DexClassLoader和PathClassLoader类加载机制
0x00
在DexClassLoader和PathClassLoader加载Dex流程一文中,我们分析了dex文件如何形成了DexFile结构体。本文中讲解类加载机制,实际上就是生成ClassObject对象。
我们以DexClassLoader为例,讲解类加载机制,PathClassLoader是一样的。
我们在加载类时通常会调用loadClass,那么我们就从loadClass来开始分析。
0x01
DexClassLoader类没有loadClass方法,所以调用的是父类ClassLoader类的loadClass方法,ClassLoader类的loadClass方法位于libcore\luni\src\main\java\java\lang\ClassLoader.java中。
protected Class<?> loadClass(String className, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> clazz = findLoadedClass(className);
if (clazz == null) {
try {
clazz = parent.loadClass(className, false);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// Don't want to see this.
}
if (clazz == null) {
clazz = findClass(className);
}
}
return clazz;
} DexClassLoader复写了父类ClassLoader的findClass方法,所以调用子类DexClassLoader类的方法findClass,代码位于libcore\dalvik\src\main\java\dalvik\system\DexClassLoader.java。
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
if (VERBOSE_DEBUG)
System.out.println("DexClassLoader " + this
+ ": findClass '" + name + "'");
int length = mFiles.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (VERBOSE_DEBUG)
System.out.println(" Now searching: " + mFiles[i].getPath());
if (mDexs[i] != null) {
String slashName = name.replace('.', '/');
Class clazz = mDexs[i].loadClass(slashName, this);
if (clazz != null) {
if (VERBOSE_DEBUG)
System.out.println(" found");
return clazz;
}
}
}
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name + " in loader " + this);
} 这里调用的是DexFile类的loadClass方法,代码位于libcore\dalvik\src\main\java\dalvik\system\DexFile.java。
public Class loadClass(String name, ClassLoader loader) {
String slashName = name.replace('.', '/');
return loadClassBinaryName(slashName, loader);
}
public Class loadClassBinaryName(String name, ClassLoader loader) {
return defineClass(name, loader, mCookie,
null);
//new ProtectionDomain(name) /*DEBUG ONLY*/);
} defineClass对应的是JNI方法,如下:
native private static Class defineClass(String name, ClassLoader loader,
int cookie, ProtectionDomain pd); 还记得
在 DexClassLoader和PathClassLoade r加载Dex流程一文中,openDexFile也是JNI方法,
对应的native方法位于dalvik\vm\native\dalvik_system_DexFile.c。
const DalvikNativeMethod dvm_dalvik_system_DexFile[] = {
{ "openDexFile", "(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;I)I",
Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_openDexFile },
{ "closeDexFile", "(I)V",
Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_closeDexFile },
{ "defineClass", "(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/ClassLoader;ILjava/security/ProtectionDomain;)Ljava/lang/Class;",
Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_defineClass },
{ "getClassNameList", "(I)[Ljava/lang/String;",
Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_getClassNameList },
{ "isDexOptNeeded", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Z",
Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_isDexOptNeeded },
{ NULL, NULL, NULL },
};
defineClass对应的是Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_defineClass方法。注意defineClass函数传递进来的参数有一个是mCookie,就是在DexClassLoader和PathClassLoader加载Dex流程一文中,openDexFile生成的,利用这个mCookie可以在native层找到openDexFile生成的DexFile结构体。
0x02
Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_defineClass代码位于dalvik\vm\native\dalvik_system_DexFile.c。
static void Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_defineClass(const u4* args,
JValue* pResult)
{
StringObject* nameObj = (StringObject*) args[0];
Object* loader = (Object*) args[1];
int cookie = args[2];
Object* pd = (Object*) args[3];
ClassObject* clazz = NULL;
DexOrJar* pDexOrJar = (DexOrJar*) cookie;
DvmDex* pDvmDex;
char* name;
char* descriptor;
name = dvmCreateCstrFromString(nameObj);
descriptor = dvmDotToDescriptor(name);
LOGV("--- Explicit class load '%s' 0x%08x\n", descriptor, cookie);
free(name);
if (!validateCookie(cookie))
RETURN_VOID();
if (pDexOrJar->isDex)
pDvmDex = dvmGetRawDexFileDex(pDexOrJar->pRawDexFile);
else
pDvmDex = dvmGetJarFileDex(pDexOrJar->pJarFile);
/* once we load something, we can't unmap the storage */
pDexOrJar->okayToFree = false;
clazz = dvmDefineClass(pDvmDex, descriptor, loader);
......
