Cocos2d-x中图字原理之深入分析
[Cocos2d-x相关教程来源于红孩儿的游戏编程之路 CSDN博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/honghaier]
红孩儿Cocos2d-X学习园地QQ群:249941957 加群写:Cocos2d-x
本章为我的Cocos2d-x教程一书初稿。望各位看官多提建议!
首先感谢CSDN对本博的支持,最近一周,本博的两篇博文HelloWorld和HelloLua深入分析入选博客精选被放在CSDN首页!!!
再感谢各位朋友的支持。“HelloWorld深入分析”的阅读量一周超四千。俺还没见过这么大场面~
OK,进入今天正题。
Cocos2d-x中图字原理之深入分析
另:Cocos2d-x版本为http://cn.cocos2d-x.org/download:
cocos2d-1.0.1-x-0.12.0 @ Mar 05, 2012
图字,顾名思义,利用图片做为纹理来显示的文字。当下流行的跨平台2D引擎Cocos2d-x和LibGdx也都有对于图字的应用支持,今天我就来为大家讲一讲图字。
首先要介绍一下,图字是怎么来的?其实这个很早很早了,记得80后在95年开始玩DOS下的仙剑奇侠传的时候,那些令人难忘的中文对话吧!DOS下做游戏,使用的是C语言,不要说写字了,很多复杂的操作甚至涉及驱动。那时候绘图就是利用将图片中的像素取出来后绘制在屏幕上,所以处理游戏中的中文,就只有把这些文字的像素预先写到BMP或二进制文件中,然后读取出来再设置屏幕像素以实现。后来进入DDRAW的时代,可以使用WINDOWS系统中的字库来写字了。把DDRAW的后台表面进行LOCK,取出其DC,然后用GDI将文字写到其DC上,这种做法后面也延续了很久,但GDI进行TextOut的效率非常慢,你要是想像梦幻西游一样满屏写了,那得卡死,解决方案是什么?还是图字。专业的游戏开发者会将所用到的字都预处理生成到一张图片中,通过一个编码与纹理UV对应文件来进行纹理UV的获取后做为顶点的UV值然后进行绘制,有也的在每一帧中实时的将需要的字使用DDRAW写字的方法绘制到相应的纹理上然后使用文字编码与纹理UV对应信息来进行绘制,这样效率就提高很多了。目前比较流行的做法是使用一张png图片来存储用到的文字。一个.fnt文件来存储文字图片说明信息。Cocos2d-x和LibGdx中都集成了相关的图字处理类。在世界范围内,也有很多游戏使用了这个方案。在游戏汉化界,了解和掌握图字的原理和修改方法也是很重要的一项工作。参考文献:http://wenku.baidu.com/view/882c07f37c1cfad6195fa7cf.html
我们以Cocos2d-x的tests工程中的LabelTest中的最后一个Label显示“中国”为例来分析一下。
打开Cocos2d-x所在目录下的tests\Resources\fonts目录,找到bitmapFontChinese.png(文字贴图文件)和bitmapFontChinese.fnt(文字图片说明信息文件)
先打开png,我们可以看到它是512x512大小,上面由12行,14列个文字组成。包括有一些汉字,常用字符,数字和字母。它的每个字都是由青色到蓝色的向下渐变。
再用UEdit或记事本打开bitmapFontChinese.fnt,可以看到它的构成,我在这里讲一下。
第一行是对字体的介绍。
info face="华康海报体W12(P)" size=32 bold=0italic=0 charset="" unicode=0stretchH=100smooth=1 aa=1 padding=0,0,0,0 spacing=1,1
解释:
face="华康海报体W12(P)":字体为”华康海报体W12(P)”,
size=32:大小为32像素
bold=0 :不加粗
italic=0:不使用斜体
charset="": charset是编码字符集,这里没有填写值即使用默认,
unicode=0:不使用Unicode
stretchH=100:纵向缩放百分比
smooth=1 :开启平滑
aa=1:开启抗锯齿
padding=0,0,0,0:内边距,文字与边框的空隙。
spacing=1,1 :外边距,就是相临边缘的距离。
第二行是对应所有字贴图的公共信息
common lineHeight=37 base=28 scaleW=512 scaleH=512pages=1 packed=0
解释:
lineHeight=37:行高,如果遇到换行符时,绘制字的位置坐标的Y值在换行后增加的像素值。
base=28 :字的基本大小
scaleW=512 :图片大小
scaleH=512:图片大小
pages=1 :此种字体共用到几张图。
packed=0:图片不压缩
第三行是对应当前字贴图的信息
//第一页,文件名称是”bitmapFontChinese.png”
page id=0 file="bitmapFontChinese.png"
第四行是当前贴图中所容纳的文字数量
chars count=204
第五行起把当前贴图中所用到的所有文字的编码以及对应在图片上的矩形位置,偏移等列出来
第一个字符编码为32,也就是空格,位置为0,0,宽高为0,0, 绘制到屏幕的相应位置时,像素偏移(0,28),绘制完后相应位置的x往后移15像素再画下一个字符,字的图块在第1页上
char id=32 x=0 y=0 width=0 height=0 xoffset=0 yoffset=28 xadvance=15 page=0 chnl=0
第一个字符编码为汉字”象”,也就是空格,位置为0,0,宽为33,高为36, 绘制到屏幕的相应位置时,像素偏移(0,-1),绘制完后相应位置的x往后移36像素再画下一个字,字的图块在第1页上
char id=35937 x=0 y=0 width=33 height=36 xoffset=0 yoffset=-1 xadvance=36 page=0 chnl=0
char id=26696 x=33 y=0 width=35 height=36 xoffset=-1 yoffset=-1 xadvance=36 page=0 chnl=0
char id=26071 x=68 y=0 width=35 height=36 xoffset=-1 yoffset=-1 xadvance=36 page=0 chnl=0
…
再后面是描述两个字在进行组合绘制时字距调整的相关信息,这里没有要进行间距调整的字组合所以为设-1。对于字组合间距调整可以看此示例图:http://www.blueidea.com/articleimg/2007/12/5160/01s.jpg
kernings count=-1
这个数字代表参与字组合间距调整的字的数量。
如果kernings count大于零,后面会有类似这样的描述:
kerning first=102 second=41 amount=2
也就是’f’与’)’进行组合显示’f)’时,’)’向右移2像素防止粘在一起。
通过上面这些信息,引擎可以通过编码找到相应的文字并取出对应的纹理块。
//Cocos2d-x中LabelBMFontChinese
下面我们来分析一下Cocos2d-x的tests工程中的LabelTest中的最后一个Label,它的类名为CCLabelBMFont.转到其类定义文件CCLabelBMFont.h
class CC_DLL CCLabelBMFont : public CCSpriteBatchNode, public CCLabelProtocol, public CCRGBAProtocol
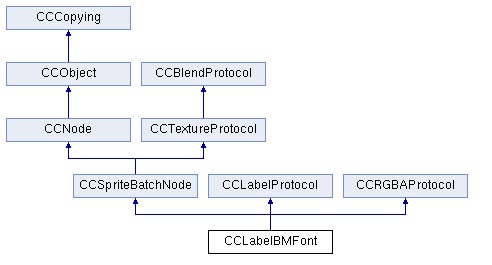
可以看到其直接派生于三个类,分别是
CCSpriteBatchNode :精灵批次管理类,用于将使用一张图的多个精灵在设置一次纹理的批次里进行绘制,提高渲染的效率。
CCLabelProtocol :文字字串类
CCRGBAProtocol:颜色调节接口类
由简入深,我们先来看一下CCRGBAProtocol,打开CCProtocols.h
class CC_DLL CCRGBAProtocol
{
public:
//设置颜色
virtual void setColor(const ccColor3B& color) = 0;
//取得颜色
virtual const ccColor3B& getColor(void) = 0;
//返回透明度
virtual GLubyte getOpacity(void) = 0;
//设置透明度
virtual void setOpacity(GLubyte opacity) = 0;
//设置是否使用Alpha值设置RGB,如果
virtual void setIsOpacityModifyRGB(bool bValue) = 0;
//取得是否使用Alpha值设置RGB
virtual bool getIsOpacityModifyRGB(void) = 0;
};
可以看到CCRGBAProtocol类是个纯虚类,只是定义了一些设置获取颜色信息的接口函数。
继续看CCLabelProtocal,明显的,它也是纯虚类,做为存储字符串的接口使用:
class CC_DLL CCLabelProtocol
{
public:
// 设置文字标签显示的字符串
virtual void setString(const char *label) = 0;
// 返回文字标签显示的字符串
virtual const char* getString(void) = 0;
};
最后来分析CCSpriteBatchNode类。它由CCNodet 和 CCTextureProtocal两个类派生而来,CCNode是基础结点类,用于将引擎中所有具有逻辑顺序和父子关系的类组织起来,基于CCNode派生的类均可以互相挂接。CCNode不是本章要详细介绍的内容,就不再详细分析了,看一下CCTextureProtocol,这是一个纹理使用接口类:
class CC_DLL CCTextureProtocol : public CCBlendProtocol
{
public:
// 返回所使用的2D纹理
virtual CCTexture2D* getTexture(void) = 0;
// 设置使用的2D纹理,并为纹理的使用计数器加1操作
virtual void setTexture(CCTexture2D *texture) = 0;
};
很简单,只有两个函数对纹理进行设置和获取,它派生于CCBlendProtocal,这是一个Alpha混合系数设置接口类,用于在开启Alpha混合状态后对Alpha混合的系数进行设置。再来看一下CCBlendProtocal,这是一个混合状态设置接口类:
class CC_DLL CCBlendProtocol
{
public:
// 为纹理设置使用的混合状态
virtual void setBlendFunc(ccBlendFunc blendFunc) = 0;
// 返回为纹理设置的混合状态
virtual ccBlendFunc getBlendFunc(void) = 0;
};
返回到类CCSpriteBatchNode的定义。我们再来分析CCSpriteBatchNode。之前说了CCSpriteBatchNode是精灵批次管理类,用于将使用一张图的多个精灵在设置一次纹理的批次里进行绘制,提高渲染的效率。既然多个精灵使用一张图,则需要将多个小图块合并在一张图上,这样只要设置使用大图做为纹理,将使用各小图块做为纹理贴图的精灵设置好顶点与UV等数据,就可以绘制出这些精灵了。Cocos2d-x提供了一个类CCTextureAtlas对使用图块的这些精灵所使用的顶点缓冲区进行管理。为了更好的理解CCSpriteBatchNode,我们看一下它的定义和实现:
#ifndef __CCTEXTURE_ATLAS_H__
#define __CCTEXTURE_ATLAS_H__
//用到的头文件
#include <string>
#include "ccTypes.h"
#include "CCObject.h"
#include "ccConfig.h"
//使用Cocos2d命名空间
namespace cocos2d {
class CCTexture2D;
//CCTextureAtlas由CCObject派生而来
class CC_DLL CCTextureAtlas : public CCObject
{
protected:
//使用此大图中的图块的精灵对应的三角形索引数组的指针
GLushort *m_pIndices;
#if CC_USES_VBO
//如果使用Vertex Buffer Object(VBO:使用显存而非内存存储顶点缓冲数据,大大提高效率),建立VBO句柄数组,第一个元素存顶点数组的句柄,第二个元素存索引数组句柄
GLuint m_pBuffersVBO[2];
//标记是否更新需要更新的图块信息。当你新加入了图块或者修改了图块,需要设置为true。
bool m_bDirty;
#endif // CC_USES_VBO
// CC_PROPERTY_READONLY宏为类定义变量及增加相应的get函数。
//当前使用图块的数量
CC_PROPERTY_READONLY(unsigned int, m_uTotalQuads, TotalQuads)
//存储图块信息的数组容量
CC_PROPERTY_READONLY(unsigned int, m_uCapacity, Capacity)
//设置所使用的大图纹理
CC_PROPERTY(CCTexture2D *, m_pTexture, Texture)
//使用此大图的图块的所有精灵的顶点缓冲信息数组
CC_PROPERTY(ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad *, m_pQuads, Quads)
public:
//构造
CCTextureAtlas();
//析构
virtual ~CCTextureAtlas();
//描述
char * description();
//静态函数:从文件中创建纹理,并初始化图块容量
static CCTextureAtlas * textureAtlasWithFile(const char* file , unsigned int capacity);
//同上,只是非静态函数。作者提示不能重复调用,否则会造成内存泄漏。
bool initWithFile(const char* file, unsigned int capacity);
//静态函数:从贴图中创建纹理,并初始化图块容量
static CCTextureAtlas * textureAtlasWithTexture(CCTexture2D *texture, unsigned int capacity);
//同上,只是非静态函数。作者提示不能重复调用,否则会造成内存泄漏。
bool initWithTexture(CCTexture2D *texture, unsigned int capacity);
//通过索引值找到对应的图块顶点缓冲数据并用新数据修改它,由CCSprite实例对象在变换顶点信息时调用。
void updateQuad(ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad* quad, unsigned int index);
//通过索引值找到对应的图块顶点缓冲数据,并在其之前插入一个新的图块。
void insertQuad(ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad* quad, unsigned int index);
//通过索引值找到对应的图块顶点缓冲数据,并把它插入另一个图块之前。
void insertQuadFromIndex(unsigned int fromIndex, unsigned int newIndex);
//移除指定位置的图块顶点缓冲数据.
