【设计模式】学习笔记13:组合模式(Composite)
本文出自 http://blog.csdn.net/shuangde800
认识组合模式
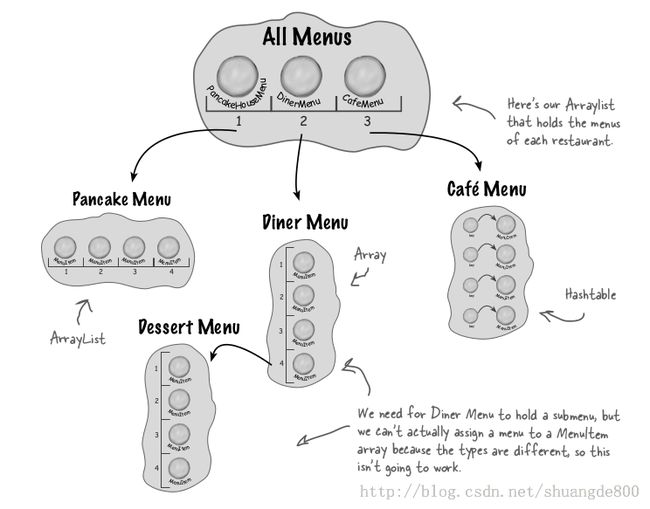
上一篇中,我们可以用迭代器来实现遍历一个集合(数组,ArrayList, Vector, HashTable等)。
假设有这样一种集合结构:餐厅里有一份菜单,菜单里面还有子菜单,其实就是一个树形的结构
那么,之前的迭代器就不能用了。
我们需要新的设计:
1. 需要某种树形结构,可以容纳菜单,子菜单和菜单项
2. 需要确定能够在每个菜单的各个项之间游走,而且至少要像现在用迭代器一样方便
3. 我们也需要更有弹性地在菜单之间游走。比方说,可能只需要遍历甜点菜单,或者可以遍历餐厅的整个菜单
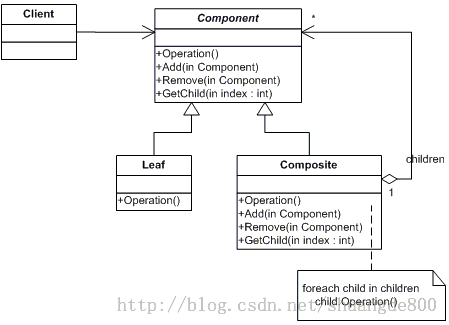
定义组合模式
组合模式允许你将对象组合成树形结构来表现“整体/部分”层次结构。组合能让客户以一致的方式处理个别对象以及对象组合
有时候又叫做部分-整体模式,它使我们树型结构的问题中,模糊了简单元素和复杂元素的概念,客户程序可以向处理简单元素一样来处理复杂元素,从而使得客户程序与复杂元素的内部结构解耦。
组合模式让你可以优化处理递归或分级数据结构。有许多关于分级数据结构的例子,使得组合模式非常有用武之地。关于分级数据结构的一个普遍性的例子是你每次使用电脑时所遇到的:文件系统。文件系统由目录和文件组成。每个目录都可以装内容。目录的内容可以是文件,也可以是目录。按照这种方式,计算机的文件系统就是以递归结构来组织的。如果你想要描述这样的数据结构,那么你可以使用组合模式Composite。
以嵌套菜单为例,这个模式能够创建一个树形结构,在同一个结构中处理嵌套菜单和菜单项组。通过将菜单和项放在相同的结构中,我们创建了一个“整体/部分”层次结构,即由菜单和菜单项组成的对象树。但是可以将它视为一个整体,像是一个丰富的大菜单。
一旦有了丰富的“大菜单”,我们就可以用这个模式来“统一处理个别对象和组合对象”。
这意味着,如果我们有了一个树形结构的菜单,子菜单和可能还带有菜单项的子菜单,那么任何一个菜单都是一种“组合”。因为它既可以包含其他菜单,也可以包含菜单项。我们可以忽略对象组合和个别对象之间的差别。
使用组合模式,只要写出简单的代码,就能够对整个菜单结构应用相同的操作!
