Neutron中的网络I/O虚拟化(by quqi99)
作者:张华 发表于:2014-04-03
版权声明:可以任意转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章原始出处和作者信息及本版权声明
(http://blog.csdn.net/quqi99 )
我的实验硬件设备如下,需CPU与主板同时支持VT-x与VT-d,网卡支持SR-IOV:
- 英特尔(Intel) 酷睿i5-4590 22纳米 Haswell架构盒装CPU处理器 (LGA1150/3.3GHz/6M三级缓存)
- 华硕(ASUS) B85-PRO GAMER 主板 (Intel B85/LGA 1150)
- Winyao WY576T PCI-E X4 双口服务器千兆网卡 intel 82576
并更新华硕主板的BIOS程序至最后的B85-PRO-GAMER-ASUS-2203.zip配合使用i5,
http://www.asus.com/au/supportonly/B85-PRO%20GAMER/HelpDesk_Download/
http://www.asus.com/au/supportonly/B85-PRO%20GAMER/HelpDesk_CPU/
http://www.asus.com/au/supportonly/B85-PRO%20GAMER/HelpDesk_Download/
http://www.asus.com/au/supportonly/B85-PRO%20GAMER/HelpDesk_CPU/
为了提升网络I/O性能,虚拟化的网络I/O模型也在不断的演化:
1,全虚拟化网卡(emulation),如VMware中的E1000用来仿真intel 82545千兆网卡,它的功能更完备,如相比一些半虚拟化的网卡(如vmnet3)会对vlan的支持更好(这点可参见我的另一篇博客《Vmware中的虚拟网络》一文: http://blog.csdn.net/quqi99/article/details/8727130)。纯软件模拟不需要硬件支持,通过CPU计算来模拟,跟宿主机的物理网卡隔离,没有平台要求,对虚拟机的操作系统也不需要修改(因为模拟的都是一个常见的硬件网卡,如IntelE1000,主流操作系统一般都自带这些驱动,因此默认情下虚拟机不需要再安装驱动。缺点就是性能差了。
2,半虚拟化网卡,如上面提到的VMware中的vnet3,以及KVM中的virtio等。在半虚拟化模型中,物理硬件资源是统一由Hypervisor来管理的,这样虚拟机和Hypervisor之间通信有可能直接接触到硬件,因此性能相对较高。缺点就是需要修改虚拟机操作系统需要安装这些半虚拟化网卡的驱动程序。
3,Pass-through直通方式,Hypervisor直接把硬件PCI设备分配给虚拟独占使用,性能当然好啦。但是浪费硬件设备,且配置复杂,首先需要在hypervisor指定通过PCIid方式分配给指定的虚拟机,然后虚拟机再识别到设备再安装驱动来使用。OpenStack中如何使用它可参见:https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Pci_passthrough
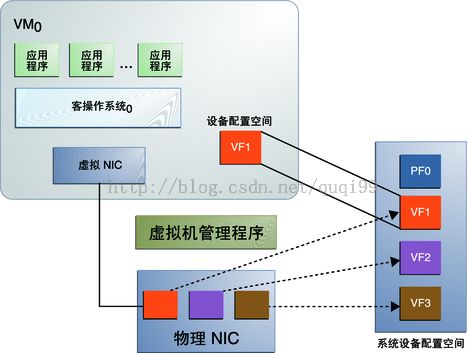
4,SR-IOV(Single Root I/O Virtualization and Sharing Specification),用来解决虚拟最后一公里的问题,即多个虚机可以同时共享使用同一个PCI硬件。它需要专门支持SR-IOV的硬件网卡,它会在Hypervisor里注册成多个网卡(每个网卡都有独立的中断,收发队列,QoS等机制),将虚拟网卡中的数据分类功能挪到了硬件SR-IOV网卡中实现。参考:http://blog.csdn.net/zhonglinzhang/article/details/17072041
linux传统tap + bridge(VEB, Virtual Ethernet Bridge)实现网络虚拟化技术有一个重要特点, 就是使用服务器的CPU来通过软件模拟网络, 而硬件厂商出于某些目的希望将由软件实现的网络虚拟化改为由硬件来实现网络虚拟化.于是, 针对云计算中的复杂网络问题, 业办提出了两种扩展技术标准:802.1Qbh和802.1Qbg:
1, 802.1Qbh Bridge Port Extension主要由Vmware和Cisco提出, 尝试从接入层到汇聚层提供一个完整的虚拟化网络解决方案, 尽可能达到软件定义一个可控网络的目的, 它扩展了传统的网络协议, 因此需要新的网络硬件设备, 成本较高.
2, 802.1Qbg Edge Virtual Bridging(EVB)主要由HP等公司联合提交, 尝试以较低成本利用现有设备改进软件模型的网络. 802.1Qbg的一个核心概念是VEPA(Virtual Ethernet Port Aggregator), 简单来说它通过端口汇聚和数据分类转发, 把Host上原来由CPU和软件做的网络处理工作通过发卡模式转移到一级硬件交换机上, 减小Host CPU负载,同时使在一级交换机上做虚拟机的流量监控成为可能, 也更加清晰地分割Host与网络设备的势力范围, 方便系统管理. EVB又分两种:
1, Tag-less VEPA, 用MAC-VID来导流, 即VEPA模式, 无论host内部的流量还是出外部的流量统统经发卡模式再到外部交换机转发
2, VN-Tagged, 用全新的Tag来导流, 如VEPA一样也需要对物理交换机做定制,核心思想是在标准以太网帧中为虚机定制增加一段专用的标记VN-Tag,用以区分不同的vif,从而识别特定的虚机的流量。
Linux Host侧的扩展技术
macvtap(SRIOV用于将硬件网卡虚机很多中断号不同的独立的虚拟网卡给虚机用, macvtap的bridge模式更像是代替了tap设备与bridge设备的组合给虚机直接用的), linux引入的新的网络设备模型, 和tap设备一样, 每一个macvtap设备拥有一个对应的linux字符设置, 并拥有和tap设备一样的IOCTL接口, 因此能直接被qemu使用.引入它的目的是: 简化虚拟环境中的交换网络, 代替传统的tap设备加bridge设备组合, 同时支持新的虚拟化网络技术, 如802.1 Qbg.
macvtap和vlan设备一样是以一对多的母子关系出现的(ip link add link eth1 name macvtap0 type macvtap, 会生成名为macvtap0@eth1的macvtap接口), 可无限嵌套子设备再做母设备创建macvtap子设备, 母设备与子设备被隐含桥接起来, 母设备相当于交换机的TRUNK品, 实际上当 MACVTAP 设备被创建并且模式不为 Passthrough时,内核隐含的创建了MACVLAN网络(如:ip link add link eth1 name eth1.10 type vlan id 10),完成转发功能。MACVTAP 设备有四种工作模式:Bridge、VEPA、Private,Passthrough:
1, Bridge, 完成与 Bridge 设备类似功能,数据可以在属于同一个母设备的子设备间交换转发. 当前的Linux实现有一个缺陷,此模式下MACVTAP子设备无法和Linux Host通讯,即虚拟机无法和Host通讯,而使用传统的Bridge设备,通过给Bridge设置IP可以完成。但使用VEPA模式可以去除这一限制. macvtap的这种bridge模式等同于传统的tap+bridge的模式.
2, VEPA, 式是对802.1Qbg标准中的VEPA机制的部分软件实现,工作在此模式下的MACVTAP设备简单的将数据转发到母设备中,完成数据汇聚功能,通常需要外部交换机支持Hairpin模式才能正常工作。
3, Private, Private模式和VEPA模式类似,区别是子 MACVTAP之间相互隔离。
3, Passthrough, 可以配合直接使用SRIOV网卡, 内核的MACVLAN数据处理逻辑被跳过,硬件决定数据如何处理,从而释放了Host CPU资源。MACVTAP Passthrough 概念与PCI Passthrough概念不同,PCI Passthrough针对的是任意PCI设备,不一定是网络设备,目的是让Guest OS直接使用Host上的 PCI 硬件以提高效率。MACVTAP Passthrough仅仅针对 MACVTAP网络设备,目的是饶过内核里MACVTAP的部分软件处理过程,转而交给硬件处理。综上所述,对于一个 SRIOV 网络设备,可以用两种模式使用它:MACVTAP Passthrough 与 PCI Passthrough
所以使用网络虚拟化具有三个层次:
1, 用户可以零成本地使用 Linux 软件实现的 Bridge、VLAN、MACVTAP设备定制与现实世界类似的虚拟网络;
2, 也可以用非常低的成本按照802.1Qbg中的VEPA模型创建升级版的虚拟网络,引出虚拟机网络流量,减少Host服务器负载;
3, 当有支持 SRIOV 的网卡存在时,可以使用 Passthrough 技术近一步减少Host负载
KVM中使用Pass-through的步骤如下:
http://www.linux-kvm.org/page/How_to_assign_devices_with_VT-d_in_KVM
1, BIOS支持CPU硬件虚拟化
Intel(VT-x): sudo cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep vmx
AMD(AMD-V): sudo cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep svm
2, BIOS支持I/O硬件虚拟化(北桥内置DMA Remapping硬件和IRQ虚拟化硬件实现I/O的租户隔离、保护及性能)
传统的DMA通过集中式的管理方式IOMMUs管理,通过在内存地址范围来区别设备,容易实现,但不容易实现DMA隔离,因此VT-d通过更新设计的IOMMU架构,实现了多个DMA保护区域的存在,最终实现了DMA虚拟化。这个技术也叫做DMA Remapping。
如果在BIOS里找不到这个选项,不要着急,可能查看Intel的CPU是否支持VT-d(http://ark.intel.com/)。例:
Intel E3-1230 v3, 支持VT-d技术, http://ark.intel.com/products/75054/Intel-Xeon-Processor-E3-1230-v3-8M-Cache-3_30-GHz
Intel 4th gen i5-4200M, 不支持VT-d技术,http://ark.intel.com/products/76348/Intel-Core-i5-4200M-Processor-3M-Cache-up-to-3_10-GHz?q=i5-4200M
1,全虚拟化网卡(emulation),如VMware中的E1000用来仿真intel 82545千兆网卡,它的功能更完备,如相比一些半虚拟化的网卡(如vmnet3)会对vlan的支持更好(这点可参见我的另一篇博客《Vmware中的虚拟网络》一文: http://blog.csdn.net/quqi99/article/details/8727130)。纯软件模拟不需要硬件支持,通过CPU计算来模拟,跟宿主机的物理网卡隔离,没有平台要求,对虚拟机的操作系统也不需要修改(因为模拟的都是一个常见的硬件网卡,如IntelE1000,主流操作系统一般都自带这些驱动,因此默认情下虚拟机不需要再安装驱动。缺点就是性能差了。
2,半虚拟化网卡,如上面提到的VMware中的vnet3,以及KVM中的virtio等。在半虚拟化模型中,物理硬件资源是统一由Hypervisor来管理的,这样虚拟机和Hypervisor之间通信有可能直接接触到硬件,因此性能相对较高。缺点就是需要修改虚拟机操作系统需要安装这些半虚拟化网卡的驱动程序。
3,Pass-through直通方式,Hypervisor直接把硬件PCI设备分配给虚拟独占使用,性能当然好啦。但是浪费硬件设备,且配置复杂,首先需要在hypervisor指定通过PCIid方式分配给指定的虚拟机,然后虚拟机再识别到设备再安装驱动来使用。OpenStack中如何使用它可参见:https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Pci_passthrough
4,SR-IOV(Single Root I/O Virtualization and Sharing Specification),用来解决虚拟最后一公里的问题,即多个虚机可以同时共享使用同一个PCI硬件。它需要专门支持SR-IOV的硬件网卡,它会在Hypervisor里注册成多个网卡(每个网卡都有独立的中断,收发队列,QoS等机制),将虚拟网卡中的数据分类功能挪到了硬件SR-IOV网卡中实现。参考:http://blog.csdn.net/zhonglinzhang/article/details/17072041

linux传统tap + bridge(VEB, Virtual Ethernet Bridge)实现网络虚拟化技术有一个重要特点, 就是使用服务器的CPU来通过软件模拟网络, 而硬件厂商出于某些目的希望将由软件实现的网络虚拟化改为由硬件来实现网络虚拟化.于是, 针对云计算中的复杂网络问题, 业办提出了两种扩展技术标准:802.1Qbh和802.1Qbg:
1, 802.1Qbh Bridge Port Extension主要由Vmware和Cisco提出, 尝试从接入层到汇聚层提供一个完整的虚拟化网络解决方案, 尽可能达到软件定义一个可控网络的目的, 它扩展了传统的网络协议, 因此需要新的网络硬件设备, 成本较高.
