linux总线设备模型-----kobject&kset
sysfs文件系统
sysfs is a ram-based filesystem initially based on ramfs.it provides a means to export kernel data structures,their attributes,and the linkages between them to userspace
-------documentation/filesystems/sysfs.txt
linux2.6内核引入了sysfs文件系统。sysfs被看成是与proc同类别的文件系统。sysfs把连接在系统上的设备和总线组织成分级的文件,使其从用户空间可以访问到。
sysfs 被加载在/sys/目录下,它的子目录包括
block:在系统中发现的每个块设备在该目录下对应一个子目录。每个子目录中又包含一些属性文件,它们描述了这个块设备的各方面属性,如设备大小。(loop块设备是使用文件来模拟的)
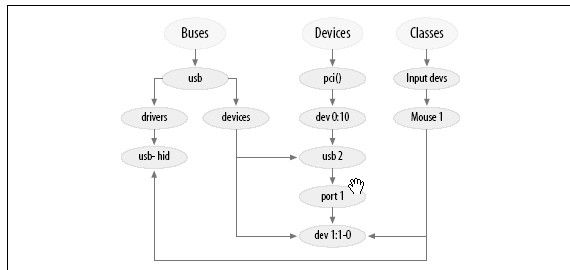
bus:在内核中注册的每条总线在该目录下对应一个子目录,如:
ide pci scsi usb pcmcia
其中每个总线目录内又包含两个子目录:
devices和drivers,devices目录包含了在整个系统中发现的属于该总线类型的设备。
drivers目录包含了注册到该总线的所有驱动
class将设备按照功能进行的分类,如/sys/class/net目录下包含了所有网络接口
devices 包含系统所有的设备。
kernel内核中的配置参数
module系统中所有模块的信息。
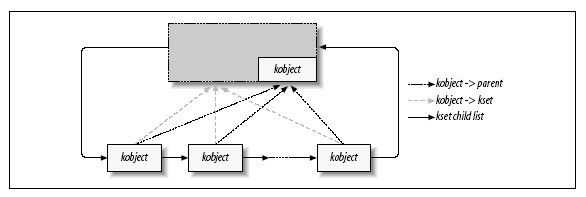
kobject 实现了基本的面向对象管理机制,是构成linux2.6设备模型的核心结构。它与sysfs文件系统紧密相连,在内核中注册的每个kobject对象对应sysfs文件系统中一个目录。
struct kobject {
const char *name;
struct list_head entry;
struct kobject *parent;指向父对象
struct kset *kset;父目录
struct kobj_type *ktype;
struct sysfs_dirent *sd;
struct kref kref;
unsigned int state_initialized:1;
unsigned int state_in_sysfs:1;
unsigned int state_add_uevent_sent:1;
unsigned int state_remove_uevent_sent:1;
};
kobject操作-----
void kobject_init(struct kobject *kobj)-------初始化kobject结构
int kobject_add(struct kobject *kobj)-----将kobject对象注册到linux系统
int kobject_init_and_add(struct kobject *kobj,struct kobj_type *ktype,struct kobject *parent,const char *fmt,.......)-------初始化kobject结构并将kobject对象注册到linux系统
void kobject_del(struct kobject *kobj)------从linux系统中删除kobject对象
struct kobject *kobject_get(struct kobject *kobj)-----将kobject对象的引用计数加1,同时返回该对象的指针。
void kobject_put(struct kobject *kobj)-----将kobject对象的引用计数减1,如果引用计数降为0,则调用release方法释放该kobject对象。
kobject 的ktype成员是一个指向kobj_type结构的指针,该结构中记录了kobject对象的一些属性。
struct kobj_type
{
void (*release)(struct kobject *kobj);
struct sysfs_ops *sysfs_ops;
struct attribute **default_attrs;
};
release:-----用于释放kobject占用的资源,当kobject的引用计数为0时被调用。
struct attribute
{
char *name;属性文件名
struct module *owner;
mode_t mode;属性的保护位
};
struct attribute(属性)------对应于kobject的目录下的一个文件,name 成员就是文件名。
struct sysfs_ops
{
ssize_t (*show)(struct kobject *,struct attribute *,char *);
ssize_t (*store)(struct kobject *,struct attribute *,const char *,size_t);
};
show----当用户读属性文件时,该函数被调用,该函数将属性值存入buffer中返回给用户态;
store----当用户写属性文件时,该函数被调用,用于存储用户传入的属性值。
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
MODULE_AUTHOR("David Xie");
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
void obj_test_release(struct kobject *kobject);
ssize_t kobj_test_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf);
ssize_t kobj_test_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count);
struct attribute test_attr = {
.name = "kobj_config",
.mode = S_IRWXUGO,
};
static struct attribute *def_attrs[] = {
&test_attr,
NULL,
};
struct sysfs_ops obj_test_sysops =
{
.show = kobj_test_show,
.store = kobj_test_store,
};
struct kobj_type ktype =
{
.release = obj_test_release,
.sysfs_ops=&obj_test_sysops,
.default_attrs=def_attrs,
};
void obj_test_release(struct kobject *kobject)
{
printk("eric_test: release .\n");
}
ssize_t kobj_test_show(struct kobject *kobject, struct attribute *attr,char *buf)
{
printk("have show.\n");
printk("attrname:%s.\n", attr->name);
sprintf(buf,"%s\n",attr->name);
return strlen(attr->name)+2;
}
ssize_t kobj_test_store(struct kobject *kobject,struct attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count)
{
printk("havestore\n");
printk("write: %s\n",buf);
return count;
}
struct kobject kobj;
static int kobj_test_init()
{
printk("kboject test init.\n");
