Android ActionBar的源代码分析(四)
上一篇已经对ActionBar的菜单项的执行过程进行了分析,有兴趣的朋友可以看一下android中ActionBar的源代码分析(三),本章对ActionBar的OverflowMenu的运行机制进行分析。
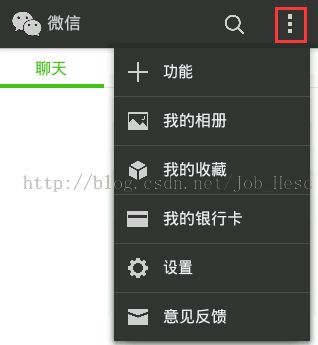
ActionBar的OverflowMenu,就是ActionBar右边的三个小点点,点击以后就出现一个下拉菜单项,如图
OverflowMenu是为了解决ActionBar的菜单项太多,在一个屏幕上显示不出来,而把过多的菜单项放到下拉菜单中显示的问题;在配置菜单属性的时候,把android:showAsAction设为ifRoom或者never,就会利用ActionBar的OverflowMenu特性在下拉菜单显示出来了,当然如果你的机器是带有物理menu键的,还需要进行特殊处理,这个可以看一下我之前写的一篇文章android2.x使用ActionBar-强制显示OverflowButton
溢出菜单按钮的构建
既然我们知道了如何使用OverflowMenu,那这个OverflowMenu在代码层次是如何实现的呢?从上几篇文章我们知道,类ActionMenuPresenter是负责ActionBar菜单项的绘制工作的,其中初始菜单参数的方法是initForMenu(),我们先看一下这个代码是如何实现的吧。
@Override
public void initForMenu(Context context, MenuBuilder menu) {
super.initForMenu(context, menu);
final Resources res = context.getResources();
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//是否显示溢出菜单按钮
final ActionBarPolicy abp = ActionBarPolicy.get(context);
if (!mReserveOverflowSet) {
mReserveOverflow = abp.showsOverflowMenuButton();
}
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//嵌入菜单最大宽度即放置ActionBar菜单项的最大宽度
if (!mWidthLimitSet) {
mWidthLimit = abp.getEmbeddedMenuWidthLimit();
}
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//ActionBar最多显示的按钮数目
// Measure for initial configuration
if (!mMaxItemsSet) {
mMaxItems = abp.getMaxActionButtons();
}
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//初始化溢出菜单按钮,并计算溢出菜单按钮宽度
int width = mWidthLimit;
if (mReserveOverflow) {
if (mOverflowButton == null) {
mOverflowButton = new OverflowMenuButton(mSystemContext);
final int spec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
mOverflowButton.measure(spec, spec);
}
width -= mOverflowButton.getMeasuredWidth(); //显示的菜单按钮宽度需要减掉溢出菜单按钮的宽度
} else {
mOverflowButton = null;
}
mActionItemWidthLimit = width;
mMinCellSize = (int) (ActionMenuView.MIN_CELL_SIZE * res.getDisplayMetrics().density);
// Drop a scrap view as it may no longer reflect the proper context/config.
mScrapActionButtonView = null;
}
这段代码首先调用父类(BaseMenuPresenter)的initForMenu()方法,父类的这个方法无非就是一些赋值操作,代码就不贴出来了,然后就根据ActionBarPolicy确定是否显示溢出菜单按钮(OverflowButton)以及ActionBar最多显示的菜单数目,最后对溢出菜单按钮进行初始化操作并计算溢出菜单按钮的宽度。可以看到,这里涉及了很多宽度的获取,包括嵌入的菜单宽度、最大按钮显示数目和溢出菜单按钮的宽度,其实就是为了确定当菜单配置为android:showAsAction=ifRoom时,何时才显示在溢出菜单中(或者干脆就不显示出来),代码逻辑可以参考ActionMenuPresenter.flagActionItems()方法,这里就不贴出来了; 溢出菜单按钮的实现类为OverflowMenuButton,后面会重点进行介绍,这里先记住它就是溢出菜单按钮吧。
溢出菜单按钮(OverflowMenuButton)什么时候放置到ActionBar上的呢?从android中ActionBar的源代码分析(二)我们可以看出,系统在创建菜单时,会调用ActionMenuPresenter的updateMenuView()方法,我们看一下这个方法的实现逻辑:
@Override
public void updateMenuView(boolean cleared) {
final ViewGroup menuViewParent = (ViewGroup) ((View) mMenuView).getParent();
if (menuViewParent != null) {
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> // 使用ActionBar的淡出淡入效果,其实系统本身并没有启用该效果
ActionBarTransition.beginDelayedTransition(menuViewParent);
}
super.updateMenuView(cleared); //使用父类的方法,构建ActionBar的按钮并添加到ActionMenuView上
((View) mMenuView).requestLayout();
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//判断菜单是否配置了ActionProvider,如果有则设置ActionProvider的子菜单侦听事件
if (mMenu != null) {
final ArrayList<MenuItemImpl> actionItems = mMenu.getActionItems();
final int count = actionItems.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final ActionProvider provider = actionItems.get(i).getActionProvider();
if (provider != null) {
provider.setSubUiVisibilityListener(this);
}
}
}
final ArrayList<MenuItemImpl> nonActionItems = mMenu != null ?
