JSP过滤器导图详解
过滤器是web开发中常用的开发方式,比如一些典型的应用场景:
用户身份认证、对用户请求进行记录和审核、对用户发送的数据进行替换和过滤、转换图像格式、对响应内容压缩、加密请求或响应等等。
本篇就了解下监听器的主要使用方法。
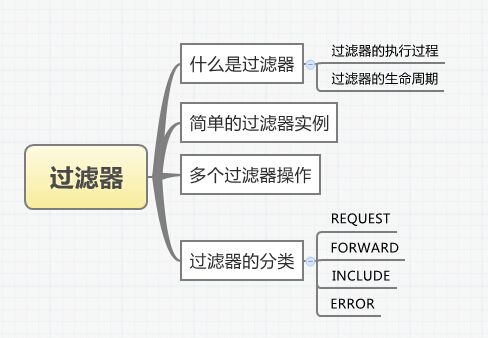
什么是过滤器?
过滤器的生命周期
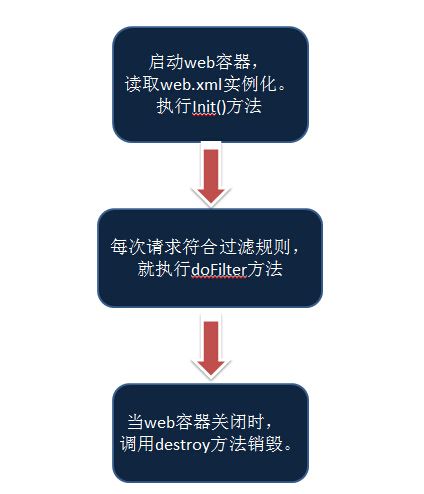
过滤器的生命周期与web容器相同,当web容器启动时,就会读取应用的web.xml配置文件,如果这里配置了过滤器,容器就会执行实例化,并调用过滤器的init方法。
之后用户的每一次请求都会执行过滤器的doFilter方法。
当web容器销毁时,就会执行destroy方法,释放资源。
过滤器的执行过程
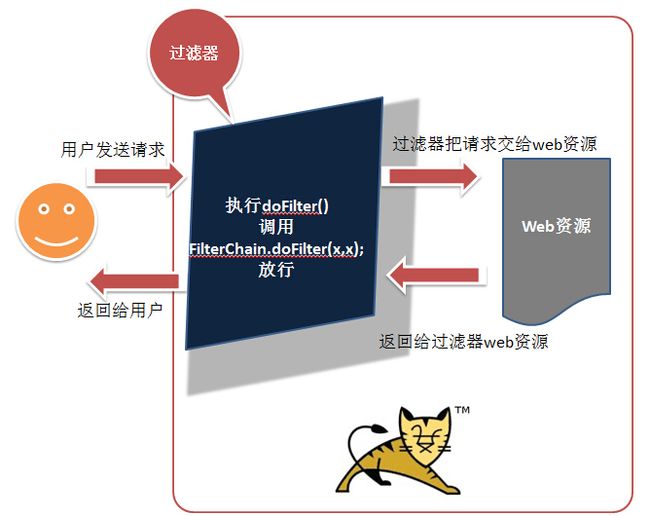
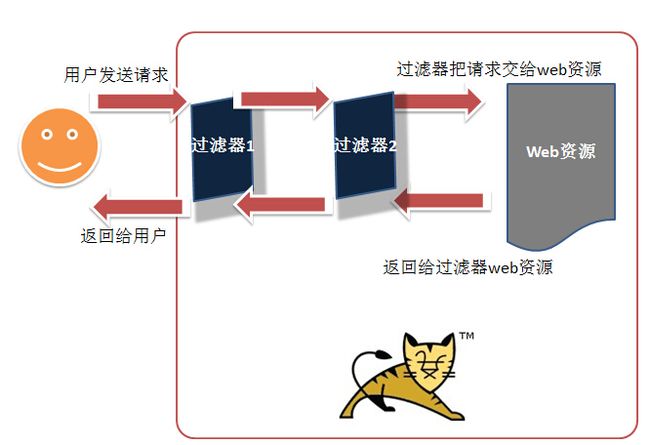
过滤器看名字就能知道大概的用法,它就像一个筛子,可以筛选特定的数据或请求。执行过程如下图所示:
用户在发送请求后,如果该请求满足过滤器的过滤规则,web容器就会执行过滤器中的doFilter方法进行特定的操作;然后通过调用FilterChain.doFilter转交给web容器。web容器执行完成后把资源返回给过滤器,再展现给用户。
简单的过滤器实例
下面通过一个简单的代码,看看过滤器的编写。
首先,需要创建一个过滤器,过滤器集成javax.servlet.Filter接口,其中必须实现三个方法:init() doFilter() destroy()
public class MyFilter implements Filter{ public void destroy() { System.out.println("MyFilter destroy"); } public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { System.out.println("MyFilter start...dofilter"); chain.doFilter(request, response);//对请求放行 System.out.println("MyFilter end...dofilter"); } public void init(FilterConfig arg0) throws ServletException { System.out.println("MyFilter init"); } }
init()方法是在web容器实例化过滤器时调用的。
doFilter()方法是每次有请求,且满足过滤规则时调用。
destroy()方法是web容器关闭时,调用。
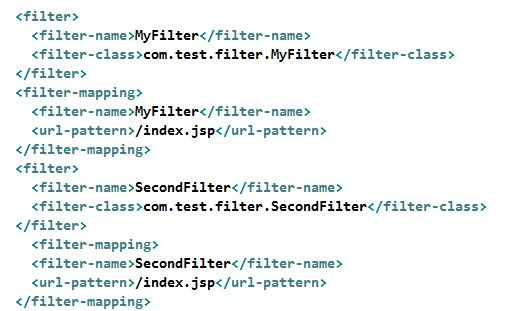
然后,在web.xml中配置相应的选项。如果是servlet3.0,那么支持注解的方式配置过滤器。
<filter> <filter-name>MyFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>com.test.filter.MyFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>MyFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/index.jsp</url-pattern> <!--<dispatcher></dispatcher>--> </filter-mapping>
其中几个必备的项:
在<filter>中配置了过滤器,filter-name是过滤器的名字,filter-class是过滤器的类;
在<filter-mapping>中配置了过滤器的映射规则,filter-name是过滤器的名字,url-pattern是过滤的规则,dispatcher是过滤器的分类(主要包括四种,稍后讲解)
这里先说下过滤器的规则,如果想要全部的请求都过滤,那么可以写/*
如果想要过滤index.jsp index.html 可以写/index*
如果只想过滤index.jsp,可以写成/index.jsp
