UI--Android中的状态切换按钮自定义
《代码里的世界》 —UI篇
用文字札记描绘自己 android学习之路
转载请保留出处 by Qiao
http://blog.csdn.net/qiaoidea/article/details/46715453
1.概述
Android中关于控制开关和页面/状态切换的使用场景还是比较多的。源生做的支持也有比如RadioGroup 和Tabhost等。这里准备通过自定义View来模仿学习下IOS两种常见UI样式: SwitchButton 和 SegmentControl。
首先先通过简易的组装View来实现两种UI的相应效果,其次呢,尝试通过绘制来达到同样的更灵活的样式。代码前后共实现按钮切换和页面切换两个样式,三种实现方案,其中,两种SwitchButton实现,一种SegmentControl实现。实现方案中关于自定义View绘制,本篇只讲述SwitchView,希望大家能举一反三,同样做到SegmentControl的相同效果。个人也更倾向于使用自定义实现,更方便灵活。
先看效果图:
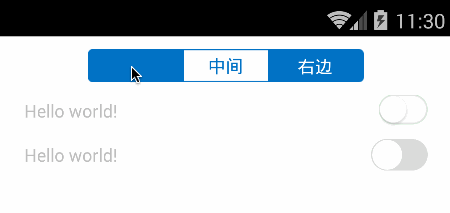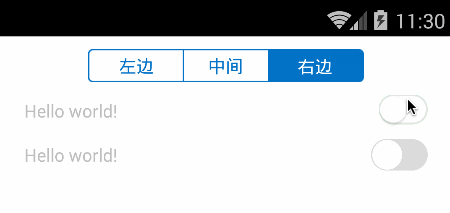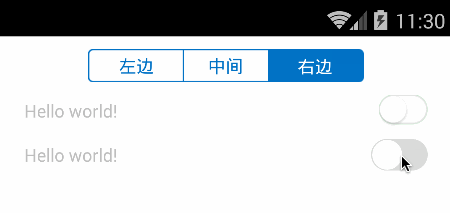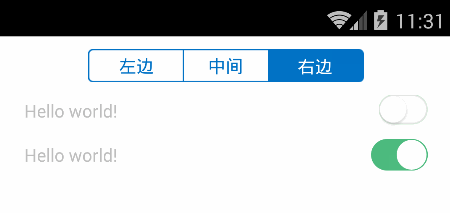
头部即为切换页面的SegmentControl,然后第一行是通过组装view来实现SwitchButton,第二行则是完全绘制出来的SwitchButton效果。接下来我们分别一一讲述代码实现。
2.SwitchButton样式两种实现
状态开关按钮常用于某些控制开关,设置选项里最为常见。
2.1 组合View实现
该方法比较简单明了,定义三个view,开启状态和关闭状态两个背景View,一个圆形按钮view。点击时候利用滑动动画移动按钮和状态背景,达到类似的视觉效果。
先看xml布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/on_bg_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/switch_on_bg" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/off_bg_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/switch_off_bg" />
</FrameLayout>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/circle_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/switch_circle" />
</merge>因为是帧布局,所以顶层使用merge(merge简化xml不解释,自行百度)。然后使用两个开关状态背景和一个圆形按钮组合而成。
1. 全局变量参数
public class SwitchView extends FrameLayout {
protected boolean isChecked; //是否选中状态
protected View onBgView;
protected View offBgView;
protected View circleView;
protected boolean autoForPerformClick = true; //是否允许点击自动切换
protected OnCheckedChangedListener onCheckedChangedListener; //切换事件监听
//...