......
free(descriptor);
RETURN_PTR(clazz);
} 首先通过cookie找到DexOrJar结构体pDexOrJar,然后根据pDexOrJar找到DvmDex结构体pDvmDex。
下面我们来分析核心函数dvmDefineClass,这个用来生成ClassObject。dvmDefineClass,findClassNoInit 方法都位于dalvik\vm\oo\Class.c。
ClassObject* dvmDefineClass(DvmDex* pDvmDex, const char* descriptor,
Object* classLoader)
{
assert(pDvmDex != NULL);
return findClassNoInit(descriptor, classLoader, pDvmDex);
}
static ClassObject* findClassNoInit(const char* descriptor, Object* loader,
DvmDex* pDvmDex)
{
Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf();
ClassObject* clazz;
bool profilerNotified = false;
......
clazz = dvmLookupClass(descriptor, loader, true);
if (clazz == NULL) {
const DexClassDef* pClassDef;
......
if (pDvmDex == NULL) {
assert(loader == NULL); /* shouldn't be here otherwise */
pDvmDex = searchBootPathForClass(descriptor, &pClassDef);
} else {
pClassDef = dexFindClass(pDvmDex->pDexFile, descriptor);
}
......
/* found a match, try to load it */
clazz = loadClassFromDex(pDvmDex, pClassDef, loader);
......
if (!dvmAddClassToHash(clazz)) {
......
}
......
}
return clazz;
} 首先调用dvmLookupClass方法,根据目标类的描述符descriptor在系统已加载类中进行查找,如果已对其加载,则返回目标类的ClassObject对象;否则,将对目标类进行加载。
我们假设没有对其加载过,然后调用dexFindClass方法找到DexClassDef结构体。我们首先来看下DexClassDef结构体,代码位于dalvik\vm\oo\Class.c。
typedef struct DexClassDef {
u4 classIdx; /* index into typeIds for this class */
u4 accessFlags;
u4 superclassIdx; /* index into typeIds for superclass */
u4 interfacesOff; /* file offset to DexTypeList */
u4 sourceFileIdx; /* index into stringIds for source file name */
u4 annotationsOff; /* file offset to annotations_directory_item */
u4 classDataOff; /* file offset to class_data_item */
u4 staticValuesOff; /* file offset to DexEncodedArray */
} DexClassDef; 为了方便理解以后的代码,我这里先附上一张图。DexClassDef就是图中最左边的部分class_def_item。
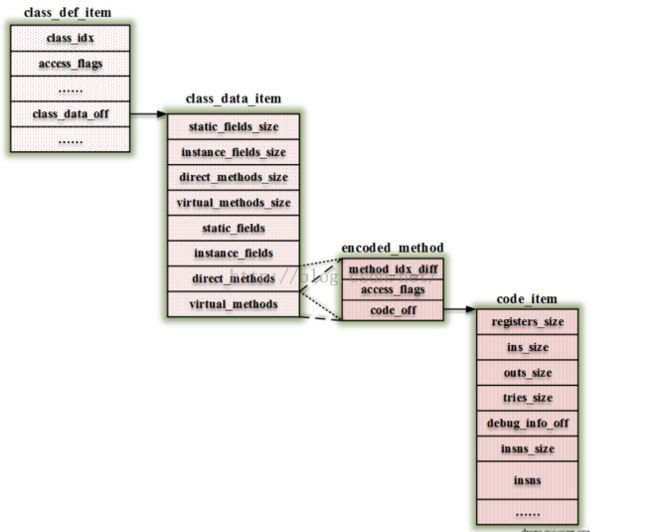
dexFindClass方法也位于dalvik\vm\oo\Class.c。
const DexClassDef* dexFindClass(const DexFile* pDexFile,
const char* descriptor)
{
const DexClassLookup* pLookup = pDexFile->pClassLookup;
u4 hash;
int idx, mask;
hash = classDescriptorHash(descriptor);
mask = pLookup->numEntries - 1;
idx = hash & mask;
/*
* Search until we find a matching entry or an empty slot.
