[置顶] Android源码之DeskClock (三) Proxy/Delegate Application 框架应用
一.概述
当项目有加壳子,插件化或热修复等需求的时候,可以使用Proxy/Delegate Application框架的方式,在正常的模式中,一个程序一般只有一个Application入口,而Proxy/Delegate模式中需要有两个Application,原程序的Application改为Delegate Application,再新加一个Proxy Application,由Proxy Application 提供一系列的个性化定制,再将所有的context和context相关的引用全部转化为Delegate Application的实例,让外界包括Delegate Application自身都以为该App的Application入口就是Delegate Application.
二.实例
1.Proxy/Delegate 之前
这里就在Android 4.4原生的DeskClock程序上应用Proxy/Delegate框架为示例
原生的DeskClock程序没有自定义Application,这里先定义一个,并print该程序目前ApplicationContext的名字(在DeskClock中使用的Log是自定义的)
/**
* Created by jesse on 15-7-17.
*/
public class MyApplication extends Application{
private final String TAG = MyApplication.class.getSimpleName();
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.i(TAG + ", onCreate " + this.getApplicationContext().getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
并且在DeskClock的入口Activity,DeskClock处也print出该程序目前ApplicationContext的名字用于后续Proxy后的对比.
Application的Manifest配置是
<application android:name="cn.jesse.MyApplication"
android:label="@string/app_label"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_alarmclock"
android:requiredForAllUsers="true"
android:supportsRtl="true">
过滤后的运行Log: 简单的流程就是先启动自定义MyApplication 之后再launch DeskClock,同时都打印出来ApplicationContext的名字
2.使用Proxy/Delegate框架之后
使用Proxy/Delegate框架,需要重新构建出来一个新的ProxyApplication,用来做代理Application,原先的MyApplication的作用为DelegateApplication
所以Manifest的配置需要更改,app的主入口更改为MyProxyApplication,把DelegateApplication的信息以meta-data子元素的形式存储(当然也可以用其他的方式)
<application android:name="cn.jesse.MyProxyApplication"
android:label="@string/app_label"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_alarmclock"
android:requiredForAllUsers="true"
android:supportsRtl="true">
<meta-data
android:name="DELEGATE_APPLICATION_CLASS_NAME"
android:value="cn.jesse.MyApplication" >
</meta-data>
</application>
定义一个抽象类,提供一个用于替换当前ProxyApplication 的ClassLoader成父类的ClassLoader的抽象方法(或者一些其他的个性化定制)
* Created by jesse on 15-7-17.
*/
public abstract class ProxyApplication extends Application{
protected abstract void initProxyApplication();
}
当我们要替换当前ProxyApplication的ClassLoader为父类的ClassLoader,所以这个替换的动作要足够得早(要保证在app Context最早被构建的入口处替换ClassLoader),要不然就会出现替换不干净的情况,就会有程序中大部分使用的DelegateApplication的ClassLoader,而一小部分是使用的ProxyApplication的ClassLoader,这样可能会出现一些意想不到的bug.
通常来说在Application的OnCreate中来做替换就足够了,但是当app有注册ContentProvider的时候ContentProvider:OnCreate的调用是在Application:OnCreate之前的,所以我们必须保证替换ClassLoader的动作要在ContentProvider之前.
通过查看源码可以看到Application是继承自ContextWrapper,而在ContextWrapper中系统在构建完成完善的Context之后第一次回调是通过attachBaseContext方法,既然这样就通过在ProxyApplication中复写该方法来获取刚出炉热喷喷的Context来转换ClassLoader.
/**
* Set the base context for this ContextWrapper. All calls will then be
* delegated to the base context. Throws
* IllegalStateException if a base context has already been set.
*
* @param base The new base context for this wrapper.
*/
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
if (mBase != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Base context already set");
}
mBase = base;
}
转换ClassLoader的入口也确定之后就可以自定义一个MyProxyApplication,继承自ProxyApplication并且复写attachBaseContext方法,print相关信息
/**
* Created by jesse on 15-7-17.
*/
public class MyProxyApplication extends ProxyApplication {
private final String TAG = MyProxyApplication.class.getSimpleName();
private Context mContext;
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
Log.i(TAG + ", attachBaseContext");
mContext = base;
this.initProxyApplication();
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.i(TAG + ", onCreate" + this.getApplicationContext().getClass().getSimpleName());
BootLoader.boot(mContext);
}
@Override
protected void initProxyApplication() {
Log.i(TAG + ", initProxyApplication");
BootLoader.resetClassLoader(mContext);
}
}
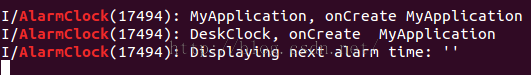
Log运行的顺序,先进入attachBaseContext->initProxyApplication->onCreate->DeskClock:onCreate (这里DeskClock的onCreate获取到的ApplicationContext的名字是(MyProxyApplication)
![[置顶] Android源码之DeskClock (三) Proxy/Delegate Application 框架应用_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/6cafd5cd335841e0a87f3f06544562d5.jpg)
入口的顺序没问题了之后,就可以在initProxyApplication方法中替换当前的ClassLoader到父类的ClassLoader,并且在MyProxyApplication的onCreate中将应用层所有的Application的引用全部从ProxyApplication替换成MyApplication(当前在DeskClock程序中没有替换ClassLoader的需求,只需要替换所有的Application的引用就能达到代理的效果,所以在initProxyApplication方法处就写了一个空方法带过).
