让32位应用程序不再为2G内存限制苦恼
最近在做个程序,虽然是小型程序,但是使用的内存量却很大,动辄达到10G。在64位系统上可以轻松实现,无奈我是基于32位的系统进行开发,程序还没跑起来就已经被终止了。
试过很多办法,包括文件内存映射等,效率不高,而且由于32位应用程序的限制,可用的内存地址最高只能到0x7FFFFFFF,能调用的内存到2G就是极限了。最后好不容易找到了AWE(Address Windowing Extensions)。
AWE是Windows的内存管理功能的一组扩展,它允许应用程序获取物理内存,然后将非分页内存的视图动态映射到32位地址空间。虽然32位地址空间限 制为4GB,但是非分页内存却可以远远大于4GB。这使需要大量内存的应用程序(如大型数据库系统)能使用的内存量远远大于32位地址空间所支持的内存 量。
与AWE有关的函数在后面介绍。
为了使用大容量内存,除了要用到AWE外,还有一样东西不能少,那就是PAE(Physical Address Extension)。PAE是基于x86的服务器的一种功能,它使运行Windows Server 2003,Enterprise Edition 和Windows Server 2003,Datacenter Edition 的计算机可以支持 4 GB 以上物理内存。物理地址扩展(PAE)允许将最多64 GB的物理内存用作常规的4 KB页面,并扩展内核能使用的位数以将物理内存地址从 32扩展到36。
一般情况下,windows系统的PAE没有生效,只有开启了PAE后windows系统才可以识别出4G以上的内存。在使用boot.int的系统中, 要启动PAE必须在boot.ini中加入/PAE选项。在Windows Vista和Windows7中则必须修改内核文件,同时设置BCD启动项。针对Vista系统和Win7系统可以使用Ready For 4GB这个软件直接完成这一操作,具体方法见Ready For 4GB的软件说明。以下就是一个开启了/PAE选项的boot.ini文件示例:
- [boot loader]
- timeout=30
- default=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)WINDOWS
- [operating systems]
- multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)WINDOWS="Windows Server 2003, Enterprise" /fastdetect /PAE
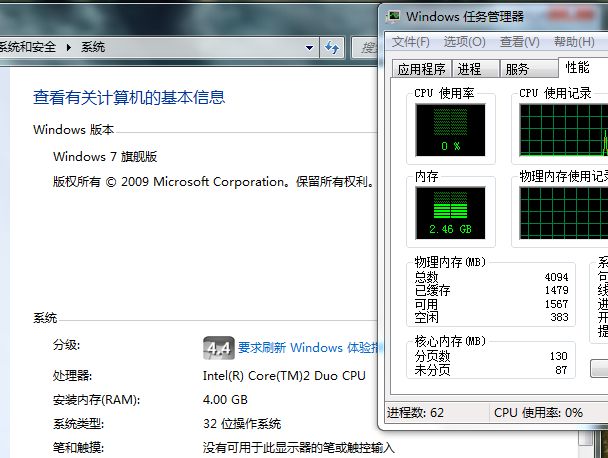
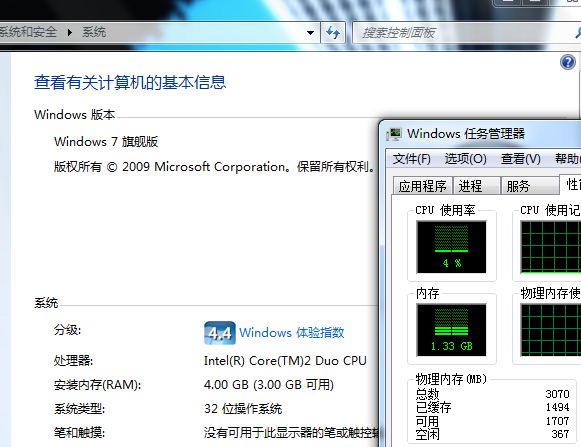
本文将以Windows 7旗舰版为例介绍如何在打开PAE的情况下使用AWE在程序中达到使用2G以上内存的目的。下图分别为开启PAE和未开启PAE时系统识别出的内存容量区别。
图二.关闭PAE
如果没有打开PAE,系统只能认出3G的内存,最多可以再多0.5G不到,这样即使使用AWE,由于系统和其他应用程序已经占去了一部分内存,剩下的内存或许也只有2G多一点了,没什么太大提高。只有当系统认出了4G以上的内存,AWE才能发挥它真正的作用。
下面我们看看windows中给出的有关AWE的API函数,它们都定义在winbase.h中。
- #if (_WIN32_WINNT >= 0x0500)
- //
- // Very Large Memory API Subset
- //
- WINBASEAPI
- BOOL
- WINAPI
- AllocateUserPhysicalPages(
- __in HANDLE hProcess,
- __inout PULONG_PTR NumberOfPages,
- __out_ecount_part(*NumberOfPages, *NumberOfPages) PULONG_PTR PageArray
- );
- WINBASEAPI
- BOOL
- WINAPI
- FreeUserPhysicalPages(
- __in HANDLE hProcess,
- __inout PULONG_PTR NumberOfPages,
- __in_ecount(*NumberOfPages) PULONG_PTR PageArray
- );
- WINBASEAPI
- BOOL
- WINAPI
- MapUserPhysicalPages(
- __in PVOID VirtualAddress,
- __in ULONG_PTR NumberOfPages,
- __in_ecount_opt(NumberOfPages) PULONG_PTR PageArray
- );
- //...