}一般状态切换是由click事件监听,根据业务逻辑来判断是否切换状态。但对于switchButton,通常我们操作时直观感受应该是先切换了状态才执行相应操作的,所以我们在performClick事件中直接根据autoForPerformClick 的状态来相应点击操作。
至于performClick ,其实就是控制条用onClickListener的方法体,具体逻辑在View源码中查看。
2. 初始化
public SwitchView(Context context) {
super(context);
initialize();
}
public SwitchView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initialize();
}
public SwitchView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
initialize();
}
protected void initialize() {
setClickable(true);
LayoutInflater layoutInflater = (LayoutInflater) getContext().getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.switch_view, this);
onBgView = findViewById(R.id.on_bg_view);
offBgView = findViewById(R.id.off_bg_view);
circleView = findViewById(R.id.circle_view);
}3. 点击响应
@Override
public boolean performClick() {
if (!autoForPerformClick) //如果不是自动响应则调用默认处理方法
return super.performClick();
/** *否则直接切换switch状态并触发事件监听 */
setChecked(!isChecked, true);
if (onCheckedChangedListener != null) {
onCheckedChangedListener.onChanged(this, isChecked);
}
return super.performClick();
}View点击后会执行performClick方法,并判断是否调用clickLisentener。这里我们直接重写performClick方法,如果自动响应autoForPerformClick为ture则直接切换Switch状态,否则调用默认处理逻辑。
4.切换状态动画
点击打开,则圆形按钮从左端滑动到右端,onBg显示,offBg隐藏;
再点击关闭,圆形按钮从右端滑动到左端,onBg隐藏,offBg显示。
public void setChecked(boolean value, boolean needAnimate) {
if (isChecked == value)
return;
isChecked = value;
float targetX = 0; //要移动的目标位置
if (getWidth() != 0) { //当前view没有渲染上去时候,getWidth()为零
targetX = getWidth() - circleView.getWidth();
} else {
measure(0, 0);
targetX = getMeasuredWidth() - circleView.getMeasuredWidth();
}
long durationMillis = needAnimate ? 200 : 0;
if (isChecked) {
onBgView.bringToFront(); //显示在最前端
onBgView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
offBgView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
//平移动画
TranslateAnimation an1 = new TranslateAnimation(0, targetX, 0, 0);
an1.setFillAfter(true);
an1.setDuration(durationMillis);
circleView.startAnimation(an1);
//透明度动画
AlphaAnimation an2 = new AlphaAnimation(0, 1);
an2.setFillAfter(true);
an2.setDuration(durationMillis);
onBgView.startAnimation(an2);
} else {
offBgView.bringToFront();
onBgView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
offBgView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
TranslateAnimation an1 = new TranslateAnimation(targetX, 0, 0, 0);
an1.setFillAfter(true);
an1.setDuration(durationMillis);
circleView.startAnimation(an1);
AlphaAnimation an2 = new AlphaAnimation(0, 1);
an2.setFillAfter(true);
an2.setDuration(durationMillis);
offBgView.startAnimation(an2);
}
} 状态切换的两个参数,value是否打开状态,needAnimate是否需要动画(否则直接切换效果)。setFillAfter保留动画结束状态,但并不影响View本身位置和状态。切换时,先将当前显示背景移动到最前端,其次添加按钮动画和渐隐动画。
至此,最基本的组合View实现已经完成了。想要了解详情的请在源码中查看。源码分为两部分,一个项目是View的实现lib,另一块是示例演示demo.
