Android输入法框架系统(下)
程序焦点获取事件导致输入法显示
从上面可以知道程序获得焦点时,程序端会先间接的调用IMMS的startInput将焦点View绑定到输入法,然后会调用IMMS的windowGainFocus函数,这个函数就可能显示输入法, 是否显示输入法由焦点view的属性决定。过程流程图如下:
代码处理逻辑如下:
//ViewRootImpl.java
case MSG_WINDOW_FOCUS_CHANGED: {
if (hasWindowFocus) {
if (imm != null && mLastWasImTarget && !isInLocalFocusMode()) {
imm.onWindowFocus(mView, mView.findFocus(),
mWindowAttributes.softInputMode,
!mHasHadWindowFocus, mWindowAttributes.flags);
}
}
}
//InputMethodManager
public void onWindowFocus(View rootView, View focusedView, int softInputMode,
boolean first, int windowFlags) {
boolean forceNewFocus = false;
synchronized (mH) {
//和上面view获取焦点事件的处理一样
focusInLocked(focusedView != null ? focusedView : rootView);
}
//确认当前focused view是否已经调用过startInputInner来绑定输入法
//因为在前面mView.dispatchWindowFocusChanged处理过程focused view已经完成
//了绑定,所以大部分情况下,该函数返回false,即不会再次调用startInputInner
if (checkFocusNoStartInput(forceNewFocus, true)) {
if (startInputInner(rootView.getWindowToken(),
controlFlags, softInputMode, windowFlags)) {
return;
}
}
synchronized (mH) {
try {
//调用IMMS windowGainedFocus函数
mService.windowGainedFocus(mClient, rootView.getWindowToken(),
controlFlags, softInputMode, windowFlags, null, null);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
}
输入法响应显示请求
从上面可以看出,输入法响应显示请求是通过IInputMethod,而这个是在输入法service完成启动通过onBind接口传递过去的,所以我们先来看下这个IInputMethod的实现是什么?
输入法service都是继承InputMethodService类
public class InputMethodService extends AbstractInputMethodService {
@Override
public AbstractInputMethodImpl onCreateInputMethodInterface() {
return new InputMethodImpl();
}
}
public abstract class AbstractInputMethodService extends Service
implements KeyEvent.Callback {
private InputMethod mInputMethod;
@Override
final public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
if (mInputMethod == null) {
mInputMethod = onCreateInputMethodInterface();
}
return new IInputMethodWrapper(this, mInputMethod);
}
}
从上可见IMMS保存的IInputMethod的实现是封装了 InputMethodImpl的类 IInputMethodWrapper,那肯定就是它负责处理消息MSG_SHOW_SOFT_INPUT,处理逻辑如下。
public IInputMethodWrapper(AbstractInputMethodService context,
InputMethod inputMethod) {
mTarget = new WeakReference<AbstractInputMethodService>(context);
mCaller = new HandlerCaller(context.getApplicationContext(), null,
this, true /*asyncHandler*/);
mInputMethod = new WeakReference<InputMethod>(inputMethod);
mTargetSdkVersion = context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion;
}
public InputMethod getInternalInputMethod() {
return mInputMethod.get();
}
@Override
public void executeMessage(Message msg) {
InputMethod inputMethod = mInputMethod.get();
switch (msg.what) {
case DO_SHOW_SOFT_INPUT:
//这个inputMethod是通过onCreateInputMethodInterface函数创建的
//InputMethodImpl对象
inputMethod.showSoftInput(msg.arg1, (ResultReceiver)msg.obj);
return;
}
}
public class InputMethodImpl extends AbstractInputMethodImpl {
public void showSoftInput(int flags, ResultReceiver resultReceiver) {
boolean wasVis = isInputViewShown();
mShowInputFlags = 0;
if (onShowInputRequested(flags, false)) {
try {
//这个是真正显示UI的函数
showWindow(true);
}
}
}
}
public class InputMethodService extends AbstractInputMethodService {
@Override public void onCreate() {
mTheme = Resources.selectSystemTheme(mTheme,
getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion,
android.R.style.Theme_InputMethod,
android.R.style.Theme_Holo_InputMethod,
android.R.style.Theme_DeviceDefault_InputMethod);
// SoftInputWindow就是大家一般用的Dialog的子类
mWindow = new SoftInputWindow(this, mTheme, mDispatcherState);
initViews();
mWindow.getWindow().setLayout(MATCH_PARENT, WRAP_CONTENT);
}
public void showWindow(boolean showInput) {
try {
mWindowWasVisible = mWindowVisible;
mInShowWindow = true;