mMenu.getNonActionItems() : null;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//判断是否存在溢出菜单
boolean hasOverflow = false;
if (mReserveOverflow && nonActionItems != null) {
final int count = nonActionItems.size();
if (count == 1) {
hasOverflow = !nonActionItems.get(0).isActionViewExpanded(); //如果只有一个菜单按钮,并且该菜单按钮是个可扩展按钮,则不显示溢出菜单按钮
} else {
hasOverflow = count > 0;
}
}
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//如果需要显示溢出菜单,则初始化溢出菜单按钮,并添加到ActionMenuView中
if (hasOverflow) {
if (mOverflowButton == null) {
mOverflowButton = new OverflowMenuButton(mSystemContext);
}
ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) mOverflowButton.getParent();
if (parent != mMenuView) {
if (parent != null) {
parent.removeView(mOverflowButton);
}
ActionMenuView menuView = (ActionMenuView) mMenuView;
menuView.addView(mOverflowButton, menuView.generateOverflowButtonLayoutParams());
}
} else if (mOverflowButton != null && mOverflowButton.getParent() == mMenuView) {
((ViewGroup) mMenuView).removeView(mOverflowButton);
}
((ActionMenuView) mMenuView).setOverflowReserved(mReserveOverflow);
}这段代码首先是设置显示ActionBar的淡出淡入效果,从类ActionBarTransition的代码中可以看出,淡出淡入的效果受TRANSITIONS_ENABLED的控制,而TRANSITIONS_ENABLED是等于false的,而且也没发现在哪能设置这个变量的值,所以按照目前来看,ActionBar的淡出淡入效果是没有启用的;然后调用父类(BaseMenuPresenter)的updateMenuView()方法构建ActionBar的菜单按钮并添加到ActionMenuView 上,接着判断菜单是否配置启用了ActionProvider,如果启用了,就设置侦听其子菜单可见行改变的事件;最后判断是否显示溢出菜单,如果显示溢出菜单则调用溢出菜单按钮的初始化方法,并把它添加到ActionMenuView上显示出来;这样溢出菜单按钮就完成了整个的构建过程;
溢出菜单弹出执行过程分析
溢出菜单按钮点击以后,就会弹出下拉菜单来,这个过程在代码层次上具体是怎么实现的呢?这就需要我们看一下类OverflowMenuButton的具体实现了,OverflowMenuButton继承于类ImageButton,也就是说它实际就是一个图片按钮;我们先看一下OverflowMenuButton的构造方法吧
public OverflowMenuButton(Context context) {
super(context, null, com.android.internal.R.attr.actionOverflowButtonStyle);
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> //设置控件可点击、可设置焦点、可用和可见性
setClickable(true);
setFocusable(true);
setVisibility(VISIBLE);
setEnabled(true);
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> //侦听控件本身的touch事件
setOnTouchListener(new ForwardingListener(this) {
@Override
public ListPopupWindow getPopup() {
if (mOverflowPopup == null) {
return null;
}
return mOverflowPopup.getPopup();
}
@Override
public boolean onForwardingStarted() { // touch事件转发开始后,显示溢出菜单
showOverflowMenu();
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onForwardingStopped() { // 溢出菜单显示后再次touch该控件,则隐藏溢出菜单
// Displaying the popup occurs asynchronously, so wait for
// the runnable to finish before deciding whether to stop
// forwarding.