其次,配置好后,创建index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> This is Filter JSP! <% System.out.println("index jsp"); %> </body> </html> View Code
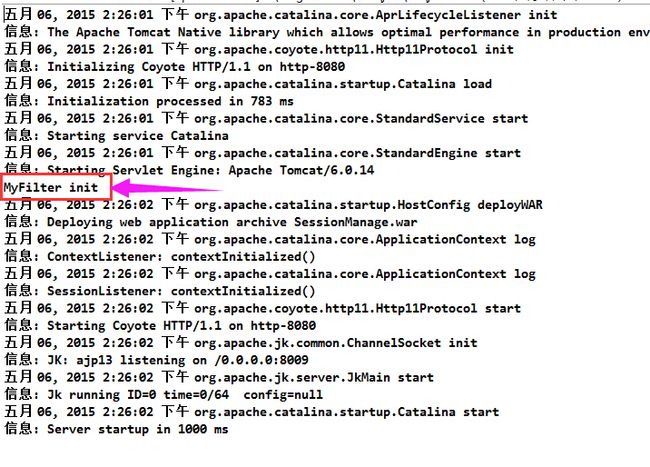
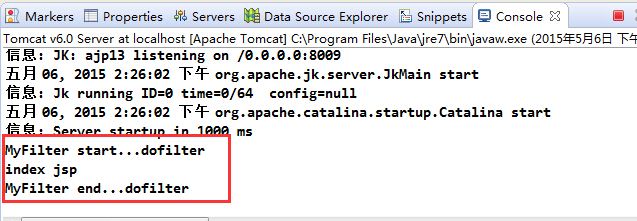
最后,当启动web容器后,可以在控制台中发现,初始化时,执行了init方法
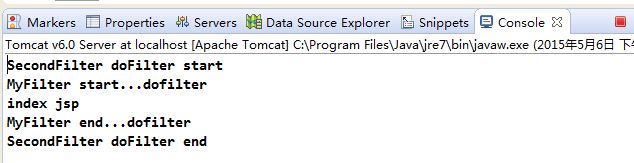
访问对应的web资源,可以看到控制台按照执行的顺序打印消息:
多个过滤器操作
多个过滤器执行与上面差不多。
在上面代码的基础上,再增加一个过滤器:
public class SecondFilter implements Filter{public void destroy() { System.out.println("SecondFilter destroy()"); } public void doFilter(ServletRequest arg0, ServletResponse arg1, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { System.out.println("SecondFilter doFilter start"); chain.doFilter(arg0, arg1); System.out.println("SecondFilter doFilter end"); } public void init(FilterConfig arg0) throws ServletException { System.out.println("SecondFilter init()"); } }
在web.xml中增加过滤器配置
<filter> <filter-name>SecondFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>com.test.filter.SecondFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>SecondFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/index.jsp</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
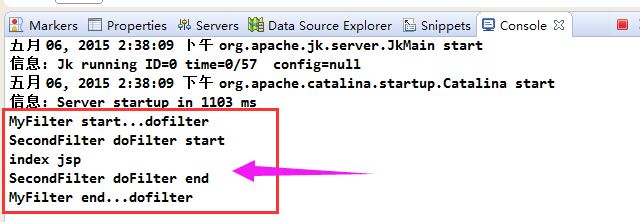
启动web容器,控制台输出init信息
访问页面,可以看到由于在web.xml中映射配置MyFilter在SecondFilter上面,
因此输出如下消息:
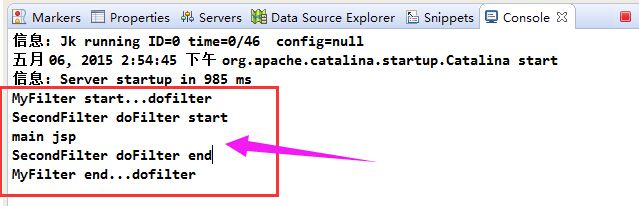
类似的,如果把SecondFilter配置放在上面,就会先执行SecondFilter的doFilter方法。
过滤器的分类
最后看一下过滤器的分类,过滤器主要包括四种,REQUEST\FORWARD\INCLUDE\ERROR(3.0额外新增了一个异步请求ASYNC)。
上面的过滤器都是采用REQUEST的方式,直接请求。由于没有配置dispathcer,默认就会按照REQUEST的方式进行。
直接看一下FORWARD的使用方法,在doFilter中执行下面的方法:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { System.out.println("MyFilter start...dofilter"); HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest)request; req.getRequestDispatcher("main.jsp").forward(request, response); System.out.println("MyFilter end...dofilter"); }
此时页面请求就会直接跳转到main.jsp,触发FORWARD类型过滤器,过滤器配置选项如下:
