adapter就是数据适配器,它的功能是将数据绑定到UI界面上;系统本身提供了几种简单的适配器,如果界面比较复杂的话最好用自定义适配器。
Android是完全遵循MVC模式设计的框架,Activity是Controller,layout是View
因为layout五花八门,很多数据都不能直接绑定上去,所以Android引入了Adapter这个机制作为复杂数据的展示的转换载体,所以各种Adapter只不过是转换的方式和能力不一样而已。
几种常用的Adapter:
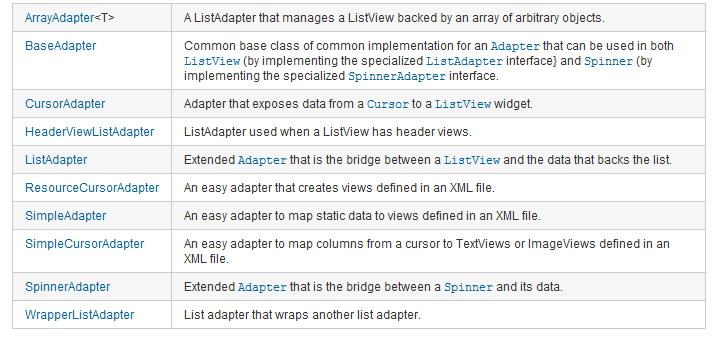
在多数情况下,你不需要白手创建自己的Adapter。Android提供了一系列Adapter来将数据绑定到UI Widget上。
因为Android负责提供数据和选择用于显示每个项目的View,所以Adapter能快速地修改要绑定的控件的外观和功能。下面的列表显示了两个最有用和最通用的本地Adapter:
❑ ArrayAdapter
ArrayAdapter是一个绑定View到一组对象的通用类。默认情况下,ArrayAdapter绑定每个对象的toString值到在layout中预先定义的TextView控件上。可变通的,构造函数允许你使用更加复杂的layout或者通过重写getView方法来扩展类从而使用TextView的替代物(如ImageView或嵌套的layout)。
❑ SimpleCursorAdapter
SimpleCursorAdapter绑定View到Content Provider查询返回的游标上。指定一个XML layout定义,然后将数据集中的每一列的值绑定到layout中的一个View上。
下面演示一下SimpleAdapter的用法:
package com.wt.app;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.ContextMenu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ContextMenu.ContextMenuInfo;
import android.view.View.OnCreateContextMenuListener;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
public class App extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//绑定Layout里面的ListView
ListView list = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.ListView01);
//生成动态数组,加入数据
ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>> listItem = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, Object>>();
int[] images=new int[]{android.R.drawable.ic_menu_add,android.R.drawable.ic_menu_delete,android.R.drawable.ic_menu_edit,android.R.drawable.ic_menu_view};
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("itemImage", images[i]);//图像资源的ID
map.put("itemTitle", "Title "+i);
map.put("itemText", "this is Text "+i);
listItem.add(map);
}
//生成适配器的Item和动态数组对应的元素
SimpleAdapter listItemAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(this,listItem,//数据源
R.layout.row,//ListItem的XML实现
//动态数组与ImageItem对应的子项
new String[] {"itemImage","itemTitle", "itemText"},
//ImageItem的XML文件里面的一个ImageView,两个TextView ID
new int[] {R.id.itemImage,R.id.itemTitle,R.id.itemText}
);
//添加并且显示
list.setAdapter(listItemAdapter);
//添加点击
list.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener() {
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, int arg2,
long arg3) {
setTitle("点击第"+arg2+"个项目");
}
});
//添加长按点击
list.setOnCreateContextMenuListener(new OnCreateContextMenuListener() {
public void onCreateContextMenu(ContextMenu menu, View v,ContextMenuInfo menuInfo) {
menu.setHeaderTitle("长按菜单-ContextMenu");
menu.add(0, 0, 0, "弹出长按菜单0");
menu.add(0, 1, 0, "弹出长按菜单1");
}
});
}
//长按菜单响应函数
@Override
public boolean onContextItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
setTitle("点击了长按菜单里面的第"+item.getItemId()+"个项目");
return super.onContextItemSelected(item);
}
}
整体布局文件,一个简单的ListView:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<ListView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/ListView01"
/>
</LinearLayout>
ListView中每行(row)怎么显示的布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/RelativeLayout01"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingTop="4dip"
android:paddingBottom="4dip"
android:paddingLeft="12dip"
android:paddingRight="12dip">
<ImageView
android:paddingTop="12dip"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/itemImage"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="20dip"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:id="@+id/itemTitle"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_below="@+id/itemTitle"
android:id="@+id/itemText"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
下面演示了BaseExpandableListAdapter的用法:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2007 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.example.android.apis.view;
import android.app.ExpandableListActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.ContextMenu;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.ContextMenu.ContextMenuInfo;
import android.widget.AbsListView;
import android.widget.BaseExpandableListAdapter;
import android.widget.ExpandableListAdapter;
import android.widget.ExpandableListView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.widget.ExpandableListView.ExpandableListContextMenuInfo;
import com.example.android.apis.R;
/**
* Demonstrates expandable lists using a custom {@link ExpandableListAdapter}
* from {@link BaseExpandableListAdapter}.