void removeQuadAtIndex(unsigned int index);
//清空所有的图块顶点缓冲数据。
void removeAllQuads();
//重新设置图块顶点缓冲数组的容量
bool resizeCapacity(unsigned int n);
//绘制指定的图块顶点缓冲
void drawNumberOfQuads(unsigned int n);
//绘制从指定的图块起后面的N个图块
void drawNumberOfQuads(unsigned int n, unsigned int start);
//绘制所有的图块顶点缓冲
void drawQuads();
private:
//初始化索引缓冲数据
void initIndices();
};
}//namespace cocos2d
#endif //__CCTEXTURE_ATLAS_H__
再看CPP:
#include "CCTextureAtlas.h"
#include "CCTextureCache.h"
#include "ccMacros.h"
// 纹理头文件
#include "CCTexture2D.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
//使用Cocos2d命名空间
namespace cocos2d {
//构造,初始化成员变量
CCTextureAtlas::CCTextureAtlas()
:m_pIndices(NULL)
#if CC_USES_VBO
, m_bDirty(false)
#endif
,m_pTexture(NULL)
,m_pQuads(NULL)
{}
//析构,释放所用的内存
CCTextureAtlas::~CCTextureAtlas()
{
// CCLOGINFO("cocos2d: deallocing CCTextureAtlas.");
CC_SAFE_FREE(m_pQuads)
CC_SAFE_FREE(m_pIndices)
#if CC_USES_VBO
//释放缓冲区对象
glDeleteBuffers(2, m_pBuffersVBO);
#endif // CC_USES_VBO
CC_SAFE_RELEASE(m_pTexture);
}
//实现通过宏CC_PROPERTY_READONLY声明的函数
//取得当前使用的图块的数量
unsigned int CCTextureAtlas::getTotalQuads()
{
return m_uTotalQuads;
}
//取得图块集的容量
unsigned int CCTextureAtlas::getCapacity()
{
return m_uCapacity;
}
//取得大纹理
CCTexture2D* CCTextureAtlas::getTexture()
{
return m_pTexture;
}
//设置大纹理
void CCTextureAtlas::setTexture(CCTexture2D * var)
{
CC_SAFE_RETAIN(var);
CC_SAFE_RELEASE(m_pTexture);
m_pTexture = var;
}
//取得使用此大图的图块的所有精灵的顶点缓冲信息数组
ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad* CCTextureAtlas::getQuads()
{
return m_pQuads;
}
//设置使用此大图的图块的所有精灵的顶点缓冲信息数组
void CCTextureAtlas::setQuads(ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad *var)
{
m_pQuads = var;
}
//静态函数:从文件中创建纹理,并初始化图块容量
CCTextureAtlas * CCTextureAtlas::textureAtlasWithFile(const char* file, unsigned int capacity)
{
//使用new来实例化一个CCTextureAtlas对象
CCTextureAtlas * pTextureAtlas = new CCTextureAtlas();
//调用成员函数进行初始化
if(pTextureAtlas && pTextureAtlas->initWithFile(file, capacity))
{
pTextureAtlas->autorelease();
return pTextureAtlas;
}
//如果失败,释放后返回NULL
CC_SAFE_DELETE(pTextureAtlas);
return NULL;
}
//静态函数:从贴图中创建纹理,并初始化图块容量
CCTextureAtlas * CCTextureAtlas::textureAtlasWithTexture(CCTexture2D *texture, unsigned int capacity)
{
//使用new来实例化一个CCTextureAtlas对象
CCTextureAtlas * pTextureAtlas = new CCTextureAtlas();
//调用成员函数进行初始化
if (pTextureAtlas && pTextureAtlas->initWithTexture(texture, capacity))
{
pTextureAtlas->autorelease();
return pTextureAtlas;
}
//如果失败,释放后返回NULL
CC_SAFE_DELETE(pTextureAtlas);
return NULL;
}
//非静态函数,从文件中创建纹理,并初始化图块容量
bool CCTextureAtlas::initWithFile(const char * file, unsigned int capacity)
{
// 由纹理管理器加载一个图片文件,返回生成的纹理
CCTexture2D *texture = CCTextureCache::sharedTextureCache()->addImage(file);
//判断生成纹理是否有效
if (texture)
{
//如果成功,使用纹理进行初始化
return initWithTexture(texture, capacity);
}
else
{
//不成功打印错误日志并返回NULL
CCLOG("cocos2d: Could not open file: %s", file);
delete this;
return NULL;
}
}
//非静态函数,设置纹理,并初始化图块容量
bool CCTextureAtlas::initWithTexture(CCTexture2D *texture, unsigned int capacity)
{
//纹理有效性判断,防止重复调用
CCAssert(texture != NULL, "texture should not be null");
//设置图块容量
m_uCapacity = capacity;
m_uTotalQuads = 0;
// 设置纹理
this->m_pTexture = texture;
CC_SAFE_RETAIN(m_pTexture);
// 判断是否重复调用
CCAssert(m_pQuads == NULL && m_pIndices == NULL, "");
//申请容量大小的的顶点缓冲信息数组
m_pQuads = (ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad*)calloc( sizeof(ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad) * m_uCapacity, 1 );
//申请容量大小的索引缓冲数组
m_pIndices = (GLushort *)calloc( sizeof(GLushort) * m_uCapacity * 6, 1 );
//如果失败,做相应处理
if( ! ( m_pQuads && m_pIndices) && m_uCapacity > 0) {
//CCLOG("cocos2d: CCTextureAtlas: not enough memory");
CC_SAFE_FREE(m_pQuads)
CC_SAFE_FREE(m_pIndices)
CC_SAFE_RELEASE_NULL(m_pTexture);
return false;
}
//初始化缓冲区对象
#if CC_USES_VBO
glGenBuffers(2, &m_pBuffersVBO[0]);
m_bDirty = true;
#endif // CC_USES_VBO
//初始化索引缓冲
this->initIndices();
return true;
}
//取得描述
char * CCTextureAtlas::description()
{
char *ret = new char[100];
sprintf(ret, "<CCTextureAtlas | totalQuads = %u>", m_uTotalQuads);
return ret;
}
//初始化索引缓冲
void CCTextureAtlas::initIndices()
{
//如果容量为0直接返回
if (m_uCapacity == 0)
return;
//按照顶点的顺序和使用的三角形渲染排列方式为索引缓冲填充数据。
for( unsigned int i=0; i < m_uCapacity; i++)
{
#if CC_TEXTURE_ATLAS_USE_TRIANGLE_STRIP
m_pIndices[i*6+0] = i*4+0;
m_pIndices[i*6+1] = i*4+0;
m_pIndices[i*6+2] = i*4+2;
m_pIndices[i*6+3] = i*4+1;
m_pIndices[i*6+4] = i*4+3;
m_pIndices[i*6+5] = i*4+3;
#else
m_pIndices[i*6+0] = (GLushort)(i*4+0);
m_pIndices[i*6+1] = (GLushort)(i*4+1);
m_pIndices[i*6+2] = (GLushort)(i*4+2);
// inverted index. issue #179
m_pIndices[i*6+3] = (GLushort)(i*4+3);
m_pIndices[i*6+4] = (GLushort)(i*4+2);
m_pIndices[i*6+5] = (GLushort)(i*4+1);
// m_pIndices[i*6+3] = i*4+2;
// m_pIndices[i*6+4] = i*4+3;
// m_pIndices[i*6+5] = i*4+1;
#endif
}
#if CC_USES_VBO
//指定m_pBuffersVBO[0]为顶点缓冲区,并激活缓冲区
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, m_pBuffersVBO[0]);
//绑定完成后为其分配内存
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(m_pQuads[0]) * m_uCapacity, m_pQuads, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
//指定m_pBuffersVBO[1]为索引缓冲区,并激活缓冲区
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, m_pBuffersVBO[1]);
//绑定完成后为其分配内存
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(m_pIndices[0]) * m_uCapacity * 6, m_pIndices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
//取消绑定
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
#endif // CC_USES_VBO
}
//通过索引值找到对应图块的顶点缓冲并用新数据修改它
void CCTextureAtlas::updateQuad(ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad *quad, unsigned int index)
{
//有效性判断
CCAssert( index >= 0 && index < m_uCapacity, "updateQuadWithTexture: Invalid index");
//如果index大于现有的数量则更新数量
m_uTotalQuads = max( index+1, m_uTotalQuads);
//修改对应的数据值
m_pQuads[index] = *quad;
//需要更新
#if CC_USES_VBO
m_bDirty = true;
#endif
}
//通过索引值找到对应图块的顶点缓冲,并在其位置之前插入一个新的图块。
void CCTextureAtlas::insertQuad(ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad *quad, unsigned int index)
{
//有效性判断
CCAssert( index < m_uCapacity, "insertQuadWithTexture: Invalid index");
//数量增加
m_uTotalQuads++;
CCAssert( m_uTotalQuads <= m_uCapacity, "invalid totalQuads");
//先将索引位置之后的数据整体后移一个位置,再用新数据填充索引位置的数据。实现插入操作。
unsigned int remaining = (m_uTotalQuads-1) - index;
if( remaining > 0) {
// texture coordinates
memmove( &m_pQuads[index+1],&m_pQuads[index], sizeof(m_pQuads[0]) * remaining );
}
m_pQuads[index] = *quad;
//设置需要更新m_pBuffersVBO中的VBO数组数据。
#if CC_USES_VBO
m_bDirty = true;
#endif
}
//通过索引值找到对应图块的顶点缓冲,并把它插入另一个图块之前。
void CCTextureAtlas::insertQuadFromIndex(unsigned int oldIndex, unsigned int newIndex)
{
//有效性判断
CCAssert( newIndex >= 0 && newIndex < m_uTotalQuads, "insertQuadFromIndex:atIndex: Invalid index");
CCAssert( oldIndex >= 0 && oldIndex < m_uTotalQuads, "insertQuadFromIndex:atIndex: Invalid index");
//两个索引相同直接返回即可
if( oldIndex == newIndex )
return;
//计算要移动的图块数量
unsigned int howMany = (oldIndex - newIndex) > 0 ? (oldIndex - newIndex) : (newIndex - oldIndex);
unsigned int dst = oldIndex;
unsigned int src = oldIndex + 1;
if( oldIndex > newIndex) {
dst = newIndex+1;
src = newIndex;
}
// 开始进行移动
ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad quadsBackup = m_pQuads[oldIndex];
memmove( &m_pQuads[dst],&m_pQuads[src], sizeof(m_pQuads[0]) * howMany );
//更新新索引位置的数据
m_pQuads[newIndex] = quadsBackup;
//设置需要更新m_pBuffersVBO中的VBO数组数据。
#if CC_USES_VBO
m_bDirty = true;
#endif
}
//移除指定位置的图块顶点缓冲
void CCTextureAtlas::removeQuadAtIndex(unsigned int index)
{
//有效性判断
CCAssert( index < m_uTotalQuads, "removeQuadAtIndex: Invalid index");
unsigned int remaining = (m_uTotalQuads-1) - index;
//将索引图块后的所有图块向前移1个位置即可
// last object doesn't need to be moved
if( remaining ) {
// texture coordinates
memmove( &m_pQuads[index],&m_pQuads[index+1], sizeof(m_pQuads[0]) * remaining );
}
//数量减1
m_uTotalQuads--;
//设置需要更新m_pBuffersVBO中的VBO数组数据。
#if CC_USES_VBO
m_bDirty = true;
#endif
}
//移除所有的顶点缓冲数据
void CCTextureAtlas::removeAllQuads()
{
//数量直接置0,这是最快的方式
m_uTotalQuads = 0;
}
// 重新设置图块顶点缓冲数组的容量
