算法系列笔记8(有关图的算法二—最短路径问题)
图的最短路径问题主要分为两类,单源最短路径问题和全对最短路径问题。单源最短路径问题指给点单个源点,求其到所有其它顶点之间的最短距离。而全对最短路径问题指所有顶点之间的最短路劲问题。此外对于单对最短路径问题,从渐进意义上来看,目前还没有比最好的单元算法更快的算法来解决这一问题。
一:单源最短路径问题
单源最短路劲问题根据其权重分为四类,当图G=(V,E)为无权图,直接使用广度优先遍历(这里不做介绍);当权值为非负值,则使用Dijkstra算法;存在负权值及负权环,可以使用Bellman-Ford算法。最后一类是有向无回图(DAG)的单源最短路径问题。
Dijkstra算法
Dijkstra算法为贪心算法,如何证明贪心策略确实有效才是关键。
基本思想:给每个顶点一个估算距离,初始化源点的估算距离为0,其它点为无穷大;优先队列Q=V,从Q中选择最小的估算距离的顶点加入集合S中,然后对从该顶点出发的每条边进行松弛,从而更新每个顶点的估算距离。
需要证明的就是从Q中选择最小估算距离的顶点加入S中,此时的估算距离就等于该顶点的最短路径。
代码如下:
// dijkstra 算法
string Graph::intToStr(int i){
string s;
stringstream ss;
ss << i;
ss >>s;
ss.clear();
return s;
}
void Graph::dijkstra(){
mPriceQueue.clear();
mPriceQueue[0] = 0;
path[0] = intToStr(0);
for(int i = 1; i < vertexNum; i++){
mPriceQueue[i] = MAXPRICE;
path[i] = "";
}
while(!mPriceQueue.empty()){
pair<int, int> pMinNode = getMinPriceVet(); // dijkstra的贪心策略就是该点就是此时的pMinNode.second就是最短路径
int minPriceVet = pMinNode.first;
minDistance[minPriceVet] = pMinNode.second; // 保存最短路径到minDistance中
GNode *p = edges[minPriceVet].next;
while(p != NULL){
if(mPriceQueue.count(p->val) && (p->weight + pMinNode.second) < mPriceQueue[p->val]){ // 松弛操作
mPriceQueue[p->val] = p->weight + pMinNode.second;
path[p->val] = path[minPriceVet] + intToStr(p->val);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
// 输出路径
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
cout << "从0到" << i << "的最短路径为: " <<path[i] << "; 距离为: " << minDistance[i] << endl;
}
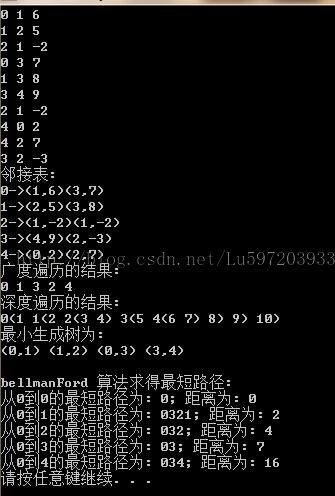
}结果:
时间复杂度分析:时间复杂度为V*Textract min + E*Trelax的时间。当Q为数组时,时间复杂的为O(V^2);当Q为二叉堆时,时间复杂度为O(Vlg(V+E));当Q为fibonacci堆时,时间复杂度为O(VlgV+E).
Bellman-Ford算法
Bellman-Ford的思想是将边按照一定的顺序,每条边都松弛V-1次。每条边都松弛V-1次,一定能使估算距离等于最短路径。
代码如下:
// BellmanFord 算法
// 按照边的顺序松弛每一条边 V-1次
void Graph::bellmanFord(){
minDistance[0] = 0;
path[0] = intToStr(0);
for(int i = 1; i < vertexNum; i++){
minDistance[i] = MAXPRICE;
path[i] = "";
}
for(int m = 0; m < vertexNum-1; m++){
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
GNode *p = edges[i].next;
while(p != NULL){
if(minDistance[p->val] > p->weight + minDistance[i]){ // 松弛每一条边
minDistance[p->val] = minDistance[i] + p->weight;
path[p->val] = path[i] + intToStr(p->val);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){ // 检查是否存在负权回路
GNode *p = edges[i].next;
while(p != NULL){
if(minDistance[p->val] > p->weight + minDistance[i]){
cout << "该图存在负权环" << endl;
return;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
// 输出路径
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
cout << "从0到" << i << "的最短路径为: " <<path[i] << "; 距离为: " << minDistance[i] << endl;
}
}
结果如下:
时间复杂度为O(VE).