2.2 自定义View绘制实现
由于该样式并不十分复杂,所以可以通过基本的图形绘制draw出同样的效果。
具体实现逻辑:通过自定view属性来确定按钮大小和中间圆钮大小,在测量onMesure方法中控制测量值mode和Size,并在onLayout方法中得到圆钮半径和起始点位置。然后进行绘制,先绘制底部on圆角矩形背景,再绘制off渐变缩放的圆角矩形,最后绘制spot圆钮。
嘴比较笨拙,又不会画图。用word的图形工具将就画下可以看就好了。
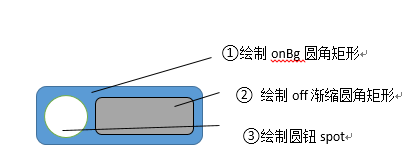
具体实现大体都类似,这里贴上主要部分代码
1.全局参数
public class SwitchButton extends View{
/** */
private float radius;
/** 开启颜色*/
private int onColor = Color.parseColor("#4ebb7f");
/** 关闭颜色*/
private int offBorderColor = Color.parseColor("#dadbda");
/** 灰色带颜色*/
private int offColor = Color.parseColor("#ffffff");
/** 手柄颜色*/
private int spotColor = Color.parseColor("#ffffff");
/** 边框颜色*/
private int borderColor = offBorderColor;
/** 画笔*/
private Paint paint ;
/** 开关状态*/
private boolean toggleOn = false;
/** 边框大小*/
private int borderWidth = 2;
/** 垂直中心*/
private float centerY;
/** 按钮的开始和结束位置*/
private float startX, endX;
/** 手柄X位置的最小和最大值*/
private float spotMinX, spotMaxX;
/**手柄大小 */
private int spotSize ;
/** 手柄X位置*/
private float spotX;
/** 关闭时内部灰色带高度*/
private float offLineWidth;
/** */
private RectF rect = new RectF();
/** 默认使用动画*/
private boolean defaultAnimate = true;
private OnSwitchChanged listener;
//...
}2.初始化与读取
读取自定义属性并赋值。讲了又讲的东西,略。
3.测量onMeasure与布局onLayout
在onMeasure方法中根据给定mode和size来限定View,如果高宽不为明确值(UNSPECIFIED/AT_MOST),则定义自身高宽为明确值。 关于MeasureSpec的详细讲解,这里附上爱哥的一篇文章–MeasureSpec,深入到赋值读取的内部,不妨试着深入研究下。当然,更直接的方法就是点开源码一探究竟咯。
onLayout方法中取得view的实际高宽,计算出圆角矩形半径,圆钮半径以及起始点x方向位置。还有On矩形和off矩形的宽度。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
/** *如果高宽未指定,则使用内置高宽明确大小 */
Resources r = Resources.getSystem();
if(widthMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED || widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
widthSize = (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, 50, r.getDisplayMetrics());
widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(widthSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
}
if(heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED || heightSize == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
heightSize = (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, 30, r.getDisplayMetrics());
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(heightSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
}
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right,
int bottom) {
super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
final int width = getWidth();
final int height = getHeight();
/** *测量相应大小 */
radius = Math.min(width, height) * 0.5f;
centerY = radius;
startX = radius;
endX = width - radius;
spotMinX = startX + borderWidth;
spotMaxX = endX - borderWidth;
spotSize = height - 4 * borderWidth;
spotX = toggleOn ? spotMaxX : spotMinX;
offLineWidth = 0;
} 前三步完成基本赋值之后,开始设置和绑定相应事件。这里不作为重点部分也省略,主要讲一下绘制过程和核心控制逻辑。
4.绘制过程
按照前面的简易示例图来绘制我们的ui图。
@Override
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
//绘制on背景
rect.set(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight());
paint.setColor(borderColor);
canvas.drawRoundRect(rect, radius, radius, paint);
//绘制off背景(缩放至0时候不绘制)
if(offLineWidth > 0){
final float cy = offLineWidth * 0.5f;
rect.set(spotX - cy, centerY - cy, endX + cy, centerY + cy);
paint.setColor(offColor);
canvas.drawRoundRect(rect, cy, cy, paint);
}
//绘制圆钮轮廓border
rect.set(spotX - 1 - radius, centerY - radius, spotX + 1.1f + radius, centerY + radius);
paint.setColor(borderColor);
canvas.drawRoundRect(rect, radius, radius, paint);
//绘制圆钮
final float spotR = spotSize * 0.5f;
rect.set(spotX - spotR, centerY - spotR, spotX + spotR, centerY + spotR);
paint.setColor(spotColor);
canvas.drawRoundRect(rect, spotR, spotR, paint);