*/
while (true) {
int offset;
offset = pLookup->table[idx].classDescriptorOffset;
if (offset == 0)
return NULL;
if (pLookup->table[idx].classDescriptorHash == hash) {
const char* str;
str = (const char*) (pDexFile->baseAddr + offset);
if (strcmp(str, descriptor) == 0) {
return (const DexClassDef*)
(pDexFile->baseAddr + pLookup->table[idx].classDefOffset);
}
}
idx = (idx + 1) & mask;
}
} 最后返回值的地方解释下,pDexFile->baseAddr指向dex文件头部,后面加上的是
DexClassDef结构体距离dex文件头部的偏移。
返回到findClassNoInit,继续执行loadClassFromDex方法,这是真正生成ClassObject对象的地方。代码位于dalvik\vm\oo\Class.c。
static ClassObject* loadClassFromDex(DvmDex* pDvmDex,
const DexClassDef* pClassDef, Object* classLoader)
{
ClassObject* result;
DexClassDataHeader header;
const u1* pEncodedData;
const DexFile* pDexFile;
assert((pDvmDex != NULL) && (pClassDef != NULL));
pDexFile = pDvmDex->pDexFile;
if (gDvm.verboseClass) {
LOGV("CLASS: loading '%s'...\n",
dexGetClassDescriptor(pDexFile, pClassDef));
}
pEncodedData = dexGetClassData(pDexFile, pClassDef);
if (pEncodedData != NULL) {
dexReadClassDataHeader(&pEncodedData, &header);
} else {
// Provide an all-zeroes header for the rest of the loading.
memset(&header, 0, sizeof(header));
}
result = loadClassFromDex0(pDvmDex, pClassDef, &header, pEncodedData,
classLoader);
if (gDvm.verboseClass && (result != NULL)) {
LOGI("[Loaded %s from DEX %p (cl=%p)]\n",
result->descriptor, pDvmDex, classLoader);
}
return result;
} dexGetClassData方法用来获取上图中的第二部分class_data_item。代码位于dalvik\libdex\DexFile.h。
DEX_INLINE const u1* dexGetClassData(const DexFile* pDexFile,
const DexClassDef* pClassDef)
{
if (pClassDef->classDataOff == 0)
return NULL;
return (const u1*) (pDexFile->baseAddr + pClassDef->classDataOff);
} loadClassFromDex0用于生成最终的ClassObject对象。
代码位于
dalvik\libdex\
DexFile.h。
static ClassObject* loadClassFromDex0(DvmDex* pDvmDex,
const DexClassDef* pClassDef, const DexClassDataHeader* pHeader,
const u1* pEncodedData, Object* classLoader)
{
ClassObject* newClass = NULL;
const DexFile* pDexFile;
const char* descriptor;
int i;
pDexFile = pDvmDex->pDexFile;
descriptor = dexGetClassDescriptor(pDexFile, pClassDef);
/*
* Make sure the aren't any "bonus" flags set, since we use them for
* runtime state.
*/
if ((pClassDef->accessFlags & ~EXPECTED_FILE_FLAGS) != 0) {
LOGW("Invalid file flags in class %s: %04x\n",
descriptor, pClassDef->accessFlags);
return NULL;
}
/*
* Allocate storage for the class object on the GC heap, so that other
* objects can have references to it. We bypass the usual mechanism
* (allocObject), because we don't have all the bits and pieces yet.
*
* Note that we assume that java.lang.Class does not override
* finalize().
*/
/* TODO: Can there be fewer special checks in the usual path? */
assert(descriptor != NULL);
if (classLoader == NULL &&
strcmp(descriptor, "Ljava/lang/Class;") == 0) {
assert(gDvm.classJavaLangClass != NULL);
newClass = gDvm.classJavaLangClass;
} else {
size_t size = classObjectSize(pHeader->staticFieldsSize);
newClass = (ClassObject*) dvmMalloc(size, ALLOC_DEFAULT);
}
if (newClass == NULL)
return NULL;
DVM_OBJECT_INIT(&newClass->obj, gDvm.classJavaLangClass);
dvmSetClassSerialNumber(newClass);
newClass->descriptor = descriptor;
assert(newClass->descriptorAlloc == NULL);
newClass->accessFlags = pClassDef->accessFlags;
dvmSetFieldObject((Object *)newClass,
offsetof(ClassObject, classLoader),
(Object *)classLoader);
newClass->pDvmDex = pDvmDex;
newClass->primitiveType = PRIM_NOT;
newClass->status = CLASS_IDX;
/*
* Stuff the superclass index into the object pointer field. The linker
* pulls it out and replaces it with a resolved ClassObject pointer.
