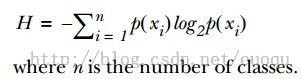机器学习理论与实战(二)决策树
决策树也是有监督机器学习方法。 电影《无耻混蛋》里有一幕游戏,在德军小酒馆里有几个人在玩20问题游戏,游戏规则是一个设迷者在纸牌中抽出一个目标(可以是人,也可以是物),而猜谜者可以提问题,设迷者只能回答是或者不是,在几个问题(最多二十个问题)之后,猜谜者通过逐步缩小范围就准确的找到了答案。这就类似于决策树的工作原理。(图一)是一个判断邮件类别的工作方式,可以看出判别方法很简单,基本都是阈值判断,关键是如何构建决策树,也就是如何训练一个决策树。
(图一)
构建决策树的伪代码如下:
Check if every item in the dataset is in the same class:
If so return the class label
Else
find the best feature to split the data
split the dataset
create a branch node
for each split
call create Branch and add the result to the branch node
return branch node
原则只有一个,尽量使得每个节点的样本标签尽可能少,注意上面伪代码中一句说:find the best feature to split the data,那么如何find thebest feature?一般有个准则就是尽量使得分支之后节点的类别纯一些,也就是分的准确一些。如(图二)中所示,从海洋中捞取的5个动物,我们要判断他们是否是鱼,先用哪个特征?
(图二)
为了提高识别精度,我们是先用“离开陆地能否存活”还是“是否有蹼”来判断?我们必须要有一个衡量准则,常用的有信息论、基尼纯度等,这里使用前者。我们的目标就是选择使得分割后数据集的标签信息增益最大的那个特征,信息增益就是原始数据集标签基熵减去分割后的数据集标签熵,换句话说,信息增益大就是熵变小,使得数据集更有序。熵的计算如(公式一)所示:
(公式一)
有了指导原则,那就进入代码实战阶段,先来看看熵的计算代码:
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
numEntries = len(dataSet)
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet: #the the number of unique elements and their occurance
currentLabel = featVec[-1]
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #收集所有类别的数目,创建字典
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob,2) #log base 2 计算熵
return shannonEnt
有了熵的计算代码,接下来看依照信息增益变大的原则选择特征的代码:
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
retDataSet = []
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #chop out axis used for splitting
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
return retDataSet
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #the last column is used for the labels
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
bestInfoGain = 0.0; bestFeature = -1
for i in range(numFeatures): #iterate over all the features
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]#create a list of all the examples of this feature
uniqueVals = set(featList) #get a set of unique values
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #calculate the info gain; ie reduction in entropy
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #compare this to the best gain so far #选择信息增益最大的代码在此
bestInfoGain = infoGain #if better than current best, set to best
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature #returns an integer
从最后一个if可以看出,选择使得信息增益最大的特征作为分割特征,现在有了特征分割准则,继续进入一下个环节,如何构建决策树,其实就是依照最上面的伪代码写下去,采用递归的思想依次分割下去,直到执行完成就构建了决策树。代码如下:
def majorityCnt(classList):
classCount={}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys(): classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
def createTree(dataSet,labels):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]#stop splitting when all of the classes are equal
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #stop splitting when there are no more features in dataSet
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet)
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}}
del(labels[bestFeat])
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featValues)
for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels = labels[:] #copy all of labels, so trees don't mess up existing labels
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value),subLabels)
return myTree
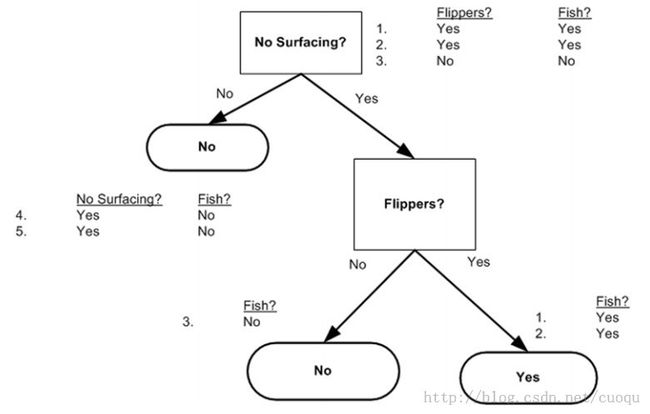
用图二的样本构建的决策树如(图三)所示:
(图三)
有了决策树,就可以用它做分类咯,分类代码如下:
def classify(inputTree,featLabels,testVec):
firstStr = inputTree.keys()[0]
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr)
key = testVec[featIndex]
valueOfFeat = secondDict[key]
if isinstance(valueOfFeat, dict):
classLabel = classify(valueOfFeat, featLabels, testVec)
else: classLabel = valueOfFeat
return classLabel
最后给出序列化决策树(把决策树模型保存在硬盘上)的代码:
def storeTree(inputTree,filename):
import pickle
fw = open(filename,'w')
pickle.dump(inputTree,fw)
fw.close()
def grabTree(filename):
import pickle
fr = open(filename)
return pickle.load(fr)
优点:检测速度快
缺点:容易过拟合,可以采用修剪的方式来尽量避免
参考文献:machine learning in action
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/cuoqu/article/details/9255977