}及诶按来便是我们的状态切换动画控制逻辑,即点击按钮之后setToggleOn或者setToggleOff执行的相应动作。
4.状态切换动画效果
/** * 执行效果,如果animate为true表示有动画效果 * 否则直接执行计算并显示最终打开"1"或者关闭"0"的效果绘制 */
private void takeEffect(boolean animate) {
if(animate){
slide();
}else{
calculateEffect(toggleOn ? 1 : 0);
}
}
/** *这里偷个懒,直接使用空的animation,根据当前interpolatedTime(0~1)渐变过程来绘制不同阶段的View,达到动画效果 *当然,也可以开启个线程或者定时任务,来实现从0到1的变换,劲儿改变视图绘制过程 */
private void slide(){
Animation animation = new Animation() {
@Override
protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime,
Transformation t) {
if(toggleOn){
calculateEffect(interpolatedTime);
}else{
calculateEffect(1-interpolatedTime);
}
}
};
animation.setDuration(200);
clearAnimation();
startAnimation(animation);
}
/** *计算绘制位置 *mapValueFromRangeToRange方法计算从当前位置相对于目标位置所对应的值 *通过颜色变化来达到透明度动画效果(颜色渐变) */
private void calculateEffect(final double value) {
final float mapToggleX = (float) mapValueFromRangeToRange(value, 0, 1, spotMinX, spotMaxX);
spotX = mapToggleX;
float mapOffLineWidth = (float) mapValueFromRangeToRange(1 - value, 0, 1, 10, spotSize);
offLineWidth = mapOffLineWidth;
final int fb = Color.blue(onColor);
final int fr = Color.red(onColor);
final int fg = Color.green(onColor);
final int tb = Color.blue(offBorderColor);
final int tr = Color.red(offBorderColor);
final int tg = Color.green(offBorderColor);
int sb = (int) mapValueFromRangeToRange(1 - value, 0, 1, fb, tb);
int sr = (int) mapValueFromRangeToRange(1 - value, 0, 1, fr, tr);
int sg = (int) mapValueFromRangeToRange(1 - value, 0, 1, fg, tg);
sb = clamp(sb, 0, 255);
sr = clamp(sr, 0, 255);
sg = clamp(sg, 0, 255);
borderColor = Color.rgb(sr, sg, sb);
postInvalidate();
}以上就是自定义View绘制的核心代码,详细查看源码SwitchButton。相较于组合方法,它更便捷,也有更高的灵活性和扩展性。同时还不需要图片资源支持。
3.SegmentControl样式实现
常见的Tab有很多种,这里使用的是IOS常见的一种切换效果SegmentControl。本篇只用最简单的拼装View实现类似效果。有兴趣的可以自己尝试绘制达到更优效果。(有空的话也会在后边放出)
- 通过view组合生成 最近单的方案,没有之一。使用现成的selector和背景来控制显示效果。各个子view分别继承 RelativeLayout并实现OnClick接口。最后在Segment中控制显示和点击切换。
- 自定义View绘制生成 这里只是提供思路。定义一个ItemView,根据在Segment中位置挥之不同效果。背景效果会用selector.xml的都知道,使用shape标签产生的drawable对象,其实就是一个GradientDrawable。所以我们自定义view可以直接通过使用GradientDrawable的setCornerRadii(float[] radii) 来绘制同样的背景效果,劲儿可以做到不同颜色。最后,使用一个ViewGroup不含这些item即可。通过click事件来切换tab就可以了。
3.1 组合View实现
首先,类似的定义一个可点击的通用的RelativLayout。(实现 Checkable接口使其可被选中也移除选中状态,详细可以参考前面的博文 微博/动态 点赞效果)。这里涉及三个新内容,稍微说明讲解下。
- checkMode 选中模式,是单选 CHECKMODE_CHECK 还是 CHECKMODE_RADIO 单选效果。使我们的自定义RelativeLayout可以做到单选和复选。
- onInitializeAccessibilityEvent 添加View接受事件源信息。即订阅checked事件。由于事件可能由内部子view点击触发,所以这里应该接收并处理相应的checked事件。当然,使用该方法首先要重写onInitializeAccessibilityNodeInfo方法,添加我们关注的状态信息。
- SavedState状态保存 当我们内部可能嵌套复杂view的时候,为了防止数据状态丢失,一般需要定义状态保存类,用以保存和恢复当前View状态。
#### 1.可点击的通用RelativeLayout
- 继承实现Clickable接口,简要略过。
//定义checked状态
public static final int[] CHECKED_STATE_SET = { android.R.attr.state_checked };
//重写SetChecked方法和isChecked方法略
/** *根据当前选择模式checkMode 来控制单复选 */
@Override
public boolean performClick() {
if (checkMode == CHECKMODE_CHECK) {
toggle();
} else if (checkMode == CHECKMODE_RADIO) {
setChecked(true);
}
return super.performClick();
}
/** *添加Drawable 的checked状态 ,并再绘制view是绘制相应状态效果 */
@Override
public int[] onCreateDrawableState(int extraSpace) {
int[] states = super.onCreateDrawableState(extraSpace + 1);
if (isChecked()) {
mergeDrawableStates(states, CHECKED_STATE_SET);
}
return states;
}
@Override
protected void drawableStateChanged() {
super.drawableStateChanged();
Drawable drawable = getBackground();
if (drawable != null) {
int[] myDrawableState = getDrawableState();
drawable.setState(myDrawableState);
invalidate();
}
}- 接受checked状态事件信息
@Override
public void onInitializeAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) {