bool CCTextureAtlas::resizeCapacity(unsigned int newCapacity)
{
//如果等于原来的容量直接返回
if( newCapacity == m_uCapacity )
return true;
//确保当前绘制的精灵数量最大不能超过容量
m_uTotalQuads = min(m_uTotalQuads, newCapacity);
//更新容量
m_uCapacity = newCapacity;
//定义指针存放要申请的图块信息与索引数组的内存地址
void * tmpQuads = NULL;
void * tmpIndices = NULL;
//为图块的顶点缓冲数组申请内存,注意:如果已占有内存则直接在原内存地址上进行内存长度调整
if (m_pQuads == NULL)
tmpQuads = calloc(sizeof(m_pQuads[0]) * m_uCapacity, 1);
else
tmpQuads = realloc( m_pQuads, sizeof(m_pQuads[0]) * m_uCapacity );
//为图块的索引缓冲数组申请内存, 如果已占有内存则直接在原内存地址上进行内存长度调整
if (m_pIndices == NULL)
tmpIndices = calloc(sizeof(m_pIndices[0]) * m_uCapacity * 6, 1);
else
tmpIndices = realloc( m_pIndices, sizeof(m_pIndices[0]) * m_uCapacity * 6 );
//如果内存申请失败的处理
if( ! ( tmpQuads && tmpIndices) ) {
//CCLOG("cocos2d: CCTextureAtlas: not enough memory");
if( tmpQuads )
free(tmpQuads);
else
free(m_pQuads);
if( tmpIndices )
free(tmpIndices);
else
free(m_pIndices);
m_pQuads = NULL;
m_pIndices = NULL;
m_uCapacity = m_uTotalQuads = 0;
return false;
}
//如果成功,则将内存地址赋给相应成员指针变量
m_pQuads = (ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad *)tmpQuads;
m_pIndices = (GLushort *)tmpIndices;
//释放顶点缓冲对象并重新创建和进行绑定
#if CC_USES_VBO
glDeleteBuffers(2, m_pBuffersVBO);
// initial binding
glGenBuffers(2, &m_pBuffersVBO[0]);
m_bDirty = true;
#endif // CC_USES_VBO
//初始化索引缓冲
this->initIndices();
//设置需要更新m_pBuffersVBO中的VBO数组数据。上面已经设了,这里重复可以不要。
#if CC_USES_VBO
m_bDirty = true;
#endif
return true;
}
//绘制所有的图块顶点缓冲数据
void CCTextureAtlas::drawQuads()
{
this->drawNumberOfQuads(m_uTotalQuads, 0);
}
//绘制指定的图块顶点缓冲数据
void CCTextureAtlas::drawNumberOfQuads(unsigned int n)
{
this->drawNumberOfQuads(n, 0);
}
//绘制从指定的图块顶点缓冲数据起后面的N个图块顶点缓冲数据
void CCTextureAtlas::drawNumberOfQuads(unsigned int n, unsigned int start)
{
// Default GL states: GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_VERTEX_ARRAY, GL_COLOR_ARRAY, GL_TEXTURE_COORD_ARRAY
// Needed states: GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_VERTEX_ARRAY, GL_COLOR_ARRAY, GL_TEXTURE_COORD_ARRAY
// Unneeded states: -
// 如果数量为零直接返回。
if (0 == n)
return;
//设置使用纹理
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_pTexture->getName());
#define kQuadSize sizeof(m_pQuads[0].bl)
//如果使用VBO所进行的渲染设置
#if CC_USES_VBO
//指定m_pBuffersVBO[0]为顶点缓冲区,并激活缓冲区
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, m_pBuffersVBO[0]);
//绑定完成后为其分配内存
#if CC_ENABLE_CACHE_TEXTTURE_DATA
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(m_pQuads[0]) * m_uCapacity, m_pQuads, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
#endif
//在绘制时如果遇到需要更新标记,则重新将顶点缓冲数据更新到绑定的对象上。
if (m_bDirty)
{
glBufferSubData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(m_pQuads[0]) * start, sizeof(m_pQuads[0]) * n, &m_pQuads[start]);
m_bDirty = false;
}
// 对顶点缓冲中的顶点格式进行解释,让显卡知道顶点格式的构成。
// 顶点缓冲中哪个是位置数据
glVertexPointer(3, GL_FLOAT, kQuadSize, (GLvoid*) offsetof( ccV3F_C4B_T2F, vertices));
//顶点缓冲中哪个是颜色数据
glColorPointer(4, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, kQuadSize, (GLvoid*) offsetof( ccV3F_C4B_T2F, colors));
//顶点缓冲中哪个是纹理坐标数据
glTexCoordPointer(2, GL_FLOAT, kQuadSize, (GLvoid*) offsetof( ccV3F_C4B_T2F, texCoords));
//指定m_pBuffersVBO[1]为索引缓冲区,并激活缓冲区 glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, m_pBuffersVBO[1]);
//绑定完成后为其分配内存
#if CC_ENABLE_CACHE_TEXTTURE_DATA
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(m_pIndices[0]) * m_uCapacity * 6, m_pIndices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
#endif
//按照相应的三角形排列进行渲染
#if CC_TEXTURE_ATLAS_USE_TRIANGLE_STRIP
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, (GLsizei)n*6, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, (GLvoid*)(start * 6 * sizeof(m_pIndices[0])));
#else
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, (GLsizei)n*6, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, (GLvoid*)(start * 6 * sizeof(m_pIndices[0])));
#endif // CC_USES_VBO
//从显存上卸载绑定的数据
//停止使用缓冲区
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
#else // ! CC_USES_VBO
//如果不使用VBO所进行的渲染设置
unsigned int offset = (unsigned int)m_pQuads;
//设置OpenGL渲染使用的顶点数据
unsigned int diff = offsetof( ccV3F_C4B_T2F, vertices);
glVertexPointer(3, GL_FLOAT, kQuadSize, (GLvoid*) (offset + diff) );
//设置OpenGL渲染使用的颜色数据
diff = offsetof( ccV3F_C4B_T2F, colors);
glColorPointer(4, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, kQuadSize, (GLvoid*)(offset + diff));
//设置OpenGL渲染使用的纹理坐标数据
diff = offsetof( ccV3F_C4B_T2F, texCoords);
glTexCoordPointer(2, GL_FLOAT, kQuadSize, (GLvoid*)(offset + diff));
//按照相应的三角形排列进行渲染
#if CC_TEXTURE_ATLAS_USE_TRIANGLE_STRIP
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, n*6, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, m_pIndices + start * 6);
#else
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, n*6, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, m_pIndices + start * 6);
#endif
#endif // CC_USES_VBO
}
}//namespace cocos2d
清楚了CCTextureAtlas,现在回过头再来看CCSpriteBatchNode。
class CC_DLL CCSpriteBatchNode : public CCNode, public CCTextureProtocol
{
public:
//析构
~CCSpriteBatchNode();
// 取得纹理图块顶点缓冲管理器。
inline CCTextureAtlas* getTextureAtlas(void) { return m_pobTextureAtlas; }
//设置纹理图块顶点缓冲管理器
inline void setTextureAtlas(CCTextureAtlas* textureAtlas)
{
//如果当前使用的纹理图块顶点缓冲管理器与要设置的纹理图块顶点缓冲管理器不同,先释放原顶点缓冲管理器,再将当前使用的顶点缓冲管理器指针指向要设置顶点缓冲管理器。
if (textureAtlas != m_pobTextureAtlas)
{
CC_SAFE_RETAIN(textureAtlas);
CC_SAFE_RELEASE(m_pobTextureAtlas);
m_pobTextureAtlas = textureAtlas;
}
}
//取得存放所有使用此图块集的CCSprite指针数组
inline CCArray* getDescendants(void) { return m_pobDescendants; }
//静态函数:通过纹理指针按照默认的图块数量29创建一个CCSpriteBatch实例对象。注意:如果游戏运行中图块数量超过这个数值,则数量递增33%以满足需要
static CCSpriteBatchNode* batchNodeWithTexture(CCTexture2D *tex);
//静态函数:通过纹理指针按照设定的图块数量创建一个CCSpriteBatch实例对象。
static CCSpriteBatchNode* batchNodeWithTexture(CCTexture2D* tex, unsigned int capacity);
//静态函数:通过图片名称按照默认的图块数量29创建一个CCSpriteBatch实例对象。
static CCSpriteBatchNode* batchNodeWithFile(const char* fileImage);
//静态函数:通过图片名称按照设定的图块数量创建一个CCSpriteBatch实例对象。
static CCSpriteBatchNode* batchNodeWithFile(const char* fileImage, unsigned int capacity);
//通过纹理指针和图块数量进行初始化。
bool initWithTexture(CCTexture2D *tex, unsigned int capacity);
//通过图片名称和图块数量进行初始化。
bool initWithFile(const char* fileImage, unsigned int capacity);
//扩容,递增1/3的图块数量
void increaseAtlasCapacity();
//通过索引移除一个子结点,参数doCleanUp决定移除的同时是否对其进行释放。
void removeChildAtIndex(unsigned int index, bool doCleanup);
//将一个指定的CCSprite指针插入到子节点指针数组的指定位置
void insertChild(CCSprite *child, unsigned int index);
//移除一个指定的CCSprite指针
void removeSpriteFromAtlas(CCSprite *sprite);
//重新构建指定的CCSprite指针下的所有子结点的索引
unsigned int rebuildIndexInOrder(CCSprite *parent, unsigned int index);
//取得指定CCSprite的所有节点的最大图块索引
unsigned int highestAtlasIndexInChild(CCSprite *sprite);
//取得指定CCSprite的所有节点的最小图块索引
unsigned int lowestAtlasIndexInChild(CCSprite *sprite);
//取得指定CCSprite的Z顺序之上或之下的最近的图块索引
unsigned int atlasIndexForChild(CCSprite *sprite, int z);
// 实现CCTextureProtocol的接口函数
// 取得纹理
virtual CCTexture2D* getTexture(void);
// 设置纹理
virtual void setTexture(CCTexture2D *texture);
//为纹理设置使用的混合状态
virtual void setBlendFunc(ccBlendFunc blendFunc);
//取得混合状态
virtual ccBlendFunc getBlendFunc(void);
//重载CCNode的相关函数
//每一帧要被调用的函数
virtual void visit(void);
//将一个CCNode指针做为自已的子结点
virtual void addChild(CCNode * child);
//将一个CCNode指针以指定的Z顺序做为自已的子结点
virtual void addChild(CCNode * child, int zOrder);
//将一个CCNode指针以指定的Z顺序并附带一个参数值做为自已的子结点
virtual void addChild(CCNode * child, int zOrder, int tag);
//将一个子结点重新设置Z顺序
virtual void reorderChild(CCNode * child, int zOrder);
//将一个子结点删除,并根所参数决定是否释放元素
virtual void removeChild(CCNode* child, bool cleanup);
//将所有的子结点移除,并根所参数决定是否释放元素
virtual void removeAllChildrenWithCleanup(bool cleanup);
//绘制函数
virtual void draw(void);
protected:
//从精灵数据中在图块管理器中插入一个新的图块,注意:并不将精灵放入子结点。 void addQuadFromSprite(CCSprite *sprite, unsigned int index);
//在子结点数组指定位置插入一个新的精灵。注意:并不新建图块。
CCSpriteBatchNode * addSpriteWithoutQuad(CCSprite*child, unsigned int z, int aTag);
private:
//更新混合状态
void updateBlendFunc();
protected:
//使用的纹理图块顶点缓冲管理器
CCTextureAtlas *m_pobTextureAtlas;