if (mPostedOpenRunnable != null) {
return false;
}
hideOverflowMenu();
return true;
}
});
}OverflowMenuButton的构造方法,首先设置控件可点击、可设置焦点、可用和可见性,然后设置侦听控件的触摸事件,这里用到了ListPopupWindow.ForwardingListener类,该类其实是实现了View.OnTouchListener接口的,有几个方法需要重写:
- onForwardingStarted()表示当手指在触摸溢出菜单按钮时回调该方法,这里是执行了showOverflowMenu()方法,按照字面的意思应该就是显示溢出菜单了,至于代码实现如何,一会再进行分析;
- onForwardingStopped()表示当溢出菜单仍然显示,再次触摸溢出菜单按钮时回调该方法,这里首先判断mPostOpenRunnable是否为空,也即是否采用了Post Runnable的处理方式,如果没有则执行hideOverflowMenu()方法,按照字面的意思就是隐藏溢出菜单,至于代码实现如何,一会再进行分析;
- getPopup()表示获取弹出菜单窗口,也即指定需要控制的弹出窗口,这里设置为溢出菜单按钮关联的PopupWindow
@Override
public boolean performClick() {
if (super.performClick()) {
return true;
}
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
showOverflowMenu();
return true;
}代码很简单,就是先判断是否父类的performClick()方法的返回值是否为true,如果为true则退出,换句话讲就是判断外部调用的onClick的侦听事件是否返回true,如果没有设置onClick事件的侦听或者侦听回调方法返回值为false,则继续执行后面的showOverflowMenu()方法,本例中由于没有侦听OverflowMenuButton的onClick事件,因此必然要走showOverflowMenu()方法。
public boolean showOverflowMenu() {
if (mReserveOverflow && !isOverflowMenuShowing() && mMenu != null && mMenuView != null &&
mPostedOpenRunnable == null && !mMenu.getNonActionItems().isEmpty()) {
OverflowPopup popup = new OverflowPopup(mContext, mMenu, mOverflowButton, true);
mPostedOpenRunnable = new OpenOverflowRunnable(popup);
// Post this for later; we might still need a layout for the anchor to be right.
((View) mMenuView).post(mPostedOpenRunnable);
// ActionMenuPresenter uses null as a callback argument here
// to indicate overflow is opening.
super.onSubMenuSelected(null);
return true;
}
return false;
}代码很简单,首先判断溢出菜单是否已经显示,如果没有显示,则实例化类OverflowPopup和OpenOverflowRunnable,并延后执行OpenOverflowRunnable中run()方法,最后调用父类的onSubMenuSelected()方法。这里的类OverflowPopup是菜单弹出的辅助类,继承于类MenuPopupHelper,负责管理弹出窗体(PopupWindow)的生命周期;而类OpenOverflowRunnable负责PopupWindow的显示,我们看一下OpenOverflowRunnable的代码逻辑:
private class OpenOverflowRunnable implements Runnable {
private OverflowPopup mPopup;
public OpenOverflowRunnable(OverflowPopup popup) {
mPopup = popup;
}
public void run() {
mMenu.changeMenuMode();
final View menuView = (View) mMenuView;
if (menuView != null && menuView.getWindowToken() != null && mPopup.tryShow()) {
mOverflowPopup = mPopup;
}
mPostedOpenRunnable = null;
}
}我们主要看run()方法,在该方法中,首先调用MenuBuilder.changeMenuMode()方法切换菜单模式,也就是说如果菜单已经弹出则隐藏,否则就弹出显示;接着调用OverflowPopup的tryShow()方法弹出溢出菜单窗体。也许有朋友就问,MenuBuilder.changeMenuMode()方法不是已经显示过一次溢出菜单了吗,这里再次显示会不会重复显示呢?当然不会,系统通过设置变量mPostedOpenRunnable是否为空来进行区分,保证只会执行一次显示溢出菜单窗体的代码。
public boolean tryShow() {
mPopup = new ListPopupWindow(mContext, null, com.android.internal.R.attr.popupMenuStyle);
mPopup.setOnDismissListener(this);
mPopup.setOnItemClickListener(this);
mPopup.setAdapter(mAdapter);
mPopup.setModal(true);
View anchor = mAnchorView;
if (anchor != null) {
final boolean addGlobalListener = mTreeObserver == null;
mTreeObserver = anchor.getViewTreeObserver(); // Refresh to latest
if (addGlobalListener) mTreeObserver.addOnGlobalLayoutListener(this);
anchor.addOnAttachStateChangeListener(this);
mPopup.setAnchorView(anchor);
mPopup.setDropDownGravity(mDropDownGravity);
} else {
return false;
}
if (!mHasContentWidth) {
mContentWidth = measureContentWidth();
mHasContentWidth = true;
}
mPopup.setContentWidth(mContentWidth);
mPopup.setInputMethodMode(PopupWindow.INPUT_METHOD_NOT_NEEDED);
mPopup.show();
mPopup.getListView().setOnKeyListener(this);
return true;