- #endif
从winbase.h中的定义可以看出,只有当你的系统版本大于或等于0x0500时,才能够使用AWE。各个版本的_WIN32_WINNT值见下表,Windows 2000以下的版本不能使用AWE。
| Minimum system required |
Minimum value for _WIN32_WINNT and WINVER |
| Windows 7 |
0x0601 |
| Windows Server 2008 |
0x0600 |
| Windows Vista |
0x0600 |
| Windows Server 2003 with SP1, Windows XP with SP2 |
0x0502 |
| Windows Server 2003, Windows XP |
0x0501 |
| Windows 2000 |
0x0500 |
如果你的系统版本符合要求,但是编译器在编译加入了AWE API的代码出错,可以在程序头文件中加入下面的代码。
- #ifndef _WIN32_WINNT
- #define _WIN32_WINNT 0x0501
- #endif
下面简要介绍一下每个API的功能。
- BOOL WINAPI AllocateUserPhysicalPages( //分配物理内存页,用于后面AWE的内存映射
- __in HANDLE hProcess, //指定可以使用此函数分配的内存页的进程
- __inout PULONG_PTR NumberOfPages, //分配的内存页数,页的大小由系统决定
- __out PULONG_PTR UserPfnArray //指向存储分配内存页帧成员的数组的指针
- );
- BOOL WINAPI FreeUserPhysicalPages( //释放AllocateUserPhysicalPages函数分配的内存
- __in HANDLE hProcess, //释放此进程虚拟地址空间中的分配的内存页
- __inout PULONG_PTR NumberOfPages, //要释放的内存页数
- __in PULONG_PTR UserPfnArray //指向存储内存页帧成员的数组的指针
- );
- BOOL WINAPI MapUserPhysicalPages( //将分配好的内存页映射到指定的地址
- __in PVOID lpAddress, //指向要重映射的内存区域的指针
- __in ULONG_PTR NumberOfPages, //要映射的内存页数
- __in PULONG_PTR UserPfnArray //指向要映射的内存页的指针
- );
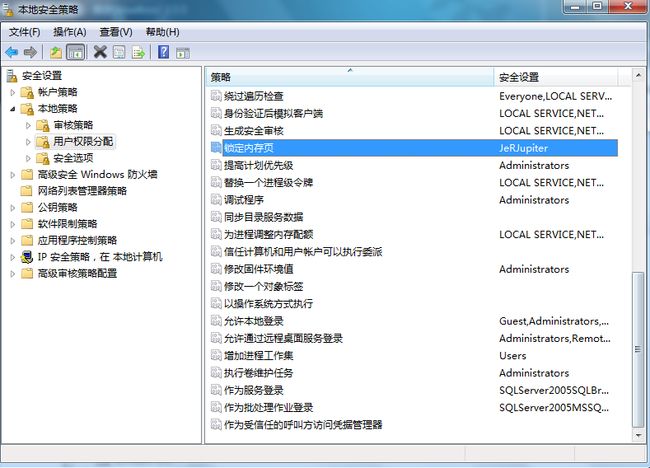
在看实例程序前还有一些设置需要做,需要对系统的本地安全策略进行设置。在win7中,打开“控制面板->系统和安全->管理工具->本地安全策略”,给“锁定内存页”添加当前用户,然后退出,重启(不重启一般无法生效!)。
经过前面的准备(再啰嗦一次:确认自己的电脑装有4G或4G以上的内存;开启PAE,使系统认出4G或以上的内存;设置好本地安全策略),我们就可以通过下面的代码来做个实验了。
代码是从MSDN中AWE的一个Example修改而来的,具体流程见代码中的注释,如果对该Example的源代码有兴趣可以参考MSDN。
- #include "AWE_TEST.h"
- #include <windows.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #define MEMORY_REQUESTED ((2*1024+512)*1024*1024) //申请2.5G内存,测试机上只有4G内存,而且系统是window7,比较占内存.申请3G容易失败.
- #define MEMORY_VIRTUAL 1024*1024*512 //申请长度0.5G的虚拟内存,即AWE窗口.
