【DataStructure】The difference among methods addAll(),retainAll() and removeAll()
In the Java collection framework, there are three similar methods, addAll(),retainAll() and removeAll(). addAll(), the retainAll(), and the removeAll()methods are equivalent to the set theoretic union, intersection, and complement operators, respectively. These are illustrated in the following picture.
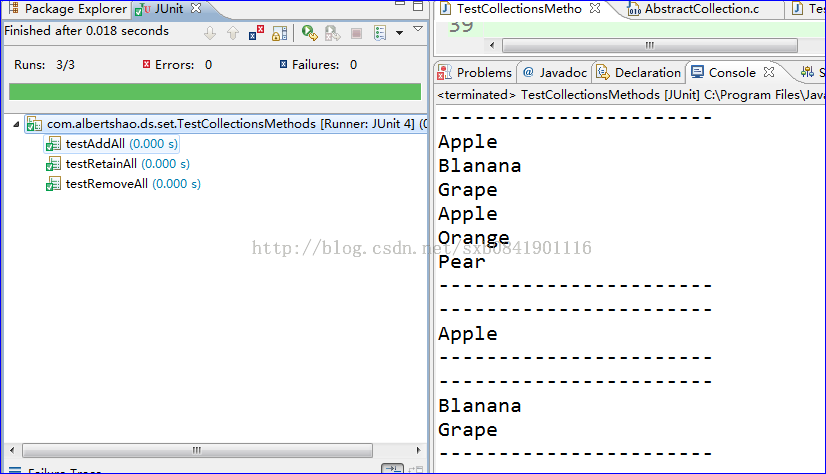
In my local machine, just for these methods, I made a test for them respectively.
package com.albertshao.ds.set;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestCollectionsMethods {
List<String> listA = null;
List<String> listB = null;
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> testList = new ArrayList<String>();
@Test
public void testAddAll() {
listA = Arrays.asList("Apple","Blanana","Grape");
listB = Arrays.asList("Apple","Orange","Pear");
Collections.addAll(testList,"Apple","Blanana","Grape","Apple","Orange","Pear");
result.addAll(listA);
result.addAll(listB);
assertEquals(testList, result);
}
@Test
public void testRetainAll() {
listA = Arrays.asList("Apple","Blanana","Grape");
listB = Arrays.asList("Apple","Orange","Pear");
Collections.addAll(testList,"Apple");
result.addAll(listA);
result.retainAll(listB);
assertEquals(testList, result);
}
@Test
public void testRemoveAll() {
listA = Arrays.asList("Apple","Blanana","Grape");
listB = Arrays.asList("Apple","Orange","Pear");
Collections.addAll(testList,"Blanana","Grape");
result.addAll(listA);
result.removeAll(listB);
assertEquals(testList, result);
}
@After
public void testPrint()
{
System.out.println("-----------------------");
if(result != null && !result.isEmpty())
{
for(String str: result)
{
System.out.println(str);
}
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
}
The result of execution is as follows:
Hope it's beneficial to you