* I'm doing it this way (rather than having a dedicated superclassIdx
* field) to save a few bytes of overhead per class.
*
* newClass->super is not traversed or freed by dvmFreeClassInnards, so
* this is safe.
*/
assert(sizeof(u4) == sizeof(ClassObject*)); /* 32-bit check */
newClass->super = (ClassObject*) pClassDef->superclassIdx;
/*
* Stuff class reference indices into the pointer fields.
*
* The elements of newClass->interfaces are not traversed or freed by
* dvmFreeClassInnards, so this is GC-safe.
*/
const DexTypeList* pInterfacesList;
pInterfacesList = dexGetInterfacesList(pDexFile, pClassDef);
if (pInterfacesList != NULL) {
newClass->interfaceCount = pInterfacesList->size;
newClass->interfaces = (ClassObject**) dvmLinearAlloc(classLoader,
newClass->interfaceCount * sizeof(ClassObject*));
for (i = 0; i < newClass->interfaceCount; i++) {
const DexTypeItem* pType = dexGetTypeItem(pInterfacesList, i);
newClass->interfaces[i] = (ClassObject*)(u4) pType->typeIdx;
}
dvmLinearReadOnly(classLoader, newClass->interfaces);
}
/* load field definitions */
/*
* Over-allocate the class object and append static field info
* onto the end. It's fixed-size and known at alloc time. This
* seems to increase zygote sharing. Heap compaction will have to
* be careful if it ever tries to move ClassObject instances,
* because we pass Field pointers around internally. But at least
* now these Field pointers are in the object heap.
*/
if (pHeader->staticFieldsSize != 0) {
/* static fields stay on system heap; field data isn't "write once" */
int count = (int) pHeader->staticFieldsSize;
u4 lastIndex = 0;
DexField field;
newClass->sfieldCount = count;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
dexReadClassDataField(&pEncodedData, &field, &lastIndex);
loadSFieldFromDex(newClass, &field, &newClass->sfields[i]);
}
}
if (pHeader->instanceFieldsSize != 0) {
int count = (int) pHeader->instanceFieldsSize;
u4 lastIndex = 0;
DexField field;
newClass->ifieldCount = count;
newClass->ifields = (InstField*) dvmLinearAlloc(classLoader,
count * sizeof(InstField));
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
dexReadClassDataField(&pEncodedData, &field, &lastIndex);
loadIFieldFromDex(newClass, &field, &newClass->ifields[i]);
}
dvmLinearReadOnly(classLoader, newClass->ifields);
}
/*
* Load method definitions. We do this in two batches, direct then
* virtual.
*
* If register maps have already been generated for this class, and
* precise GC is enabled, we pull out pointers to them. We know that
* they were streamed to the DEX file in the same order in which the
* methods appear.
*
* If the class wasn't pre-verified, the maps will be generated when
* the class is verified during class initialization.