*/
public class ExpandableList1 extends ExpandableListActivity {
ExpandableListAdapter mAdapter;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Set up our adapter
mAdapter = new MyExpandableListAdapter();
setListAdapter(mAdapter);
registerForContextMenu(getExpandableListView());
}
@Override
public void onCreateContextMenu(ContextMenu menu, View v, ContextMenuInfo menuInfo) {
menu.setHeaderTitle("Sample menu");
menu.add(0, 0, 0, R.string.expandable_list_sample_action);
}
@Override
public boolean onContextItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
ExpandableListContextMenuInfo info = (ExpandableListContextMenuInfo) item.getMenuInfo();
String title = ((TextView) info.targetView).getText().toString();
int type = ExpandableListView.getPackedPositionType(info.packedPosition);
if (type == ExpandableListView.PACKED_POSITION_TYPE_CHILD) {
int groupPos = ExpandableListView.getPackedPositionGroup(info.packedPosition);
int childPos = ExpandableListView.getPackedPositionChild(info.packedPosition);
Toast.makeText(this, title + ": Child " + childPos + " clicked in group " + groupPos,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
} else if (type == ExpandableListView.PACKED_POSITION_TYPE_GROUP) {
int groupPos = ExpandableListView.getPackedPositionGroup(info.packedPosition);
Toast.makeText(this, title + ": Group " + groupPos + " clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* A simple adapter which maintains an ArrayList of photo resource Ids.
* Each photo is displayed as an image. This adapter supports clearing the
* list of photos and adding a new photo.
*
*/
public class MyExpandableListAdapter extends BaseExpandableListAdapter {
// Sample data set. children[i] contains the children (String[]) for groups[i].
private String[] groups = { "People Names", "Dog Names", "Cat Names", "Fish Names" };
private String[][] children = {
{ "Arnold", "Barry", "Chuck", "David" },
{ "Ace", "Bandit", "Cha-Cha", "Deuce" },
{ "Fluffy", "Snuggles" },
{ "Goldy", "Bubbles" }
};
public Object getChild(int groupPosition, int childPosition) {
return children[groupPosition][childPosition];
}
public long getChildId(int groupPosition, int childPosition) {
return childPosition;
}
public int getChildrenCount(int groupPosition) {
return children[groupPosition].length;
}
public TextView getGenericView() {
// Layout parameters for the ExpandableListView
AbsListView.LayoutParams lp = new AbsListView.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, 64);
TextView textView = new TextView(ExpandableList1.this);
textView.setLayoutParams(lp);
// Center the text vertically
textView.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL | Gravity.LEFT);
// Set the text starting position
textView.setPadding(36, 0, 0, 0);
return textView;
}
public View getChildView(int groupPosition, int childPosition, boolean isLastChild,
View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
TextView textView = getGenericView();
textView.setText(getChild(groupPosition, childPosition).toString());
return textView;
}
public Object getGroup(int groupPosition) {
return groups[groupPosition];
}
public int getGroupCount() {
return groups.length;
}
public long getGroupId(int groupPosition) {
return groupPosition;
}
public View getGroupView(int groupPosition, boolean isExpanded, View convertView,
ViewGroup parent) {
TextView textView = getGenericView();
textView.setText(getGroup(groupPosition).toString());
return textView;
}
public boolean isChildSelectable(int groupPosition, int childPosition) {
return true;
}
public boolean hasStableIds() {
return true;
}
}
}
SimpleCursorTreeAdapter用法:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2007 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.example.android.apis.view;
import android.app.ExpandableListActivity;
import android.content.ContentUris;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.provider.Contacts.People;
import android.widget.ExpandableListAdapter;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorTreeAdapter;
/**
* Demonstrates expandable lists backed by Cursors
*/
public class ExpandableList2 extends ExpandableListActivity {
private int mGroupIdColumnIndex;
private String mPhoneNumberProjection[] = new String[] {
People.Phones._ID, People.Phones.NUMBER
};
private ExpandableListAdapter mAdapter;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Query for people
Cursor groupCursor = managedQuery(People.CONTENT_URI,
new String[] {People._ID, People.NAME}, null, null, null);
// Cache the ID column index
mGroupIdColumnIndex = groupCursor.getColumnIndexOrThrow(People._ID);
// Set up our adapter
mAdapter = new MyExpandableListAdapter(groupCursor,
this,
android.R.layout.simple_expandable_list_item_1,
android.R.layout.simple_expandable_list_item_1,
new String[] {People.NAME}, // Name for group layouts
new int[] {android.R.id.text1},
new String[] {People.NUMBER}, // Number for child layouts
new int[] {android.R.id.text1});
setListAdapter(mAdapter);
}
public class MyExpandableListAdapter extends SimpleCursorTreeAdapter {
public MyExpandableListAdapter(Cursor cursor, Context context, int groupLayout,
int childLayout, String[] groupFrom, int[] groupTo, String[] childrenFrom,
int[] childrenTo) {
super(context, cursor, groupLayout, groupFrom, groupTo, childLayout, childrenFrom,
childrenTo);
}
@Override
protected Cursor getChildrenCursor(Cursor groupCursor) {
// Given the group, we return a cursor for all the children within that group
// Return a cursor that points to this contact's phone numbers
Uri.Builder builder = People.CONTENT_URI.buildUpon();
ContentUris.appendId(builder, groupCursor.getLong(mGroupIdColumnIndex));
builder.appendEncodedPath(People.Phones.CONTENT_DIRECTORY);
Uri phoneNumbersUri = builder.build();
// The returned Cursor MUST be managed by us, so we use Activity's helper
// functionality to manage it for us.
return managedQuery(phoneNumbersUri, mPhoneNumberProjection, null, null, null);
}
}
}