}在这个代码中,首先是实例化ListPopupWindow,然后对这个ListPopupWindow对象进行各种属性赋值操作,最后调用show方法显示出来。这里的类ListPopupWindow通俗来讲就是一个包含一个ListView的PopupWindow,其具体的用法百度上有一大堆,有兴趣的朋友可以研究一下哈,这里就不过多赘述。使用ListPopupWindow时,有三个方法要注意:
- setDismissListener() 负责侦听弹出窗体关闭的事件;这里把this传入,也就是说OverflowPopup的父类MenuPopupHelper是实现了接口PopupWindow.OnDismissListener的,也即实现了接口方法onDismiss()的,关于onDismiss()方法,稍后在分析溢出菜单隐藏时再进行介绍;
- setOnItemClickListener() 负责侦听弹出窗体的菜单项点击事件;这里把this传入,也就是说OverflowPopup的父类MenuPopupHelper是实现了接口AdapterView.OnItemClickListener的,也就是实现了接口方法onItemClick()的,在这个方法中,会调用MenuBuilder的performItemAction()方法,这个方法在上一章已经进行过介绍,有兴趣的朋友可以看android中ActionBar的源代码分析(三)
- setAdapter() 这个就是设置ListView的数据适配类;这里传入的是mAdapter,其实现类为MenuPopupHelper.MenuAdapter,实现代码如下:
private class MenuAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private MenuBuilder mAdapterMenu;
private int mExpandedIndex = -1;
public MenuAdapter(MenuBuilder menu) {
mAdapterMenu = menu;
findExpandedIndex();
}
public int getCount() {
ArrayList<MenuItemImpl> items = mOverflowOnly ?
mAdapterMenu.getNonActionItems() : mAdapterMenu.getVisibleItems();
if (mExpandedIndex < 0) {
return items.size();
}
return items.size() - 1;
}
public MenuItemImpl getItem(int position) {
ArrayList<MenuItemImpl> items = mOverflowOnly ?
mAdapterMenu.getNonActionItems() : mAdapterMenu.getVisibleItems();
if (mExpandedIndex >= 0 && position >= mExpandedIndex) {
position++;
}
return items.get(position);
}
public long getItemId(int position) {
// Since a menu item's ID is optional, we'll use the position as an
// ID for the item in the AdapterView
return position;
}
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = mInflater.inflate(ITEM_LAYOUT, parent, false);
}
MenuView.ItemView itemView = (MenuView.ItemView) convertView;
if (mForceShowIcon) {
((ListMenuItemView) convertView).setForceShowIcon(true);
}
itemView.initialize(getItem(position), 0);
return convertView;
}
void findExpandedIndex() {
final MenuItemImpl expandedItem = mMenu.getExpandedItem();
if (expandedItem != null) {
final ArrayList<MenuItemImpl> items = mMenu.getNonActionItems();
final int count = items.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final MenuItemImpl item = items.get(i);
if (item == expandedItem) {
mExpandedIndex = i;
return;
}
}
}
mExpandedIndex = -1;
}
@Override
public void notifyDataSetChanged() {
findExpandedIndex();
super.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
}我们重点看getCount()和getView()方法即可,在getCount()方法中,获取ActionBar的不可见菜单项,然后判断在这些不可见菜单项中是否有可扩展折叠菜单项,如果有则排除掉,换句话讲就是可扩展折叠的菜单项是不会显示在溢出菜单中的;在getView()方法中通过inflater布局文件framework\data\res\layout\popup_menu_item_layout.xml来创建视图,并对菜单项进行初始化操作,下面是popup_menu_item_layout.xml的内容
<com.android.internal.view.menu.ListMenuItemView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?android:attr/dropdownListPreferredItemHeight"
android:minWidth="196dip"
android:paddingEnd="16dip">
<!-- Icon will be inserted here. -->
<!-- The title and summary have some gap between them, and this 'group' should be centered vertically. -->
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_marginStart="16dip"
android:duplicateParentState="true">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLargePopupMenu"
android:singleLine="true"
android:duplicateParentState="true"
android:ellipsize="marquee"
android:fadingEdge="horizontal"