<filter> <filter-name>MyFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>com.test.filter.MyFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>MyFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/index.jsp</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <filter> <filter-name>SecondFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>com.test.filter.SecondFilter</filter-class> </filter> <!-- <filter-mapping> <filter-name>SecondFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/index.jsp</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> --> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>SecondFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/main.jsp</url-pattern> <dispatcher>FORWARD</dispatcher> </filter-mapping>
启动后发现,原本请求Index.jsp跳转到了main.jsp。
此时,如果第二个过滤器采用的是REQUEST,就不会触发了。
另外,还可以使用JSP页面标签,执行跳转,此时过滤器也可以触发。比如在JSP页面中添加<jsp:forward>标签
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%> <jsp:forward page="/main.jsp"></jsp:forward> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> </body> </html>
INCLUDE与FORWARD类似,使用方法也相同,只是名字不同而已,就不做过多的介绍了。
然后看一下ERROR过滤器,通常我们会在web.xml中配置错误页面,如下:
<error-page> <error-code>404</error-code> <location>/error.jsp</location> </error-page>
此时,如果访问不存在的页面,http://localhost:8080/xxx.jsp就会跳转到error.jsp
此时如果过滤器通过REQUEST方式,想要触发,url填写的是/error.jsp并不会起作用,此时就需要把dispathcer改成 ERROR,并且放置在error-page标签下面:
<error-page> <error-code>404</error-code> <location>/error.jsp</location> </error-page> <!-- 需要放在errorpage下面 --> <filter> <filter-name>ErrorFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>com.test.filter.ErrorFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>ErrorFilter</filter-name> <rl-pattern>/error.jsp</url-pattern> <dispatcher>ERROR</dispatcher> </filter-mapping>
这样就会触发ERROR过滤器了。
参考
【1】过滤器的应用:http://www.ylzx8.cn/web/web/979338.html
【2】过滤器视频教程:http://www.imooc.com/learn/213
本本文借鉴:http://www.cnblogs.com/xing901022/p/4482057.html#_labelTop