showWindowInner(showInput);
} finally {
mWindowWasVisible = true;
mInShowWindow = false;
}
}
void showWindowInner(boolean showInput) {
initialize();
updateFullscreenMode();
//这个函数会创建输入法的键盘
updateInputViewShown();
if (!mWindowAdded || !mWindowCreated) {
mWindowAdded = true;
mWindowCreated = true;
initialize();
//创建输入法dialog里的词条选择View
View v = onCreateCandidatesView();
if (v != null) {
setCandidatesView(v);
}
}
if (mShowInputRequested) {
if (!mInputViewStarted) {
mInputViewStarted = true;
onStartInputView(mInputEditorInfo, false);
}
} else if (!mCandidatesViewStarted) {
mCandidatesViewStarted = true;
onStartCandidatesView(mInputEditorInfo, false);
}
if (!wasVisible) {
mImm.setImeWindowStatus(mToken, IME_ACTIVE, mBackDisposition);
onWindowShown();
//这个是Dialog的window,这里开始就显示UI了
mWindow.show();
}
}
public void updateInputViewShown() {
boolean isShown = mShowInputRequested && onEvaluateInputViewShown();
if (mIsInputViewShown != isShown && mWindowVisible) {
mIsInputViewShown = isShown;
mInputFrame.setVisibility(isShown ? View.VISIBLE : View.GONE);
if (mInputView == null) {
initialize();
//这个是核心view,创建显示键盘的根view
View v = onCreateInputView();
if (v != null) {
setInputView(v);
}
}
}
}
}
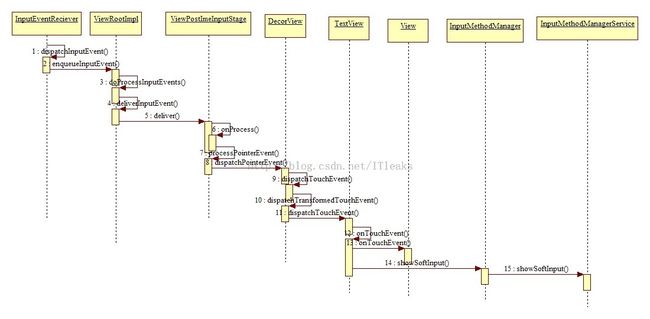
用户单击输入框View导致输入法显示
在上一篇InputChannel章节我们说到,事件传递到程序端,最后让ViewPostImeInputStage来处。处理逻辑如下:
final class ViewPostImeInputStage extends InputStage {
public ViewPostImeInputStage(InputStage next) {
super(next);
}
@Override
protected int onProcess(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (q.mEvent instanceof KeyEvent) {
} else {
final int source = q.mEvent.getSource();
if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER) != 0) {
//处理touch事件
return processPointerEvent(q);
}
}
}
private int processPointerEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
final MotionEvent event = (MotionEvent)q.mEvent;
if (mView.dispatchPointerEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
return FORWARD;
}
}
从上可知最后会调用DecorView的dispatchPointerEvent,DecorView也是一个view,所以该函数其实就是View的dispatchPointerEvent函数。
//View.java
public final boolean dispatchPointerEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (event.isTouchEvent()) {
return dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
}
//DecorView又是一个ViewGroup,所以会调用ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent
//ViewGroup.java
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onTouchEvent(ev, 1);
}
boolean handled = false;
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(ev)) {
final int action = ev.getAction();
final int actionMasked = action & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK;
// Handle an initial down.
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
// Throw away all previous state when starting a new touch gesture.
// The framework may have dropped the up or cancel event for the previous gesture
// due to an app switch, ANR, or some other state change.
cancelAndClearTouchTargets(ev);
resetTouchState();
}
// Check for interception.
final boolean intercepted;
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags &
FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;
if (!disallowIntercept) {
//先给该view一个处理事件的机会,如果Intercept,则事件不会往
//下发送
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed
} else {
intercepted = false;
}
} else {
// There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down
// so this view group continues to intercept touches.
intercepted = true;
}
//按照冒泡法,将触摸事件传递给每个child处理
if (mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
// Dispatch to touch targets, excluding the new touch target if we already
// dispatched to it. Cancel touch targets if necessary.