//混合状态
ccBlendFunc m_blendFunc;
//指向存放所有使用此纹理中的图块的CCSprite指针数组的指针
CCArray* m_pobDescendants;
};
再看CPP:
//加入用到的头文件
#include "CCSpriteBatchNode.h"
#include "ccConfig.h"
#include "CCSprite.h"
#include "effects/CCGrid.h"
#include "CCDrawingPrimitives.h"
#include "CCTextureCache.h"
#include "CCPointExtension.h"
//使用cocos2d命名空间
namespace cocos2d
{
//定义整型常量defaultCapacity做为默认创建的图块数量
const int defaultCapacity = 29;
//静态函数:通过纹理指针按照默认的图块数量29创建一个CCSpriteBatch实例对象。
CCSpriteBatchNode::batchNodeWithTexture(CCTexture2D *tex)
{
//使用new创建一个CCSpriteBatchNode实例对象。
CCSpriteBatchNode *batchNode = new CCSpriteBatchNode();
//使用纹理指针和默认图块数量对CCSpriteBatchNode实例对象进行初始化。
batchNode->initWithTexture(tex, defaultCapacity);
//设置其由内存管理器进行内存释放。
batchNode->autorelease();
//返回新创建的CCSpriteBatchNode实例对象
return batchNode;
}
//静态函数:通过纹理指针按照设定的图块数量创建一个CCSpriteBatch实例对象。
CCSpriteBatchNode* CCSpriteBatchNode::batchNodeWithTexture(CCTexture2D* tex, unsigned int capacity)
{
//同上一函数
CCSpriteBatchNode *batchNode = new CCSpriteBatchNode();
batchNode->initWithTexture(tex, capacity);
batchNode->autorelease();
return batchNode;
}
//静态函数:通过图片名称按照设定的图块数量创建一个CCSpriteBatch实例对象。
CCSpriteBatchNode* CCSpriteBatchNode::batchNodeWithFile(const char *fileImage, unsigned int capacity)
{
//同上一函数
CCSpriteBatchNode *batchNode = new CCSpriteBatchNode();
//这里参数1改为图片名称
batchNode->initWithFile(fileImage, capacity);
batchNode->autorelease();
return batchNode;
}
//静态函数:通过图片名称按照默认的图块数量29创建一个CCSpriteBatch实例对象
CCSpriteBatchNode* CCSpriteBatchNode::batchNodeWithFile(const char *fileImage)
{
//同上
CCSpriteBatchNode *batchNode = new CCSpriteBatchNode();
batchNode->initWithFile(fileImage, defaultCapacity);
batchNode->autorelease();
return batchNode;
}
//通过纹理指针和图块数量进行初始化。注意:这个函数才是真正进行初始化的实现过程。
bool CCSpriteBatchNode::initWithTexture(CCTexture2D *tex, unsigned int capacity)
{
//设置混合系数,源混合系数为CC_BLEND_SRC,目标混合系数为CC_BLEND_DST,则图像绘制时按照纹理或色彩的Alpha值与背景进行混合。
m_blendFunc.src = CC_BLEND_SRC;
m_blendFunc.dst = CC_BLEND_DST;
//创建一个图片集管理器
m_pobTextureAtlas = new CCTextureAtlas();
//将纹理和图块数量做为参数初始化图片集,这里可知图块集还是依靠CCTextureAtlas类。
m_pobTextureAtlas->initWithTexture(tex, capacity);
//更新混合状态
updateBlendFunc();
// 新建一个CCArray实例,将m_pChildren指向它
m_pChildren = CCArray::array();
//新建一个存放所有使用此图块集的CCSprite指针数组,将m_pobDescendants指向它
m_pobDescendants = CCArray::array();
//分别进行引用计数加1操作。
m_pChildren->retain();
m_pobDescendants->retain();
return true;
}
//通过纹理文件名和图块数量进行初始化。
bool CCSpriteBatchNode::initWithFile(const char* fileImage, unsigned int capacity)
{
//使用纹理管理器加载一个图片,生成的纹理返回给变量pTexture2D
CCTexture2D *pTexture2D = CCTextureCache::sharedTextureCache()->addImage(fileImage);
//以变量pTexture2D为参数调用上一个函数进行初始化
return initWithTexture(pTexture2D, capacity);
}
//析构
CCSpriteBatchNode::~CCSpriteBatchNode()
{
//释放图块集
CC_SAFE_RELEASE(m_pobTextureAtlas);
CC_SAFE_RELEASE(m_pobDescendants);
}
// 是基类CCNode虚函数,是每帧会被调用到的函数。
void CCSpriteBatchNode::visit(void)
{
//如果不显示,则直接返回。
if (! m_bIsVisible)
{
return;
}
//矩阵压栈,保存渲染此结点前的所有OpenGL所需矩阵的值
glPushMatrix();
//如果
if (m_pGrid && m_pGrid->isActive())
{
m_pGrid->beforeDraw();
transformAncestors();
}
//矩阵变量
transform();
//基类CCNode虚函数,用于实现当前CCNode的绘制。
draw();
//
if (m_pGrid && m_pGrid->isActive())
{
m_pGrid->afterDraw(this);
}
//矩阵出栈。恢复渲染此结点前的所有OpenGL所需矩阵的值
glPopMatrix();
}
//将一个CCSprite指针以指定的Z顺序并附带一个参数值做为子结点
void CCSpriteBatchNode::addChild(CCNode *child, int zOrder, int tag)
{
//有效性判断
CCAssert(child != NULL, "child should not be null");
//将结点转为CCSprite
CCSprite *pSprite = (CCSprite*)(child);
// check CCSprite is using the same texture id
//确保pSprite的纹理与图片集的纹理相同才可以放为子结点
CCAssert(pSprite->getTexture()->getName() == m_pobTextureAtlas->getTexture()->getName(), "");
CCNode::addChild(child, zOrder, tag);
//根据填入的Z顺序值取得pSprite所在的子结点索引放在变量uIndex中
unsigned int uIndex = atlasIndexForChild(pSprite, zOrder);
//将pSprite插入到第uIndex个位置
insertChild(pSprite, uIndex);
}
//将一个CCNode指针做为子结点
void CCSpriteBatchNode::addChild(CCNode *child)
{
//调用基类的addChild
CCNode::addChild(child);
}
//将一个CCNode指针以指定的Z顺序做为子结点
void CCSpriteBatchNode::addChild(CCNode *child, int zOrder)
{
//调用基类的addChild
CCNode::addChild(child, zOrder);
}
//将子结点重新设置Z顺序。
void CCSpriteBatchNode::reorderChild(CCNode *child, int zOrder)
{
//结点参数有效性判断
CCAssert(child != NULL, "the child should not be null");
//确保此结点是挂在子结点树上。
CCAssert(m_pChildren->containsObject(child), "sprite batch node should contain the child");
//如果顺序已经与结点的Z顺序相等则直接返回
if (zOrder == child->getZOrder())
{
return;
}
//子结点引用计数加1
child->retain();
//将子结点从子结点树上移除
removeChild((CCSprite*)child, false);
//按照新的Z顺序插入结点树
addChild(child, zOrder);
//引用计数减1
child->release();
}
//将一个CCNode指针从子结点数组中删除,并根所参数决定是否释放元素
void CCSpriteBatchNode::removeChild(CCNode *child, bool cleanup)
{
//将结点转为CCSprite
CCSprite *pSprite = (CCSprite*)(child);
// explicit null handling
if (pSprite == NULL)
{
return;
}
//确保子结点树中有pSprite
CCAssert(m_pChildren->containsObject(pSprite), "sprite batch node should contain the child");
//移除一个指定的CCSprite指针
removeSpriteFromAtlas(pSprite);
//调用基类的移除子结点函数
CCNode::removeChild(pSprite, cleanup);
}
//通过索引移除一个子结点,参数doCleanUp决定移除的同时是否对其进行释放。
void CCSpriteBatchNode::removeChildAtIndex(unsigned int uIndex, bool bDoCleanup)
{
removeChild((CCSprite*)(m_pChildren->objectAtIndex(uIndex)), bDoCleanup);
}
//将所有的子结点数组元素移除,并根所参数决定是否释放元素
void CCSpriteBatchNode::removeAllChildrenWithCleanup(bool bCleanup)
{
// 如果有子结点
if (m_pChildren && m_pChildren->count() > 0)
{
//遍历子结点调用移除子结点函数
CCObject* pObject = NULL;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(m_pChildren, pObject)
{
CCSprite* pChild = (CCSprite*) pObject;
if (pChild)
{
removeSpriteFromAtlas(pChild);
}
}
}
//调用基类的移除子结点函数
CCNode::removeAllChildrenWithCleanup(bCleanup);
//清空使用此图块集的CCSprite指针数组
m_pobDescendants->removeAllObjects();
//清空图块集管理器中的图块信息
m_pobTextureAtlas->removeAllQuads();
}
//绘制当前CCNode
void CCSpriteBatchNode::draw(void)
{
//调用基类CCNode的draw函数
CCNode::draw();
// 如果图块集为空直接返回
if (m_pobTextureAtlas->getTotalQuads() == 0)
{
return;
}
// 如果图块集不为空
if (m_pobDescendants && m_pobDescendants->count() > 0)
{
//遍历所有使用此图块集的CCSprite
CCObject* pObject = NULL;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(m_pobDescendants, pObject)
{
CCSprite* pChild = (CCSprite*) pObject;
if (pChild)
{
// 更新CCSprite的矩阵,注意:此句内部实现将子结点pChild所指的精灵的位置更新到对应的图块集顶点缓冲中。
pChild->updateTransform();
#if CC_SPRITEBATCHNODE_DEBUG_DRAW
// 如果开启调试,则绘制CCSprite的包围矩形
CCRect rect = pChild->boundingBox();
CCPoint vertices[4]={
ccp(rect.origin.x,rect.origin.y),
ccp(rect.origin.x+rect.size.width,rect.origin.y),
ccp(rect.origin.x+rect.size.width,rect.origin.y+rect.size.height),
ccp(rect.origin.x,rect.origin.y+rect.size.height),
};
ccDrawPoly(vertices, 4, true);
#endif // CC_SPRITEBATCHNODE_DEBUG_DRAW
}
}
}
// 设置ALPHA混合状态
bool newBlend = m_blendFunc.src != CC_BLEND_SRC || m_blendFunc.dst != CC_BLEND_DST;
if (newBlend)
{
glBlendFunc(m_blendFunc.src, m_blendFunc.dst);
}
//绘制图块集
m_pobTextureAtlas->drawQuads();
//恢复原ALPHA混合状态
if (newBlend)
{
glBlendFunc(CC_BLEND_SRC, CC_BLEND_DST);
}
}
//扩容,递增1/3的图块数量
void CCSpriteBatchNode::increaseAtlasCapacity(void)
{
// this is likely computationally expensive
// 如果当前需要的图块数量比实际图块数量大,则将图块的数量增加1/3。
unsigned int quantity = (m_pobTextureAtlas->getCapacity() + 1) * 4 / 3;
// 打印图块数量的变化信息
CCLOG("cocos2d: CCSpriteBatchNode: resizing TextureAtlas capacity from [%lu] to [%lu].",
(long)m_pobTextureAtlas->getCapacity(),
(long)quantity);
//图块集重新设置数量,resizeCapacity按新的图块集数量重新计算每个图块的纹理UV
if (! m_pobTextureAtlas->resizeCapacity(quantity))
{
// 如果失败,返回出错信息。
CCLOG("cocos2d: WARNING: Not enough memory to resize the atlas");
CCAssert(false, "Not enough memory to resize the atla");
}
}
//重新构建指定的CCSprite指针下的所有子结点的索引
unsigned int CCSpriteBatchNode::rebuildIndexInOrder(CCSprite *pobParent, unsigned int uIndex)
{
//取得参数pobParent的所有子结点数组
CCArray *pChildren = pobParent->getChildren();
//如果子结点数组不为空
if (pChildren && pChildren->count() > 0)
{
//遍历子结点数组并
CCObject* pObject = NULL;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(pChildren, pObject)
{
CCSprite* pChild = (CCSprite*) pObject;
if (pChild && (pChild->getZOrder() < 0))
{