*/
u4 classDefIdx = dexGetIndexForClassDef(pDexFile, pClassDef);
const void* classMapData;
u4 numMethods;
if (gDvm.preciseGc) {
classMapData =
dvmRegisterMapGetClassData(pDexFile, classDefIdx, &numMethods);
/* sanity check */
if (classMapData != NULL &&
pHeader->directMethodsSize + pHeader->virtualMethodsSize != numMethods)
{
LOGE("ERROR: in %s, direct=%d virtual=%d, maps have %d\n",
newClass->descriptor, pHeader->directMethodsSize,
pHeader->virtualMethodsSize, numMethods);
assert(false);
classMapData = NULL; /* abandon */
}
} else {
classMapData = NULL;
}
if (pHeader->directMethodsSize != 0) {
int count = (int) pHeader->directMethodsSize;
u4 lastIndex = 0;
DexMethod method;
newClass->directMethodCount = count;
newClass->directMethods = (Method*) dvmLinearAlloc(classLoader,
count * sizeof(Method));
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
dexReadClassDataMethod(&pEncodedData, &method, &lastIndex);
loadMethodFromDex(newClass, &method, &newClass->directMethods[i]);
if (classMapData != NULL) {
const RegisterMap* pMap = dvmRegisterMapGetNext(&classMapData);
if (dvmRegisterMapGetFormat(pMap) != kRegMapFormatNone) {
newClass->directMethods[i].registerMap = pMap;
/* TODO: add rigorous checks */
assert((newClass->directMethods[i].registersSize+7) / 8 ==
newClass->directMethods[i].registerMap->regWidth);
}
}
}
dvmLinearReadOnly(classLoader, newClass->directMethods);
}
if (pHeader->virtualMethodsSize != 0) {
int count = (int) pHeader->virtualMethodsSize;
u4 lastIndex = 0;
DexMethod method;
newClass->virtualMethodCount = count;
newClass->virtualMethods = (Method*) dvmLinearAlloc(classLoader,
count * sizeof(Method));
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
dexReadClassDataMethod(&pEncodedData, &method, &lastIndex);
loadMethodFromDex(newClass, &method, &newClass->virtualMethods[i]);
if (classMapData != NULL) {
const RegisterMap* pMap = dvmRegisterMapGetNext(&classMapData);
if (dvmRegisterMapGetFormat(pMap) != kRegMapFormatNone) {
newClass->virtualMethods[i].registerMap = pMap;
/* TODO: add rigorous checks */
assert((newClass->virtualMethods[i].registersSize+7) / 8 ==
newClass->virtualMethods[i].registerMap->regWidth);
}
}
}
dvmLinearReadOnly(classLoader, newClass->virtualMethods);
}
newClass->sourceFile = dexGetSourceFile(pDexFile, pClassDef);
/* caller must call dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc */
return newClass;
}
这里我们先看一下ClassObject结构体,代码位于dalvik\vm\oo\Object.h中。
struct ClassObject {
Object obj; /* MUST be first item */
/* leave space for instance data; we could access fields directly if we
freeze the definition of java/lang/Class */
u4 instanceData[CLASS_FIELD_SLOTS];
/* UTF-8 descriptor for the class; from constant pool, or on heap
if generated ("[C") */
const char* descriptor;
char* descriptorAlloc;
/* access flags; low 16 bits are defined by VM spec */
u4 accessFlags;
/* VM-unique class serial number, nonzero, set very early */
u4 serialNumber;
/* DexFile from which we came; needed to resolve constant pool entries */
/* (will be NULL for VM-generated, e.g. arrays and primitive classes) */
DvmDex* pDvmDex;
/* state of class initialization */
ClassStatus status;
/* if class verify fails, we must return same error on subsequent tries */
ClassObject* verifyErrorClass;
/* threadId, used to check for recursive <clinit> invocation */
u4 initThreadId;
/*
* Total object size; used when allocating storage on gc heap. (For
* interfaces and abstract classes this will be zero.)
*/
size_t objectSize;
/* arrays only: class object for base element, for instanceof/checkcast
(for String[][][], this will be String) */
ClassObject* elementClass;
/* arrays only: number of dimensions, e.g. int[][] is 2 */
int arrayDim;
/* primitive type index, or PRIM_NOT (-1); set for generated prim classes */
PrimitiveType primitiveType;
/* superclass, or NULL if this is java.lang.Object */
ClassObject* super;
/* defining class loader, or NULL for the "bootstrap" system loader */
Object* classLoader;
/* initiating class loader list */
/* NOTE: for classes with low serialNumber, these are unused, and the
values are kept in a table in gDvm. */
InitiatingLoaderList initiatingLoaderList;
/* array of interfaces this class implements directly */
int interfaceCount;
ClassObject** interfaces;
/* static, private, and <init> methods */
int directMethodCount;
Method* directMethods;
/* virtual methods defined in this class; invoked through vtable */
int virtualMethodCount;
Method* virtualMethods;
/*
* Virtual method table (vtable), for use by "invoke-virtual". The
* vtable from the superclass is copied in, and virtual methods from
* our class either replace those from the super or are appended.