2, 802.1Qbg Edge Virtual Bridging(EVB)主要由HP等公司联合提交, 尝试以较低成本利用现有设备改进软件模型的网络. 802.1Qbg的一个核心概念是VEPA(Virtual Ethernet Port Aggregator), 简单来说它通过端口汇聚和数据分类转发, 把Host上原来由CPU和软件做的网络处理工作通过发卡模式转移到一级硬件交换机上, 减小Host CPU负载,同时使在一级交换机上做虚拟机的流量监控成为可能, 也更加清晰地分割Host与网络设备的势力范围, 方便系统管理. EVB又分两种:
1, Tag-less VEPA, 用MAC-VID来导流, 即VEPA模式, 无论host内部的流量还是出外部的流量统统经发卡模式再到外部交换机转发
2, VN-Tagged, 用全新的Tag来导流, 如VEPA一样也需要对物理交换机做定制,核心思想是在标准以太网帧中为虚机定制增加一段专用的标记VN-Tag,用以区分不同的vif,从而识别特定的虚机的流量。
Linux Host侧的扩展技术
macvtap(SRIOV用于将硬件网卡虚机很多中断号不同的独立的虚拟网卡给虚机用, macvtap的bridge模式更像是代替了tap设备与bridge设备的组合给虚机直接用的), linux引入的新的网络设备模型, 和tap设备一样, 每一个macvtap设备拥有一个对应的linux字符设置, 并拥有和tap设备一样的IOCTL接口, 因此能直接被qemu使用.引入它的目的是: 简化虚拟环境中的交换网络, 代替传统的tap设备加bridge设备组合, 同时支持新的虚拟化网络技术, 如802.1 Qbg.
macvtap和vlan设备一样是以一对多的母子关系出现的(ip link add link eth1 name macvtap0 type macvtap, 会生成名为macvtap0@eth1的macvtap接口), 可无限嵌套子设备再做母设备创建macvtap子设备, 母设备与子设备被隐含桥接起来, 母设备相当于交换机的TRUNK品, 实际上当 MACVTAP 设备被创建并且模式不为 Passthrough时,内核隐含的创建了MACVLAN网络(如:ip link add link eth1 name eth1.10 type vlan id 10),完成转发功能。MACVTAP 设备有四种工作模式:Bridge、VEPA、Private,Passthrough:
1, Bridge, 完成与 Bridge 设备类似功能,数据可以在属于同一个母设备的子设备间交换转发. 当前的Linux实现有一个缺陷,此模式下MACVTAP子设备无法和Linux Host通讯,即虚拟机无法和Host通讯,而使用传统的Bridge设备,通过给Bridge设置IP可以完成。但使用VEPA模式可以去除这一限制. macvtap的这种bridge模式等同于传统的tap+bridge的模式.
2, VEPA, 式是对802.1Qbg标准中的VEPA机制的部分软件实现,工作在此模式下的MACVTAP设备简单的将数据转发到母设备中,完成数据汇聚功能,通常需要外部交换机支持Hairpin模式才能正常工作。
3, Private, Private模式和VEPA模式类似,区别是子 MACVTAP之间相互隔离。
3, Passthrough, 可以配合直接使用SRIOV网卡, 内核的MACVLAN数据处理逻辑被跳过,硬件决定数据如何处理,从而释放了Host CPU资源。MACVTAP Passthrough 概念与PCI Passthrough概念不同,PCI Passthrough针对的是任意PCI设备,不一定是网络设备,目的是让Guest OS直接使用Host上的 PCI 硬件以提高效率。MACVTAP Passthrough仅仅针对 MACVTAP网络设备,目的是饶过内核里MACVTAP的部分软件处理过程,转而交给硬件处理。综上所述,对于一个 SRIOV 网络设备,可以用两种模式使用它:MACVTAP Passthrough 与 PCI Passthrough
所以使用网络虚拟化具有三个层次:
1, 用户可以零成本地使用 Linux 软件实现的 Bridge、VLAN、MACVTAP设备定制与现实世界类似的虚拟网络;
2, 也可以用非常低的成本按照802.1Qbg中的VEPA模型创建升级版的虚拟网络,引出虚拟机网络流量,减少Host服务器负载;
3, 当有支持 SRIOV 的网卡存在时,可以使用 Passthrough 技术近一步减少Host负载
KVM中使用Pass-through的步骤如下:
http://www.linux-kvm.org/page/How_to_assign_devices_with_VT-d_in_KVM
1, BIOS支持CPU硬件虚拟化
Intel(VT-x): sudo cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep vmx
AMD(AMD-V): sudo cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep svm
2, BIOS支持I/O硬件虚拟化(北桥内置DMA Remapping硬件和IRQ虚拟化硬件实现I/O的租户隔离、保护及性能)
传统的DMA通过集中式的管理方式IOMMUs管理,通过在内存地址范围来区别设备,容易实现,但不容易实现DMA隔离,因此VT-d通过更新设计的IOMMU架构,实现了多个DMA保护区域的存在,最终实现了DMA虚拟化。这个技术也叫做DMA Remapping。
如果在BIOS里找不到这个选项,不要着急,可能查看Intel的CPU是否支持VT-d(http://ark.intel.com/)。例:
Intel E3-1230 v3, 支持VT-d技术, http://ark.intel.com/products/75054/Intel-Xeon-Processor-E3-1230-v3-8M-Cache-3_30-GHz
Intel 4th gen i5-4200M, 不支持VT-d技术,http://ark.intel.com/products/76348/Intel-Core-i5-4200M-Processor-3M-Cache-up-to-3_10-GHz?q=i5-4200M
首先内核得支持,当然,默认编译的内核一般都是支持的,可以不用管它。
set "Bus options (PCI etc.)" -> "Support for DMA Remapping Devices" to "*"
set "Bus options (PCI etc.)" -> "Enable DMA Remapping Devices" to "*"
set "Bus options (PCI etc.)" -> "PCI Stub driver" to "*"
optional setting:
set "Bus options (PCI etc.)" -> "Support for Interrupt Remapping" to "*"
在/etc/default/grub添加下列选择,然后使用sudo update-grub2 (注意,不是update-grub)命令更新grub后重启机器:
set "Bus options (PCI etc.)" -> "Support for DMA Remapping Devices" to "*"
set "Bus options (PCI etc.)" -> "Enable DMA Remapping Devices" to "*"
set "Bus options (PCI etc.)" -> "PCI Stub driver" to "*"
optional setting:
set "Bus options (PCI etc.)" -> "Support for Interrupt Remapping" to "*"
在/etc/default/grub添加下列选择,然后使用sudo update-grub2 (注意,不是update-grub)命令更新grub后重启机器:
Intel(VT-d): GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash intel_iommu=on pci=assign-busses"
AMD(AMD-Vi): GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash amd_iommu=on pci=assign-busses"
AMD(AMD-Vi): GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash amd_iommu=on pci=assign-busses"
也可以添加iommu=pt使用passthrough模式。
如果报错:SR-IOV: bus number out of range,那是因为我的主板比较老不支持SR-IOV去设置给每个pci卡分配中断号,可使用pci=assign-busses参数强制分配。
3, 验证是否IOMMU是否配置成功:
可以使用“find /sys/kernel/iommu_groups/ -type l”命令看到已经隔离在不同的组下了(类似的方法是下面的:virsh nodedev-list --tree),这样VFIO框架就可以从用户态直通访问了。也可以使用sudo dmesg |grep -i DMAR -i IOMMO来判断 (DMAR与IOMMO都必须有)。
root@desktop:~# lspci |grep Ethernet
00:19.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation Ethernet Connection I217-V (rev 05)
05:00.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01)
05:00.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01)
06:10.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01)
06:10.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01)
root@desktop:~# find /sys/kernel/iommu_groups/ -type l
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/0/devices/0000:00:00.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/1/devices/0000:00:01.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/2/devices/0000:00:02.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/3/devices/0000:00:03.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/4/devices/0000:00:14.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/5/devices/0000:00:16.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/6/devices/0000:00:19.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/7/devices/0000:00:1a.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/8/devices/0000:00:1b.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:00:1c.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:00:1c.3