注意:这里有个应用就是差分约束系统。其实线性规划的一种特殊情况,即A矩阵每行只有一个1和-1,其它的都为0,这样可以构造约束图,求得最短路径就是差分约束系统的解。这里不详细介绍了。
DAG图的单源最短路径
算法的基本思想:求DAG图的拓扑排序,然后按照拓扑排序顶点的顺序对其每条边进行松弛操作即如果d[v] > d[u]+w[u,v],则d[v] = d[u]+w[u,v]。其时间复杂度为O(V+E).
二:全对最短路径问题
求所有的两两顶点之间的最短路径,最基本的思想就是对所有的顶点都运用单源最短路径问题。这样当无权值时,时间复杂度为O(V^2+VE)<即V*BFS>;权值非负为O(V^2lgV+VE)<即V*Dijkstra>;一般情况为O(V^2*E),此时对于稠密图E=O(V^2),要达到O(V^4)了,效率会非常差,因此需要其他算法来改进时间复杂度。主要有三种方法,第一种为动态规划方法(结合矩阵乘法);第二种为Floyd-Warshall算法;第三种为Johnson算法,对于稀疏图要优于Floy-Warshall算法。
动态规划方法
其中dijm表示从i到j的最短路径,其中最多经过m条边。此时当m=V-1即为我们要求的最短路径(对于无负权环)。D(1)=W为权重矩阵。即求D(V-1).
此外将(1)式看做某种新运算*,那么每次都是求D(m) = D(m-1) * W。
代码如下:
// 用动态规划求全最短路径
void Graph::dpAllDistance(){
int Adj[maxSize][maxSize];
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
minAllDistance[i][j] = MAXPRICE;
if(i == j) minAllDistance[i][j] = 0;
AllPath[i][j] = intToStr(i);
Adj[i][j] = minAllDistance[i][j];
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
GNode *p = edges[i].next;
while(p != NULL){
minAllDistance[i][p->val] = p->weight; // 经过了1条边 即为权重
Adj[i][p->val] = p->weight;
AllPath[i][p->val] = AllPath[i][p->val] + intToStr(p->val);
p = p->next;
}
}
for(int m = 2; m < vertexNum; m++){ // 至多经过m条边
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
for(int k = 0; k < vertexNum; k++){
if(minAllDistance[i][j] > minAllDistance[i][k] + Adj[k][j]){
minAllDistance[i][j] = minAllDistance[i][k] + Adj[k][j];
AllPath[i][j] = AllPath[i][k] + intToStr(j);
}
}
}
}
}
// 检测是否存在负权环
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
if(minAllDistance[i][i] < 0){
cout << "该图存在负权环" << endl;
return;
}
}
// 将全对最短路径输出
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
cout << "从" <<i << "到" << j <<"的最短路径为: " << AllPath[i][j] << " 距离为: " << minAllDistance[i][j] << endl;
}
}
}
时间复杂度:此时时间复杂度仍然为O(V^4),但是采用D(m) = D(m/2)*D(m/2)来计算,时间复杂度即为O(V^3*lgV).
![]()
Floyd-Warshall算法
定义dijk表示从i到j考虑了从中间节点{1,2,3…k}经过的所有情况的最小值。当k=n时,即考虑了所有顶点,此时即为最短路径。
代码如下:
// floyd-warshall算法求最短路径问题
void Graph::floydWarshall(){
int Adj[maxSize][maxSize];
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
minAllDistance[i][j] = MAXPRICE;
if(i == j) minAllDistance[i][j] = 0;
AllPath[i][j] = intToStr(i);
Adj[i][j] = minAllDistance[i][j];
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
GNode *p = edges[i].next;
while(p != NULL){
minAllDistance[i][p->val] = p->weight; // 经过了1条边 即为权重
Adj[i][p->val] = p->weight;
AllPath[i][p->val] = AllPath[i][p->val] + intToStr(p->val);
p = p->next;
}
}
for(int k = 0; k < vertexNum; k++){
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
if(minAllDistance[i][j] > minAllDistance[i][k] + minAllDistance[k][j]){
minAllDistance[i][j] = minAllDistance[i][k] + minAllDistance[k][j];
AllPath[i][j] = AllPath[i][k] + AllPath[k][j];
}
}
}
}
// 检测是否存在负权环
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
if(minAllDistance[i][i] < 0){
cout << "该图存在负权环" << endl;
return;
}
}
// 将全对最短路径输出
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
cout << "从" <<i << "到" << j <<"的最短路径为: " << AllPath[i][j] << " 距离为: " << minAllDistance[i][j] << endl;
}
}
结果如下:
时间复杂度为O(V^3).
