JSP自定义标签——简单标签(2)
在前一篇博客中,我们已经学习了自定义的简单标签的基本使用方法,这一篇我们来学习如何在简单标签中添加标签属性。对自定义标签添加一些属性,可以使我们的标签功能更加灵活和复用。例如前一篇博客使用简单标签来对标签体内容执行一定的次数,就无法在标签上规定要执行的次数,必须在标签处理器类中修改,很不方便,如果使用带属性的标签就能很好的解决这个问题。
要想使简单标签具有属性,通常需要满足以下两个步骤:
① 在标签处理器类中定义属性,同时为每个属性生成setter方法;
② 在TLD文件中对于的<tag>标签下添加属性的<attribute>标签,同时<attribute>标签下定义其从标签,其中<name>从标签是必须要有的。<attribute>标签所拥有的从标签如下:
name标签:用于指定标签中属性的名称。
required标签:指定该属性是否必须。
rtexprvalue标签:指定该属性是否支持运行时表达式,如JSP表达式(<%=value %>)和EL表达式( ${value} )。如果我们设定为“false”的话,那么该属性只能支持字符串。
例1:使用简单标签来控制标签体内容执行次数(带属性标签方式)
编写标签处理器类:
1 package com.fjdingsd.simpletag; 2 public class LoopTagBody extends SimpleTagSupport { 3 private int count; //定义一个属性,用来指定循环次数 4 5 public void setCount(int count) { //为该属性设置setter方法 6 this.count = count; 7 } 8 @Override 9 public void doTag() throws JspException, IOException { 10 JspFragment fragment = this.getJspBody(); 11 for(int i=0;i<this.count;i++) { //使用属性就可以指定循环次数 12 fragment.invoke(null); 13 } 14 } 15 }
在TLD文件中定义和描述标签处理器类,同时指定标签所在的uri:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> 2 <taglib xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-jsptaglibrary_2_0.xsd" 5 version="2.0"> 6 <description>A tag library exercising SimpleTag handlers.</description> 7 <tlib-version>1.0</tlib-version> 8 <short-name>SimpleTagLibrary</short-name> 9 <uri>simpletag</uri> 10 11 <tag> 12 <name>loopbody</name> 13 <tag-class>com.fjdingsd.simpletag.LoopTagBody</tag-class> 14 <body-content>scriptless</body-content> 15 <attribute> 16 <name>count</name> 17 <required>true</required> 18 <rtexprvalue>true</rtexprvalue> 19 </attribute> 20 </tag> 21 </taglib>
在JSP页面的开头导入taglib指令:
<%@ taglib uri="simpletag" prefix="simple" %>
最后就能在JSP页面的主体中使用刚才定义好的带属性的简单标签了,使用“count”属性就能指定标签体循环的次数:
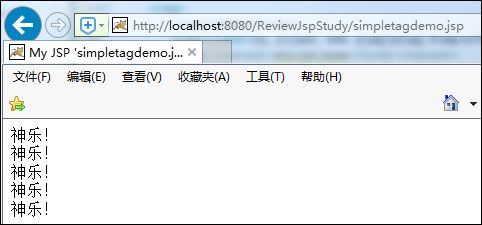
1 <simple:loopbody count="5"> 2 神乐! <br> 3 </simple:loopbody>
在浏览器中观察:
通过上面的例子我们也可以看到,虽然“count”属性在标签处理器LoopTagBody类中的类型为int整型,但是在标签上传入的是字符串类型,这是因为JSP容器支持将标签的属性类型(字符串)转换为八大基本数据类型。如果在标签处理器类中定义一个非八大基本数据类型的属性,那么上面的以上面的方式必定要报错,因为JSP容器无法将字符串转换为其它类型。除非在标签属性中使用其它类型:
例2:
1 package com.fjdingsd.simpletag; 2 public class DateAttributeTag extends SimpleTagSupport { 3 private Date date; 4 5 public void setDate(Date date) { 6 this.date = date; 7 } 8 @Override 9 public void doTag() throws JspException, IOException { 10 this.getJspContext().getOut().write(date.toString()); 11 } 12 }
在TLD文件中描述(这里省略首尾,详细内容请看例1):
1 <tag> 2 <name>showtime</name> <tag-class>com.fjdingsd.simpletag.DateAttributeTag</tag-class> 3 <body-content>empty</body-content> 4 <attribute> 5 <name>date</name> 6 <required>true</required> 7 <rtexprvalue>true</rtexprvalue> 8 </attribute> 9 </tag>
注:这里<rtexprvalue>标签是必须要的。
在JSP页面中导入taglib指令(此处略)后,在JSP页面的主体中使用刚才定义的简单标签:
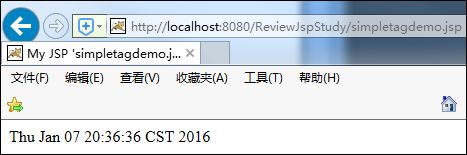
<simple:showtime date="<%=new Date() %>"/>
在浏览器中观察:
因为在JSP页面属性上若以字符串,则因为在标签处理器类并非八大基本数据类型,因此只能使用JSP表达式或EL表达式将对象传入,因此必须在TLD文件中将<rtexprvalue>标签设置为“true”。
简单标签的应用,包括无属性的和带属性的标签如何使用都已经学习完毕,内容就这么多,剩下的就可以根据所学的进行开发了。
例3:使用简单标签来防盗链
如果某个JSP页面需要防止被别的网站盗链,可以在该JSP页面的最开始部分使用一个简单标签,添加一些属性如指定从哪过来的网站才可以浏览本页面内容,指定如果是非指定网址过来的链接应该先让请求跳到哪里去。
编写标签处理器类:
1 package com.fjdingsd.simpletag; 2 public class RefererTag extends SimpleTagSupport { 3 private String site; //指定允许来访请求的网址 4 private String location; //若非指定来访请求的网址应该先跳转到哪里去 5 6 public void setSite(String site) { 7 this.site = site; 8 } 9 public void setLocation(String location) { 10 this.location = location; 11 } 12 @Override 13 public void doTag() throws JspException, IOException { 14 PageContext pageContext = (PageContext) this.getJspContext(); 15 HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) pageContext.getRequest(); 16 HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) pageContext.getResponse(); 17 18 String requestUrl = request.getHeader("referer"); 19 20 if(requestUrl==null || !requestUrl.startsWith(site)) { 21 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+this.location); 22 throw new SkipPageException(); 23 } 24 } 25 }
在TLD文件中描述(这里省略首尾,详细内容请看例1):
1 <tag> 2 <name>referer</name> 3 <tag-class>com.fjdingsd.simpletag.RefererTag</tag-class> 4 <body-content>empty</body-content> 5 <attribute> 6 <name>site</name> 7 <required>true</required> 8 <rtexprvalue>true</rtexprvalue> 9 </attribute> 10 <attribute> 11 <name>location</name> 12 <required>true</required> 13 <rtexprvalue>true</rtexprvalue> 14 </attribute> 15 </tag>
在JSP页面中导入taglib指令(此处略)后,在JSP页面的主体中使用刚才定义的简单标签:
1 <simple:referer site="http://www.fjdingsd.com" location="/index.jsp" /> 2 3 <!DOCTYPE HTML> 4 <html> 5 <head> 6 <title>My JSP 'simpletagdemo.jsp' starting page</title> 7 </head> 8 。。。 9 </html>
结果:若想访问该JSP页面,只有满足请求的URL前缀为page属性指定的网址才能访问,如果是别的web中的超链接或者直接在浏览器中输入该JSP的URL,都会被跳转到location属性指定的网页。
例4:使用简单标签将标签体中的HTML过滤转义
编写标签处理器类:
1 package com.fjdingsd.simpletag; 2 public class HtmlFilterTag extends SimpleTagSupport { 3 4 @Override 5 public void doTag() throws JspException, IOException { 6 JspFragment fragment = this.getJspBody(); 7 StringWriter writer = new StringWriter(); 8 fragment.invoke(writer); 9 StringBuffer buffer = writer.getBuffer(); 10 String content = filter(buffer.toString()); 11 this.getJspContext().getOut().write(content); 12 } 13 14 public String filter(String message) { 15 16 if (message == null) 17 return (null); 18 19 char content[] = new char[message.length()]; 20 message.getChars(0, message.length(), content, 0); 21 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(content.length + 50); 22 for (int i = 0; i < content.length; i++) { 23 switch (content[i]) { 24 case '<': 25 result.append("<"); 26 break; 27 case '>': 28 result.append(">"); 29 break; 30 case '&': 31 result.append("&"); 32 break; 33 case '"': 34 result.append("""); 35 break; 36 default: 37 result.append(content[i]); 38 } 39 } 40 return (result.toString()); 41 } 42 }
其中过滤方法filter方法可以在Tomcat中参考代码(位置:【Tomcat】--->【webapps】--->【examples】--->【WEB-INF】--->【classes】--->【utils】--->“HTMLFilter.java”)。
在TLD文件中定义和描述标签:
1 <tag> 2 <name>filterhtml</name> 3 <tag-class>com.fjdingsd.simpletag.HtmlFilterTag</tag-class> 4 <body-content>scriptless</body-content> 5 </tag>
在JSP页面中的主体部分中使用刚才自定义的简单标签:
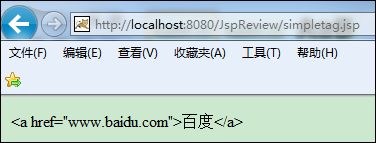
1 <simple:filterhtml> 2 <a href="www.baidu.com">百度</a> 3 </simple:filterhtml>
浏览器中观察: