Trie树的实现
一、定义:
Trie,又称字典树,是一种用于快速检索的二十六叉树结构。典型的空间换时间
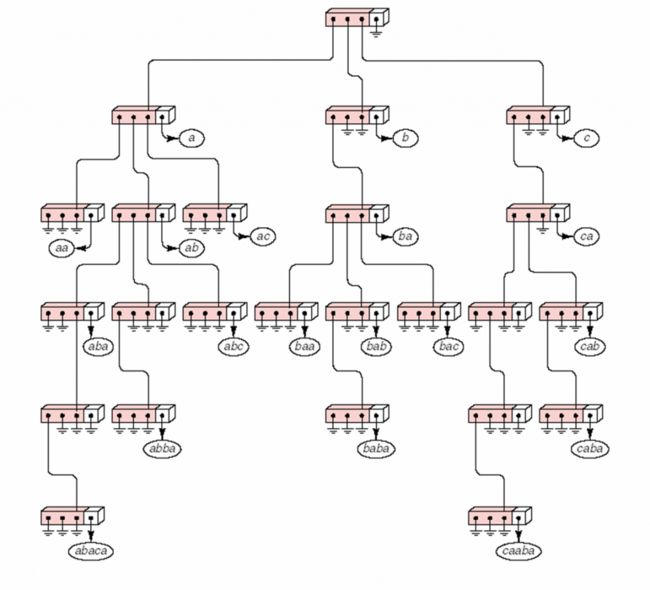
二、结构图:
三、原理:
Trie把要查找的关键词看作一个字符序列,并根据构成关键词字符的先后顺序检索树结构;
特别地:和二叉查找树不同,在Trie树中,每个结点上并非存储一个元素。
四、性质:
0、利用串的公共前缀,节约内存
2、根节点不包含字符,除根节点外的每一个节点都只代表一个字母,这里不是包含。
3、从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。
4、每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符都不相同。
五、效率分析
0、当存储大量字符串时,Trie耗费的空间较少。因为键值并非显式存储的,而是与其他键值共享子串。
1、查询快。在trie树中查找一个关键字的时间和树中包含的结点数无关,而取决于组成关键字的字符数。对于长度为m的键值,最坏情况下只需花费O(m)的时间(对比:二叉查找树的查找时间和树中的结点数有关O(log2n)。)
2、如果要查找的关键字可以分解成字符序列且不是很长,利用trie树查找速度优于二叉查找树。
3、若关键字长度最大是5,则利用trie树,利用5次比较可以从265=11881376个可能的关键字中检索出指定的关键字。而利用二叉查找树至少要进行log2265=23.5次比较。
六、应用:用于字符串的统计与排序,经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。
1、字典树在串的快速检索中的应用。
给出N个单词组成的熟词表,以及一篇全用小写英文书写的文章,请你按最早出现的顺序写出所有不在熟词表中的生词。在这道题中,我们可以用字典树,先把熟词建一棵树,然后读入文章进行比较,这种方法效率是比较高的。
2、字典树在“串”排序方面的应用
给定N个互不相同的仅由一个单词构成的英文名,让你将他们按字典序从小到大输出用字典树进行排序,采用数组的方式创建字典树,这棵树的每个结点的所有儿子很显然地按照其字母大小排序。对这棵树进行先序遍历即可。
3.、字典树在最长公共前缀问题的应用
对所有串建立字典树,对于两个串的最长公共前缀的长度即他们所在的结点的公共祖先个数,于是,问题就转化为最近公共祖先问题。
代码
#ifndef _TRIE_
#define _TRIE_
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
const int MaxBranchNum = 26;//如果区分大小写,可以扩展到52
/*定义trie树结点*/
class TrieNode
{
public:
char* word; //节点表示的单词
int count; //单词出现的次数
TrieNode* nextBranch[MaxBranchNum];//指向26个字符节点的指针
public:
TrieNode() : word(NULL),count(0)
{
memset(nextBranch,NULL,sizeof(TrieNode*) * MaxBranchNum);
}
};
/*定义类Trie*/
class Trie
{
public:
Trie();
~Trie();
void Insert(const char* str);//插入字符串str
bool Search(const char* str,int& count);//查找字符串str,并返回出现的次数
bool Remove(const char* str);//删除字符串str
void PrintALL();//打印trie树中所有的结点
void PrintPre(const char* str);//打印以str为前缀的单词
private:
TrieNode* pRoot;
private:
void Destory(TrieNode* pRoot);
void Print(TrieNode* pRoot);
};
#endif //_TRIE_
Trie::Trie()
{
pRoot = new TrieNode();//注意字典树的根不存放字符
}
Trie::~Trie()
{
Destory(pRoot);
}
/*插入一个单词*/
void Trie::Insert(const char* str)
{
assert(NULL != str);
int index;
TrieNode* pLoc = pRoot;
for (int i = 0;str[i];i++)
{
index = str[i] - 'a';//如果区分大小写,可以扩展
if(index < 0 || index > MaxBranchNum)//不执行插入
{
return;
}
if (NULL == pLoc->nextBranch[index])//该单词的前缀不存在,要生成该结点
{
pLoc->nextBranch[index] = new TrieNode();
}
pLoc = pLoc->nextBranch[index];
}
if (NULL != pLoc->word)//单词已经出现过
{
pLoc->count++;
return;
}
else //单词没有出现过,应该插入单词
{
pLoc->count++;
