分析OpenSurf(2)
①积分图像的实现
首先在Integral.cpp里面找到Integral(),如下:
IplImage *Integral(IplImage *source)
{
//转换成单通道图像 convert the image to single channel 32f
IplImage *img = getGray(source);
IplImage *int_img = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(img), IPL_DEPTH_32F, 1);
//给变量赋值 set up variables for data access
int height = img->height;
int width = img->width;
int step = img->widthStep/sizeof(float);
float *data = (float *) img->imageData;
float *i_data = (float *) int_img->imageData;
//仅限第一行 first row only
float rs = 0.0f;
for(int j=0; j<width; j++)
{
rs += data[j];
i_data[j] = rs;
}
//把左边和上边的像素进行积分 remaining cells are sum above and to the left
for(int i=1; i<height; ++i)
{
rs = 0.0f;
for(int j=0; j<width; ++j)
{
rs += data[i*step+j];
i_data[i*step+j] = rs + i_data[(i-1)*step+j];
}
}
//释放灰度图 release the gray image
cvReleaseImage(&img);
//返回积分图像 return the integral image
return int_img;
}
1. 首先将原输入转化为灰度图像,并创建一个大小等于灰度图像gray-image的图像数组--积分图像int_img。
2. 获取图像的信息,比如大小(高height和宽width)以及gray-image和积分图像int_img的数据首地址data && i_data。(注意此时数据类型为float)
3. 首先计算第一行像素的积分值,相当于一维数据的累加。其他数据通过迭代计算获取,i_data[i*step+j] = rs + i_data[(i-1)*step+j],若当前点为(i,j),其中rs就为第 i 行第 j 列之前(包括第 i 行第 j 列)所有像素值和。 如下所示:
[其中黑色为当前点i_data[i*step+j],绿色为当前点同一列上一行的点i_data[(i-1)*step+j],而rs=横放着的和黑色点同行的那块矩形框对应的区域像素值之和]
4. 释放灰度图像,并返回积分图像。
integral.h中的相关函数: BoxIntegral().
inline float BoxIntegral(IplImage *img, int row, int col, int rows, int cols)
其中,几个参数意思分别为源图像,row,col为A点的坐标值,rows和cols分别为高和宽。
利用上面的积分图像计算 A B 这样的box区域里面所有像素点的灰度值之和。S=int_img(D)+int_img(A)-int_img(B)-int_img(C).
C D
②Hessian矩阵特征的计算
FastHessian,计算hessian矩阵的类,它的定义在fasthessian.h里,实现在fasthessian.cpp里。
class FastHessian {
public:
//! Constructor without image
FastHessian(std::vector<Ipoint> &ipts,
const int octaves = OCTAVES,
const int intervals = INTERVALS,
const int init_sample = INIT_SAMPLE,
const float thres = THRES);
//! Constructor with image
FastHessian(IplImage *img,
std::vector<Ipoint> &ipts,
const int octaves = OCTAVES,
const int intervals = INTERVALS,
const int init_sample = INIT_SAMPLE,
const float thres = THRES);
//! Destructor
~FastHessian();
//! Save the parameters
void saveParameters(const int octaves,
const int intervals,
const int init_sample,
const float thres);
//!设置或重设源积分图像 Set or re-set the integral image source
void setIntImage(IplImage *img);
//!寻找图像特征并写入特征向量 Find the image features and write into vector of features
void getIpoints();
private:
//---------------- Private Functions -----------------//
//! Build map of DoH(Determinant of Hessian) responses
void buildResponseMap();
//! Calculate DoH responses for supplied layer
void buildResponseLayer(ResponseLayer *r);
//! 3x3x3 Extrema test
int isExtremum(int r, int c, ResponseLayer *t, ResponseLayer *m, ResponseLayer *b);
//! 插值函数Interpolation functions - adapted from Lowe's SIFT implementation
void interpolateExtremum(int r, int c, ResponseLayer *t, ResponseLayer *m, ResponseLayer *b);
void interpolateStep(int r, int c, ResponseLayer *t, ResponseLayer *m, ResponseLayer *b,
double* xi, double* xr, double* xc );
CvMat* deriv3D(int r, int c, ResponseLayer *t, ResponseLayer *m, ResponseLayer *b);
CvMat* hessian3D(int r, int c, ResponseLayer *t, ResponseLayer *m, ResponseLayer *b);
//---------------- Private Variables -----------------//
//! Pointer to the integral Image, and its attributes
IplImage *img;
int i_width, i_height;
//! Reference to vector of features passed from outside
std::vector<Ipoint> &ipts;
//!海森矩阵行列式的响应栈 Response stack of determinant of hessian values
std::vector<ResponseLayer *> responseMap;
//! 高斯金字塔的组数
int octaves;
//! 每组的层数
int intervals;
//! 特征点检测的初始抽样步骤 Initial sampling step for Ipoint detection
int init_sample;
//! Threshold value for blob resonses
float thresh;
};
在public里面定义了两种构造函数分别对应有无源图像这一项参数,紧接着还定义了析构函数~FastHessian等函数。下面在fasthessian.cpp对这些函数的实现一一解释:
两个构造函数都是调用了saveParameters(octaves, intervals, init_sample, thresh)设置构造金字塔的参数,而带图像的构造函数另外多加了一句setIntImage(img)用来设置当前图像。
//! Save the parameters
void FastHessian::saveParameters(const int octaves, const int intervals,
const int init_sample, const float thresh)
{
// Initialise variables with bounds-checked values
this->octaves =
(octaves > 0 && octaves <= 4 ? octaves : OCTAVES);
this->intervals =
(intervals > 0 && intervals <= 4 ? intervals : INTERVALS);
this->init_sample =
(init_sample > 0 && init_sample <= 6 ? init_sample : INIT_SAMPLE);
this->thresh = (thresh >= 0 ? thresh : THRES);
}
//! Set or re-set the integral image source
void FastHessian::setIntImage(IplImage *img)
{
// Change the source image
this->img = img;
i_height = img->height;
i_width = img->width;
}
由于在h头文件中已设置
static const int OCTAVES = 5;//组数 static const int INTERVALS = 4;//每组层数 static const float THRES = 0.0004f;//阈值 static const int INIT_SAMPLE = 2;//初始采样因子
所以 saveParameters的作用就是调整参数,以防过大或过小。
FastHessian::getIpoints()提取兴趣点:
//! Find the image features and write into vector of features
void FastHessian::getIpoints()
{
// filter index map
static const int filter_map [OCTAVES][INTERVALS] = {{0,1,2,3}, {1,3,4,5}, {3,5,6,7}, {5,7,8,9}, {7,9,10,11}};
// Clear the vector of exisiting ipts
ipts.clear();
// Build the response map
buildResponseMap();
// Get the response layers
...<BR> ...