TouchTarget predecessor = null;
TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget;
while (target != null) {
final TouchTarget next = target.next;
if (alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget && target == newTouchTarget) {
handled = true;
} else {
final boolean cancelChild = resetCancelNextUpFlag(target.child)
|| intercepted;
//真正处理函数
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild,
target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) {
handled = true;
}
if (cancelChild) {
if (predecessor == null) {
mFirstTouchTarget = next;
} else {
predecessor.next = next;
}
target.recycle();
target = next;
continue;
}
}
predecessor = target;
target = next;
}
}
}
return handled;
}
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel,
View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {
// child == null意味着该parent已经调用完所有的child的dispatchTouchEvent
//所以从这里可以看出是child优先处理触摸事件的
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
} else {
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
}
return handled;
}
//这里的child如果仍就是一个ViewGroup,则和上面的逻辑一样。如果是一般的view,则
//直接调用view. dispatchTouchEvent
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
//这个就是我们常使用view.setOnTouchListener调用保存下来的信息
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null && (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
return true;
}
//view的默认处理,即调用onTouchEvent函数
if (onTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//TextView.java
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//非TextView只会执行View. onTouchEvent,该函数是另一种将view和输入法绑定的调用
//而TextView会调用imm.showSoftInput会显示输入法
final boolean superResult = super.onTouchEvent(event);
if ((mMovement != null || onCheckIsTextEditor()) && isEnabled()
&& mText instanceof Spannable && mLayout != null) {
if (touchIsFinished && (isTextEditable() || textIsSelectable)) {
// Show the IME, except when selecting in read-only text.
final InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.peekInstance();
viewClicked(imm);
//这个是真正显示输入法的调用
if (!textIsSelectable && mEditor.mShowSoftInputOnFocus) {
handled |= imm != null && imm.showSoftInput(this, 0);
}
handled = true;
}
if (handled) {
return true;
}
}
return superResult;
}
//View.java的onTouchEvent
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
if (((viewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE ||
(viewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE)) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) {
// take focus if we don't have it already and we should in
// touch mode.
boolean focusTaken = false;
//让view获得焦点
if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {
focusTaken = requestFocus();
}
}
break;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
return requestFocusNoSearch(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
}
private boolean requestFocusNoSearch(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
// 该view必须是可以获取焦点的
if ((mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE_MASK) != FOCUSABLE ||
(mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != VISIBLE) {
return false;
}
// 这个检查得到对象大家可能经常用过,就是这个属性
//android:descendantFocusability=”blocksDescendants”,这个属性可以解决listView
//等容器类View没法获取点击事件问题,它的实现就在此,当父亲设置了这个属性
//子view就没法获取焦点了
if (hasAncestorThatBlocksDescendantFocus()) {
return false;
}
//获取焦点处理逻辑
handleFocusGainInternal(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
return true;
}
void handleFocusGainInternal(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) == 0) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FOCUSED;
View oldFocus = (mAttachInfo != null) ? getRootView().findFocus() : null;
//由于当前焦点view没法知道旧的焦点view,没法告知旧的焦点view失去焦点
//所以必须叫父亲去做这个事情
if (mP arent != null) {
mParent.requestChildFocus(this, this);
}
//这个函数很重要,编辑类view(比如TextEditor)和普通view的差别就在此
//和输入法相关的处理也在此
onFocusChanged(true, direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
refreshDrawableState();
}
}
//基类View的处理:
protected void onFocusChanged(boolean gainFocus, int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.peekInstance();
if (!gainFocus) {
} else if (imm != null && mAttachInfo != null
&& mAttachInfo.mHasWindowFocus) {
//通知IMMS该view获得了焦点,到此,这后面的逻辑就和上面的window获
//得焦点导致view和输入法绑定的逻辑一样了
imm.focusIn(this);
}
}
输入法传递输入文本信息给view
输入法如何获得输入文本信息通信接口
从上面的输入法绑定的分析中可以知道,输入法其startInput接口被调用的时候获得了文本信息通信接口,这个通信接口是IInputContext的封装InputConnection,获取点如下:
//InputMethodService.java
void doStartInput(InputConnection ic, EditorInfo attribute, boolean restarting) {
if (!restarting) {
doFinishInput();
}
mInputStarted = true;
//这个就是通信接口
mStartedInputConnection = ic;
}
public InputConnection getCurrentInputConnection() {
InputConnection ic = mStartedInputConnection;
if (ic != null) {
return ic;
}
return mInputConnection;
}
输入法如何传递文本信息给view
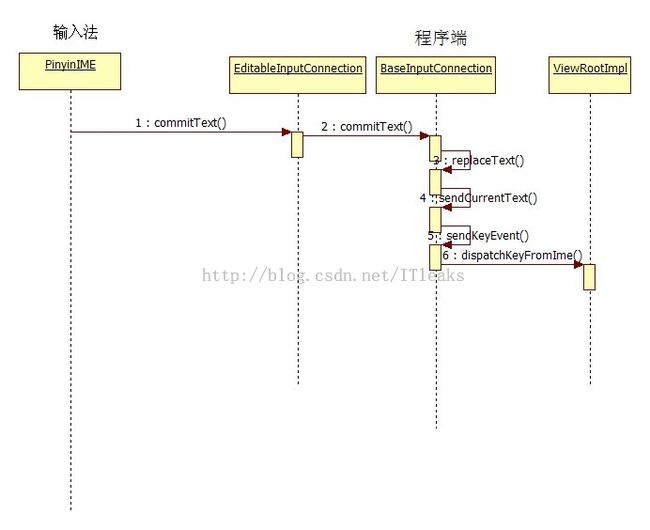
从上可见,输入法要传递文本信息时,肯定是先调用getCurrentInputConnection拿到接口,然后再传递信息,我们以pinyin输入法的实现来解释这个过程。
Pinyin输入法传递输入信息最后都会调用到sendKeyChar函数
public void sendKeyChar(char charCode) {
switch (charCode) {
case '\n': // Apps may be listening to an enter key to perform an action
if (!sendDefaultEditorAction(true)) {
sendDownUpKeyEvents(KeyEvent.KEYCODE_ENTER);
}
break;
default:
// Make sure that digits go through any text watcher on the client side.
