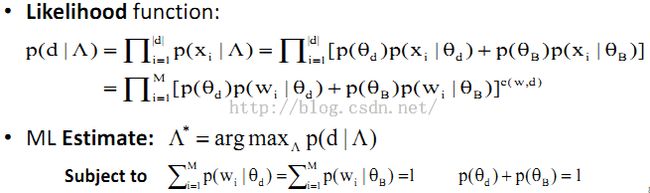《textanalytics》课程简单总结(2):topic mining
coursera上的公开课《https://www.coursera.org/course/textanalytics》系列,讲的非常不错哦。
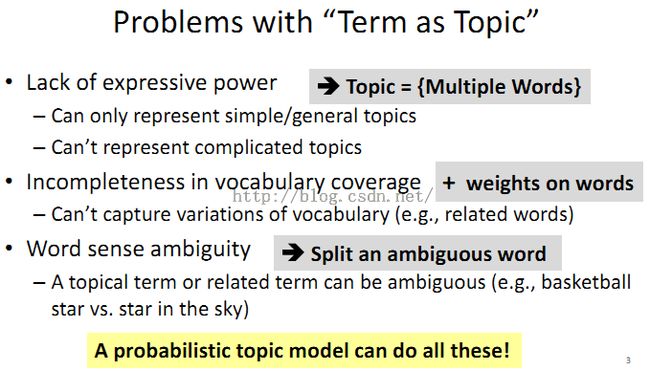
1、“term as topic”有很多问题:
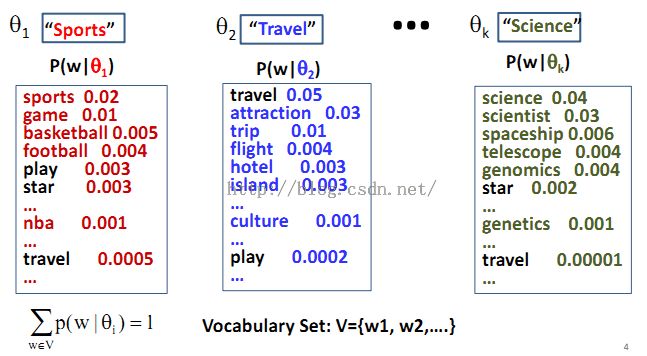
2、Improved Idea: Topic = Word Distribution:
3、定义问题(Probabilistic Topic Mining and Analysis):
4、解决问题之道(Generative Model for Probabilistic Topic Mining and Analysis):
– Model data generation with a prob. model: P(Data |Model, λ)
– Infer the most likely parameter values λ* given a particular data set: λ* = argmaxλ p(Data| Model, λ)
– Take λ* as the “knowledge” to be mined for the text mining problem
– Adjust the design of the model to discover different knowledge
其中:λ=({ theta1, …, thetak }, { π11, …, π1k }, …, { πN1, …, πNk })
5、The Simplest Language Model(generative model): Unigram LM
通过独立的生成每一个词进而产生文档,因此:
• p(w1 w2 ... wn)=p(w1)p(w2)…p(wn)
• 参数为: {p(wi)} ,且 p(w1)+…+p(wN)=1 (N is voc. size)
• Text = sample drawn according to this word distribution,例如:
p(“today is Wed”) = p(“today”)p(“is”)p(“Wed”) = 0.0002 * 0.001 * 0.000015
6、两种估计文本产生概率的办法:
•最大似然估计
问题是,样本一般较小。
• 贝叶斯估计
“最好”意味着“和‘先验’一致,同时能很好解释样本数据”,即Maximum a Posteriori (MAP) estimate。
问题是,如何定义“先验”。
7、多个Unigram Language Model混合(以两个为例):
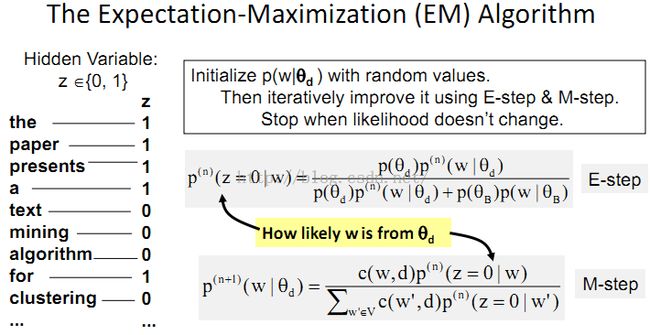
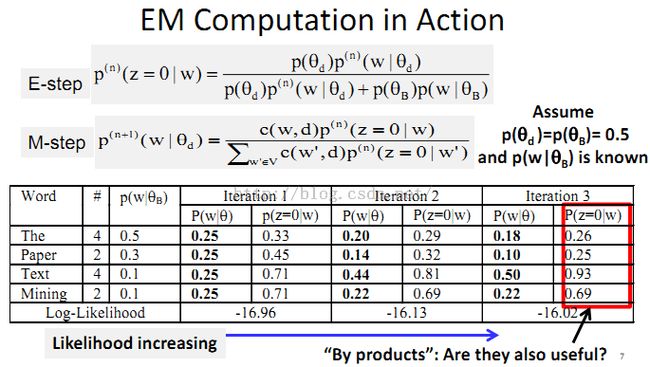
8、Probabilistic Topic Models: Expectation-Maximization (EM) Algorithm
例子:
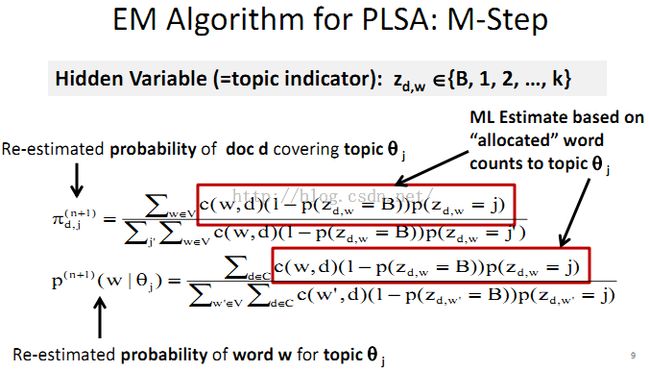
9、Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis (PLSA)
本质思想:
数学关系:
PLSA中的EM:
11、LDA
内容参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/mmc2015/article/details/45009759
http://blog.csdn.net/mmc2015/article/details/45010307
http://blog.csdn.net/mmc2015/article/details/45011027
http://blog.csdn.net/mmc2015/article/details/45024447