uIndex = rebuildIndexInOrder(pChild, uIndex);
}
}
}
// 如果pobParent
if (! pobParent->isEqual(this))
{
pobParent->setAtlasIndex(uIndex);
uIndex++;
}
//如果子结点数组不为空
if (pChildren && pChildren->count() > 0)
{
//遍历子结点数组并
CCObject* pObject = NULL;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(pChildren, pObject)
{
CCSprite* pChild = (CCSprite*) pObject;
if (pChild && (pChild->getZOrder() >= 0))
{
uIndex = rebuildIndexInOrder(pChild, uIndex);
}
}
}
return uIndex;
}
//取得指定CCSprite的所有节点的最大图块索引
unsigned int CCSpriteBatchNode::highestAtlasIndexInChild(CCSprite *pSprite)
{
//取得指定CCSprite的子结点数组
CCArray *pChildren = pSprite->getChildren();
//如果没有子结点,直接返回指定CCSprite的图块索引
if (! pChildren || pChildren->count() == 0)
{
return pSprite->getAtlasIndex();
}
else
{
return highestAtlasIndexInChild((CCSprite*)(pChildren->lastObject()));
}
}
//取得指定CCSprite的所有节点的最小图块索引
unsigned int CCSpriteBatchNode::lowestAtlasIndexInChild(CCSprite *pSprite)
{
CCArray *pChildren = pSprite->getChildren();
//取得指定CCSprite的子结点数
if (! pChildren || pChildren->count() == 0)
{
//取得指定CCSprite的子结点数组
return pSprite->getAtlasIndex();
}
else
{
return lowestAtlasIndexInChild((CCSprite*)(pChildren->objectAtIndex(0)));
}
}
//取得对应的子结点的Z顺序之上或之下的最近图块索引
unsigned int CCSpriteBatchNode::atlasIndexForChild(CCSprite *pobSprite, int nZ)
{
//取得pobSprite的父节点的所有子结点数组。
CCArray *pBrothers = pobSprite->getParent()->getChildren();
//查询pobSprite在所有子结点数组中的索引
unsigned int uChildIndex = pBrothers->indexOfObject(pobSprite);
// 判断当前节点是否是pobSprite的父结点,将结果存入bIgnoreParent。
bool bIgnoreParent = (CCSpriteBatchNode*)(pobSprite->getParent()) == this;
// 新建指针变量pPrevious,用于存储pobSprite的前一个结点。
CCSprite *pPrevious = NULL;
if (uChildIndex > 0 &&
uChildIndex < UINT_MAX)
{
//取得pobSprite在所有子结点中的位置前一个节点。
pPrevious = (CCSprite*)(pBrothers->objectAtIndex(uChildIndex - 1));
}
// 如果当前节点是pobSprite的父结点。
if (bIgnoreParent)
{
//如果pobSprite就是第一个子结点。则返回0。
if (uChildIndex == 0)
{
return 0;
}
//如果pobSprite不是第一个子结点,则返回pobSprite的前一个结点的最大图块索引,加1返回。
return highestAtlasIndexInChild(pPrevious) + 1;
}
// 当前节点不是pobSprite的父结点。
// 如果pobSprite是其父节点的第一子结点
if (uChildIndex == 0)
{
//新建指针变量p,指向pobSprite的父结点。
CCSprite *p = (CCSprite*)(pobSprite->getParent());
// less than parent and brothers
// 如果nZ小于零,即在其之下的最近索引
if (nZ < 0)
{
//返回pobSprite的父结点的图块索引。
return p->getAtlasIndex();
}
else
{ //如果nZ大于零,即在其之上的最近索引
//返回pobSprite的父结点的图块索引值加1。
return p->getAtlasIndex() + 1;
}
}
else
{
//如果pobSprite不是其父节点的第一子结点
if ((pPrevious->getZOrder() < 0 && nZ < 0) || (pPrevious->getZOrder() >= 0 && nZ >= 0))
{
//返回pobSprite前一个节点的的最大图块索引加1
return highestAtlasIndexInChild(pPrevious) + 1;
}
// 否则返回其父节点的图块索引值加1
// else (previous < 0 and sprite >= 0 )
CCSprite *p = (CCSprite*)(pobSprite->getParent());
return p->getAtlasIndex() + 1;
}
// 如果进行到这一步,已经出错了。打印出错信息。
CCAssert(0, "should not run here");
return 0;
}
//将一个CCSprite插入到子节点指针数组的指定位置
void CCSpriteBatchNode::insertChild(CCSprite *pobSprite, unsigned int uIndex)
{
//pobSprite应用此图片集
pobSprite->useBatchNode(this);
//设置图块集索引值
pobSprite->setAtlasIndex(uIndex);
//设置pobSprite在绘制时需要进行绑定图块的更新
pobSprite->setDirty(true);
//如果图块集已经达到最大容量则进行扩容
if (m_pobTextureAtlas->getTotalQuads() == m_pobTextureAtlas->getCapacity())
{
increaseAtlasCapacity();
}
//在图块集管理器中新增加一个图块,并指定其索引
ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad quad = pobSprite->getQuad();
m_pobTextureAtlas->insertQuad(&quad, uIndex);
//将pobSprite放入到使用此图集子结点数组的对应位置
m_pobDescendants->insertObject(pobSprite, uIndex);
// 更新索引
unsigned int i = 0;
//如果使用此图集的子结点数组不为空,遍历并重设一下大于此索引的所有子结点。
if (m_pobDescendants && m_pobDescendants->count() > 0)
{
CCObject* pObject = NULL;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(m_pobDescendants, pObject)
{
CCSprite* pChild = (CCSprite*) pObject;
if (pChild)
{
if (i > uIndex)
{
pChild->setAtlasIndex(pChild->getAtlasIndex() + 1);
}
++i;
}
}
}
// 取得pobSprite的子结点数组
CCArray *pChildren = pobSprite->getChildren();
// 如果不为空,遍历并将子结点也按照Z顺序放入到当前CCSpriteBatchNode的子结点数组中。
if (pChildren && pChildren->count() > 0)
{
CCObject* pObject = NULL;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(pChildren, pObject)
{
CCSprite* pChild = (CCSprite*) pObject;
if (pChild)
{
unsigned int uIndex = atlasIndexForChild(pChild, pChild->getZOrder());
insertChild(pChild, uIndex);
}
}
}
}
//移除一个CCSprite
void CCSpriteBatchNode::removeSpriteFromAtlas(CCSprite *pobSprite)
{
// 从图块管理器中移除目标精灵pobSprite所用的图块信息
m_pobTextureAtlas->removeQuadAtIndex(pobSprite->getAtlasIndex());
//重置目标精灵pobSprite所使用的图块信息
pobSprite->useSelfRender();
//取得目标精灵pobSprite在CCSpriteBatchNode的子结点中数组中的位置
unsigned int uIndex = m_pobDescendants->indexOfObject(pobSprite);
//如果找到后,从子结点数组中移除它
if (uIndex != UINT_MAX)
{
m_pobDescendants->removeObjectAtIndex(uIndex);
// 取得子结点的数组元素数量,遍历大于当前索引的子结点,向前移一个位置。注意:这个for循环从uIndex开始计数。
unsigned int count = m_pobDescendants->count();
for(; uIndex < count; ++uIndex)
{
CCSprite* s = (CCSprite*)(m_pobDescendants->objectAtIndex(uIndex));
s->setAtlasIndex( s->getAtlasIndex() - 1 );
}
}
// 取得目标精灵的子结点数组,遍历并从当前CCSpriteBatchNode的子结点数组中移除。
CCArray *pChildren = pobSprite->getChildren();
if (pChildren && pChildren->count() > 0)
{
CCObject* pObject = NULL;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(pChildren, pObject)
{
CCSprite* pChild = (CCSprite*) pObject;
if (pChild)
{
removeSpriteFromAtlas(pChild);
}
}
}
}
//更新Alpha混合状态
void CCSpriteBatchNode::updateBlendFunc(void)
{
//如果当前图块集对应的纹理有Alpha通道
if (! m_pobTextureAtlas->getTexture()->getHasPremultipliedAlpha())
{
//设置GL_SRC_ALPHA表示使用源颜色的alpha值来作源混合因子。
m_blendFunc.src = GL_SRC_ALPHA;
// GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA表示用1.0减去源颜色的alpha值来作为目标混合因子。
m_blendFunc.dst = GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA;
}
}
// 设置Alpha混合状态
void CCSpriteBatchNode::setBlendFunc(ccBlendFunc blendFunc)
{
m_blendFunc = blendFunc;
}
// 取得Alpha混合状态
ccBlendFunc CCSpriteBatchNode::getBlendFunc(void)
{
return m_blendFunc;
}
//取得图块集所应用的纹理贴图。
CCTexture2D* CCSpriteBatchNode::getTexture(void)
{
return m_pobTextureAtlas->getTexture();
}
//设置图块集所应用的纹理贴图
void CCSpriteBatchNode::setTexture(CCTexture2D *texture)
{
m_pobTextureAtlas->setTexture(texture);
//设置完后跟据纹理贴图是否有Alpha通道更新一下混合状态。
updateBlendFunc();
}
//从精灵数据中在图块管理器中插入一个新的图块,注意:并不将精灵放入子结点。
void CCSpriteBatchNode::addQuadFromSprite(CCSprite *sprite, unsigned int index)
{
//判断sprite是否有效。
CCAssert( sprite != NULL, "Argument must be non-nil");
//如果指定的索引大于图块集的数量或者图块集的数量已经达到最大值,则需要对图块集进行扩容。
while(index >= m_pobTextureAtlas->getCapacity() || m_pobTextureAtlas->getCapacity() == m_pobTextureAtlas->getTotalQuads())
{
this->increaseAtlasCapacity();
}
//让sprite使用此图集管理器
sprite->useBatchNode(this);
//设置sprite的图块索引
sprite->setAtlasIndex(index);
//新建一个图块顶点信息放入图块信息管理器中。
ccV3F_C4B_T2F_Quad quad = sprite->getQuad();
m_pobTextureAtlas->insertQuad(&quad, index);
//设置在缓制sprite时更新一下图块信息
sprite->setDirty(true);
//将sprite的顶点位置信息填充入图块顶点缓冲管理器中的顶点数据中。
sprite->updateTransform();
}
//在子结点数组指定位置插入一个新的精灵。注意:并不新建图块。
CCSpriteBatchNode * CCSpriteBatchNode::addSpriteWithoutQuad(CCSprite*child, unsigned int z, int aTag)
{
//判断sprite是否有效。
CCAssert( child != NULL, "Argument must be non-nil");
//设置sprite的图块索引
child->setAtlasIndex(z);
//遍历子结点数组查看当前Z值应该排在哪个位置。
int i=0;
if (m_pobDescendants && m_pobDescendants->count() > 0)
{
CCObject* pObject = NULL;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(m_pobDescendants, pObject)
{
CCSprite* pChild = (CCSprite*) pObject;
if (pChild && (pChild->getAtlasIndex() >= z))
{
++i;
}
}
}
//取得位置i,插入child到数组中。
m_pobDescendants->insertObject(child, i);
//基类同名函数
CCNode::addChild(child, z, aTag);
return this;
}
}
分析这个类的确是费功夫啊,呵呵。继续之前。喝口水先。话说今天听新闻,北京PM2.5浓度又升高了,我可怜的嗓子,担忧中…
走到这里,我们已经了解了CCSpriteBatchNode的作用。其实红孩儿在开发引擎的经历中也有过类似的设计,为了渲染大量相同类型的模型,按照纹理将子模型归类,并将这些纹理进行合并生成大纹理,渲染时设置大纹理就可以渲染出多个不同类型的子模型,如果开启克隆实例,则可以在一个批次内渲出上百个模型。原理相通,目的只有一个,提高渲染效率。
CCLabelBMFont类中关于图字纹理和图块的相关知识我们了解完了,但是我们仍然没有发现Fnt用在哪里,所以我们只理解了一半,现在我们来理解另一半。CCLabelBMFont中使用到一个类CCBMFontConfiguration,它就是用来读取Fnt文件中的文字图片说明信息的。在CCLabelBMFont.h中我们找到它
class CC_DLL CCBMFontConfiguration : public CCObject
{
public:
//通过map容器对字的编码值和对应的信息做映射
std::map<unsigned int, ccBMFontDef>* m_pBitmapFontArray;