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:00:1c.4
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:03:00.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:04:00.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:05:00.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:05:00.1
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:06:10.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:06:10.1
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/10/devices/0000:00:1d.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/11/devices/0000:00:1f.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/11/devices/0000:00:1f.2
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/11/devices/0000:00:1f.3
root@desktop:~# dmesg |grep -e DMAR -e IOMMU
[ 0.000000] ACPI: DMAR 00000000d897b3f8 0000B8 (v01 INTEL HSW 00000001 INTL 00000001)
[ 0.000000] Intel-IOMMU: enabled
[ 0.023199] dmar: IOMMU 0: reg_base_addr fed90000 ver 1:0 cap c0000020660462 ecap f0101a
[ 0.023203] dmar: IOMMU 1: reg_base_addr fed91000 ver 1:0 cap d2008020660462 ecap f010da
[ 0.023269] IOAPIC id 8 under DRHD base 0xfed91000 IOMMU 1
[ 0.499504] DMAR: No ATSR found
[ 0.499530] IOMMU 0 0xfed90000: using Queued invalidation
[ 0.499530] IOMMU 1 0xfed91000: using Queued invalidation
[ 0.499532] IOMMU: Setting RMRR:
[ 0.499541] IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:02.0 [0xdb000000 - 0xdf1fffff]
[ 0.499893] IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:1d.0 [0xd88e9000 - 0xd88f6fff]
[ 0.499915] IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:1a.0 [0xd88e9000 - 0xd88f6fff]
[ 0.499933] IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:14.0 [0xd88e9000 - 0xd88f6fff]
[ 0.499946] IOMMU: Prepare 0-16MiB unity mapping for LPC
[ 0.499953] IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:1f.0 [0x0 - 0xffffff]
[ 0.972215] [drm] DMAR active, disabling use of stolen memory
查看设备由什么驱动管理使用lspci -vv -s 00:01b.0命令:
root@desktop:~# lspci -vv -s 06:10.0
06:10.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01)
Subsystem: Device 1d1a:0000
Control: I/O- Mem- BusMaster- SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx-
Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR- <PERR- INTx-
Region 0: [virtual] Memory at df600000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=16K]
Region 3: [virtual] Memory at df620000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=16K]
Capabilities: [70] MSI-X: Enable- Count=3 Masked-
Vector table: BAR=3 offset=00000000
PBA: BAR=3 offset=00002000
Capabilities: [a0] Express (v2) Endpoint, MSI 00
DevCap: MaxPayload 512 bytes, PhantFunc 0, Latency L0s <512ns, L1 <64us
ExtTag- AttnBtn- AttnInd- PwrInd- RBE+ FLReset+
DevCtl: Report errors: Correctable- Non-Fatal- Fatal- Unsupported-
RlxdOrd- ExtTag- PhantFunc- AuxPwr- NoSnoop- FLReset-
MaxPayload 128 bytes, MaxReadReq 128 bytes
DevSta: CorrErr- UncorrErr- FatalErr- UnsuppReq- AuxPwr- TransPend-
LnkCap: Port #0, Speed 2.5GT/s, Width x4, ASPM L0s L1, Exit Latency L0s <4us, L1 <64us
ClockPM- Surprise- LLActRep- BwNot-
LnkCtl: ASPM Disabled; RCB 64 bytes Disabled- CommClk-
ExtSynch- ClockPM- AutWidDis- BWInt- AutBWInt-
LnkSta: Speed unknown, Width x0, TrErr- Train- SlotClk- DLActive- BWMgmt- ABWMgmt-
DevCap2: Completion Timeout: Range ABCD, TimeoutDis+, LTR-, OBFF Not Supported
DevCtl2: Completion Timeout: 50us to 50ms, TimeoutDis-, LTR-, OBFF Disabled
LnkSta2: Current De-emphasis Level: -6dB, EqualizationComplete-, EqualizationPhase1-
EqualizationPhase2-, EqualizationPhase3-, LinkEqualizationRequest-
Capabilities: [100 v1] Advanced Error Reporting
UESta: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol-
UEMsk: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol-
UESvrt: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol-
CESta: RxErr- BadTLP- BadDLLP- Rollover- Timeout- NonFatalErr-
CEMsk: RxErr- BadTLP- BadDLLP- Rollover- Timeout- NonFatalErr-
AERCap: First Error Pointer: 00, GenCap- CGenEn- ChkCap- ChkEn-
Capabilities: [150 v1] Alternative Routing-ID Interpretation (ARI)
ARICap: MFVC- ACS-, Next Function: 0
ARICtl: MFVC- ACS-, Function Group: 0
Kernel driver in use: pci-stub
root@desktop:~# lspci |grep Ethernet
00:19.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation Ethernet Connection I217-V (rev 05)
05:00.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01)
05:00.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01)
06:10.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01)
06:10.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01)
root@desktop:~# find /sys/kernel/iommu_groups/ -type l
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/0/devices/0000:00:00.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/1/devices/0000:00:01.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/2/devices/0000:00:02.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/3/devices/0000:00:03.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/4/devices/0000:00:14.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/5/devices/0000:00:16.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/6/devices/0000:00:19.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/7/devices/0000:00:1a.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/8/devices/0000:00:1b.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:00:1c.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:00:1c.3