kobject_init_and_add(&kobj,&ktype,NULL,"kobject_test");初始化并添加
return 0;
}
static int kobj_test_exit()
{
printk("kobject test exit.\n");
kobject_del(&kobj);删除注册
return 0;
}
module_init(kobj_test_init);
module_exit(kobj_test_exit);
kset是具有相同类型的kobject的集合,在sysfs中体现成一个目录,在内核中用kset数据结构表示:
struct kset {
struct list_head list;连接该kset中所有kobject的链表头
spinlock_t list_lock;
struct kobject kobj;内嵌的kobject
struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;处理热插拔事件的操作集合
};
kset操作---
int kset_register(struct kset *kset)在内核中注册一个kset
void kset_unregister(struct kset *kset)从内核中注销一个kset
热插拔事件------
在linux系统中,当系统配置发生变化时,如:添加kset到系统;移动kobject,一个通知会从内核空间发送到用户空间,这就是热插拔事件。热插拔事件会导致用户空间中相应的处理程序(udev,mdev)被调用,这些处理程序会通过加载驱动程序,创建设备节点等来响应热插拔事件。
操作集合
struct kset_uevent_ops
{
int (*filter) (struct kset *kset,struct kobject *kobj);
const char *(*name)(struct kset *kset,struct kobject *kobj);
int (*uevent)(struct kset *kset,struct kobject *kobj,struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
}
三个函数调用时机------
当kset所管理的kobject和kset状态发生变化时(如被加入,移动),这三个函数将被调用。
三个函数功能------
filter:决定是否将事件传递到用户空间。如果filter返回0,将不传递事件。
name----用于将字符串传递给用户空间的热插拔处理程序。
uevent---将用户空间需要的参数添加到环境变量中。
linux-2.6.21.5/lib/kobject.c
kobject_set_name()
给kobject赋名字 -- kobject->name[20]和kobject->k_name
/**
* kobject_set_name - Set the name of an object
* @kobj: object.
* @fmt: format string used to build the name
*
* If strlen(name) >= KOBJ_NAME_LEN, then use a dynamically allocated
* string that @kobj->k_name points to. Otherwise, use the static
* @kobj->name array.
*/
int kobject_set_name(struct kobject * kobj, const char * fmt, ...)
{
int error = 0;
int limit = KOBJ_NAME_LEN;
int need;
va_list args;
char * name;
/*
* First, try the static array
*/
va_start(args, fmt);
need = vsnprintf(kobj->name, limit, fmt, args);
va_end(args);
if (need < limit)
name = kobj->name;
else {
/*
* Need more space? Allocate it and try again
*/
limit = need + 1;
name = kmalloc(limit,GFP_KERNEL);
if (!name) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto Done;
}
va_start(args, fmt);
need = vsnprintf(name, limit, fmt, args);
va_end(args);
/* Still? Give up. */
if (need >= limit) {
kfree(name);
error = -EFAULT;
goto Done;
}
}
/* Free the old name, if necessary. */
if (kobj->k_name && kobj->k_name != kobj->name)
kfree(kobj->k_name);
/* Now, set the new name */
kobj->k_name = name;
Done:
return error;
}
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/kobject.h>
MODULE_AUTHOR("David Xie");
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
struct kset kset_p;
struct kset kset_c;
int kset_filter(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj)
{
printk("Filter: kobj %s.\n",kobj->name);
return 1;
}
const char *kset_name(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj)
{
static char buf[20];
printk("Name: kobj %s.\n",kobj->name);
sprintf(buf,"%s","kset_name");
return buf;
}
int kset_uevent(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj,struct kobj_uevent_env *env)
{
int i = 0;
printk("uevent: kobj %s.\n",kobj->name);
while( i < env->envp_idx){
printk("%s.\n",env->envp[i]);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
struct kset_uevent_ops uevent_ops =
{
.filter = kset_filter,
.name = kset_name,
.uevent = kset_uevent,
};
int kset_test_init()
{
printk("kset test init.\n");
kobject_set_name(&kset_p.kobj,"kset_p");
kset_p.uevent_ops = &uevent_ops;
kset_register(&kset_p);
kobject_set_name(&kset_c.kobj,"kset_c");
kset_c.kobj.kset = &kset_p;
kset_register(&kset_c);
return 0;
}
int kset_test_exit()
{
printk("kset test exit.\n");
kset_unregister(&kset_p);
kset_unregister(&kset_c);
return 0;
}
module_init(kset_test_init);
module_exit(kset_test_exit);