if (charCode >= '0' && charCode <= '9') {
sendDownUpKeyEvents(charCode - '0' + KeyEvent.KEYCODE_0);
} else {
InputConnection ic = getCurrentInputConnection();
if (ic != null) {
//这个是真正传递信息到view的跨进程接口
ic.commitText(String.valueOf((char) charCode), 1);
}
}
break;
}
}
View接收输入文本信息
从上面可知,输入法端最后会通过InputConnection逻辑来传递文本信息,那程序view端的InputConnection是如何创建的呢?
//InputMethodManager.java
boolean startInputInner(IBinder windowGainingFocus, int controlFlags, int softInputMode,
EditorInfo tba = new EditorInfo();
tba.packageName = view.getContext().getPackageName();
tba.fieldId = view.getId();
//由具体的view创建
InputConnection ic = view.onCreateInputConnection(tba);
return true;
}
//我们先看下textView会创建怎样的InputConnection?
//TextView.java
@Override
public InputConnection onCreateInputConnection(EditorInfo outAttrs) {
{
outAttrs.hintText = mHint;
if (mText instanceof Editable) {
//露面了,是 EditableInputConnection, textView作为参数传入
InputConnection ic = new EditableInputConnection(this);
return ic;
}
}
return null;
}
接下来肯定是EditableInputConnection 接收文本消息了
public class EditableInputConnection extends BaseInputConnection {
//该函数很重要,super.commitText会将字符添加到Editable里
@Override
public Editable getEditable() {
TextView tv = mTextView;
if (tv != null) {
return tv.getEditableText();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean commitText(CharSequence text, int newCursorPosition) {
mTextView.resetErrorChangedFlag();
//调用父类的方法
boolean success = super.commitText(text, newCursorPosition);
mTextView.hideErrorIfUnchanged();
return success;
}
}
public class BaseInputConnection implements InputConnection {
public boolean commitText(CharSequence text, int newCursorPosition) {
replaceText(text, newCursorPosition, false);
sendCurrentText();
return true;
}
private void replaceText(CharSequence text, int newCursorPosition,
boolean composing) {
//获取eidtor
final Editable content = getEditable();
if (content == null) {
return;
}
beginBatchEdit();
………………..
//修改editor
content.replace(a, b, text);
endBatchEdit();
}
private void sendCurrentText() {
Editable content = getEditable();
if (content != null) {
final int N = content.length();
// 将输入文本模拟为为一个key事件,这样view就会更新内容了
KeyEvent event = new KeyEvent(SystemClock.uptimeMillis(),
content.toString(), KeyCharacterMap.VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD, 0);
sendKeyEvent(event);
content.clear();
}
}
public boolean sendKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
//同ViewRootImpl有按键事件,到此为止就像是外接键盘的按键事件似的
synchronized (mIMM.mH) {
ViewRootImpl viewRootImpl = mTargetView != null ? mTargetView.getViewRootImpl() : null;
if (viewRootImpl == null) {
if (mIMM.mServedView != null) {
viewRootImpl = mIMM.mServedView.getViewRootImpl();
}
}
if (viewRootImpl != null) {
//发送信息
viewRootImpl.dispatchKeyFromIme(event);
}
}
/********************************
* 本文来自博客 “爱踢门”
* 转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/itleaks
******************************************/