序算法的简单比较
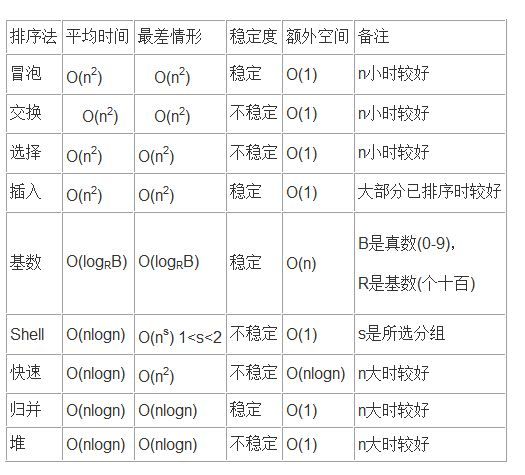
1.稳定性比较
插入排序、冒泡排序、二叉树排序、二路归并排序及其他线形排序是稳定的
选择排序(从代码看,有位置置换)、希尔排序、快速排序、堆排序是不稳定的
2.时间复杂性比较
插入排序、冒泡排序、选择排序的时间复杂性为O(n2)
其它非线形排序的时间复杂性为O(nlog2n)
线形排序的时间复杂性为O(n);
3.辅助空间的比较
线形排序、二路归并排序的辅助空间为O(n),其它排序的辅助空间为O(1);
4.其它比较
插入、冒泡排序的速度较慢,但参加排序的序列局部或整体有序时,这种排序能达到较快的速度。
反而在这种情况下,快速排序反而慢了。
当n较小时,对稳定性不作要求时宜用选择排序,对稳定性有要求时宜用插入或冒泡排序。
若待排序的记录的关键字在一个明显有限范围内时,且空间允许是用桶排序。
当n较大时,关键字元素比较随机,对稳定性没要求宜用快速排序。
当n较大时,关键字元素可能出现本身是有序的,对稳定性有要求时,空间允许的情况下。
宜用归并排序。
当n较大时,关键字元素可能出现本身是有序的,对稳定性没有要求时宜用堆排序。
*************************************************************************************
重温经典排序思想--常用排序全解
/*
=============================================================================
相关知识介绍(所有定义只为帮助读者理解相关概念,并非严格定义):
1、稳定排序和非稳定排序
简单地说就是所有相等的数经过某种排序方法后,仍能保持它们在排序之前的相对次序,我们就
说这种排序方法是稳定的。反之,就是非稳定的。
比如:一组数排序前是a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,其中a2=a4,经过某种排序后为a1,a2,a4,a3,a5,
则我们说这种排序是稳定的,因为a2排序前在a4的前面,排序后它还是在a4的前面。假如变成a1,a4,
a2,a3,a5就不是稳定的了。
2、内排序和外排序
在排序过程中,所有需要排序的数都在内存,并在内存中调整它们的存储顺序,称为内排序;
在排序过程中,只有部分数被调入内存,并借助内存调整数在外存中的存放顺序排序方法称为外排序。
3、算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度
所谓算法的时间复杂度,是指执行算法所需要的计算工作量。
一个算法的空间复杂度,一般是指执行这个算法所需要的内存空间。
时间复杂度与空间复杂度详细讲解
**********************************************************************
//快速排序的优化
**********************************************************************
代码:
sort.h:
#ifndef SORT_H
#define SORT_H
#include <vector>
#include "stdlib.h"
using namespace std;
namespace itlab
{
template<typename Type> void bubbleSort(vector<Type>&, int, int);
template<typename Type> void selectSort(vector<Type>&, int, int);
template<typename Type> void insertSort(vector<Type>&, int, int);
template<typename Type> void quickSort(vector<Type>&, int, int);
template<typename Type> void mergSort(vector<Type>&, int, int);
template<typename Type> void heapSort(vector<Type>&, int, int);
template<typename Type> const Type& median3(vector<Type>&, int, int);
template<typename Type> void merg(vector<Type>&, int, int, int, int);
template<typename Type> void filterDown(vector<Type>&, int, int);
#include "Sort_impl.h"
}
#endif
sort_impl.h
/**
* Bubble sort algorithm.
* "a" ----> array of Comparable items.
* "left" ----> the left-most index of the subarray.
* "right" ----> the right-most index of the subarray.
*/
template<typename Type>
void bubbleSort( vector<Type> &a, int left, int right )
{
for (int i=left; i<right; i++)
{
//若array有序,遍历一次,则sorted=true,直接跳出函数即可;
bool sorted = true;
for (int j=right; j>i; j--)
{
if (a[j] < a[j-1])
{
swap(a[j],a[j-1]);
sorted = false;
}
}
if (sorted)
{
return;
}
}
}
/**
* selection sort algorithm.