super.onInitializeAccessibilityEvent(event);
event.setClassName(CheckedRelativeLayout.class.getName());
event.setChecked(checked);
}
@Override
public void onInitializeAccessibilityNodeInfo(AccessibilityNodeInfo info) {
super.onInitializeAccessibilityNodeInfo(info);
info.setClassName(CheckedRelativeLayout.class.getName());
info.setCheckable(true);
info.setChecked(checked);
}- 保存View状态和恢复
View自身重写保存和恢复的方法
@Override
public Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {//保存
Parcelable superState = super.onSaveInstanceState();
SavedState ss = new SavedState(superState);
ss.checked = isChecked();
return ss;
}
@Override
public void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {//恢复
SavedState ss = (SavedState) state;
super.onRestoreInstanceState(ss.getSuperState());
setChecked(ss.checked);
requestLayout();
}用于保存数据的基本状态类型
static class SavedState extends BaseSavedState {
boolean checked;
SavedState(Parcelable superState) {
super(superState);
}
private SavedState(Parcel in) {
super(in);
checked = (Boolean) in.readValue(null);
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel out, int flags) {
super.writeToParcel(out, flags);
out.writeValue(checked);
}
public static final Creator<SavedState> CREATOR = new Creator<SavedState>() {
public SavedState createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new SavedState(in);
}
public SavedState[] newArray(int size) {
return new SavedState[size];
}
};
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CompoundButton.SavedState{" + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this)) + " checked=" + checked + "}";
}2.控制tab切换的SegmentView
代码比较易于理解,这里直接贴出来查阅即可。
基本思路,水平线性布局包裹对应左中右不同item个数的选项,并通过设置对应left/right/center来设置背景。然后分别为每个Item设置同一个点击事件,点击之后检查是否当前item被选中,改变statu,同时出发切换事件。详细代码:
public class SegmentView extends LinearLayout {
protected final static int SEGMENT_LEFT_BG = R.drawable.segment_left_selector;
protected final static int SEGMENT_CENTER_BG = R.drawable.segment_center_selector;
protected final static int SEGMENT_RIGHT_BG = R.drawable.segment_right_selector;
protected int leftBg = SEGMENT_LEFT_BG;
protected int centerBg = SEGMENT_CENTER_BG;
protected int rightBg = SEGMENT_RIGHT_BG;
protected CheckedRelativeLayout2[] checkedRelativeLayouts;
protected int index = -1;
protected float textSize = -1;
protected int textColorN = Color.BLACK, textColorP = Color.BLACK;
protected OnIndexChangedListener onIndexChangedListener;
public SegmentView(Context context) {
super(context);
initialize();
}
public SegmentView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initialize();
initFromAttributes(context, attrs);
}
public SegmentView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
initialize();
initFromAttributes(context, attrs);
}
protected void initialize() {
setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
}
protected void initFromAttributes(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.SegmentView);
String content = a.getString(R.styleable.SegmentView_content);
index = a.getInt(R.styleable.SegmentView_index, index);
textSize = a.getDimension(R.styleable.SegmentView_textSize, textSize);
textColorN = a.getColor(R.styleable.SegmentView_textColorN, textColorN);
textColorP = a.getColor(R.styleable.SegmentView_textColorP, textColorP);
leftBg = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.SegmentView_leftBg, leftBg);
centerBg = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.SegmentView_centerBg, centerBg);
rightBg = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.SegmentView_rightBg, rightBg);
a.recycle();
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(content)) {