}
首先初始化filter_map,清空标记特征点的ipts结构体。
创建高斯平滑层函数参数ResponseMap(),大小与论文所给完全一致,
// Oct1: 9, 15, 21, 27
// Oct2: 15, 27, 39, 51
// Oct3: 27, 51, 75, 99
// Oct4: 51, 99, 147,195
// Oct5: 99, 195,291,387
这些都是每组模板的大小,每组间隔递增,6,12,24,48,96 。ResponseMap这个结构体向量包含4个参数ResponseLayer(int width, int height, int step, int filter)定义在responsemap.h里面,其中width和height等于实际图像大小除以step(step初始值为2),而filter则是滤波器半径。
然后使用buildResponseLayer(responseMap[i])对图像处理后将数据存放在responses和laplacian两个数组里面。
void FastHessian::buildResponseLayer(ResponseLayer *rl)
{
float *responses = rl->responses; // response storage
unsigned char *laplacian = rl->laplacian; // laplacian sign storage
int step = rl->step; // step size for this filter 滤波器尺度因子
int b = (rl->filter - 1) / 2; // border for this filter 滤波器边界
int l = rl->filter / 3; // lobe for this filter (filter size / 3)
int w = rl->filter; // filter size 滤波器大小
float inverse_area = 1.f/(w*w); // normalisation factor 标准化因子
float Dxx, Dyy, Dxy;
for(int r, c, ar = 0, index = 0; ar < rl->height; ++ar)
{
for(int ac = 0; ac < rl->width; ++ac, index++)
{
// get the image coordinates
r = ar * step;
c = ac * step;
// Compute response components
Dxx = BoxIntegral(img, r - l + 1, c - b, 2*l - 1, w)
- BoxIntegral(img, r - l + 1, c - l / 2, 2*l - 1, l)*3;
Dyy = BoxIntegral(img, r - b, c - l + 1, w, 2*l - 1)
- BoxIntegral(img, r - l / 2, c - l + 1, l, 2*l - 1)*3;
Dxy = + BoxIntegral(img, r - l, c + 1, l, l)
+ BoxIntegral(img, r + 1, c - l, l, l)
- BoxIntegral(img, r - l, c - l, l, l)
- BoxIntegral(img, r + 1, c + 1, l, l);
// Normalise the filter responses with respect to their size
Dxx *= inverse_area;
Dyy *= inverse_area;
Dxy *= inverse_area;
// Get the determinant of hessian response & laplacian sign
responses[index] = (Dxx * Dyy - 0.81f * Dxy * Dxy);
laplacian[index] = (Dxx + Dyy >= 0 ? 1 : 0);
#ifdef RL_DEBUG
// create list of the image coords for each response
rl->coords.push_back(std::make_pair<int,int>(r,c));
#endif
}
}
}
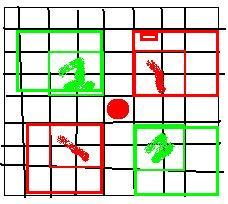
其中计算Dxy和Dyy的示意图如下,其他的Dxx(Dyy的转置)读者自己参考。【此时w=9,l=9/3=3,对应于右图的总计算区域高度和宽度2*l-1】
圆点为当前点,将红色方形区域1内的积分值减去绿色方形2区域内的积分值=Dxy*w2
绿色方形区域2内的积分值减去2*红色色方形区域1内的积分值=Dyy*w2 (==用一整块区域-3*红色区域)
最后将计算后的结果存放到ResponseLayer里面的response和laplacian一维数组里,数组的大小即为ResponseLayer->width * ResponseLayer->width。
这样就计算出了每一层的所有像素点的det(Happrox)=Dxx*Dyy-(0.9*Dxy)2,下面开始判断当前点是否是极值点。