poj 1177 & hdu 1828 Picture(线段树+离散化)
Picture
Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1095 Accepted Submission(s): 608
Write a program to calculate the perimeter. An example with 7 rectangles is shown in Figure 1.
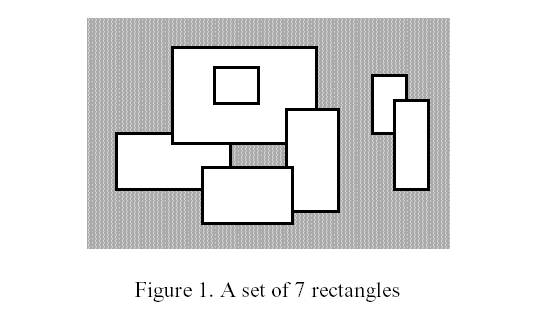
The corresponding boundary is the whole set of line segments drawn in Figure 2.

The vertices of all rectangles have integer coordinates.
0 <= number of rectangles < 5000
All coordinates are in the range [-10000,10000] and any existing rectangle has a positive area.
Please process to the end of file.
7 -15 0 5 10 -5 8 20 25 15 -4 24 14 0 -6 16 4 2 15 10 22 30 10 36 20 34 0 40 16
228
分析:这道题算是经典题吧,线段树+离散化。。。什么是离散化,囧,原来是那种东东,没什么好说的,开始时读入弄错了好像,
居然没检查出来,还有,为什么坐标想同的每次都要分开计算,甚是不解~~~还有这样竟然没有0ms。。。跟暴力差不多
注意:题目数据貌似有错。。。
大家试一下这组
3
0 0 1 2
0 2 1 4
1 1 2 3
答案:12
ac的程序输出16.。。。
原来那个觉得是对的(就是加上这句 if(x[i].d!=x[i+1].d) )输出12.。。。
如果有错请指正。
这题实在是揪心,第三次更新啦。。。囧,发现陈宏的解题方法有漏洞,不能简单地用前后两测度想减来求值(+abs(lt[1].m-gk))。。。
附上一组数据:
13
0 0 1 1
0 1 1 4
0 4 1 6
1 0 2 1
1 1 2 4
1 4 2 6
2 0 3 2
2 2 3 3
2 5 3 6
3 1 4 4
3 5 5 6
4 0 5 2
4 2 5 5
答案:32
如果你是按y轴排序来做的,自己转换一下坐标试试
好吧最后发现陈牛的思想是对的,但是论文里貌似没讲清楚坐标相同的处理要按先插入后删除,这样才能保持正确性,正确代码在最后~~~
贴下代码(有漏洞):
#include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> using namespace std; const int maxn=5001; const int maxtree=65556; struct tree { int l,r,t,g,m; bool a,b; }lt[maxtree]; struct data { int d,p; }x[maxn*2]; int y[maxn][2],c; bool flag[maxn]; void maketree(int v,int l,int r) { lt[v].l=l,lt[v].r=r,lt[v].t=lt[v].g=lt[v].m=lt[v].a=lt[v].b=0; if(l+1==r)return; int m=(l+r)>>1,now=v<<1; maketree(now,l,m); maketree(now+1,m,r); } void updata(int v) { if(lt[v].t)lt[v].g=lt[v].a=lt[v].b=1,lt[v].m=lt[v].r-lt[v].l; else if(lt[v].l+1==lt[v].r)lt[v].g=lt[v].a=lt[v].b=lt[v].m=0; else { int now=v<<1; lt[v].a=lt[now].a,lt[v].b=lt[now+1].b; lt[v].g=lt[now].g+lt[now+1].g-(lt[now].b<[now+1].a); lt[v].m=lt[now].m+lt[now+1].m; } } void ltwork(int v,int l,int r) { if(l<=lt[v].l&<[v].r<=r)lt[v].t+=c; else if(lt[v].l+1<lt[v].r) { int now=v<<1; if(l<lt[now].r)ltwork(now,l,r); if(r>lt[now].r)ltwork(now+1,l,r); } updata(v); } bool cmp(data a,data b){return a.d<b.d;} int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { //freopen("car.in","r",stdin); //freopen("car.out","w",stdout); int i,j,n,gk,ans; scanf("%d",&n); for(i=j=0;i<n;++i,j+=2) scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x[j].d,&y[i][0],&x[j+1].d,&y[i][1]),x[j].p=x[j+1].p=i; sort(x,x+j,cmp); maketree(1,-10000,10000); for(i=0;i<n;++i)flag[i]=1; for(i=ans=gk=0;i<j;++i) { if(c=flag[x[i].p])flag[x[i].p]=0;else c=-1; ltwork(1,y[x[i].p][0],y[x[i].p][1]); //if(x[i].d!=x[i+1].d)//这句不能加,相同坐标每次也要算,囧 ans+=(x[i+1].d-x[i].d)*lt[1].g*2+abs(lt[1].m-gk),gk=lt[1].m; } printf("%d/n",ans); return 0; }
无数次修改。。。汗:
#include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn=5001; const int maxtree=65556; struct tree { int l,r,t,g,m; bool a,b; }lt[maxtree]; struct data { int d,p; bool o; }x[maxn*2]; int y[maxn][2],c; inline int ab(int a){return a>0?a:-a;} void maketree(int v,int l,int r) { lt[v].l=l,lt[v].r=r,lt[v].t=lt[v].g=lt[v].m=lt[v].a=lt[v].b=0; if(l+1==r)return; int m=(l+r)>>1,now=v<<1; maketree(now,l,m); maketree(now+1,m,r); } void updata(int v) { if(lt[v].t)lt[v].g=lt[v].a=lt[v].b=1,lt[v].m=lt[v].r-lt[v].l; else if(lt[v].l+1==lt[v].r)lt[v].g=lt[v].a=lt[v].b=lt[v].m=0; else { int now=v<<1; lt[v].a=lt[now].a,lt[v].b=lt[now+1].b; lt[v].g=lt[now].g+lt[now+1].g-(lt[now].b<[now+1].a); lt[v].m=lt[now].m+lt[now+1].m; } } void ltwork(int v,int l,int r) { if(l<=lt[v].l&<[v].r<=r)lt[v].t+=c; else if(lt[v].l+1<lt[v].r) { int now=v<<1; if(l<lt[now].r)ltwork(now,l,r); if(r>lt[now].r)ltwork(now+1,l,r); } updata(v); } bool cmp(data a,data b){return (a.d<b.d||(a.d==b.d&&a.o<b.o));} int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { int i,j,n,gk,ans; //freopen("a.in","r",stdin); //freopen("a.out","w",stdout); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=j=0;i<n;++i,j+=2) scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x[j].d,&y[i][0],&x[j+1].d,&y[i][1]),x[j].p=x[j+1].p=i,x[j].o=0,x[j+1].o=1; sort(x,x+j,cmp); maketree(1,-10000,10000); for(i=ans=gk=0;i<j;++i) { if(!(c=x[i].o))c=-1; ltwork(1,y[x[i].p][0],y[x[i].p][1]); ans+=(x[i+1].d-x[i].d)*lt[1].g*2+ab(lt[1].m-gk),gk=lt[1].m; } printf("%d/n",ans); return 0; }
n久之后又回来做这题:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
#define lson l,m,ls
#define rson m,r,rs
using namespace std;
const int mm=11111;
const int mn=mm<<2;
struct seg
{
int x,y1,y2,v;
}g[mm];
int y[mm],t[mn],s[mn],a[mn],b[mn],sum[mn];
int val,L,R;
void build()
{
for(int i=0;i<mn;++i)s[i]=a[i]=b[i]=sum[i]=t[i]=0;
}
void updata(int l,int r,int rt)
{
if(L<=y[l]&&R>=y[r])t[rt]+=val;
else
{
int m=(l+r)>>1;
if(L<y[m])updata(lson);
if(R>y[m])updata(rson);
}
if(t[rt])s[rt]=a[rt]=b[rt]=1,sum[rt]=y[r]-y[l];
else if(l==r)s[rt]=a[rt]=b[rt]=sum[rt]=0;
else
{
a[rt]=a[ls],b[rt]=b[rs];
s[rt]=s[ls]+s[rs]-(b[ls]&a[rs]);
sum[rt]=sum[ls]+sum[rs];
}
}
bool cmp(seg a,seg b)
{
return a.x<b.x||(a.x==b.x&&a.v>b.v);
}
int main()
{
int i,j,n,m,tmp,ans;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
for(j=i=0;i<n;++i,j+=2)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&g[j].x,&y[j],&g[j+1].x,&y[j+1]);
g[j].y1=g[j+1].y1=y[j];
g[j].y2=g[j+1].y2=y[j+1];
g[j].v=1,g[j+1].v=-1;
}
sort(y,y+j);
sort(g,g+j,cmp);
for(m=i=0;i<j;++i)
if(y[m]<y[i])y[++m]=y[i];
build();
for(ans=tmp=i=0;i<j;++i)
{
L=g[i].y1,R=g[i].y2,val=g[i].v;
updata(0,m,1);
ans+=(g[i+1].x-g[i].x)*s[1]*2+abs(sum[1]-tmp),tmp=sum[1];
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}