String[] contentStrings = content.split(",");
setContent(contentStrings);
}
setIndex(index);
}
public void setContent(String... content) {
View[] views = new View[content.length];
for (int i = 0, len = content.length; i < len; i++) {
String s = content[i];
TextView tv = new TextView(getContext());
tv.setTextColor(textColorN);
tv.setText(s);
if (textSize != -1) {
tv.setTextSize(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_PX, textSize);
}
views[i] = tv;
}
setContent(views);
}
public void setContent(View... content) {
removeAllViews();
int lastIndex = content.length - 1;
checkedRelativeLayouts = new CheckedRelativeLayout2[content.length];
checkedRelativeLayouts[0] = createLeftView(content[0]);
checkedRelativeLayouts[lastIndex] = createRightView(content[lastIndex]);
for (int i = 1; i < lastIndex; i++) {
checkedRelativeLayouts[i] = createCenterView(content[i]);
}
for (View view : checkedRelativeLayouts) {
LayoutParams llp = new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
llp.weight = 1;
addView(view, llp);
}
}
public int getIndex() {
return index;
}
public void setIndex(int i) {
if (i < 0)
return;
checkedRelativeLayouts[i].setChecked(true);
}
public void setTextColorN(int textColorN) {
this.textColorN = textColorN;
}
public void setTextColorP(int textColorP) {
this.textColorP = textColorP;
}
protected CheckedRelativeLayout.OnCheckedChangeListener checkedChangeListener = new CheckedRelativeLayout.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CheckedRelativeLayout layout, boolean isChecked) {
if (isChecked) {
for (CheckedRelativeLayout2 item : checkedRelativeLayouts) {
if (!item.equals(layout)) {
item.setChecked(false);
}
}
if (onIndexChangedListener != null) {
int i = indexOf(checkedRelativeLayouts, layout);
index = i;
if (onIndexChangedListener != null) {
onIndexChangedListener.onChanged(SegmentView.this, index);
}
}
}
}
};
protected CheckedRelativeLayout2 createLeftView(View contentView) {
CheckedRelativeLayout2 layout = new CheckedRelativeLayout2(getContext());
layout.setBackgroundResource(leftBg);
layout.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
layout.addView(contentView);
layout.setOnCheckedChangeListener(checkedChangeListener);
return layout;
}
protected CheckedRelativeLayout2 createCenterView(View contentView) {
CheckedRelativeLayout2 layout = new CheckedRelativeLayout2(getContext());
layout.setBackgroundResource(centerBg);
layout.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
layout.addView(contentView);
layout.setOnCheckedChangeListener(checkedChangeListener);
return layout;
}
protected CheckedRelativeLayout2 createRightView(View contentView) {
CheckedRelativeLayout2 layout = new CheckedRelativeLayout2(getContext());
layout.setBackgroundResource(rightBg);
layout.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
layout.addView(contentView);
layout.setOnCheckedChangeListener(checkedChangeListener);
return layout;
}
public void setOnIndexChangedListener(OnIndexChangedListener l) {
this.onIndexChangedListener = l;
}
protected class CheckedRelativeLayout2 extends CheckedRelativeLayout {
protected TextView textView;
public CheckedRelativeLayout2(Context context) {
super(context);
}
@Override
public void addView(View child) {
super.addView(child);
if (child instanceof TextView) {
textView = (TextView) child;
}
}
@Override
public void setChecked(boolean checked) {
super.setChecked(checked);
if (textView != null) {
if (checked) {
textView.setTextColor(textColorP);
} else {
textView.setTextColor(textColorN);
}
}
}
}
public static interface OnIndexChangedListener {
public void onChanged(SegmentView view, int index);
}
