Linux Gstreamer and GST-OMX插件
Gstreamer是linux上的多媒体框架。如下所示:

从上面这个图中可以看到,底层是以plugin插件形式存在包括codec标准,parser,audio, protocol等,
也包括用户自己开发的plugin和第三方开发的plugin。
core framework提供了plugin之间的交互机制和管理,通过将一些plugin连接起来形成一个系统,并且对上
提供访问的接口。APP是构建在framework上的。
通过这个框架,底层开发者可以专注于开发plugin,APP开发者通过调用这个plugin来组成完成某种功能的
APP,plugin之间的通信都是由gstreamer framework提供的。
目前已经有一些成熟的plugin已经开发,并且作为library提供给了用户:
gst-plugins-base: an essential exemplary set of elements
gst-plugins-good: a set of good-quality plug-ins under LGPL
gst-plugins-ugly: a set of good-quality plug-ins that might pose distribution problems
gst-plugins-bad: a set of plug-ins that need more quality
plugin中的element实际上就是实现该element支持的API,供上层来调用.
Gstreamer中的几个术语:
Elements: plugin的实例,在一个APP中可能需要创建多个elements并且把这些elements连接在一起形成系统
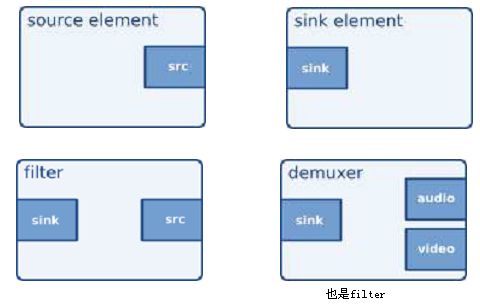
elements可以分为:
source element: 没有输入,只有输出pad,用来产生数据。
sink element: 只有输入pad,没有输出pad,是数据的目的地。如disk,soundcard
filter element: 包含输入pad和输出pad,接收输入的数据并且产生输出数据
输入输出Pad的数目可以是N个(N >= 1)
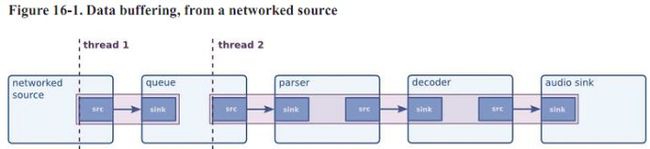
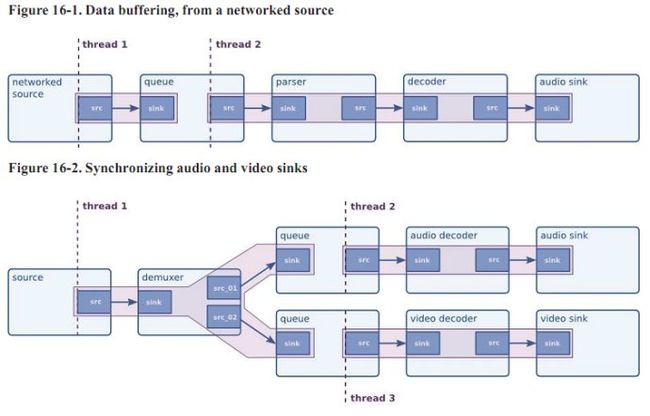
queue element: 是一个特殊的element,作为thread的边界存在。Gstreamer是可以
支持多线程的,线程的边界通过queue来隔开。
element state:
element有4个状态:

Pads:element的输入输出端口。elements之间就是通过Pad来进行连接的。数据通过Pads在elements之间
进行传递。
输入pad称为 sink pad
输出pad称为 source pad
element并不禁止自己的source pad和sink pad连接在一起形成一个loop。
pad的capability 定义了该pad上能够处理的data的类型和一些参数(Gstcaps数据结构):

bin:是一些elements的集合。对这个bin进行的操作会影响到该bin包含的所有的elements。
pipeline: pipeline也是一个bin,不过它是一个top level bin。