Johnson算法
Johnson算法采用了重赋权重方法。重赋权重方法不会改变最短路径,此外通过重赋权重产生的都是非负权重。
伪代码:
时间复杂度为O(V)*Dijkstra算法。
算法全部代码:
graph.h
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#define maxSize 10
#define MAXPRICE 0x10000000 // 将此值设为权值的最大值
struct GNode{
int val;
int weight;
GNode *next;
};
class Graph{
public:
void createGraph(int n, int e);
void destroyGraph(GNode *p);
~Graph(){
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
destroyGraph(edges[i].next);
//cout << "析构:" << i << endl;
}
}
void showGraph();
void bfsTravel(); // 广度遍历
void dfsTravel(); // 深度遍历
void showTopSort(); // 输出拓扑序列
void componentSC(); // 建立图g的强连通分量
void prim();
void dijkstra();
void bellmanFord();
// 动态规划求全最短路径
void dpAllDistance();
void floydWarshall();
private:
int vertex[maxSize]; // 存放顶点
GNode edges[maxSize]; // 存放邻接表
int vertexNum; //顶点个数
int edgesNum; //边条数
//bfs and dfs 遍历
int visited[maxSize];
void bfs(int s);
void dfs(int s);
int beginTime[maxSize]; // 深度开始访问x的时间
int endTime[maxSize]; // 结束访问x的时间
static int time;
vector<int> topSort; // topSort的逆序为有向无回路的拓扑排序
void buildTransGraph(Graph &g); // 建立图g的转置
// prim
map<int, int> mPriceQueue; // 保存最小生成树和dijkstra算法的造价
pair<int, int> getMinPriceVet();
int preNode[maxSize]; // 用于保存最小生成树的边 值为该结点的前驱
// 保存dijkstra 路径
string path[maxSize]; // 保存最终的最短路径
int minDistance[maxSize]; // 保存最终的最小距离
string intToStr(int i);
// 保存所有路劲
int minAllDistance[maxSize][maxSize];
string AllPath[maxSize][maxSize];
};
#endifgraph.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "graph.h"
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int Graph::time = 0;
void Graph::createGraph(int n, int e){
vertexNum = n;
edgesNum = e;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
vertex[i] = i;
edges[i].val = i;
edges[i].weight = 0;
edges[i].next = NULL;
}
for(int i = 0; i < e; i++){
int source, dest, wei;
cin >> source >> dest >> wei;
GNode *newNode = new GNode();
newNode->val = dest;
newNode->weight = wei;
newNode ->next = NULL;
GNode *p = &edges[source];
while(p->next != NULL) p = p->next;
p->next = newNode;
// 无向图 有向图就将这段删除掉
/*GNode *newNode2 = new GNode();
newNode2->val = source;
newNode2->weight = wei;
newNode2 ->next = NULL;
GNode *p2 = &edges[dest];
while(p2->next != NULL) p2 = p2->next;
p2->next = newNode2;*/
}
}
void Graph::destroyGraph(GNode *p){
if(p == NULL) return;
else{
destroyGraph(p->next);
delete p;
}
}
void Graph::showGraph(){
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
int j = i;
cout << i << "->";
GNode *p = edges[j].next;
while( p != NULL) {
cout << "(" << p->val <<"," << p->weight << ")" ;
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// 广度遍历图
void Graph::bfs(int s){
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
visited[s] = 1;
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << u <<" ";
GNode *p = edges[u].next;
while(p != NULL){
if(!visited[p->val]){ // 未被访问,则将其加入队列中并标志为访问过
q.push(p->val);
visited[p->val] = 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
}
void Graph::bfsTravel(){
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int)*vertexNum);
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
if(!visited[i]){
bfs(i);
cout << endl;
}
}
}
// 深度优先遍历
void Graph::dfs(int s){
visited[s] = 1;
time += 1;
beginTime[s] = time;
cout << s << "(" << beginTime[s] << " "; // shen
GNode *p = edges[s].next;
while(p != NULL){
if(!visited[p->val])
dfs(p->val);
p = p->next;
}
time += 1;
endTime[s] = time;
topSort.push_back(s);