* "a" ----> array of Comparable items.
* "left" ----> the left-most index of the subarray.
* "right" ----> the right-most index of the subarray.
*/
template<typename Type>
void selectSort( vector<Type> &a, int left, int right )
{
for (int i=left; i<right; i++)
{
int minPos = i;
for (int j=i+1; j<right; j++)
{
if (a[j]<a[minPos])
{
minPos = j;
}
}
if (i!=minPos)
{
swap(a[i],a[minPos]);
}
}
}
/**
* Insertion sort algorithm.
* "a" ----> array of Comparable items.
* "left" ----> the left-most index of the subarray.
* "right" ----> the right-most index of the subarray.
*/
template<typename Type>
void insertSort( vector<Type> &a, int left, int right )
{
for (int i=left+1; i<=right; i++)//one insertion;
{
Type tmp = a[i];
int j;
// for (j=i-1; j>=left && a[j]>tmp; j--)// insert a[i];
// {
// a[j+1] = a[j];
// }
// a[j+1]=tmp;
for (j=i; j>left && a[j-1]>tmp; j--)
{
a[j] = a[j-1];
}
a[j] = tmp;
}
}
/**
* Internal quicksort method that makes recursive calls.
* Uses median-of-three partitioning and a cutoff of 20.
* "a" ----> array of Comparable items.
* "left" ----> the left-most index of the subarray.
* "right" ----> the right-most index of the subarray.
*/
template <typename Type>
void quickSort( vector<Type> &a, int left, int right )
{
if ( left+20 <= right)
{
Type pivot = median3(a, left, right);
//begin partitioning
int i = left, j = right-1;
for(;;)
{
while (a[++i] < pivot){ }
while (pivot < a[--j]){ }
if (i < j)
swap(a[i], a[j]);
else
break;
}
//Restore pivot
swap(a[i], a[right-1]);//restore pivot;pivot的位置已经确定!下一步只对除a[i]外的两个子序列排序。i指向的肯定是第一个大于pivot的值
//sort small elements
quickSort(a, left, i-1);
//sort large elements
quickSort(a, i+1, right);
}
else
insertSort(a,left,right);
}
/**
* Return median of left, center, and right.
* Order these and hide the pivot.
*/
template <typename Type>
const Type& median3( vector<Type> &a, int left, int right )
{
int center = (left + right) / 2;
//顺序不能错;
if (a[left] > a[center])
{
swap(a[left], a[center]);
}
if (a[left] > a[right])
{
swap(a[left], a[right]);
}
if (a[center] > a[right])
{
swap(a[center], a[right]);
}
swap( a[center], a[right-1] );///////////////////////////
return a[right-1];
}
/**
* Merg sort algorithm (nonrecursion).
* "a" ----> array of Comparable items.
* "left" ----> the left-most index of the subarray.
* "right" ----> the right-most index of the subarray.
*/
template <typename Type>
void mergSort( vector<Type> &a, int left, int right )
{
int left1, right1, left2, right2,
n = right - left + 1,
size = 1;
while( size < n )
{
left1 = left;
while( left1+size < n )
{
left2 = left1+size;
right1 = left2-1;
if( left2+size > n )
right2 = right;
else
right2 = left2+size-1;
merg( a, left1, right1, left2, right2 );
left1 = right2+1;
}
size *= 2;
}
}
/**
* Merg two subsequence to a bigger one.
* The first subsequence is a[left1] ... a[right1], and
* The second subsqeuence is a[left2] ... a[right2].
*/
template <typename Type>
void merg( vector<Type> &a, int left1, int right1, int left2, int right2 )
{
int k = 0,
i = left1,
j = left2,
n1 = right1-left1+1,
n2 = right2-left2+1;
Type *tmp = new Type[n1+n2];
//开始并排
while( i <= right1 && j <= right2 )
if( a[i] < a[j] )
tmp[k++] = a[i++];
else
tmp[k++] = a[j++];
//合并完成后,有个子序列还没排完
while( i <= right1 )
tmp[k++] = a[i++];
while( j <= right2 )
tmp[k++] = a[j++];
//重新放回序列
for( int i=0; i<n1; ++i )
a[left1++] = tmp[i];
for( int i=0; i<n2; ++i )
a[left2++] = tmp[n1+i];
delete []tmp;
}
/**
* Heap sort algorthm.
* "a" ----> array of Comparable items.
* "left" ----> the left-most index of the subarray.
* "right" ----> the right-most index of the subarray.
