【Android 开发】:Android五种布局的使用方法
在Android布局中,有五种常用的布局,下面我们就来学习一下这几种布局的使用方式
1) 线性布局:LinearLayout
2) 帧布局: FrameLayout
3) 相对布局: RelativeLayout
4) 表格布局: TableLayout
5) 绝对布局: AbsoluteLayout
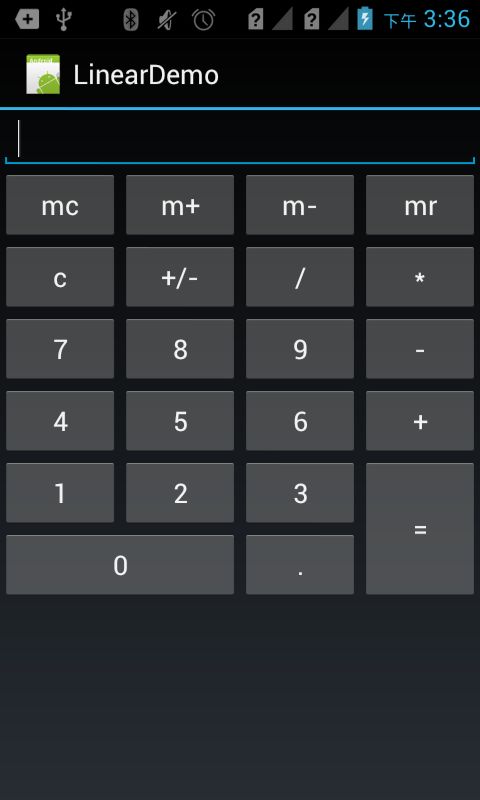
1. 线性布局
android:layout_width和android_layout_height属性说明
属性 描述 wrap_content
填满父控件的空白 fill_parent
match_parent表示大小刚好足够显示当前控件里的内容Android中fill_parent和match_parent是一样的。
在Android2.2中启动match_parent,不用fill_parent
android:layout_weight权重的描述:
layout_weight 用于给一个线性布局中的诸多视图的重要度赋值。 所有的视图都有一个layout_weight值,默认为零,意思是需要显示多大的视图就占据多大的屏幕空间。若赋一个高于零的值,则将父视图中的可用空间分割,分割大小具体取决于每一个视图的layout_weight 值以及该值在当前屏幕布局的整体 layout_weight值和在其它视图屏幕布局的layout_weight值中所占的比率而定。
[注意]:在进行权重的设计时,如果两个控件的权重比例不是一样的,要留意android:layout_width 属性,如果设计成:"wrap_content" 当文本字体很多的时候,权重就无效了,所以如果要防止这种情况发生,建议直接设置成:android:layout_width="0dp"
程序Demo:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <EditText android:id="@+id/msg" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="mc" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="m+" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="m-" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="mr" /> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="c" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="+/-" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="/" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="*" /> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="7" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="8" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="9" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="-" /> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="4" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="5" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="6" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="+" /> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <LinearLayout android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="3" android:orientation="vertical" > <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="1" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="2" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="3" /> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="2" android:text="0" /> <Button android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="." /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="=" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
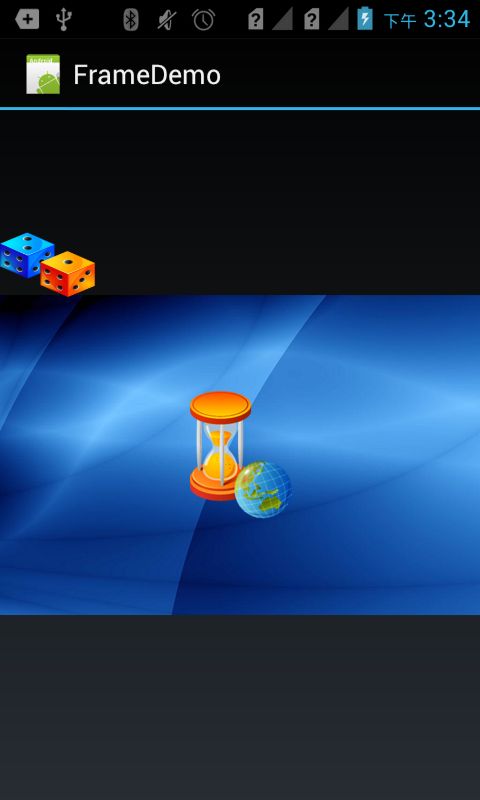
2. 帧布局
帧布局是最简单的布局方式、所有添加到这个布局中的视图都是以层叠的方式显示。第一个添加到框架布局中的视图显示在最底层,最后一个被放在最顶层,上一层的视图会覆盖下一层的视图,因此框架布局类似堆栈布局。
属性值 描述 top 将视图放到屏幕的顶端 Buttom 将视图放到屏幕的底端 Left 将视图放在屏幕的左侧 Right 将视图放在屏幕的右侧 Center_vertical 将视图按照垂直方向居中显示 horizontal_vertical 将视图按照水平方向居中显示 程序Demo:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <ImageView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:background="@drawable/bre" /> <ImageView android:layout_width="63dp" android:layout_height="46dp" android:layout_marginTop="80dp" android:background="@drawable/one" /> <ImageView android:layout_width="85dp" android:layout_height="85dp" android:layout_marginTop="80dp" android:background="@drawable/two" android:layout_gravity="center" android:layout_marginBottom="80dp" /> </FrameLayout>