cout << endTime[s] << ")" <<" ";
}
void Graph::dfsTravel(){
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int)*vertexNum);
memset(beginTime, 0, sizeof(int)*vertexNum); // 结点开始访问的时间
memset(endTime, 0, sizeof(int)*vertexNum); // 结点结束访问的时间
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
if(!visited[i]){
dfs(i);
cout << endl;
}
}
}
// 输出拓扑排序
void Graph::showTopSort(){
for(vector<int>::reverse_iterator iter = topSort.rbegin(); iter != topSort.rend(); iter ++)
cout << *iter << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// 创建图g的转置
void Graph::buildTransGraph(Graph &g){
this->vertexNum = g.vertexNum;
this->edgesNum = g.edgesNum;
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
this->vertex[i] = g.vertex[i];
this->edges[i].val = g.edges[i].val;
this->edges[i].weight = g.edges[i].weight;
this->edges[i].next = NULL;
}
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
GNode *p = g.edges[i].next;
while(p != NULL){
GNode *newNode = new GNode();
newNode->val = i;
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->weight = p->weight;
GNode *q = &edges[p->val];
while(q->next != NULL) q = q->next;
q->next = newNode;
p = p->next;
}
}
}
//强连通分量
void Graph::componentSC(){
//time = 0;
//dfsTravel(); // 对图g进行深度搜索得到完成x访问所需要的时间 并由此得到其拓扑排序
Graph g2;
g2.buildTransGraph(*this); // 得到图G的转置
time = 0;
memset(g2.visited, 0, sizeof(int)*vertexNum);
cout << "强连通分量: " << endl;
for(vector<int>::reverse_iterator iter = topSort.rbegin(); iter != topSort.rend(); iter++){ // 对转置图g2进行深度搜索得到强连通分量
if(!g2.visited[*iter])
g2.dfs(*iter);
}
cout << endl;
}
// 最小生成树
/*最小生成树采用的是贪心算法:设T是图G的MST(minimum spanning tree),
A属于V, (u,v)是连接A与V-A之间的一条边且权值最小,则(u,v)边属于最小生成树
lowcost存放代价*/
pair<int, int> Graph::getMinPriceVet(){
pair<int, int> p;
int minPrice = MAXPRICE;
int minPriceVet = 0;
for(map<int, int>::iterator iter = mPriceQueue.begin(); iter != mPriceQueue.end(); iter++){
if((*iter).second < minPrice){
minPrice = (*iter).second;
minPriceVet = (*iter).first;
p = *iter;
}
}
mPriceQueue.erase(minPriceVet); // 或者采用数组 此时就需要设置visited标记数组来判断该顶点是否已经加入S中了
return p;
}
void Graph::prim(){
mPriceQueue.clear();
mPriceQueue[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < vertexNum; i++){
mPriceQueue[i] = MAXPRICE;
}
while(!mPriceQueue.empty()){
pair<int, int> pMinNode = getMinPriceVet();
int minPriceVet = pMinNode.first;
GNode *p = edges[minPriceVet].next;
while(p != NULL){
if(mPriceQueue.count(p->val) && p->weight < mPriceQueue[p->val]){
mPriceQueue[p->val] = p->weight;
preNode[p->val] = minPriceVet;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
// 展示最小生成树的边
for(int i = 1; i < vertexNum; i++)
{
cout << "(" << preNode[i] << "," << i << ") ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// dijkstra 算法
string Graph::intToStr(int i){
string s;
stringstream ss;
ss << i;
ss >>s;
ss.clear();
return s;
}
void Graph::dijkstra(){
mPriceQueue.clear();
mPriceQueue[0] = 0;
path[0] = intToStr(0);
for(int i = 1; i < vertexNum; i++){
mPriceQueue[i] = MAXPRICE;
path[i] = "";
}
while(!mPriceQueue.empty()){
pair<int, int> pMinNode = getMinPriceVet(); // dijkstra的贪心策略就是该点就是此时的pMinNode.second就是最短路径
int minPriceVet = pMinNode.first;
minDistance[minPriceVet] = pMinNode.second; // 保存最短路径到minDistance中
GNode *p = edges[minPriceVet].next;
while(p != NULL){
if(mPriceQueue.count(p->val) && (p->weight + pMinNode.second) < mPriceQueue[p->val]){ // 松弛操作
mPriceQueue[p->val] = p->weight + pMinNode.second;