先从AndroidManifest配置文件中的metadata拿到DelegateApplication的属性
String className = CLASS_NAME;
ApplicationInfo appInfo = getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(super.getPackageName(), PackageManager.GET_META_DATA);
Bundle bundle = appInfo.metaData;
if (bundle != null && bundle.containsKey(KEY)) {
className = bundle.getString(KEY);
if (className.startsWith("."))
className = super.getPackageName() + className;
}
根据className反射得到MyApplication,创建MyApplication实例并且取得MyProxyApplication的实例
Class delegateClass = Class.forName(className, true, getClassLoader());
Application delegate = (Application) delegateClass.newInstance();
Application proxyApplication = (Application)getApplicationContext();
使用反射更换MyProxyApplication context成员中的mOuterContext属性
Class contextImplClass = Class.forName("android.app.ContextImpl");
Field mOuterContext = contextImplClass.getDeclaredField("mOuterContext");
mOuterContext.setAccessible(true);
mOuterContext.set(mContext, delegate);
获取MyProxyApplication Context的PackageInfo对象,替换掉其中的mApplication属性
Field mPackageInfoField = contextImplClass.getDeclaredField("mPackageInfo");
mPackageInfoField.setAccessible(true);
Object mPackageInfo = mPackageInfoField.get(mContext);
Class loadedApkClass = Class.forName("android.app.LoadedApk");
Field mApplication = loadedApkClass.getDeclaredField("mApplication");
mApplication.setAccessible(true);
mApplication.set(mPackageInfo, delegate);
再根据之前反射得到的packageInfo对象获取到mActivityThread属性,替换掉其中的mInitialApplication属性
Class activityThreadClass = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread");
Field mAcitivityThreadField = loadedApkClass.getDeclaredField("mActivityThread");
mAcitivityThreadField.setAccessible(true);
Object mActivityThread = mAcitivityThreadField.get(mPackageInfo);
Field mInitialApplicationField = activityThreadClass.getDeclaredField("mInitialApplication");
mInitialApplicationField.setAccessible(true);
mInitialApplicationField.set(mActivityThread, delegate);
拿着之前的mActivityThread对象获取到mAllApplications属性,注意该属性是一个list,这里就移除MyProxyApplication添加DelegateApplication,至此应用层MyProxyApplication的Context的引用全部都替换成了MyApplication的引用.
Field mAllApplicationsField = activityThreadClass.getDeclaredField("mAllApplications");
mAllApplicationsField.setAccessible(true);
ArrayList<Application> al = (ArrayList<Application>)mAllApplicationsField.get(mActivityThread);
al.add(delegate);
al.remove(proxyApplication);
给MyApplication通过反射和attach内部方法设置baseContext,并调用MyApplication的onCreate方法完成DelegateApplication的初始化.
Method attach = Application.class.getDeclaredMethod("attach", Context.class);
attach.setAccessible(true);
attach.invoke(delegate, mContext);
delegate.onCreate();
完成这些步骤之后再重新运行查看Log,观察DeskClock处获取的ApplicationContext的名字已经变成MyApplication.
![[置顶] Android源码之DeskClock (三) Proxy/Delegate Application 框架应用_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/4924d6e060f9453d94f55327da6efc55.jpg)
但是这样还没有完全结束,还记得开头说的ContentProvider吗?他的构造是在Application的onCreate之前的,那么ContentProvider部分有没有需要替换的Context引用呢?从framework/base/core/java/android/app下可以找到ActivityThread.java从其中装载ContentProvider的部分可以看到,如果当前Context的包名和ProviderInfo的包名一样的话,ContentProvider就会引用当前的MyProxyApplication的Context.由于当前的MyProxyApplication只是做代理启动用的,所以在MyProxyApplication处复写getPackageName并且返回空就可以避免ContentProvider复用当前Context了.
private IActivityManager.ContentProviderHolder installProvider(Context context,
IActivityManager.ContentProviderHolder holder, ProviderInfo info,
boolean noisy, boolean noReleaseNeeded, boolean stable) {
ContentProvider localProvider = null;
IContentProvider provider;
if (holder == null || holder.provider == null) {
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER || noisy) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Loading provider " + info.authority + ": "
+ info.name);
}
Context c = null;
ApplicationInfo ai = info.applicationInfo;
if (context.getPackageName().equals(ai.packageName)) {
c = context;
} else if (mInitialApplication != null &&
mInitialApplication.getPackageName().equals(ai.packageName)) {
c = mInitialApplication;
} else {
try {
c = context.createPackageContext(ai.packageName,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
三.总结
这篇只是先简单的走了下Proxy/Delegate框架的流程,这个框架其实是有很多使用场景的,例如多dex动态加载,插件化,线上程序热修复bug等可以灵活使用出很多有趣的技术,有时间的话还会再发一篇以Proxy/Delegate实现的线上程序热修复bug的博客.
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/l2show/article/details/46914881