//FNT文件中的字图块公共项:Height
unsigned int m_uCommonHeight;
//FNT文件中的信息:边距,文字与边框的空隙
ccBMFontPadding m_tPadding;
//FNT文件中的信息:用到的png图
std::string m_sAtlasName;
//FNT文件中的信息:两个字在先后绘制时的间距调整的信息结构的哈希字典(其实就是个数组,以哈希算法进行存储)。
struct _KerningHashElement *m_pKerningDictionary;
public:
//构造
CCBMFontConfiguration();
//析构
virtual ~CCBMFontConfiguration();
//取得描述
char * description();
//静态函数:将FNT文件加载进来返回一个CCBMFontConfiguration实例对象。
static CCBMFontConfiguration * configurationWithFNTFile(const char *FNTfile);
//使用FNT文件初始化
bool initWithFNTfile(const char *FNTfile);
private:
//解析FNT文件
void parseConfigFile(const char *controlFile);
//从文件中取得字符的编码及UV对应信息
void parseCharacterDefinition(std::string line, ccBMFontDef *characterDefinition);
//从文件取得字体说明
void parseInfoArguments(std::string line);
//从文件取得字符图块公共信息
void parseCommonArguments(std::string line);
//从文件取得图片文件名称
void parseImageFileName(std::string line, const char *fntFile);
//从文件取得要调整间距的字组合信息容量
void parseKerningCapacity(std::string line);
//从文件取得要调整间距的字组合信息
void parseKerningEntry(std::string line);
//从文件取得调整间距的字组合信息字典
void purgeKerningDictionary();
};
太棒了,它对Fnt文件做了全面的解析。马上看CPP他是怎么现实的。
初始化全局容器指针为空
CCMutableDictionary<std::string, CCBMFontConfiguration*> *configurations = NULL;
//全局函数:从Fnt文件中取得一个CCBMFontConfiguration实例对象
CCBMFontConfiguration* FNTConfigLoadFile( const char *fntFile)
{
//创建CCBMFontConfiguration指针变量pRet并置空
CCBMFontConfiguration *pRet = NULL;
//如果容器为空则新建容器
if( configurations == NULL )
{
configurations = new CCMutableDictionary<std::string, CCBMFontConfiguration*>();
}
//在容器中取得该文件对应的CCBMFontConfiguration
std::string key(fntFile);
pRet = configurations->objectForKey(key);
if( pRet == NULL )
{
//如果为空则调用CCBMFontConfiguration静态函数新建一个CCBMFontConfiguration读取文件返回信息结构给pRet
pRet = CCBMFontConfiguration::configurationWithFNTFile(fntFile);
//并将其加入容器中
configurations->setObject(pRet, key);
}
return pRet;
}
//释放容器中的数据并释放容器占用内存
void FNTConfigRemoveCache( void )
{
if (configurations)
{
configurations->removeAllObjects();
CC_SAFE_RELEASE_NULL(configurations);
}
}
//用于进行获取间距调整信息的哈希参数结构
typedef struct _KerningHashElement
{
int key; // key for the hash. 16-bit for 1st element, 16-bit for 2nd element
int amount;
UT_hash_handle hh;
} tKerningHashElement;
//静态函数,从Fnt文件中取得一个CCBMFontConfiguration实例对象
CCBMFontConfiguration * CCBMFontConfiguration::configurationWithFNTFile(const char *FNTfile)
{
//新建一个CCBMFontConfiguration实例对象
CCBMFontConfiguration * pRet = new CCBMFontConfiguration();
//使用FNT文件信息初始化
if (pRet->initWithFNTfile(FNTfile))
{
pRet->autorelease();
return pRet;
}
CC_SAFE_DELETE(pRet);
return NULL;
}
//由FNT文件对CCBMFontConfiguration实例对象进行初始化
bool CCBMFontConfiguration::initWithFNTfile(const char *FNTfile)
{
//有效性判断
CCAssert(FNTfile != NULL && strlen(FNTfile)!=0, "");
//解析FNT文件
m_pKerningDictionary = NULL;
this->parseConfigFile(FNTfile);
return true;
}
//构造函数
CCBMFontConfiguration::CCBMFontConfiguration()
: m_pBitmapFontArray(new std::map<unsigned int, ccBMFontDef>)
, m_uCommonHeight(0)
, m_pKerningDictionary(NULL)
{
}
//析构
CCBMFontConfiguration::~CCBMFontConfiguration()
{
//打印日志
CCLOGINFO( "cocos2d: deallocing CCBMFontConfiguration" );
//释放占用内存
CC_SAFE_DELETE(m_pBitmapFontArray);
this->purgeKerningDictionary();
m_sAtlasName.clear();
}
//取得描述
char * CCBMFontConfiguration::description(void)
{
char *ret = new char[100];
sprintf(ret, "<CCBMFontConfiguration | Kernings:%d | Image = %s>", HASH_COUNT(m_pKerningDictionary), m_sAtlasName.c_str());
return ret;
}
//释放间距信息字典
void CCBMFontConfiguration::purgeKerningDictionary()
{
tKerningHashElement *current;
while(m_pKerningDictionary)
{
current = m_pKerningDictionary;
HASH_DEL(m_pKerningDictionary,current);
free(current);
}
}
//解析FNT文件
void CCBMFontConfiguration::parseConfigFile(const char *controlFile)
{
//通过文件名找出对应的文件路径
std::string fullpath = CCFileUtils::fullPathFromRelativePath(controlFile);
//打开文件进行读操作,执行后会将文件读取到CCFileData创建的内存志中。
CCFileData data(fullpath.c_str(), "rb");
//取得文件大小
unsigned long nBufSize = data.getSize();
//取得CCFileData存储读取信息的内存块。
char* pBuffer = (char*) data.getBuffer();
//有效检查
CCAssert(pBuffer, "CCBMFontConfiguration::parseConfigFile | Open file error.");
if (!pBuffer)
{
return;
}
std::string line;
//将文件信息放入到字符串strLeft中
std::string strLeft(pBuffer, nBufSize);
//遍历字符串中每个字符进行解析
while (strLeft.length() > 0)
{
//根据换行符取出每一行
int pos = strLeft.find('\n');
//如果不是结尾
if (pos != (int)std::string::npos)
{
//取出此行
line = strLeft.substr(0, pos);
//更新当前字符串为新一行位置后面的字符串
strLeft = strLeft.substr(pos + 1);
}
else
{
//取后一行
line = strLeft;
strLeft.erase();
}
//如果是字体介绍信息
if(line.substr(0,strlen("info face")) == "info face")
{
//解析信息行
this->parseInfoArguments(line);
}
//如果是图块公共信息
else if(line.substr(0,strlen("common lineHeight")) == "common lineHeight")
{
//解析图块公共信息
this->parseCommonArguments(line);
}
//如果是指定索引的图片说明信息
else if(line.substr(0,strlen("page id")) == "page id")
{
//解析指定索引的图片的说明信息
this->parseImageFileName(line, controlFile);
}
//如果是本图片中的字符数量
else if(line.substr(0,strlen("chars c")) == "chars c")
{
//本句忽略了,无意义,后面读取字符时可以统计
}
//如果是字符信息
else if(line.substr(0,strlen("char")) == "char")
{
//一个字符的编码对应信息
ccBMFontDef characterDefinition;
//将本行字符串解析到字符的编码对应信息中
this->parseCharacterDefinition(line, &characterDefinition);
通过信息索引存入哈希字典
(*m_pBitmapFontArray)[ characterDefinition.charID ] = characterDefinition;
}
//如果有间距调整信息
else if(line.substr(0,strlen("kernings count")) == "kernings count")
{
//那也得解析啊~
this->parseKerningCapacity(line);
}
//解析后面的间距调整
else if(line.substr(0,strlen("kerning first")) == "kerning first")
{
//解析间距调整信息
this->parseKerningEntry(line);
}
}
}
//解析指定索引的图片的说明信息
void CCBMFontConfiguration::parseImageFileName(std::string line, const char *fntFile)
{
//先取得id
int index = line.find('=')+1;
int index2 = line.find(' ', index);
std::string value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
//这里只使用了第一张图。所以要求索引为0
CCAssert(atoi(value.c_str()) == 0, "LabelBMFont file could not be found");
// 取得文件名称
index = line.find('"')+1;
index2 = line.find('"', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
//将文件名对应的全路径存入到字符串m_sAtlasName中
m_sAtlasName = CCFileUtils::fullPathFromRelativeFile(value.c_str(), fntFile);
}
//解析字体介绍信息
void CCBMFontConfiguration::parseInfoArguments(std::string line)
{
//实际使用中,其实只用到了内边距padding,因为最终显示结果还是需要从图块中获取,既然已经有了图块,那至于字体的字体,大小,是否平滑等信息其实不会影响什么,只是用来做一个说明罢了。
// 内边距padding
int index = line.find("padding=");
int index2 = line.find(' ', index);
std::string value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "padding=%d,%d,%d,%d", &m_tPadding.top, &m_tPadding.right, &m_tPadding.bottom, &m_tPadding.left);
CCLOG("cocos2d: padding: %d,%d,%d,%d", m_tPadding.left, m_tPadding.top, m_tPadding.right, m_tPadding.bottom);
}
//解析字块公共信息
void CCBMFontConfiguration::parseCommonArguments(std::string line)
{
// LineHeight:行高
int index = line.find("lineHeight=");
int index2 = line.find(' ', index);
std::string value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "lineHeight=%u", &m_uCommonHeight);
// scaleW:图片宽
index = line.find("scaleW=") + strlen("scaleW=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
CCAssert(atoi(value.c_str()) <= CCConfiguration::sharedConfiguration()->getMaxTextureSize(), "CCLabelBMFont: page can't be larger than supported");
// scaleH:图片高
index = line.find("scaleH=") + strlen("scaleH=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
CCAssert(atoi(value.c_str()) <= CCConfiguration::sharedConfiguration()->getMaxTextureSize(), "CCLabelBMFont: page can't be larger than supported");
// pages:共有几张文字图片供使用
index = line.find("pages=") + strlen("pages=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
CCAssert(atoi(value.c_str()) == 1, "CCBitfontAtlas: only supports 1 page");
//packed忽略
}
//解析字符编码与UV对应信息块
void CCBMFontConfiguration::parseCharacterDefinition(std::string line, ccBMFontDef *characterDefinition)
{
//读取编码值
int index = line.find("id=");
int index2 = line.find(' ', index);
std::string value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "id=%u", &characterDefinition->charID);
// 在图块中的像素横向位置