android:textAlignment="viewStart" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/shortcut"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/title"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmallPopupMenu"
android:singleLine="true"
android:duplicateParentState="true"
android:textAlignment="viewStart" />
</RelativeLayout>
<!-- Checkbox, and/or radio button will be inserted here. -->
</com.android.internal.view.menu.ListMenuItemView>可以看到,其实每一个溢出菜单的菜单项的实现类为ListMenuItemView,它继承于LinearLayout;ListMenuItemView包含三个子视图:一个ImageView,负责显示菜单图标;一个TextView,负责显示菜单标题;一个TextView,负责显示菜单的快捷方式,默认情况下快捷方式是不显示的。其中两个TextView是在布局文件中列出,还有一个ImageView,是通过代码来创建的,可以看一下ListMenuItemView的setIcon()方法如下:
public void setIcon(Drawable icon) {
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//判断图标是否需要显示
final boolean showIcon = mItemData.shouldShowIcon() || mForceShowIcon;
if (!showIcon && !mPreserveIconSpacing) {
return;
}
if (mIconView == null && icon == null && !mPreserveIconSpacing) {
return;
}
//如果需要显示图标,则创建控件并添加进来
if (mIconView == null) {
insertIconView();
}
//设置可见性
if (icon != null || mPreserveIconSpacing) {
mIconView.setImageDrawable(showIcon ? icon : null);
if (mIconView.getVisibility() != VISIBLE) {
mIconView.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
}
} else {
mIconView.setVisibility(GONE);
}
}声明一下,setIcon()方法是在ListMenuItemView.initialize()方法中调用的,而ListMenuItemView.initialize()又是由类MenuPopupHelper.MenuAdapter在方法getView()中调用的;
public boolean shouldShowIcon() {
return mMenu.getOptionalIconsVisible();
}很简单,就是直接调用MenuBuilder.getOptionalIconsVisible()的方法进行判断,而getOptionalIconsVisible()是直接返回mOptionalIconsVisible的值,mOptionalIconsVisible的默认值为false,它是通过setOptionalIconsVisible()设置进来的,不幸的是setOptionalIconsVisible()的方法修饰符为Internal,外部是无法访问的,只能通过反射的方式来修改;这就是为什么在默认情况下,溢出菜单显示的菜单项只有文字没有图标的原因了!
溢出菜单隐藏执行过程分析
上面提到ListPopupWindow是一个包含ListView的PopupWindow,OverflowPopup在创建ListPopupWindow时,调用ListPopupWindow.setDismiss()去侦听弹出窗体关闭的事件,而传入参数为this,也就是OverflowPopup的父类MenuPopupHelper是实现了接口PopupWindow.OnDismissListener的,也即实现了接口方法onDismiss()的,onDismiss()方法的代码如下: public void onDismiss() {
mPopup = null;
mMenu.close();
if (mTreeObserver != null) {
if (!mTreeObserver.isAlive()) mTreeObserver = mAnchorView.getViewTreeObserver();
mTreeObserver.removeGlobalOnLayoutListener(this);
mTreeObserver = null;
}
mAnchorView.removeOnAttachStateChangeListener(this);
}这里调用了MenuBuilder.close()方法进行关闭弹出菜单操作,下面是MenuBuilder.close()方法的实现代码:
public void close() {
close(true);
}
final void close(boolean allMenusAreClosing) {
if (mIsClosing) return;
mIsClosing = true;
for (WeakReference<MenuPresenter> ref : mPresenters) {
final MenuPresenter presenter = ref.get();
if (presenter == null) {
mPresenters.remove(ref);
} else {
presenter.onCloseMenu(this, allMenusAreClosing);
}
}
mIsClosing = false;
}其实就是调用了ActionMenuPresenter.onCloseMenu()方法执行关闭操作:
public void onCloseMenu(MenuBuilder menu, boolean allMenusAreClosing) {
dismissPopupMenus();
super.onCloseMenu(menu, allMenusAreClosing);
}
public boolean dismissPopupMenus() {
boolean result = hideOverflowMenu();
result |= hideSubMenus();
return result;
}可以看到执行关闭菜单的操作,都是执行了hideOverflowMenu()方法来实现的:
public boolean hideOverflowMenu() {
if (mPostedOpenRunnable != null && mMenuView != null) {
((View) mMenuView).removeCallbacks(mPostedOpenRunnable);
mPostedOpenRunnable = null;
return true;
}
MenuPopupHelper popup = mOverflowPopup;
if (popup != null) {
popup.dismiss();
return true;
}
return false;
}
hideOverflowMenu()方法实现逻辑很简单,其实就是调用了PopupWindow的dismiss方法进行的。