public static <T> int indexOf(T[] array, T obj) {
for (int i = 0, len = array.length; i < len; i++) {
if (array[i].equals(obj))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
} 该方法比较简陋,背景颜色定制性不高。即只能通过既定drawable北京来实现。不过,其实是可以通过selector来定义相关背景drawable的。不妨试一下。
3.2 自定义View实现
本来此方法只是简单提及的一个想法而已,今天有空就一并写了。时间匆忙,代码稍微有些混乱,不过还是能起到一定示范效用的,这里也贴出来供大家参考。
整体思路:
定义子item 设置其选中状态和字体/背景色。通过测量方法保证显示范围和字体大小,通过GradientDrawable绘制圆角背景,并画对应字体。
定义Segment 继承自ViewGroup,读取自定义属性,根据文本内容添加子View。然后重写OnMeasure方法和OnLayout方法来测量和布局子View。最后添加点击事件,提供监听接口。
代码如下:
import com.qiao.demo.R;
import com.qiao.demo.R.styleable;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.graphics.drawable.GradientDrawable;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.TypedValue;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
public class SegmentView extends ViewGroup implements OnClickListener{
private final float r = TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, 4, getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
private int bgColor = 0xff0072c6;
private int fgColor = Color.WHITE;
private float mTextSize = 3f*r;
private String []mText= {"item1","item2","item3"};
private int checkedItem=1;
private OnItemClickListener listener;
public SegmentView(Context context) {
super(context);
initFromAttributes(context, null);
initalize();
}
public SegmentView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initFromAttributes(context,attrs);
initalize();
}
protected void initFromAttributes(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
if(attrs==null) return;
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.SegmentView0);
String content = a.getString(R.styleable.SegmentView0_content0);
if(!isEmpty(content)){
mText = content.split(",");
}
checkedItem = a.getInt(R.styleable.SegmentView0_index0, checkedItem);
mTextSize = a.getDimension(R.styleable.SegmentView0_textSize0, mTextSize);
bgColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.SegmentView0_bgColor, bgColor);
fgColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.SegmentView0_textColor, fgColor);
a.recycle();
}
public void initalize(){
int length = mText.length;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
View view = new ItemView(getContext(),mText[i],getGravity(i,length),i==checkedItem);
view.setOnClickListener(this);
addView(view,LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int count = getChildCount();
int childWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
int maxWidth = 0;
int maxHeight = 0;
if(widthSize>=0){
maxWidth = widthSize/count;
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(maxWidth,widthMode);
}
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(child, childWidthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,child.getMeasuredWidth());
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,child.getMeasuredHeight());
}
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(maxWidth*count, widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec));
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if(!changed) return;
int count = getChildCount();
int left = 0;
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
child.layout(left,0,left+child.getMeasuredWidth(),child.getMeasuredHeight());
left += child.getMeasuredWidth();
}
}
private int getGravity(int i,int len){
if(i==0){
if(i==len-1)
return ItemView.GRAVITY_SINGLE;
else
return ItemView.GRAVITY_LEFT;
}else if(i==len-1){
return ItemView.GRAVITY_RIGHT;
}else
return ItemView.GRAVITY_CENTER;
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int count = getChildCount();
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