利用组合设计菜单
1. 实现菜单组件
// 菜单组件的抽象类
// 菜单组件的角色是为叶子节点和组合节点提供一个共同的接口
// 所有的组件都必须实现MenuComponent接口
// 但是叶节点和在组合节点的角色不同,所以有些方法可能不适合某些节点
// 面对这种情况,最好抛出运行时异常
public abstract class MenuComponent {
public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public MenuComponent getChild(int i) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public String getName() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public String getDescription() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public double getPrice() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void print() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
2. 实现菜单项
// 这是组合类图的叶类,这里是菜单项
public class MenuItem extends MenuComponent {
String name;
String description;
boolean vegetarian;
double price;
public MenuItem(String name,
String description,
boolean vegetarian,
double price)
{
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.vegetarian = vegetarian;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
return vegetarian;
}
// 这里和之前的实现不一样
// 我们覆盖了print()方法
// 对菜单项来说,此方法会打印出完整的菜单条目
// 包括名字,描述,价格等
public void print() {
System.out.print(" " + getName());
if (isVegetarian()) {
System.out.print("(v)");
}
System.out.println(", " + getPrice());
System.out.println(" -- " + getDescription());
}
}
3. 实现组合菜单
public class Menu extends MenuComponent {
// 菜单可以有任意数目的儿子
// 且这些儿子必须属于MenuComonent类型
// 在内部ArrayList里记录它们
ArrayList menuComponents = new ArrayList();
String name;
String description;
// 和菜单项不一样,这里只描述菜单名
public Menu(String name, String description) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
}
// 这个方法添加一个子菜单或者菜单项
public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
menuComponents.add(menuComponent);
}
// 删除一个子菜单或者菜单项
public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
menuComponents.remove(menuComponent);
}
// 获取一个儿子节点
public MenuComponent getChild(int i) {
return (MenuComponent)menuComponents.get(i);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
// 递归打印菜单
public void print() {
System.out.print("\n" + getName());
System.out.println(", " + getDescription());
System.out.println("---------------------");
Iterator iterator = menuComponents.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuComponent menuComponent = (MenuComponent)iterator.next();
menuComponent.print();
}
}
}
组合迭代器
组合模式的迭代器需要用递归来实现
public class CompositeIterator implements Iterator {
Stack stack = new Stack();
// 将我们需要遍历的顶层组合的迭代器传入
// 放进一个栈数据结构中
public CompositeIterator(Iterator iterator) {
stack.push(iterator);
}
// 当客户想要取得下一个元素的时候
// 我们先调用hashNext()来判断是否还有下一个元素
public Object next() {
if (hasNext()) {
Iterator iterator = (Iterator) stack.peek();
MenuComponent component = (MenuComponent) iterator.next();
if (component instanceof Menu) {
// 如果元素是菜单,我们有了另一个需要被包含进遍历中的组合
// 将它放进栈中
stack.push(component.createIterator());
}
return component;
} else {
return null;
}
}
public boolean hasNext() {
if (stack.empty()) { //如果栈空了,说明没有下一个元素了
return false;
} else {
Iterator iterator = (Iterator) stack.peek();
if (!iterator.hasNext()) {
stack.pop();
return hasNext();
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
// 不支持删除
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
空迭代器
public class Menu extends MenuComponent {
// 其它部分代码不需要修改
public Iterator createIterator() {
return new CompositeIterator(menuComponents.iterator()) ;
}
}
public class NullIterator implements Iterator {
public Object next() {
return null;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return false;
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
public class MenuItem extends MenuComponent {
// 其它部分代码不需要修改
public Iterator createIterator() {
return new NullIterator(); // 返回空迭代器
}
}