<> Chapter 1 学习笔记
<<Signals and systems>> Chapter 1
下决心要啃完这本信号与系统!
这个人的名字我在键盘上敲了N次... Alan V. alppenhiem
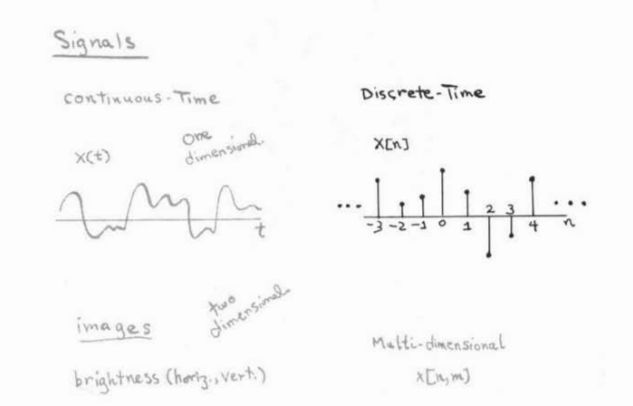
两大信号类别:
离散信号以及连续信号
左右两边分别时是典型的连续周期信号和离散周期信号的表现形式.
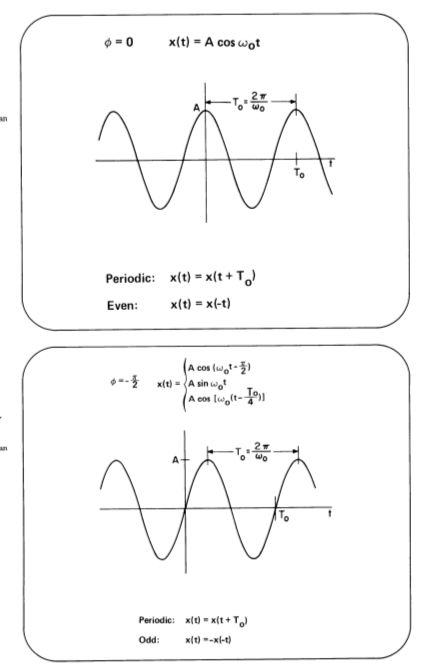
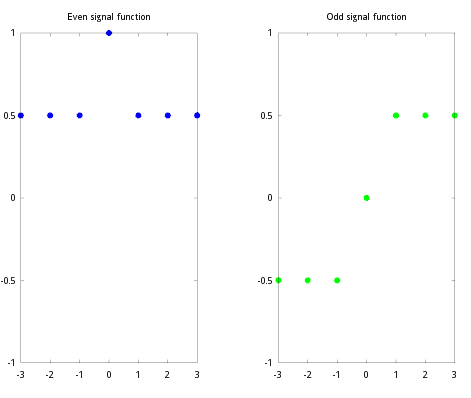
注意信号函数的奇偶性
Even : x( -t) = x(t)
Odd : x(- t) = - x(t)
下图上面单位阶跃函数(unit step function)的离散形式,下面是单位脉冲函数的离散形式(unit impulse function)
这是最重要的基本信号类型,其他的类型都是围绕这些基础信号类型变化的!
一个非常重要的事实就是: 任何信号都能分解成一个奇函数信号和偶函数信号的线性叠加和.
可能会疑问,为什么啊?
想想一个信号x(t) ,如果表示为x( - t) ,这意味着什么?