*/
int vtableCount;
Method** vtable;
/*
* Interface table (iftable), one entry per interface supported by
* this class. That means one entry for each interface we support
* directly, indirectly via superclass, or indirectly via
* superinterface. This will be null if neither we nor our superclass
* implement any interfaces.
*
* Why we need this: given "class Foo implements Face", declare
* "Face faceObj = new Foo()". Invoke faceObj.blah(), where "blah" is
* part of the Face interface. We can't easily use a single vtable.
*
* For every interface a concrete class implements, we create a list of
* virtualMethod indices for the methods in the interface.
*/
int iftableCount;
InterfaceEntry* iftable;
/*
* The interface vtable indices for iftable get stored here. By placing
* them all in a single pool for each class that implements interfaces,
* we decrease the number of allocations.
*/
int ifviPoolCount;
int* ifviPool;
/* instance fields
*
* These describe the layout of the contents of a DataObject-compatible
* Object. Note that only the fields directly defined by this class
* are listed in ifields; fields defined by a superclass are listed
* in the superclass's ClassObject.ifields.
*
* All instance fields that refer to objects are guaranteed to be
* at the beginning of the field list. ifieldRefCount specifies
* the number of reference fields.
*/
int ifieldCount;
int ifieldRefCount; // number of fields that are object refs
InstField* ifields;
/* bitmap of offsets of ifields */
u4 refOffsets;
/* source file name, if known */
const char* sourceFile;
/* static fields */
int sfieldCount;
StaticField sfields[]; /* MUST be last item */
} 这里我们着重关心Method结构体,代码位于
dalvik\vm\oo\
Object.h中。
struct Method {
/* the class we are a part of */
ClassObject* clazz;
/* access flags; low 16 bits are defined by spec (could be u2?) */
u4 accessFlags;
/*
* For concrete virtual methods, this is the offset of the method
* in "vtable".
*
* For abstract methods in an interface class, this is the offset
* of the method in "iftable[n]->methodIndexArray".
*/
u2 methodIndex;
/*
* Method bounds; not needed for an abstract method.
*
* For a native method, we compute the size of the argument list, and
* set "insSize" and "registerSize" equal to it.
*/
u2 registersSize; /* ins + locals */
u2 outsSize;
u2 insSize;
/* method name, e.g. "<init>" or "eatLunch" */
const char* name;
/*
* Method prototype descriptor string (return and argument types).
*
* TODO: This currently must specify the DexFile as well as the proto_ids
* index, because generated Proxy classes don't have a DexFile. We can
* remove the DexFile* and reduce the size of this struct if we generate
* a DEX for proxies.
*/
DexProto prototype;
/* short-form method descriptor string */
const char* shorty;
/*
* The remaining items are not used for abstract or native methods.
* (JNI is currently hijacking "insns" as a function pointer, set
* after the first call. For internal-native this stays null.)
*/
/* the actual code */
const u2* insns; /* instructions, in memory-mapped .dex */
/* cached JNI argument and return-type hints */
int jniArgInfo;
/*
* Native method ptr; could be actual function or a JNI bridge. We
* don't currently discriminate between DalvikBridgeFunc and
* DalvikNativeFunc; the former takes an argument superset (i.e. two
* extra args) which will be ignored. If necessary we can use
* insns==NULL to detect JNI bridge vs. internal native.
*/
DalvikBridgeFunc nativeFunc;
/*
* Register map data, if available. This will point into the DEX file
* if the data was computed during pre-verification, or into the
* linear alloc area if not.
*/
const RegisterMap* registerMap;
/* set if method was called during method profiling */
bool inProfile;
} 我们着重分析ClassObject结构体中Method型的directMethods字段是怎么生成的。代码在loadClassFromDex0中,我们再次截取出来。
if (pHeader->directMethodsSize != 0) {
int count = (int) pHeader->directMethodsSize;
u4 lastIndex = 0;
DexMethod method;
newClass->directMethodCount = count;
newClass->directMethods = (Method*) dvmLinearAlloc(classLoader,
count * sizeof(Method));
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
dexReadClassDataMethod(&pEncodedData, &method, &lastIndex);
loadMethodFromDex(newClass, &method, &newClass->directMethods[i]);
if (classMapData != NULL) {
const RegisterMap* pMap = dvmRegisterMapGetNext(&classMapData);
if (dvmRegisterMapGetFormat(pMap) != kRegMapFormatNone) {
newClass->directMethods[i].registerMap = pMap;
/* TODO: add rigorous checks */
assert((newClass->directMethods[i].registersSize+7) / 8 ==
newClass->directMethods[i].registerMap->regWidth);
}
}
}
dvmLinearReadOnly(classLoader, newClass->directMethods);
} dexReadClassDataMethod方法用于读取上图中的第三部分encoded_method。代码位于dalvik\libdex\DexClass.h中。
DEX_INLINE void dexReadClassDataMethod(const u1** pData, DexMethod* pMethod,
u4* lastIndex) {
u4 index = *lastIndex + readUnsignedLeb128(pData);
pMethod->accessFlags = readUnsignedLeb128(pData);
pMethod->codeOff = readUnsignedLeb128(pData);
pMethod->methodIdx = index;
*lastIndex = index;
} 最后loadMethodFromDex是真正生成
ClassObject结构体中Method型的
directMethods字段的时候,代码位于dalvik\vm\oo\Class.c中。
static void loadMethodFromDex(ClassObject* clazz, const DexMethod* pDexMethod,
Method* meth)
{
DexFile* pDexFile = clazz->pDvmDex->pDexFile;
const DexMethodId* pMethodId;
const DexCode* pDexCode;
pMethodId = dexGetMethodId(pDexFile, pDexMethod->methodIdx);
meth->name = dexStringById(pDexFile, pMethodId->nameIdx);
dexProtoSetFromMethodId(&meth->prototype, pDexFile, pMethodId);
meth->shorty = dexProtoGetShorty(&meth->prototype);
meth->accessFlags = pDexMethod->accessFlags;
meth->clazz = clazz;
meth->jniArgInfo = 0;
if (dvmCompareNameDescriptorAndMethod("finalize", "()V", meth) == 0) {
SET_CLASS_FLAG(clazz, CLASS_ISFINALIZABLE);
}
pDexCode = dexGetCode(pDexFile, pDexMethod);
if (pDexCode != NULL) {
/* integer constants, copy over for faster access */
meth->registersSize = pDexCode->registersSize;
meth->insSize = pDexCode->insSize;
meth->outsSize = pDexCode->outsSize;
/* pointer to code area */
meth->insns = pDexCode->insns;
} else {
/*
* We don't have a DexCode block, but we still want to know how
* much space is needed for the arguments (so we don't have to
* compute it later). We also take this opportunity to compute
* JNI argument info.
*
* We do this for abstract methods as well, because we want to
* be able to substitute our exception-throwing "stub" in.
*/
int argsSize = dvmComputeMethodArgsSize(meth);
if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(meth))
argsSize++;
meth->registersSize = meth->insSize = argsSize;
assert(meth->outsSize == 0);
assert(meth->insns == NULL);
if (dvmIsNativeMethod(meth)) {
meth->nativeFunc = dvmResolveNativeMethod;
meth->jniArgInfo = computeJniArgInfo(&meth->prototype);
}
}
} Method结构体在上面我们已经介绍过了。这个方法的关键在于dexGetCode,这个方法用于找到DexCode结构体。我们首先介绍下DexCode结构体。代码位于
dalvik\libdex\
DexClass.h中。
typedef struct DexCode {
u2 registersSize;
u2 insSize;
u2 outsSize;
u2 triesSize;
u4 debugInfoOff; /* file offset to debug info stream */
u4 insnsSize; /* size of the insns array, in u2 units */
u2 insns[1];
/* followed by optional u2 padding */
/* followed by try_item[triesSize] */
/* followed by uleb128 handlersSize */
/* followed by catch_handler_item[handlersSize] */
} DexCode;
dexGetCode方法,位于dalvik\libdex\DexClass.h中。
DEX_INLINE const DexCode* dexGetCode(const DexFile* pDexFile,
const DexMethod* pDexMethod)
{
if (pDexMethod->codeOff == 0)
return NULL;
return (const DexCode*) (pDexFile->baseAddr + pDexMethod->codeOff);
}
获取的DexCode其实就是上图中的第四部分code_item。
这样逐层返回就生成了ClassObject对象,并返回给Java层,在Java层表现为Class。参见这个Java方法protected Class<?> loadClass(String className, boolean resolve)。