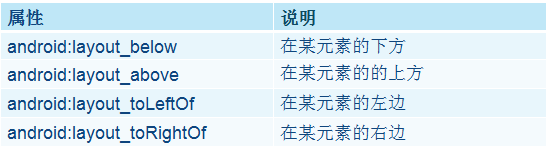
3. 相对布局
RelativeLayout可以设置某一个视图相对于其他视图的位置,这些位置可以包括上下左右等
程序Demo:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:gravity="center" > <Button android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Button" android:textSize="16dp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/button" android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button" android:text="Button1" android:textSize="16dp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/button1" android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/button1" android:text="Button2" android:textSize="16dp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_above="@id/button1" android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button1" android:text="Button3" android:textSize="16dp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/button1" android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button1" android:text="Button4" android:textSize="16dp" /> </RelativeLayout>
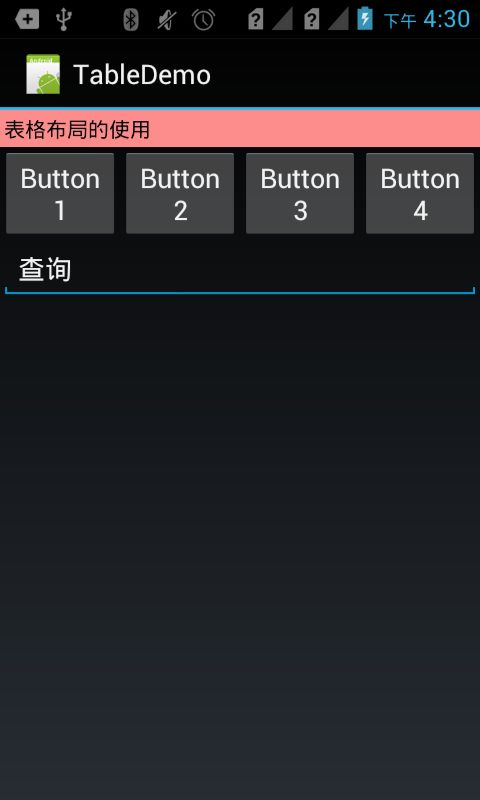
4. 表格布局
在TableLayout布局中,一个列的宽度由该列中最宽的那个单元格指定,而表格的宽度是由父容器指定的。
在TableLayout中,可以为列设置三种属性:
1) Shrinkable: 如果一个列被标识为Shrinkable,则该列的宽度可以进行收缩,以使表格能够适应其父容器的大小。
2) Stretchable:如果一个列被标识为Stretchable,则该列的宽度可以进行拉伸,以使填满表格中的空闲空间。
3) Collapsed: 如果一个列被标识为Collapsed,则该列会被隐藏
注意:一个列可以同时具有Shrinkable属性和Stretchable属性,在这种情况下,该列的宽度将任意拉伸或收缩以适应父容器
TableLayout继承自LinearLayout类,除了继承来自父类的属性和方法,TableLayout类中还包含表格布局所特有的属性和方法,如下表:

注意:TableLayout中所谓的列序号是从0开始计算的。setShrinkAllColumns和setStretchAllColumns实现的功能是将表格中的所有列设置为Shrinkable或Stretchable。
程序Demo:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <TableLayout android:id="@+id/tablelayout1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#FFFFFF" android:stretchColumns="0" > <TableRow android:id="@+id/tablerow1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > <TextView android:id="@+id/textview1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:background="#fd8d8d" android:padding="4px" android:text="表格布局的使用" android:textColor="#000000" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout> <TableLayout android:id="@+id/tablelayout2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:stretchColumns="0,1,2,3" > <TableRow android:id="@+id/tablerow2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="Button1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="Button2" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="Button3" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="Button4" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout> <TableLayout android:id="@+id/tablelayout3" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:stretchColumns="0" > <TableRow android:id="@+id/tablerow3" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > <EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:text="查询" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout> </LinearLayout>