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:00:1c.4
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:03:00.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:04:00.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:05:00.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:05:00.1
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:06:10.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/9/devices/0000:06:10.1
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/10/devices/0000:00:1d.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/11/devices/0000:00:1f.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/11/devices/0000:00:1f.2
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/11/devices/0000:00:1f.3
root@desktop:~# dmesg |grep -e DMAR -e IOMMU
[ 0.000000] ACPI: DMAR 00000000d897b3f8 0000B8 (v01 INTEL HSW 00000001 INTL 00000001)
[ 0.000000] Intel-IOMMU: enabled
[ 0.023199] dmar: IOMMU 0: reg_base_addr fed90000 ver 1:0 cap c0000020660462 ecap f0101a
[ 0.023203] dmar: IOMMU 1: reg_base_addr fed91000 ver 1:0 cap d2008020660462 ecap f010da
[ 0.023269] IOAPIC id 8 under DRHD base 0xfed91000 IOMMU 1
[ 0.499504] DMAR: No ATSR found
[ 0.499530] IOMMU 0 0xfed90000: using Queued invalidation
[ 0.499530] IOMMU 1 0xfed91000: using Queued invalidation
[ 0.499532] IOMMU: Setting RMRR:
[ 0.499541] IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:02.0 [0xdb000000 - 0xdf1fffff]
[ 0.499893] IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:1d.0 [0xd88e9000 - 0xd88f6fff]
[ 0.499915] IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:1a.0 [0xd88e9000 - 0xd88f6fff]
[ 0.499933] IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:14.0 [0xd88e9000 - 0xd88f6fff]
[ 0.499946] IOMMU: Prepare 0-16MiB unity mapping for LPC
[ 0.499953] IOMMU: Setting identity map for device 0000:00:1f.0 [0x0 - 0xffffff]
[ 0.972215] [drm] DMAR active, disabling use of stolen memory
查看设备由什么驱动管理使用lspci -vv -s 00:01b.0命令:
root@desktop:~# lspci -vv -s 06:10.0
06:10.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation 82576 Virtual Function (rev 01)
Subsystem: Device 1d1a:0000
Control: I/O- Mem- BusMaster- SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx-
Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR- <PERR- INTx-
Region 0: [virtual] Memory at df600000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=16K]
Region 3: [virtual] Memory at df620000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=16K]
Capabilities: [70] MSI-X: Enable- Count=3 Masked-
Vector table: BAR=3 offset=00000000
PBA: BAR=3 offset=00002000
Capabilities: [a0] Express (v2) Endpoint, MSI 00
DevCap: MaxPayload 512 bytes, PhantFunc 0, Latency L0s <512ns, L1 <64us
ExtTag- AttnBtn- AttnInd- PwrInd- RBE+ FLReset+
DevCtl: Report errors: Correctable- Non-Fatal- Fatal- Unsupported-
RlxdOrd- ExtTag- PhantFunc- AuxPwr- NoSnoop- FLReset-
MaxPayload 128 bytes, MaxReadReq 128 bytes
DevSta: CorrErr- UncorrErr- FatalErr- UnsuppReq- AuxPwr- TransPend-
LnkCap: Port #0, Speed 2.5GT/s, Width x4, ASPM L0s L1, Exit Latency L0s <4us, L1 <64us
ClockPM- Surprise- LLActRep- BwNot-
LnkCtl: ASPM Disabled; RCB 64 bytes Disabled- CommClk-
ExtSynch- ClockPM- AutWidDis- BWInt- AutBWInt-
LnkSta: Speed unknown, Width x0, TrErr- Train- SlotClk- DLActive- BWMgmt- ABWMgmt-
DevCap2: Completion Timeout: Range ABCD, TimeoutDis+, LTR-, OBFF Not Supported
DevCtl2: Completion Timeout: 50us to 50ms, TimeoutDis-, LTR-, OBFF Disabled
LnkSta2: Current De-emphasis Level: -6dB, EqualizationComplete-, EqualizationPhase1-
EqualizationPhase2-, EqualizationPhase3-, LinkEqualizationRequest-
Capabilities: [100 v1] Advanced Error Reporting
UESta: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol-
UEMsk: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol-
UESvrt: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol-
CESta: RxErr- BadTLP- BadDLLP- Rollover- Timeout- NonFatalErr-
CEMsk: RxErr- BadTLP- BadDLLP- Rollover- Timeout- NonFatalErr-
AERCap: First Error Pointer: 00, GenCap- CGenEn- ChkCap- ChkEn-
Capabilities: [150 v1] Alternative Routing-ID Interpretation (ARI)
ARICap: MFVC- ACS-, Next Function: 0
ARICtl: MFVC- ACS-, Function Group: 0
Kernel driver in use: pci-stub
4, unbind device from host kernel driver (example PCI device 01:00.0)
有两种方式,一是通过fio-pci在用户态直通使用PCI设备,二是使用pci-stub使用设备
4.1 pci-stub方式如下:
Load the PCI Stub Driver if it is compiled as a module
modprobe pci_stub
lspci -n
locate the entry for device 01:00.0 and note down the vendor & device ID 8086:10b9
...
01:00.0 0200: 8086:10b9 (rev 06)
...
echo "8086 10b9" > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/pci-stub/new_id
echo 0000:01:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:01:00.0/driver/unbind
echo 0000:01:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/pci-stub/bind
Load the PCI Stub Driver if it is compiled as a module
modprobe pci_stub
lspci -n
locate the entry for device 01:00.0 and note down the vendor & device ID 8086:10b9
...
01:00.0 0200: 8086:10b9 (rev 06)
...