index = line.find("x=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "x=%f", &characterDefinition->rect.origin.x);
// 在图块中的像素纵向位置
index = line.find("y=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "y=%f", &characterDefinition->rect.origin.y);
// 对应图块的宽
index = line.find("width=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "width=%f", &characterDefinition->rect.size.width);
// 对应图块的高
index = line.find("height=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "height=%f", &characterDefinition->rect.size.height);
// 当前字在绘制时的像素偏移横向位置
index = line.find("xoffset=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "xoffset=%d", &characterDefinition->xOffset);
// 当前字在绘制时的像素偏移纵向位置
index = line.find("yoffset=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "yoffset=%d", &characterDefinition->yOffset);
// 绘制完当前字后,光标向后移多少像素以绘制下一个字
index = line.find("xadvance=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "xadvance=%d", &characterDefinition->xAdvance);
}
//解析某两个字在一起时字距调整信息并存入哈希字典
void CCBMFontConfiguration::parseKerningCapacity(std::string line)
{
//同样没有什么意义,字数量可以统过后面的解析统计出来
}
//解析字距调整信息
void CCBMFontConfiguration::parseKerningEntry(std::string line)
{
// first解析第一个字
int first;
int index = line.find("first=");
int index2 = line.find(' ', index);
std::string value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "first=%d", &first);
// second:解析第二个字
int second;
index = line.find("second=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "second=%d", &second);
// amount:解析要调整的像素个数,负值向左,正值向右
int amount;
index = line.find("amount=");
index2 = line.find(' ', index);
value = line.substr(index, index2-index);
sscanf(value.c_str(), "amount=%d", &amount);
//将对应关系存入哈希字典
tKerningHashElement *element = (tKerningHashElement *)calloc( sizeof( *element ), 1 );
element->amount = amount;
element->key = (first<<16) | (second&0xffff);
HASH_ADD_INT(m_pKerningDictionary,key, element);
}
CCBMFontConfiguration类分析完了,CCLabelBMFont就很容易理解了。快马加鞭向前冲哟~
class CC_DLL CCLabelBMFont : public CCSpriteBatchNode, public CCLabelProtocol, public CCRGBAProtocol
{
//容量
CC_PROPERTY(GLubyte, m_cOpacity, Opacity)
//颜色
CC_PROPERTY_PASS_BY_REF(ccColor3B, m_tColor, Color)
//是否使用透明度来设置RGB值
CC_PROPERTY(bool, m_bIsOpacityModifyRGB, IsOpacityModifyRGB)
protected:
// 要渲染的字符串
std::string m_sString;
//使用的设置
CCBMFontConfiguration *m_pConfiguration;
public:
//构造函数。
CCLabelBMFont()
: m_cOpacity(0)
, m_bIsOpacityModifyRGB(false)
, m_sString("")
, m_pConfiguration(NULL)
{}
//析构
virtual ~CCLabelBMFont();
//释放占用的内存
static void purgeCachedData();
//由一个字符串和字体fnt文件创建图字
bool initWithString(const char *str, const char *fntFile);
//重点函数:根据字符串和字体信息进行纹理图对应
void createFontChars();
//设置要渲染的字符串
virtual void setString(const char *label);
//取得要渲染的字符串
virtual const char* getString(void);
//设置要渲染的字符串,setString的别名函数
virtual void setCString(const char *label);
//设置锚点
virtual void setAnchorPoint(const CCPoint& var);
//绘制函数
#if CC_LABELBMFONT_DEBUG_DRAW
virtual void draw();
#endif // CC_LABELBMFONT_DEBUG_DRAW
private:
char * atlasNameFromFntFile(const char *fntFile);
int kerningAmountForFirst(unsigned short first, unsigned short second);
};
CPP文件:
//释放占用的内存
void CCLabelBMFont::purgeCachedData()
{
//释放文字FNT信息指针
FNTConfigRemoveCache();
}
//静态函数:由一个字符串和字体fnt文件创建图字
CCLabelBMFont *CCLabelBMFont::labelWithString(const char *str, const char *fntFile)
{
//new 出一个新的CCLabelBMFont
CCLabelBMFont *pRet = new CCLabelBMFont();
//调用其成员函数initWithString创建图字
if(pRet && pRet->initWithString(str, fntFile))
{
//交由内存管理器进行内存管理。
pRet->autorelease();
return pRet;
}
CC_SAFE_DELETE(pRet)
return NULL;
}
//由一个字符串和字体fnt文件创建图字
bool CCLabelBMFont::initWithString(const char *theString, const char *fntFile)
{
//有效性判断
CCAssert(theString != NULL, "");
CC_SAFE_RELEASE(m_pConfiguration);// allow re-init
//调用FNTConfigLoadFile读取Fnt文件并返回出信息的内存地址给指针变量m_pConfiguration
m_pConfiguration = FNTConfigLoadFile(fntFile);
//用到它就给它的引用计数器加1
m_pConfiguration->retain();
//有效性判断
CCAssert( m_pConfiguration, "Error creating config for LabelBMFont");
//由信息指针取得字体图和字符串长度来初始化图块集管理器。
if (CCSpriteBatchNode::initWithFile(m_pConfiguration->m_sAtlasName.c_str(), strlen(theString)))
{
//如果成功,容量设为255
m_cOpacity = 255;
//使用白色
m_tColor = ccWHITE;
//m_tContentSize是CCNode中变量,为结点原始大小,不受矩阵变换影响,这里初始化为零大小
m_tContentSize = CCSizeZero;
//如果纹理有Alpha通道,则使用透明度设置RGB值。
m_bIsOpacityModifyRGB = m_pobTextureAtlas->getTexture()->getHasPremultipliedAlpha();
//设置锚点在正中心
setAnchorPoint(ccp(0.5f, 0.5f));
//设置字符串
this->setString(theString);
return true;
}
return false;
}
//析构函数
CCLabelBMFont::~CCLabelBMFont()
{
//释放字符串容器,释放
m_sString.clear();
CC_SAFE_RELEASE(m_pConfiguration);
}
// 由参1和参2组成key从哈希表中找到元素的数量。
int CCLabelBMFont::kerningAmountForFirst(unsigned short first, unsigned short second)
{
int ret = 0;
//将两个字合并为双字做为key来进行哈希表查找
unsigned int key = (first<<16) | (second & 0xffff);
//如果Fnt信息中有字距调整信息
if( m_pConfiguration->m_pKerningDictionary ) {
//使用哈希算法找到对应的字距信息值
tKerningHashElement *element = NULL;
HASH_FIND_INT(m_pConfiguration->m_pKerningDictionary, &key, element);
//如果找到返回
if(element)
ret = element->amount;
}
return ret;
}
//计算Char对应的UTF8码的掩码和长度
#define UTF8_COMPUTE(Char, Mask, Len) \
if (Char < 128) \
{ \
Len = 1; \
Mask = 0x7f; \
} \
else if ((Char & 0xe0) == 0xc0) \
{ \
Len = 2; \
Mask = 0x1f; \
} \
else if ((Char & 0xf0) == 0xe0) \
{ \
Len = 3; \
Mask = 0x0f; \
} \
else if ((Char & 0xf8) == 0xf0) \
{ \
Len = 4; \
Mask = 0x07; \
} \
else if ((Char & 0xfc) == 0xf8) \
{ \
Len = 5; \
Mask = 0x03; \
} \
else if ((Char & 0xfe) == 0xfc) \
{ \
Len = 6; \
Mask = 0x01; \
} \
else \
Len = -1;
//计算Char对应的UTF8码的长度
#define UTF8_LENGTH(Char) \
((Char) < 0x80 ? 1 : \
((Char) < 0x800 ? 2 : \
((Char) < 0x10000 ? 3 : \
((Char) < 0x200000 ? 4 : \
((Char) < 0x4000000 ? 5 : 6)))))
//取得Char对应的UTF8码
#define UTF8_GET(Result, Chars, Count, Mask, Len) \
(Result) = (Chars)[0] & (Mask); \
for ((Count) = 1; (Count) < (Len); ++(Count)) \
{ \
if (((Chars)[(Count)] & 0xc0) != 0x80) \
{ \
(Result) = -1; \
break; \
} \
(Result) <<= 6; \
(Result) |= ((Chars)[(Count)] & 0x3f); \
}
//判断Char是否是有效的Unicode码
#define UNICODE_VALID(Char) \
((Char) < 0x110000 && \
(((Char) & 0xFFFFF800) != 0xD800) && \
((Char) < 0xFDD0 || (Char) > 0xFDEF) && \
((Char) & 0xFFFE) != 0xFFFE)
//用于获取UTF8下个字符的编码偏移。
static const char utf8_skip_data[256] = {
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5,
5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 1, 1
};
static const char *const g_utf8_skip = utf8_skip_data;
//取得UTP8编码字符的下一个字符。
#define cc_utf8_next_char(p) (char *)((p) + g_utf8_skip[*(unsigned char *)(p)])
//返回取得字符串转换为UTF8后的字符长度
static long
cc_utf8_strlen (const char * p, int max)
{
long len = 0;
const char *start = p;
if (!(p != NULL || max == 0))
{
return 0;
}
if (max < 0)
{
while (*p)
{
p = cc_utf8_next_char (p);
++len;
}
}
else
{
if (max == 0 || !*p)
return 0;
p = cc_utf8_next_char (p);
while (p - start < max && *p)
{
++len;
p = cc_utf8_next_char (p);
}
/* only do the last len increment if we got a complete
* char (don't count partial chars)
*/
if (p - start == max)
++len;
}
return len;
}
//将Unicode编码字符串p转换为UTF8编码
static unsigned int
cc_utf8_get_char (const char * p)
{
int i, mask = 0, len;
unsigned int result;
unsigned char c = (unsigned char) *p;
UTF8_COMPUTE (c, mask, len);
if (len == -1)
return (unsigned int) - 1;
UTF8_GET (result, p, i, mask, len);
return result;
}
//重点函数:由字符串和字编码纹理块对应信息设置到
void CCLabelBMFont::createFontChars()
{
int nextFontPositionX = 0; //下一个字的横向绘制位置
int nextFontPositionY = 0; //下一个字的纵向绘制位置
unsigned short prev = -1; //上一个字编码
int kerningAmount = 0; //字间距调整的像素数量
CCSize tmpSize = CCSizeZero;//
int longestLine = 0; // 最长的一行的宽度
unsigned int totalHeight = 0;//字符串的总高度
unsigned int quantityOfLines = 1;
//如果字符串长度为零直接返回
if (0 == m_sString.length())
{
return;
}
//取得字符串转换为UTF8后的字符长度
int utf8len = cc_utf8_strlen(m_sString.c_str(), -1);
if (utf8len == 0)
{
return;
}
//将字符串转换为UTF8的字符串
unsigned short* pUniStr = new unsigned short[utf8len+1];
pUniStr[utf8len] = 0;
const char* p = m_sString.c_str();
for (int i = 0; i < utf8len; ++i)
{
pUniStr[i] = cc_utf8_get_char(p);