- //检测"锁定内存页"权限的函数
- BOOL LoggedSetLockPagesPrivilege ( HANDLE hProcess, BOOL bEnable);
- void _cdecl main()
- {
- BOOL bResult; // 通用bool变量
- ULONG_PTR NumberOfPages; // 申请的内存页数
- ULONG_PTR NumberOfPagesInitial; // 初始的要申请的内存页数
- ULONG_PTR *aPFNs; // 页信息,存储获取的内存页成员
- PVOID lpMemReserved; // AWE窗口
- SYSTEM_INFO sSysInfo; // 系统信息
- INT PFNArraySize; // PFN队列所占的内存长度
- GetSystemInfo(&sSysInfo); // 获取系统信息
- printf("This computer has page size %d./n", sSysInfo.dwPageSize);
- //计算要申请的内存页数.
- NumberOfPages = MEMORY_REQUESTED/sSysInfo.dwPageSize;
- printf ("Requesting %d pages of memory./n", NumberOfPages);
- // 计算PFN队列所占的内存长度
- PFNArraySize = NumberOfPages * sizeof (ULONG_PTR);
- printf ("Requesting a PFN array of %d bytes./n", PFNArraySize);
- aPFNs = (ULONG_PTR *) HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(), 0, PFNArraySize);
- if (aPFNs == NULL)
- {
- printf ("Failed to allocate on heap./n");
- return;
- }
- // 开启"锁定内存页"权限
- if( ! LoggedSetLockPagesPrivilege( GetCurrentProcess(), TRUE ) )
- {
- return;
- }
- // 分配物理内存,长度2.5GB
- NumberOfPagesInitial = NumberOfPages;
- bResult = AllocateUserPhysicalPages( GetCurrentProcess(),
- &NumberOfPages,
- aPFNs );
- if( bResult != TRUE )
- {
- printf("Cannot allocate physical pages (%u)/n", GetLastError() );
- return;
- }
- if( NumberOfPagesInitial != NumberOfPages )
- {
- printf("Allocated only %p pages./n", NumberOfPages );
- return;
- }
- // 保留长度0.5GB的虚拟内存块(这个内存块即AWE窗口)的地址
- lpMemReserved = VirtualAlloc( NULL,
- MEMORY_VIRTUAL,
- MEM_RESERVE | MEM_PHYSICAL,
- PAGE_READWRITE );
- if( lpMemReserved == NULL )
- {
- printf("Cannot reserve memory./n");
- return;
- }
- char *strTemp;
- for (int i=0;i<5;i++)
- {
- // 把物理内存映射到窗口中来
- // 分5次映射,每次映射0.5G物理内存到窗口中来.
- // 注意,在整个过程中,lpMenReserved的值都是不变的
- // 但是映射的实际物理内存却是不同的
- // 这段代码将申请的2.5G物理内存分5段依次映射到窗口中来
- // 并在每段的开头写入一串字符串.
- bResult = MapUserPhysicalPages( lpMemReserved,
- NumberOfPages/5,
- aPFNs+NumberOfPages/5*i);
- if( bResult != TRUE )
- {
- printf("MapUserPhysicalPages failed (%u)/n", GetLastError() );
- return;
- }
- // 写入字符串,虽然是写入同一个虚存地址,
- // 但是窗口映射的实际内存不同,所以是写入了不同的内存块中
- strTemp=(char*)lpMemReserved;
- sprintf(strTemp,"This is the %dth section!",i+1);
- // 解除映射
- bResult = MapUserPhysicalPages( lpMemReserved,
- NumberOfPages/5,
- NULL );
- if( bResult != TRUE )
- {
- printf("MapUserPhysicalPages failed (%u)/n", GetLastError() );
- return;
- }
- }
- // 现在再从5段内存中读出刚才写入的字符串
- for (int i=0;i<5;i++)
- {
- // 把物理内存映射到窗口中来
- bResult = MapUserPhysicalPages( lpMemReserved,
- NumberOfPages/5,
- aPFNs+NumberOfPages/5*i);
- if( bResult != TRUE )
- {
- printf("MapUserPhysicalPages failed (%u)/n", GetLastError() );
- return;
- }
- // 将映射到窗口中的不同内存块的字符串在屏幕中打印出来
- strTemp=(char*)lpMemReserved;
- printf("%s/n",strTemp);
- // 解除映射
- bResult = MapUserPhysicalPages( lpMemReserved,
- NumberOfPages/5,
- NULL );
- if( bResult != TRUE )
- {
- printf("MapUserPhysicalPages failed (%u)/n", GetLastError() );
- return;
- }
- }
- // 释放物理内存空间
- bResult = FreeUserPhysicalPages( GetCurrentProcess(),
- &NumberOfPages,
- aPFNs );
- if( bResult != TRUE )
- {
- printf("Cannot free physical pages, error %u./n", GetLastError());
- return;
- }
- // 释放虚拟内存地址
- bResult = VirtualFree( lpMemReserved,
- 0,
- MEM_RELEASE );
- // 释放PFN队列空间
- bResult = HeapFree(GetProcessHeap(), 0, aPFNs);
- if( bResult != TRUE )
- {
- printf("Call to HeapFree has failed (%u)/n", GetLastError() );
- }
- }
- /*****************************************************************
- 输入:
- HANDLE hProcess: 需要获得权限的进程的句柄
- BOOL bEnable: 启用权限 (TRUE) 或 取消权限 (FALSE)?
- 返回值: TRUE 表示权限操作成功, FALSE 失败.
- *****************************************************************/
- BOOL
- LoggedSetLockPagesPrivilege ( HANDLE hProcess,
- BOOL bEnable)
- {
- struct {
- DWORD Count;
- LUID_AND_ATTRIBUTES Privilege [1];
- } Info;
- HANDLE Token;
- BOOL Result;
- // 打开进程的安全信息
- Result = OpenProcessToken ( hProcess,
- TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES,
- & Token);
- if( Result != TRUE )
- {
- printf( "Cannot open process token./n" );
- return FALSE;
- }
- // 开启 或 取消?
- Info.Count = 1;
- if( bEnable )
- {
- Info.Privilege[0].Attributes = SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED;
- }
- else
- {
- Info.Privilege[0].Attributes = 0;
- }
- // 获得LUID
- Result = LookupPrivilegeValue ( NULL,
- SE_LOCK_MEMORY_NAME,
- &(Info.Privilege[0].Luid));
- if( Result != TRUE )
- {
- printf( "Cannot get privilege for %s./n", SE_LOCK_MEMORY_NAME );
- return FALSE;
- }
- // 修改权限
- Result = AdjustTokenPrivileges ( Token, FALSE,
- (PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES) &Info,
- 0, NULL, NULL);
- // 检查修改结果
- if( Result != TRUE )
- {
- printf ("Cannot adjust token privileges (%u)/n", GetLastError() );
- return FALSE;
- }
- else
- {
- if( GetLastError() != ERROR_SUCCESS )
- {
- printf ("Cannot enable the SE_LOCK_MEMORY_NAME privilege; ");
- printf ("please check the local policy./n");
- return FALSE;
- }
- }
- CloseHandle( Token );
- return TRUE;
- }
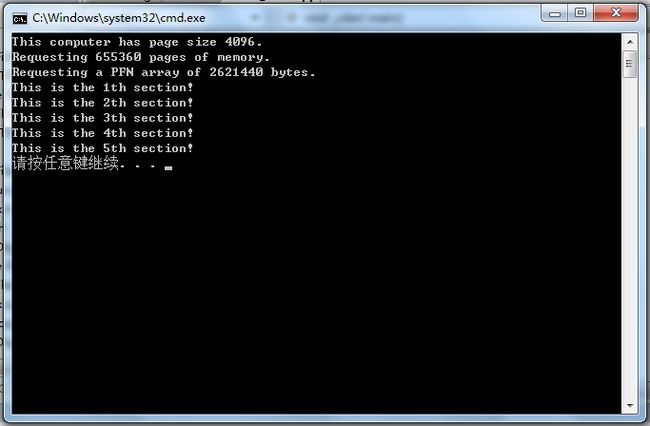
程序运行结果如下:
可以看出系统分页的大小为4K,总共申请了655360个分页,也就是2.5G。每个分页成员占4字节,总共2621440字节。2.5G内存分成5段512M的块,成功写入了字符串并成功读取。
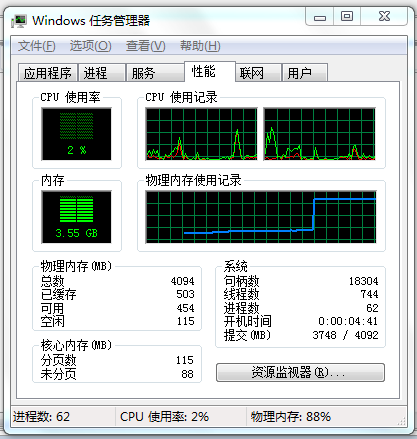
在调试过程中,在执行了AllocateUserPhysicalPages函数后设置断点,查看任务管理器,可以看出成功分配了物理内存后,实际物理内存被占用了2.5G,从而验证了AWE的效果。
通过上述示例,我们成功的在32位系统中识别出了4G的内存,并且在32位程序中成功使用了超过2G的内存。借助PAE和AWE,即使在32位系统上,我们也能够顺利开发对内存消耗较大的应用程序,而不需要依赖于64位平台。