echo "8086 10b9" > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/pci-stub/new_id
echo 0000:01:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:01:00.0/driver/unbind
echo 0000:01:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/pci-stub/bind
或者:
lspci -n -s 00:01b.0
00:1b.0 0403: 8086:1e20 (rev 04)
vim /etc/default/grub
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="rd.lvm.lv=fedora-server/root rd.lvm.lv=fedora-server/swap rhgb quiet intel_iommu=on pci-stub.ids=8086:0152,10de:1401,8086:1e20"
00:1b.0 0403: 8086:1e20 (rev 04)
vim /etc/default/grub
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="rd.lvm.lv=fedora-server/root rd.lvm.lv=fedora-server/swap rhgb quiet intel_iommu=on pci-stub.ids=8086:0152,10de:1401,8086:1e20"
或者使用libvirt的命令 (
识别设备:
virsh nodedev-list --tree |grep pci;
获取设备xml :
virsh nodedev-dumpxml pci_8086_3a6c;
detach设备:
virsh nodedev-dettach pci_8086_3a6c
4.2 VFIO方式:
VFIO可以用于实现高效的用户态驱动。在虚拟化场景可以用于device passthrough。通过用户态配置IOMMU接口,可以将DMA地址空间映射限制在进程虚拟空间中。这对高性能驱动和虚拟化场景device passthrough尤其重要。
相对于传统方式,VFIO对UEFI支持更好。VFIO技术实现了用户空间直接访问设备。无须root特权,更安全,功能更多。
sudo modprobe vfio
sudo modprobe vfio-pci
设备unbind
a. 查看iommu_group及其下所有设备
cd /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:0d:00.0/
readlink iommu_group #查看iommu_group名字
ll iommu_group/devices #查看iommu_group下设备
VFIO可以用于实现高效的用户态驱动。在虚拟化场景可以用于device passthrough。通过用户态配置IOMMU接口,可以将DMA地址空间映射限制在进程虚拟空间中。这对高性能驱动和虚拟化场景device passthrough尤其重要。
相对于传统方式,VFIO对UEFI支持更好。VFIO技术实现了用户空间直接访问设备。无须root特权,更安全,功能更多。
sudo modprobe vfio
sudo modprobe vfio-pci
设备unbind
a. 查看iommu_group及其下所有设备
cd /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:0d:00.0/
readlink iommu_group #查看iommu_group名字
ll iommu_group/devices #查看iommu_group下设备
或者: find /sys/kernel/iommu_groups/ -type l
b. 需要将iommu_group下所有设备unbind并添加到iommu_group中
echo 0000:0d:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:0d:00.0/driver/unbind
echo 1180 e823 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/vfio-pci/new_id
b. 需要将iommu_group下所有设备unbind并添加到iommu_group中
echo 0000:0d:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:0d:00.0/driver/unbind
echo 1180 e823 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/vfio-pci/new_id
5, assign device:
VFIO方式:启动虚拟机(多了个iommu组名) -device vfio-pci,host=0000:03:00.0
PCI方式:qemu-system-x86_64 -m 512 -boot c -net none -hda /root/ia32e_rhel5u1.img -device pci-assign,host=01:00.0
PCI方式:qemu-system-x86_64 -m 512 -boot c -net none -hda /root/ia32e_rhel5u1.img -device pci-assign,host=01:00.0
<devices>
......
<hostdev mode='subsystem' type='pci' managed='yes'>
<source>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x03' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
</source>
</hostdev>
......
</devices>
OpenStack中使用的Pass-through步骤如下:
https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Pci_passthrough
1,计算节点中定义虚机中可用的pci设备
pci_passthrough_whitelist=[{ "vendor_id":"8086","product_id":"1520"}]
2,控制节点中定义别名:
pci_alias={"vendor_id":"8086", "product_id":"1520", "name":"a1"}
3, 启动pci devices filter
scheduler_driver=nova.scheduler.filter_scheduler.FilterScheduler
scheduler_available_filters=nova.scheduler.filters.all_filters
scheduler_available_filters=nova.scheduler.filters.pci_passthrough_filter.PciPassthroughFilter
scheduler_default_filters=RamFilter,ComputeFilter,AvailabilityZoneFilter,ComputeCapabilitiesFilter,ImagePropertiesFilter,PciPassthroughFilter
4, 根据别名定义flavor,a1:2中的2是指要求两块pci设备:
nova flavor-key m1.large set "pci_passthrough:alias"="a1:2"
5, 根据flavor启动虚机:
nova boot --image new1 --key_name test --flavor m1.large 123
KVM中使用SR-IOV配置可参见:http://hj192837.blog.51cto.com/655995/1061407/
对于硬件支持SR-IOV的网卡(如 intel 82576芯片就支持,我买的是300块钱的Winyao WY576T PCI-E X4 双口服务器千兆网卡)。
在启动igb模块后(sudo modprobe -r igb && sudo modprobe igb max_vfs=2)就能用lspci命令看到这块物理网卡已经被注册成了多个SR-IOV网卡。使用下列方法持久化:
1, vi /etc/modprobe.d/igb.conf
options igb max_vfs=2
2, update kernel,
update-initramfs -k all -t -u
3, igbvf驱动应该是hypervisor里用的,所以host应该禁用它
vi /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-igbvf.conf
blacklist igbvf
使用virsh nodedev-dupxml命令查看这些SR-IOV的具体信息格式如下, 其中pci_000_0b_00_0由vish nodedev-list命令得到, 后面的0b_00_0是lspci里显示的插槽信息:
root@desktop:~# virsh nodedev-list |grep pci |grep 06
pci_0000_06_10_0
pci_0000_06_10_1
root@desktop:~# virsh nodedev-dumpxml pci_0000_06_10_0
<device>
<name>pci_0000_06_10_0</name>
<path>/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:06:10.0</path>
<parent>pci_0000_00_1c_4</parent>
<capability type='pci'>
<domain>0</domain>
<bus>6</bus>
<slot>16</slot>
<function>0</function>
<product id='0x10ca'>82576 Virtual Function</product>
<vendor id='0x8086'>Intel Corporation</vendor>
<capability type='phys_function'>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x05' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
</capability>
<iommuGroup number='9'>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x1c' function='0x0'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x1c' function='0x3'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x1c' function='0x4'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x03' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x04' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x05' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x05' slot='0x00' function='0x1'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x06' slot='0x10' function='0x0'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x06' slot='0x10' function='0x1'/>
</iommuGroup>
</capability>
</device>
使用“virsh nodedev-dettach pci_0000_0b_10_0”命令可以将一块SR-IOV网卡的虚拟功能从host分离,从而使虚机可以通过如下格式用到它的虚拟功能。
root@desktop:~# virsh nodedev-dettach pci_0000_06_10_0
Device pci_0000_06_10_0 detached
root@desktop:~# cat /tmp/new-device.xml
<interface type='hostdev' managed='yes'>
<source>
<address type='pci' domain='0' bus='6' slot='16' function='0' />
</source>
</interface>
root@desktop:~# virsh attach-device vm1 /tmp/new-device.xml --live --config
Device attached successfully
再查看虚机的配置,会多出如下片断:
root@desktop:~# virsh dumpxml vm1
...
<devices>
...
<interface type='hostdev' managed='yes'>
<mac address='52:54:00:f0:d3:b8'/>
<driver name='kvm'/>
<source>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x06' slot='0x10' function='0x0'/>
</source>
<alias name='hostdev0'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x07' function='0x0'/>
</interface>
...