p = cc_utf8_next_char (p);
}
unsigned int stringLen = cc_wcslen(pUniStr);
//统计行数
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < stringLen - 1; ++i)
{
unsigned short c = pUniStr[i];
if (c == '\n')
{
quantityOfLines++;
}
}
//由行高乘行数最得要显示的字符串占用的总高度
totalHeight = m_pConfiguration->m_uCommonHeight * quantityOfLines;
//统计字符串的起始位置高度
nextFontPositionY = -(m_pConfiguration->m_uCommonHeight - m_pConfiguration->m_uCommonHeight * quantityOfLines);
//遍历所有的字
for (unsigned int i= 0; i < stringLen; i++)
{
unsigned short c = pUniStr[i];
if (c == '\n')
{
//如果遇到换行符则进行换行处理
nextFontPositionX = 0;
nextFontPositionY -= m_pConfiguration->m_uCommonHeight;
continue;
}
//查找是当前字的纹理映射信息结点
std::map<unsigned int, ccBMFontDef>::iterator it = m_pConfiguration->m_pBitmapFontArray->find(c);
CCAssert(it != m_pConfiguration->m_pBitmapFontArray->end(), "LabelBMFont: character is not supported");
//根据上一个字与当前字进行间距调整信息哈希表的查找,返回调整的像素偏移量。
kerningAmount = this->kerningAmountForFirst(prev, c);
//取得当前字的纹理映射信息结点
const ccBMFontDef& fontDef = (*(m_pConfiguration->m_pBitmapFontArray))[c];
//取得当前字在贴图上的像素矩形
CCRect rect = fontDef.rect;
//取得对应当前字的精灵
CCSprite *fontChar;
fontChar = (CCSprite*)(this->getChildByTag(i));
if( ! fontChar )
{
//如果找不到,则新建精灵,并将纹理上对应像素块信息传给精灵进行初始化。
fontChar = new CCSprite();
fontChar->initWithBatchNodeRectInPixels(this, rect);
//将精灵加入到子结点,设置i为附带查找唯一ID
this->addChild(fontChar, 0, i);
fontChar->release();
}
else
{
// 将纹理上对应像素块信息传给精灵。 fontChar->setTextureRectInPixels(rect, false, rect.size);
//设置其显示,完全不透明。
fontChar->setIsVisible(true);
fontChar->setOpacity(255);
}
//设置字的纵向偏移
float yOffset = (float)(m_pConfiguration->m_uCommonHeight) - fontDef.yOffset;
//计算字的位置,注意:因为锚点设的精灵正中心,所以位置应该是左下角位置加上大小的一半再进行相关偏移和间距调整计算。
fontChar->setPositionInPixels( ccp( nextFontPositionX + fontDef.xOffset + fontDef.rect.size.width / 2.0f + kerningAmount,
(float) nextFontPositionY + yOffset - rect.size.height/2.0f ) );
// NSLog(@"position.y: %f", fontChar.position.y);
// 更新绘制下一个字的横向位置
nextFontPositionX += (*(m_pConfiguration->m_pBitmapFontArray))[c].xAdvance + kerningAmount;
//更新上一个字符供循环再次使用
prev = c;
// 设置是否用透明度设置色彩 fontChar->setIsOpacityModifyRGB(m_bIsOpacityModifyRGB);
//设置色彩,
fontChar->setColor(m_tColor);
//如果透明度小于255,设置透明度
if( m_cOpacity != 255 )
{
fontChar->setOpacity(m_cOpacity);
}
//取得最长的一行的宽度
if (longestLine < nextFontPositionX)
{
longestLine = nextFontPositionX;
}
}
//设置当前字符串在屏幕上占用的矩形位置
tmpSize.width = (float) longestLine;
tmpSize.height = (float) totalHeight;
//调用基类CCNode的函数设置为原始大小
this->setContentSizeInPixels(tmpSize);
//释放字符串
CC_SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(pUniStr);
}
//LabelBMFont重载基类 CCLabelProtocol的接口函数
//设置字符串
void CCLabelBMFont::setString(const char *newString)
{
//将newString保存入字符串成员变量m_sString
m_sString.clear();
m_sString = newString;
//因CCLabelBMFont派生于CCSpriteBatchNode,m_pChildren为其子节点数组,这里进行遍历将其所有显示中的字精灵都设为不显示
if (m_pChildren && m_pChildren->count() != 0)
{
CCObject* child;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(m_pChildren, child)
{
CCNode* pNode = (CCNode*) child;
if (pNode)
{
pNode->setIsVisible(false);
}
}
}
//重新由字符串和字体信息创建要显示的字精灵
this->createFontChars();
}
//取得字符串
const char* CCLabelBMFont::getString(void)
{
return m_sString.c_str();
}
// setString别名函数
void CCLabelBMFont::setCString(const char *label)
{
setString(label);
}
//LabelBMFont 重载基类 CCRGBAProtocol 的接口函数
//设置颜色
void CCLabelBMFont::setColor(const ccColor3B& var)
{
m_tColor = var;
//因CCLabelBMFont派生于CCSpriteBatchNode,m_pChildren为其子节点数组,这里进行遍历设置
if (m_pChildren && m_pChildren->count() != 0)
{
CCObject* child;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(m_pChildren, child)
{
CCSprite* pNode = (CCSprite*) child;
if (pNode)
{
pNode->setColor(m_tColor);
}
}
}
}
//取得颜色
const ccColor3B& CCLabelBMFont::getColor()
{
return m_tColor;
}
//设置透明度
void CCLabelBMFont::setOpacity(GLubyte var)
{
m_cOpacity = var;
if (m_pChildren && m_pChildren->count() != 0)
{
CCObject* child;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(m_pChildren, child)
{
CCNode* pNode = (CCNode*) child;
if (pNode)
{
CCRGBAProtocol *pRGBAProtocol = dynamic_cast<CCRGBAProtocol*>(pNode);
if (pRGBAProtocol)
{
pRGBAProtocol->setOpacity(m_cOpacity);
}
}
}
}
}
//取得透明度
GLubyte CCLabelBMFont::getOpacity()
{
return m_cOpacity;
}
//设置是否使用透明度设置RGB值
void CCLabelBMFont::setIsOpacityModifyRGB(bool var)
{
m_bIsOpacityModifyRGB = var;
if (m_pChildren && m_pChildren->count() != 0)
{
CCObject* child;
CCARRAY_FOREACH(m_pChildren, child)
{
CCNode* pNode = (CCNode*) child;
if (pNode)
{
//因子结点即是精灵CCSprite,CCSprite又派生于CCRGBAProtocol,故进行转换
CCRGBAProtocol *pRGBAProtocol = dynamic_cast<CCRGBAProtocol*>(pNode);
if (pRGBAProtocol)
{
//调用setIsOpacityModifyRGB进行设置
pRGBAProtocol->setIsOpacityModifyRGB(m_bIsOpacityModifyRGB);
}
}
}
}
}
//取得是否使用透明度设置RGB值
bool CCLabelBMFont::getIsOpacityModifyRGB()
{
return m_bIsOpacityModifyRGB;
}
// 设置锚点
void CCLabelBMFont::setAnchorPoint(const CCPoint& point)
{
if( ! CCPoint::CCPointEqualToPoint(point, m_tAnchorPoint) )
{
CCSpriteBatchNode::setAnchorPoint(point);
this->createFontChars();
}
}
//绘制图字标签,Debug模式下手动调用绘制
#if CC_LABELBMFONT_DEBUG_DRAW
void CCLabelBMFont::draw()
{
//绘制图块集
CCSpriteBatchNode::draw();
//绘制边框
const CCSize& s = this->getContentSize();
CCPoint vertices[4]={
ccp(0,0),ccp(s.width,0),
ccp(s.width,s.height),ccp(0,s.height),
};
ccDrawPoly(vertices, 4, true);
}
#endif // CC_LABELBMFONT_DEBUG_DRAW
}
终于,结束了代码的分析,赶快喝口水。照例做个总结:
1. 图字的原理:将所要绘制的字绘制到图片上,通过编码取得对应的矩形块UV进行顶点缓冲的设置之后进行绘制。Cocos2d-x提供的两个类非常重要:(1) CCTextureAtlas(2) CCSpriteBatchNode。
2. 图字的组成:一张纹理,一个纹理描述信息文件。缺一不可。要做好图字,必须深入理解图字纹理描述信息文件的格式,可能看Cocos2d-x提供的类: CCBMFontConfiguration,并掌握图字工具的使用。
呃,网上提供了一些图字工具,比较常用的有
Hiero:
和 Bitmap Font Generator:

Hiero你要下载可以直接将下面代码拷贝后保存为Hiero.jnlp文件然后执行,前提是你机器上必须装JAVA运行环境。
Hiero.jnlp:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <jnlp spec='1.0+' codebase='http://n4te.com/' href='hiero/hiero.jnlp'> <information> <title>Hiero</title> <vendor>Esoteric Software</vendor> <homepage href='http://n4te.com/'/> <description>Hiero</description> <description kind='short'>Hiero</description> </information> <security> <all-permissions/> </security> <resources> <j2se href='http://java.sun.com/products/autodl/j2se' version='1.5+' max-heap-size='128m'/> <jar href='hiero/hiero.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/jflac-1.3.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/jlayer-1.0.1.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/jmacdecoder-1.74.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/jorbis-0.0.17.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/lucene-analyzers-2.4.0.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/lucene-core-2.4.0.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/lwjgl.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/singsong-slick.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/slick.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/twl.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/xpp3-1.1.3_8.jar'/> <jar href='hiero/yamlbeans-0.9.3.jar'/> </resources> <resources os='Windows'> <j2se href='http://java.sun.com/products/autodl/j2se' version='1.5+' max-heap-size='128m'/> <nativelib href='hiero/natives-win.jar'/> </resources> <resources os='Mac'> <j2se href='http://java.sun.com/products/autodl/j2se' version='1.5+' max-heap-size='128m'/> <nativelib href='hiero/natives-mac.jar'/> </resources> <resources os='Linux'> <j2se href='http://java.sun.com/products/autodl/j2se' version='1.5+' max-heap-size='128m'/> <nativelib href='hiero/natives-linux.jar'/> </resources> <resources os='SunOS'> <j2se href='http://java.sun.com/products/autodl/j2se' version='1.5+' max-heap-size='128m'/> <nativelib href='hiero/natives-solaris.jar'/> </resources> <application-desc main-class='org.newdawn.slick.tools.hiero.Hiero'/> </jnlp>
Bitmap Font Generator的下载地址为:
http://www.angelcode.com/products/bmfont/
懂了生成的文件格式,如何使用应该不是什么问题了,在这里就不进行详细的使用教程了。但是红孩儿认为要是想做出更专业更漂亮的字,还是自已开发一个图字生成器,可以生成更多的效果。比如红孩儿几年前做2D游戏时写过的图字生成器。其原理就是根据语系和字体将需要的字生成图片和编码对应信息。显示字时设置字体然后绘制到HDC上然后使用GetPixel取得像素值保存到图片里就行了~