path[p->val] = path[minPriceVet] + intToStr(p->val);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
// 输出路径
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
cout << "从0到" << i << "的最短路径为: " <<path[i] << "; 距离为: " << minDistance[i] << endl;
}
}
// BellmanFord 算法
// 按照边的顺序松弛每一条边 V-1次
void Graph::bellmanFord(){
minDistance[0] = 0;
path[0] = intToStr(0);
for(int i = 1; i < vertexNum; i++){
minDistance[i] = MAXPRICE;
path[i] = "";
}
for(int m = 0; m < vertexNum-1; m++){
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
GNode *p = edges[i].next;
while(p != NULL){
if(minDistance[p->val] > p->weight + minDistance[i]){ // 松弛每一条边
minDistance[p->val] = minDistance[i] + p->weight;
path[p->val] = path[i] + intToStr(p->val);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){ // 检查是否存在负权回路
GNode *p = edges[i].next;
while(p != NULL){
if(minDistance[p->val] > p->weight + minDistance[i]){
cout << "该图存在负权环" << endl;
return;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
// 输出路径
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
cout << "从0到" << i << "的最短路径为: " <<path[i] << "; 距离为: " << minDistance[i] << endl;
}
}
// 用动态规划求全最短路径
void Graph::dpAllDistance(){
int Adj[maxSize][maxSize];
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
minAllDistance[i][j] = MAXPRICE;
if(i == j) minAllDistance[i][j] = 0;
AllPath[i][j] = intToStr(i);
Adj[i][j] = minAllDistance[i][j];
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
GNode *p = edges[i].next;
while(p != NULL){
minAllDistance[i][p->val] = p->weight; // 经过了1条边 即为权重
Adj[i][p->val] = p->weight;
AllPath[i][p->val] = AllPath[i][p->val] + intToStr(p->val);
p = p->next;
}
}
for(int m = 2; m < vertexNum; m++){ // 至多经过m条边
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
for(int k = 0; k < vertexNum; k++){
if(minAllDistance[i][j] > minAllDistance[i][k] + Adj[k][j]){
minAllDistance[i][j] = minAllDistance[i][k] + Adj[k][j];
AllPath[i][j] = AllPath[i][k] + intToStr(j);
}
}
}
}
}
// 检测是否存在负权环
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
if(minAllDistance[i][i] < 0){
cout << "该图存在负权环" << endl;
return;
}
}
// 将全对最短路径输出
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
cout << "从" <<i << "到" << j <<"的最短路径为: " << AllPath[i][j] << " 距离为: " << minAllDistance[i][j] << endl;
}
}
}
// floyd-warshall算法求最短路径问题
void Graph::floydWarshall(){
int Adj[maxSize][maxSize];
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
minAllDistance[i][j] = MAXPRICE;
if(i == j) minAllDistance[i][j] = 0;
AllPath[i][j] = intToStr(i);
Adj[i][j] = minAllDistance[i][j];
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
GNode *p = edges[i].next;
while(p != NULL){
minAllDistance[i][p->val] = p->weight; // 经过了1条边 即为权重
Adj[i][p->val] = p->weight;
AllPath[i][p->val] = AllPath[i][p->val] + intToStr(p->val);
p = p->next;
}
}
for(int k = 0; k < vertexNum; k++){
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
if(minAllDistance[i][j] > minAllDistance[i][k] + minAllDistance[k][j]){
minAllDistance[i][j] = minAllDistance[i][k] + minAllDistance[k][j];
AllPath[i][j] = AllPath[i][k] + AllPath[k][j];
}
}
}
}
// 检测是否存在负权环
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
if(minAllDistance[i][i] < 0){
cout << "该图存在负权环" << endl;
return;
}
}
// 将全对最短路径输出
for(int i = 0; i < vertexNum; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < vertexNum; j++){
cout << "从" <<i << "到" << j <<"的最短路径为: " << AllPath[i][j] << " 距离为: " << minAllDistance[i][j] << endl;
}
}
}