</devices
这时候,虚机里多出一块网卡,与物理网络同网段:
root@vm1:~# ip addr show eth4
4: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 2c:53:4a:02:20:3d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.99.169/24 brd 192.168.99.255 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::5054:ff:fe3b:6128/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
OpenStack是如何使用并实现SR-IOV特性的呢?见:https://review.openstack.org/#/c/67500/
nova boot --flavor m1.large --image <image-uuid> --nic net-id=<net-uuid>,vnic-type=<normal|direct|macvtap> vm
neutron port-create <net-uuid-or-name> --binding:vnic-type <normal|direct|macvtap>
nova boot --flavor m1.large --image <image-uuid> --nic port-id=<port-uuid-from-above> vm
1,port-binding用于nova和neutron之间传递数据,所以port-binding要增加vnic-type参数,见:https://review.openstack.org/#/c/72334/
最后它也要挪到能存储任意key-val的binding:profile字典中去,见:https://blueprints.launchpad.net/neutron/+spec/ml2-binding-profile
Replace binding:capabilities with binding:vif_details, https://review.openstack.org/#/c/72452/
2,Implements ML2 mechanism driver for SR-IOV capable NIC based switching, https://review.openstack.org/#/c/74464/
使用了SR-IOV后,就是由硬件桥(Hardware-based Virtual Ethernet Bridging, HW VEB)来通过direct和macvtap方式提供port (VF).
1, Nova端通过pci_passthrough_whitelist将VFs关联到physical_network来支持对sr-iov port的调度.
pci_passthrough_whitelist = {"address":"*:0a:00.*","physical_network":"physnet1"}
2, Neutron端
Neutron sriovnicswitch ML2用来提供port binding功能向nova提供信息
Nuetron sriovnicswitch agent当SR-IOV硬件支持VF link state更新时可以用来处理port更新事件
a, cat /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini
[securitygroup]
firewall_driver = neutron.agent.firewall.NoopFirewallDriver
[ml2]
tenant_network_types = vlan
type_drivers = vlan
mechanism_drivers = openvswitch,sriovnicswitch
[ml2_type_vlan]
network_vlan_ranges = physnet1:2:100
b, cat /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf_sriov.ini
[ml2_sriov]
agent_required = True
[sriov_nic]
physical_device_mappings = physnet1:eth1
# eth1:0000:07:00.2; 0000:07:00.3, eth2:0000:05:00.1; 0000:05:00.2
neutron-server --config-file /etc/neutron/neutron.conf --config-file /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini --config-file /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf_sriov.ini
演化的根本思想是:虚机 -- 虚机网卡(tap) -- 虚拟化层(用户空间) -- 内核网桥 -- 物理网卡。
1, virtio技术通过同时修改物理机操作系统与虚拟化软件从而不需要再模拟完整的虚机网卡,从而绕开一层,提升性能。
2, vhost_net使虚拟机的网络通讯直接绕过用户空间的虚拟化层,直接可以和内核通讯,从而提供虚拟机的网络性能
3, macvtap则是绕过内核网桥
2014-08-04今天接触了Snabb Switch,
传统的neutron实际技术是tap + linux bridge + veth,然后通过iptables或ovs流表来实际anti-spoofing与security-group的支持.
Snabb NFV switch的思想是将能将硬件做的事尽量由硬件网卡来做, 如iptables/ebtables/ovs/bridge这些事。
在openstack中运行Snabb需要两个插件:
1, ML2 Snabb Mechanism Driver,
2, Snabb Switch, 运行在每个计算节点上,类似于ovs, 但是它集成了neturon snabb l2 agent的功能, 它在软件和硬件SR-IOV之上提供数据平面,软件提供virtio-net抽象,security group过滤,带宽控制,ethernet-over-ip遂道。SR-IOV硬件则提供zero-copy DMA加速功能, 见:https://github.com/SnabbCo/snabbswitch/blob/snabbnfv-readme/src/designs/nfv/README.md#snabb-switch-operation
Reference
1, https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/SR-IOV-Passthrough-For-Networking
2, http://www.openstack.cn/p2865.html
3, http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E38902_01/html/E38873/glbzi.html
......
<hostdev mode='subsystem' type='pci' managed='yes'>
<source>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x03' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
</source>
</hostdev>
......
</devices>
OpenStack中使用的Pass-through步骤如下:
https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Pci_passthrough
1,计算节点中定义虚机中可用的pci设备
pci_passthrough_whitelist=[{ "vendor_id":"8086","product_id":"1520"}]
2,控制节点中定义别名:
pci_alias={"vendor_id":"8086", "product_id":"1520", "name":"a1"}
3, 启动pci devices filter
scheduler_driver=nova.scheduler.filter_scheduler.FilterScheduler
scheduler_available_filters=nova.scheduler.filters.all_filters
scheduler_available_filters=nova.scheduler.filters.pci_passthrough_filter.PciPassthroughFilter
scheduler_default_filters=RamFilter,ComputeFilter,AvailabilityZoneFilter,ComputeCapabilitiesFilter,ImagePropertiesFilter,PciPassthroughFilter
4, 根据别名定义flavor,a1:2中的2是指要求两块pci设备:
nova flavor-key m1.large set "pci_passthrough:alias"="a1:2"
5, 根据flavor启动虚机:
nova boot --image new1 --key_name test --flavor m1.large 123
KVM中使用SR-IOV配置可参见:http://hj192837.blog.51cto.com/655995/1061407/
对于硬件支持SR-IOV的网卡(如 intel 82576芯片就支持,我买的是300块钱的Winyao WY576T PCI-E X4 双口服务器千兆网卡)。
在启动igb模块后(sudo modprobe -r igb && sudo modprobe igb max_vfs=2)就能用lspci命令看到这块物理网卡已经被注册成了多个SR-IOV网卡。使用下列方法持久化:
1, vi /etc/modprobe.d/igb.conf
options igb max_vfs=2
2, update kernel,
update-initramfs -k all -t -u
3, igbvf驱动应该是hypervisor里用的,所以host应该禁用它
vi /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-igbvf.conf
blacklist igbvf
使用virsh nodedev-dupxml命令查看这些SR-IOV的具体信息格式如下, 其中pci_000_0b_00_0由vish nodedev-list命令得到, 后面的0b_00_0是lspci里显示的插槽信息:
root@desktop:~# virsh nodedev-list |grep pci |grep 06
pci_0000_06_10_0
pci_0000_06_10_1
root@desktop:~# virsh nodedev-dumpxml pci_0000_06_10_0
<device>
<name>pci_0000_06_10_0</name>
<path>/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:06:10.0</path>
<parent>pci_0000_00_1c_4</parent>
<capability type='pci'>
<domain>0</domain>
<bus>6</bus>
<slot>16</slot>
<function>0</function>
<product id='0x10ca'>82576 Virtual Function</product>
<vendor id='0x8086'>Intel Corporation</vendor>
<capability type='phys_function'>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x05' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
</capability>
<iommuGroup number='9'>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x1c' function='0x0'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x1c' function='0x3'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x1c' function='0x4'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x03' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x04' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x05' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x05' slot='0x00' function='0x1'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x06' slot='0x10' function='0x0'/>
<address domain='0x0000' bus='0x06' slot='0x10' function='0x1'/>
</iommuGroup>
</capability>
</device>
使用“virsh nodedev-dettach pci_0000_0b_10_0”命令可以将一块SR-IOV网卡的虚拟功能从host分离,从而使虚机可以通过如下格式用到它的虚拟功能。
root@desktop:~# virsh nodedev-dettach pci_0000_06_10_0
Device pci_0000_06_10_0 detached
root@desktop:~# cat /tmp/new-device.xml
<interface type='hostdev' managed='yes'>
<source>
<address type='pci' domain='0' bus='6' slot='16' function='0' />
</source>
</interface>
root@desktop:~# virsh attach-device vm1 /tmp/new-device.xml --live --config
Device attached successfully
再查看虚机的配置,会多出如下片断:
root@desktop:~# virsh dumpxml vm1
...
