深入理解光照计算模型(1)
Ambient Lighting (Direct3D 9)
Ambient lighting provides constant lighting for a scene. It lights all object vertices the same because it is not dependent on any other lighting factors such as vertex normals, light direction, light position, range, or attenuation. It is the fastest type of lighting but it produces the least realistic results. Direct3D contains a single global ambient light property that you can use without creating any light. Alternatively, you can set any light object to provide ambient lighting. The ambient lighting for a scene is described by the following equation.
Ambient Lighting = Ca * [Ga + sum(Atti * Spoti * Lai)]
Where:
| Parameter | Default value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | (0,0,0,0) | D3DCOLORVALUE | Material ambient color |
| Ga | (0,0,0,0) | D3DCOLORVALUE | Global ambient color |
| Atteni | (0,0,0,0) | D3DCOLORVALUE | Light attenuation of the ith light. See Attenuation and Spotlight Factor (Direct3D 9). |
| Spoti | (0,0,0,0) | D3DVECTOR | Spotlight factor of the ith light. See Attenuation and Spotlight Factor (Direct3D 9). |
| sum | N/A | N/A | Sum of the ambient light |
| Lai | (0,0,0,0) | D3DVECTOR | Light ambient color of the ith light |
The value for Ca is either:
- vertex color1, if AMBIENTMATERIALSOURCE = D3DMCS_COLOR1, and the first vertex color is supplied in the vertex declaration.
- vertex color2, if AMBIENTMATERIALSOURCE = D3DMCS_COLOR2, and the second vertex color is supplied in vertex declaration.
- material ambient color.
Note If either AMBIENTMATERIALSOURCE option is used, and the vertex color is not provided, then the material ambient color is used.
To use the material ambient color, use SetMaterial as shown in the example code below.
Ga is the global ambient color. It is set using SetRenderState(D3DRS_AMBIENT). There is one global ambient color in a Direct3D scene. This parameter is not associated with a Direct3D light object.
Lai is the ambient color of the ith light in the scene. Each Direct3D light has a set of properties, one of which is the ambient color. The term, sum(Lai) is a sum of all the ambient colors in the scene.
Example
In this example, the object is colored using the scene ambient light and a material ambient color.
#define GRAY_COLOR 0x00bfbfbf
// create material
D3DMATERIAL9 mtrl;
ZeroMemory(&mtrl, sizeof(mtrl));
mtrl.Ambient.r = 0.75f;
mtrl.Ambient.g = 0.0f;
mtrl.Ambient.b = 0.0f;
mtrl.Ambient.a = 0.0f;
m_pd3dDevice->SetMaterial(&mtrl);
m_pd3dDevice->SetRenderState(D3DRS_AMBIENT, GRAY_COLOR);
According to the equation, the resulting color for the object vertices is a combination of the material color and the light color.
These two images show the material color, which is gray, and the light color, which is bright red.
The resulting scene is shown below. The only object in the scene is a sphere. Ambient light lights all object vertices with the same color. It is not dependent on the vertex normal or the light direction. As a result, the sphere looks like a 2D circle because there is no difference in shading around the surface of the object.
To give objects a more realistic look, apply diffuse or specular lighting in addition to ambient lighting.
Attenuation and Spotlight Factor (Direct3D 9)
The diffuse and specular lighting components of the global illumination equation contain terms that describe light attenuation and the spotlight cone. These terms are described below.
Attenuation
The attenuation of a light depends on the type of light and the distance between the light and the vertex position. To calculate attenuation, use one of the following equations.
Atten = 1/( att0i + att1i * d + att2i * d2)
Where:
| Parameter | Default value | Type | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| att0i | 0.0 | FLOAT | Constant attenuation factor | 0 to +infinity |
| att1i | 0.0 | FLOAT | Linear attenuation factor | 0 to +infinity |
| att2i | 0.0 | FLOAT | Quadratic attenuation factor | 0 to +infinity |
| d | N/A | FLOAT | Distance from vertex position to light position | N/A |
- Atten = 1, if the light is a directional light.
- Atten = 0, if the distance between the light and the vertex exceeds the light's range.
The att0, att1, att2 values are specified by the Attenuation0, Attenuation1, and Attenuation2 members of D3DLIGHT9.
The distance between the light and the vertex position is always positive.
d = | Ldir |
Where:
| Parameter | Default value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ldir | N/A | D3DVECTOR | Direction vector from vertex position to the light position |
If d is greater than the light's range, that is, the Range member of a D3DLIGHT9 structure, Direct3D makes no further attenuation calculations and applies no effects from the light to the vertex.
The attenuation constants act as coefficients in the formula - you can produce a variety of attenuation curves by making simple adjustments to them. You can set Attenuation1 to 1.0 to create a light that doesn't attenuate but is still limited by range, or you can experiment with different values to achieve various attenuation effects.
The attenuation at the maximum range of the light is not 0.0. To prevent lights from suddenly appearing when they are at the light range, an application can increase the light range. Or, the application can set up attenuation constants so that the attenuation factor is close to 0.0 at the light range. The attenuation value is multiplied by the red, green, and blue components of the light's color to scale the light's intensity as a factor of the distance light travels to a vertex.
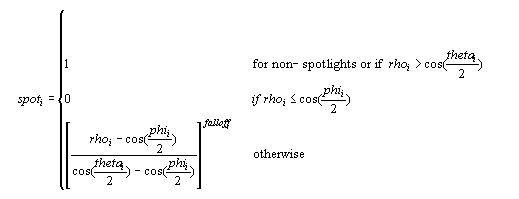
Spotlight Factor
| Parameter | Default value | Type | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rhoi | N/A | FLOAT | cosine(angle) for spotlight i | N/A |
| phii | 0.0 | FLOAT | Penumbra angle of spotlight i in radians | [thetai, pi) |
| thetai | 0.0 | FLOAT | Umbra angle of spotlight i in radians | [0, pi) |
| falloff | 0.0 | FLOAT | Falloff factor | (-infinity, +infinity) |
Where:
rho = norm(Ldcs) . norm(Ldir)
and:
| Parameter | Default value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ldcs | N/A | D3DVECTOR | The negative of the light direction in camera space |
| Ldir | N/A | D3DVECTOR | Direction vector from vertex position to the light position |
After computing the light attenuation, Direct3D also considers spotlight effects if applicable, the angle that the light reflects from a surface, and the reflectance of the current material to calculate the diffuse and specular components for that vertex. For more information, see SpotLight.