*/
template <typename Type>
void heapSort(vector<Type> &a, int left, int right)
{
int n = right-left+1;
vector<Type> tmp(n);
//assign value to tmp[]; sorting tmp[];
for ( int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
tmp[i] = a[left+i];
}
//从第一个拥有孩子节点的位置n/2,开始排序,
//从下向上,形成一个大根堆;
for (int i=n/2; i>=0; i--)
{
filterDown(tmp, i, n);
}
//每循环一次,把大根与末尾元素互换;
//然后从上到下排序一次,再次形成一个大根堆
for (int j=n-1; j>=0; j--)
{
swap(tmp[0], tmp[j]);
filterDown(tmp,0,j);
}
//assign sorted value to array
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
a[left+i] = tmp[i];
}
}
/**
* Percolate down the heap.
* "i" ----> the position from which to percolate down.
* "n" ----> the logical size of the binary heap.
*/
template <typename Type>
void filterDown( vector<Type> &a, int i, int n )//a为待排序列,i为某个排序父节点位置,n为待排序列元素个数;
{
int child;
Type tmp;
for (tmp=a[i]; 2*i+1<n; i=child)
{
child = 2*i+1;
if (child!=n-1 && a[child]<a[child+1])
{
child++;//找出孩子节点中最大的一个
}
if (tmp < a[child])
{
//a[i] = a[child];
swap(a[i],a[child]);//若父节点小于孩子节点,则互换
}
else
break;
}
}
sort.cpp
其中,C/C++生成随机数。
/*****************************************************************************
* sort_test.cpp
*
* Sorting algorithm testing.
*
*
*****************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include "sort.h"
#include <random>
using namespace std;
using namespace itlab;
#define random(x) (rand()%x)
const int SIZE = 10;
template <typename Type>
void printVector( const vector<Type> &a )
{
vector<int>::const_iterator itr = a.begin();
while( itr != a.end() )
cout << *itr++ << "\t";
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> a( SIZE );
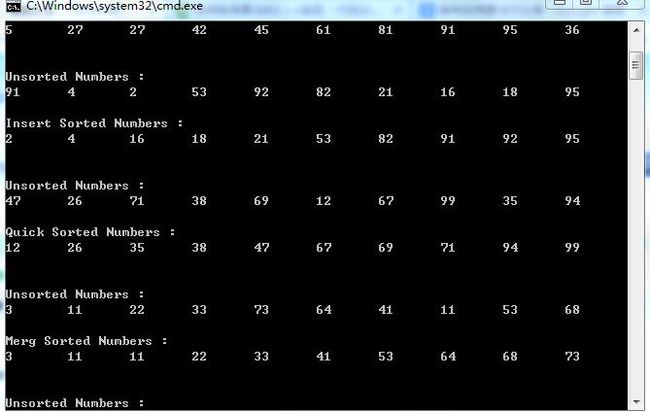
cout << "Unsorted Numbers : " << endl;
for( unsigned i=0; i<a.size(); ++i )
a[i] = random(100);
printVector( a );
cout << "Bubble Sorted Numbers : " << endl;
bubbleSort( a, 0, a.size()-1 );
printVector( a );
cout << endl;
cout << "Unsorted Numbers : " << endl;
for( unsigned i=0; i<a.size(); ++i )
a[i] = random(100);
printVector( a );
cout << "Select Sorted Numbers : " << endl;
selectSort( a, 0, a.size()-1 );
printVector( a );
cout << endl;
cout << "Unsorted Numbers : " << endl;
for( unsigned i=0; i<a.size(); ++i )
a[i] = random(100);
printVector( a );
cout << "Insert Sorted Numbers : " << endl;
insertSort( a, 0, a.size()-1 );
printVector( a );
cout << endl;
cout << "Unsorted Numbers : " << endl;
for( unsigned i=0; i<a.size(); ++i )
a[i] = random(100);
printVector( a );
cout << "Quick Sorted Numbers : " << endl;
quickSort( a, 0, a.size()-1 );
printVector( a );
cout << endl;
cout << "Unsorted Numbers : " << endl;
for( unsigned i=0; i<a.size(); ++i )
a[i] = random(100);
printVector( a );
cout << "Merg Sorted Numbers : " << endl;
mergSort( a, 0, a.size()-1 );
printVector( a );
cout << endl;
cout << "Unsorted Numbers : " << endl;
for( unsigned i=0; i<a.size(); ++i )
a[i] = random(100);
printVector( a );
cout << "Heap Sorted Numbers : " << endl;
heapSort( a, 0, a.size()-1 );
printVector( a );
cout << endl;
return 0;
}