<devices>
...
<interface type='hostdev' managed='yes'>
<mac address='52:54:00:f0:d3:b8'/>
<driver name='kvm'/>
<source>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x06' slot='0x10' function='0x0'/>
</source>
<alias name='hostdev0'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x07' function='0x0'/>
</interface>
...
</devices
这时候,虚机里多出一块网卡,与物理网络同网段:
root@vm1:~# ip addr show eth4
4: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 2c:53:4a:02:20:3d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.99.169/24 brd 192.168.99.255 scope global eth1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::5054:ff:fe3b:6128/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
OpenStack是如何使用并实现SR-IOV特性的呢?见:https://review.openstack.org/#/c/67500/
nova boot --flavor m1.large --image <image-uuid> --nic net-id=<net-uuid>,vnic-type=<normal|direct|macvtap> vm
neutron port-create <net-uuid-or-name> --binding:vnic-type <normal|direct|macvtap>
nova boot --flavor m1.large --image <image-uuid> --nic port-id=<port-uuid-from-above> vm
1,port-binding用于nova和neutron之间传递数据,所以port-binding要增加vnic-type参数,见:https://review.openstack.org/#/c/72334/
最后它也要挪到能存储任意key-val的binding:profile字典中去,见:https://blueprints.launchpad.net/neutron/+spec/ml2-binding-profile
Replace binding:capabilities with binding:vif_details, https://review.openstack.org/#/c/72452/
2,Implements ML2 mechanism driver for SR-IOV capable NIC based switching, https://review.openstack.org/#/c/74464/
使用了SR-IOV后,就是由硬件桥(Hardware-based Virtual Ethernet Bridging, HW VEB)来通过direct和macvtap方式提供port (VF).
1, Nova端通过pci_passthrough_whitelist将VFs关联到physical_network来支持对sr-iov port的调度.
pci_passthrough_whitelist = {"address":"*:0a:00.*","physical_network":"physnet1"}
2, Neutron端
Neutron sriovnicswitch ML2用来提供port binding功能向nova提供信息
Nuetron sriovnicswitch agent当SR-IOV硬件支持VF link state更新时可以用来处理port更新事件
a, cat /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini
[securitygroup]
firewall_driver = neutron.agent.firewall.NoopFirewallDriver
[ml2]
tenant_network_types = vlan
type_drivers = vlan
mechanism_drivers = openvswitch,sriovnicswitch
[ml2_type_vlan]
network_vlan_ranges = physnet1:2:100
b, cat /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf_sriov.ini
[ml2_sriov]
agent_required = True
[sriov_nic]
physical_device_mappings = physnet1:eth1
# eth1:0000:07:00.2; 0000:07:00.3, eth2:0000:05:00.1; 0000:05:00.2
neutron-server --config-file /etc/neutron/neutron.conf --config-file /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini --config-file /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf_sriov.ini
演化的根本思想是:虚机 -- 虚机网卡(tap) -- 虚拟化层(用户空间) -- 内核网桥 -- 物理网卡。
1, virtio技术通过同时修改物理机操作系统与虚拟化软件从而不需要再模拟完整的虚机网卡,从而绕开一层,提升性能。
2, vhost_net使虚拟机的网络通讯直接绕过用户空间的虚拟化层,直接可以和内核通讯,从而提供虚拟机的网络性能
3, macvtap则是绕过内核网桥
2014-08-04今天接触了Snabb Switch,
传统的neutron实际技术是tap + linux bridge + veth,然后通过iptables或ovs流表来实际anti-spoofing与security-group的支持.
Snabb NFV switch的思想是将能将硬件做的事尽量由硬件网卡来做, 如iptables/ebtables/ovs/bridge这些事。
在openstack中运行Snabb需要两个插件:
1, ML2 Snabb Mechanism Driver,
2, Snabb Switch, 运行在每个计算节点上,类似于ovs, 但是它集成了neturon snabb l2 agent的功能, 它在软件和硬件SR-IOV之上提供数据平面,软件提供virtio-net抽象,security group过滤,带宽控制,ethernet-over-ip遂道。SR-IOV硬件则提供zero-copy DMA加速功能, 见:https://github.com/SnabbCo/snabbswitch/blob/snabbnfv-readme/src/designs/nfv/README.md#snabb-switch-operation
Reference
1, https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/SR-IOV-Passthrough-For-Networking
2, http://www.openstack.cn/p2865.html
3, http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E38902_01/html/E38873/glbzi.html
4, http://vfio.blogspot.jp/2015/05/vfio-gpu-how-to-series-part-3-host.html
5, https://bluehatrecord.wordpress.com/2015/12/05/performing-iommu-based-gpu-pci-passthrough-with-fedora-22/
6, https://bluehatrecord.wordpress.com/2015/07/26/implementing-pci-device-passthrough-iommu-with-intel-vt-d-kvm-qemu-and-libvirtd-on-fedora-21/
5, https://bluehatrecord.wordpress.com/2015/12/05/performing-iommu-based-gpu-pci-passthrough-with-fedora-22/
6, https://bluehatrecord.wordpress.com/2015/07/26/implementing-pci-device-passthrough-iommu-with-intel-vt-d-kvm-qemu-and-libvirtd-on-fedora-21/
7,
http://blog.csdn.net/halcyonbaby/article/details/37776211
8, https://hakzsam.wordpress.com/2015/02/21/471/