if(v.equals(child)){
checkedItem = i;
((ItemView)child).setChecked(true);
}else{
((ItemView)child).setChecked(false);
}
child.postInvalidate();
}
if(listener!=null){
listener.onItemClick((ItemView)v, checkedItem);
}
}
/** * segment子集item */
class ItemView extends View{
public final static int GRAVITY_SINGLE = 1<<0;
public final static int GRAVITY_LEFT = 1<<1;
public final static int GRAVITY_CENTER = 1<<2;
public final static int GRAVITY_RIGHT = 1<<3;
private GradientDrawable drawable;
private int gravity = GRAVITY_SINGLE;
private boolean isChecked;
private String text;
private Paint mTextPaint;
private Rect mTextBound = new Rect();
private ItemView(Context context,String text,int gravity,boolean isChecked){
super(context);
this.text = text;
this.gravity = gravity;
this.isChecked = isChecked;
init();
}
private void init(){
mTextPaint = new Paint();
mTextPaint.setTextSize(mTextSize);
mTextPaint.getTextBounds(text, 0, text.length(), mTextBound);
drawable = new GradientDrawable();
drawable.setStroke((int)(r/5), bgColor);
setItemGravity(gravity);
setChecked(isChecked);
}
public void setItemGravity(int gravity){
this.gravity = gravity;
switch (gravity){
case GRAVITY_SINGLE:
drawable.setCornerRadii(new float[]{r,r,r,r,r,r,r,r});
break;
case GRAVITY_LEFT:
drawable.setCornerRadii(new float[]{r,r,0,0,0,0,r,r});
break;
case GRAVITY_CENTER:
drawable.setCornerRadii(new float[]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0});
break;
case GRAVITY_RIGHT:
drawable.setCornerRadii(new float[]{0,0,r,r,r,r,0,0});
break;
}
}
public void setChecked(boolean isChecked){
this.isChecked = isChecked;
mTextPaint.setColor(isChecked? fgColor:bgColor);
drawable.setColor(isChecked? bgColor:fgColor);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if(widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
widthSize = mTextBound.width() + (int)(8*r);
widthMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
}
if(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
heightSize = mTextBound.height() + (int)(4*r);
heightMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
}
widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(widthSize,widthMode);
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(heightSize,heightMode);
setMeasuredDimension(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
int height = getMeasuredHeight();
int width = getMeasuredWidth();
if(height>=0){
float textSize = Math.min(mTextSize,height-2*r);
if(width>0){
textSize = Math.min(textSize,(width-2*r)*2/text.length()); //英文比中文短(中文为两个字符),故取mText.length()/2作为平均宽度
}
if(textSize != mTextSize ){
mTextPaint.setTextSize(textSize);
mTextPaint.getTextBounds(text, 0, text.length(), mTextBound);
}
}
}
@Override
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
Rect rect = canvas.getClipBounds();
drawable.setBounds(new Rect(rect));
drawable.draw(canvas);
int l = (rect.width() - mTextBound.width())/2;
int b = (rect.height() + mTextBound.height())/2;
canvas.drawText(text, l, b, mTextPaint);
}
}
public void setOnItemClickListener(OnItemClickListener onItemClickListener){
this.listener = onItemClickListener;
}
interface OnItemClickListener{
void onItemClick(ItemView item,int checkedItem);
}
public static boolean isEmpty(String str){
return null==str || str.trim().length() == 0;
}
}
参照前面两段讲述完全可以理解了。使用时候可以方便的通过自定义属性来控制字体颜色和点击背景。可以动态变更View高宽。有问题的同学可以在文末提出或指正。
3.总结
感觉自己学习进步的速度很慢,常常伴随着焦急浮躁。这篇文章也是积累了好久才慢吞吞的写完了。代码方面,个人也有不少不良习惯,助事业不够清晰,不过总体上不是有碍观瞻吧。
同样的东西,尝试用不同想法写两遍,我觉得是有好处的。至少于我,能看到不少有意思的东西。
最后, 附上本文的 示例源码 . 由于资源上传较早,第二部分的自定义View并没有打包上传。不过上便已经贴出完整代码了,可以直接拿来使用。
后边在考虑是写一写非UI层面的东西,还是继续写关于常见的增删改UI界面。待定,总之,fighting..