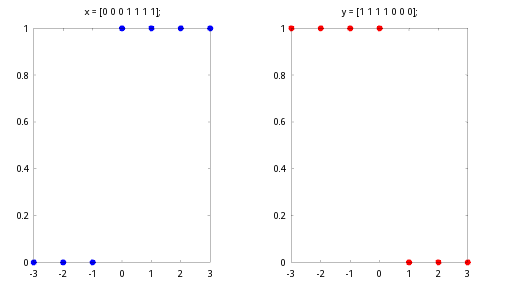
x(-t )和x(t) 在时间轴t上是“镜像对称的” ,比方说这里的x 和y。 也就是说任意信号x(t) 都可以通过x(-t) 得到它的"镜像信号"
这就会引出一个性质,
(x(t) + x(-t))/2 这就会得到一个偶函数
(x(t) - x(-t))/2 这就会得到一个奇函数
这两个函数相加即可得到x(t),So ....任何信号都能分解成一个奇函数信号和偶函数信号的线性叠加和
x = [0 0 0 1 1 1 1];
y = [1 1 1 1 0 0 0];
figure(1);
subplot(1,2,1);
scatter(-3:3,x,"filled" );
title('x = [0 0 0 1 1 1 1];');
subplot(1,2,2);
scatter(-3:3,y,'r',"filled");
title('y = [1 1 1 1 0 0 0];');
figure(2);
subplot(1,2,1);
scatter(-3:3,(x+y)/2,"filled");
axis([-3,3,-1,1]);
title('Even signal function');
subplot(1,2,2);
scatter(-3:3,(x-y)/2,'g',"filled");
axis([-3,3,-1,1]);
title('Odd signal function');
Basic system properties
system with and without memory.
一定要死死的抓住这个定义:
A system is said to be memoryless if its output for each value of the independent variable at a given time is dependent only on the input at that same time.
y[x] = x[n]*x[n] 就是memoryless的system
一旦输出y[n] 涉及x[n]之前x[n-1], x[n-2]... 任意一个信号就memory system!
典型的discrete-time system with memory 是累加器(accumulator)
y[n] =
sum = 0;
for -NAN to n
sum = sum + x[k];
end
(坑爹,只能用伪代码表示累加...)
另外典型的memory system operation就是delay
y[n] = x[n -1];
Causality (因果性)
既然输出y[n] 可能取决于x[n-1]等等以前的输入信号,而形成memory system...那如果y[n] 取决于x[n+1]等等未来时刻的输入信号呢??
这里就要谈到系统的另外一种性质了——causality
A system is causal if the output at any time depends only on values of the input at the present time and in the past.
y[n] = y[n -1] + x[n]; 就是满足causality条件的
y[n] = x[n] - x[n+1]就不满足causality 条件!
所有的memoryless system都是causality的,因为当前输出仅仅取决于当前的输入.
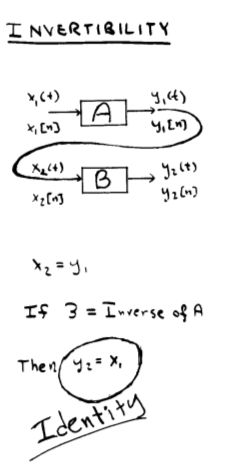
Invertibility and inverse systems
A system is said to be invertible if distinct inputs lead to distinct outputs.
比方说y(t) = 2*x(t) 对应的inverse system就是w(t) = (1/2)*y(t);
stability
A stable system is one in which small inputs lead to responses that do not diverge.
简单的说一个稳定的系统就是要最后能够收敛下来,不收敛的系统是不稳定的.
Time invariance
A system is time invariant if the behavior and characteristics of the sytem are fixed over time.
说白了 就是对系统今天做的测试和昨天做的测试结果是一致的.
下面是一个典型的时不变系统的证明过程:
Linearity
The system is linear if
1. the response to x1(t) + x2(t) is y1(t)+y2(t)
2. the response to ax1(t) is ay1(t) ,where a is any complex constant。
第一条是可加性,第二条是齐次性.
举个反例子说明:
y(t) = x(t)*x(t); 这个系统不是线性系统。
输入5x(t)的不是不是5y(t),而是25*y(t).不满足齐次性
Octave 画图提示:
stem函数画散点图
x = 1:10;y = 2*x; stem(x, y,'filled')
scatter也可以用.
《有阳台的房间》