pLoc->word = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
assert(NULL != pLoc->word);
strcpy(pLoc->word,str);
}
}
/*查找一个单词,如果存在该单词,则返回其出现次数*/
bool Trie::Search(const char* str,int& count)
{
assert(str != NULL);
int i = 0;
int index = -1;;
TrieNode* pLoc = pRoot;
while(pLoc && *str)
{
index = *str - 'a';//如果区分大小写,可以扩展
if(index < 0 || index > MaxBranchNum)//不是一个单词,不执行插入
{
return false;
}
pLoc = pLoc->nextBranch[index];
str++;
}
if (pLoc && pLoc->word)//条件成立,找到该单词
{
count = pLoc->count;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Trie::Remove(const char* str)
{
assert(NULL != str);
int index = -1;;
TrieNode* pLoc = pRoot;
while(pLoc && *str)
{
index = *str - 'a';//如果区分大小写,可以扩展
if(index < 0 || index > MaxBranchNum)//不是一个单词,不执行插入
{
return false;
}
pLoc = pLoc->nextBranch[index];
str++;
}
if (pLoc && pLoc-> word)//条件成立,找到该单词
{
delete[] pLoc->word;
pLoc->word = NULL;
return true;
}
return false;
}
void Trie::PrintALL()
{
Print(pRoot);
}
void Trie::PrintPre(const char* str)
{
assert(str != NULL);
int i = 0;
int index = -1;;
TrieNode* pLoc = pRoot;
while(pLoc && *str)
{
index = *str - 'a';//如果区分大小写,可以扩展
if(index < 0 || index > MaxBranchNum)//不是一个单词,不执行插入
{
return;
}
pLoc = pLoc->nextBranch[index];
str++;
}
if (pLoc)//条件成立,找到该单词
{
Print(pLoc);
}
}
/*按照字典顺序输出以pRoot为根的所有的单词*/
void Trie::Print(TrieNode* pRoot)
{
if (NULL == pRoot)
{
return;
}
//输出单词
if (NULL != pRoot->word)
{
cout<<pRoot->word<<" "<<pRoot->count<<endl;
}
//递归处理分支
for (int i = 0;i < MaxBranchNum;i++)
{
Print(pRoot->nextBranch[i]);
}
}
/*销毁trie树*/
void Trie::Destory(TrieNode* pRoot)
{
if (NULL == pRoot)
{
return;
}
for (int i = 0;i < MaxBranchNum;i++)
{
Destory(pRoot->nextBranch[i]);
}
//销毁单词占得空间
if (NULL != pRoot->word)
{
delete []pRoot->word;
pRoot->word = NULL;
}
delete pRoot;//销毁结点
pRoot = NULL;
}
int main()
{
Trie t;
string str;
int count = -1;
ifstream in("word.txt");
//把单词输入字典树
while(in >> str)
{
transform(str.begin(),str.end(),str.begin(),tolower);//大写变小写
t.Insert(str.c_str());
}
//查找
bool isFind = t.Search("the",count);
if (isFind)
{
cout<<"存在the,出现次数:"<<count<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"不存在the!"<<endl;
}
//输出
t.PrintALL();
//删除
bool isDel = t.Remove("the");
if (isDel)
{
cout<<"删除成功!"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"删除失败!"<<endl;
}
//输出以w开头的单词
t.PrintPre("w");
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
}