Bus: Bus是pipeline传输message给APP时的通路,从下面的图中可以看到,从pipeline中发给APP的message
需要通过BUS(events/Queries 不需要通过BUS)。在创建pipeline时缺省会创建bus,因此用户不需要
去单独创建bus。APP需要做的就是为message设置message handler(APP提供callback函数给
pipeline调用),当pipeline需要发信息给APP时,调用这些APP提供的callback函数。
gst_bus_add_watch () or gst_bus_add_signal_watch ()
例子:

如果使用的是GLIB,那么还可以有另外一种方式来声明callback,见文档。
Gstreamer定义了一些特殊的message包括error/EOS/State-change/element message,plugin也可以自
定义一些message。
通信 communication:
从框架来看,APP需要和pipeline进行数据和控制信息的通信包括进行play、pause等的控制以及数据的传输
pipeline中的elements之间也需要进行数据和信息的传输:

buffers: 在pad上传输的data是通过buffer传输的。 elements <-> elements
buffer的创建有2种方式,一种是由当前的element自己创建,然后把这个buffer传递给下一个element。
另外一种方式就是dwonstream-allocated buffers,就是由下一个element来创建要求大小的buffer,并提供buffer操作函数,当前element通过调用buffer操作函数将数据写入这个buffer中完成buffer数据传递。
区别在于buffer的创建是在数据传输的源端element创建还是在数据接收端element来创建。
events: APP向elements发出的或者elements之间的传输都可以通过events。 APP -> elements, elements<->
messages: elements向APP传输的信息。 elements -> APP
queries: APP向elements请求信息,或者elements之间的信息请求。APP->Elements, elements<->
注意方向,APP和elements之间的传输是有方向的。
Gstreamer的数据驱动(schedule):
Gstreamer是一个多thread的框架。但是为了performance的原因,不会对每一个element都创建一个thread,
而是根据应用的特点和element的工作特点来进行thread的划分,thread的边界必须是queue element。
Gstreamer中pad支持两种schedule方式:docs/design/part-activation.txt
push-based scheduling: 这种scheduling方法中,downstream elements的sink pad上需要定义chain函数
(gst_pad_set_chain_function ),upstream elements调用这个chain函数来完成
将buffer从upstream(source pad)到downstream elements(sink pad)的传递。
这种scheduling方式中source elements递归调用downstream elements的chain函
数,最后一直调用到目的elements的才能函数。
(由于chain函数是定义在sink pad上,而source element是没有sink pad的,因此
source element是不提供chain函数的).
调用的顺序是从sink element到source element。(递归调用).
sink-to-source elements order。

B_chain_function(C_chain_function(buffer2),buffer1)
在这种模式下,upstream elements通过调用downstream elements sink pad上定义的chain函数
主动的将数据传输给downstream elements,因此数据驱动是由upstream element发起的。
Pull-based scheduling:
在这种模式下,upstream elements 的source pad上提供了数据访问函数,downstream elements通过
sink pad主动的去调用upstream elements的函数来要数据,
因此数据驱动是由downstream elements发起的(在sink pad上调用source pad 上的
gst_pad_pull_range())。
具体到某一个element上的PAD可以有下面几种情况:
(1) 该element的所有PAD全部使用push-based mode
(2) 该element的所有pad都采用pull-based mode。
(3) 该element的sinkpad采用pull-based mode,而该element的sourcepad采用push-based
mode. 这种elements只能是queue element。在queue element的sink pad和source pad
上各有一个thread,每一个thread只能有一种数据驱动mode。(GstTask)
核心代码:
push-based mode://source pad主动调用chain函数
#define GST_PAD_CHAINFUNC(pad) (GST_PAD_CAST(pad)->chainfunc)
GstFlowReturn gst_pad_push (GstPad * pad, GstBuffer * buffer)
{
g_return_val_if_fail (GST_IS_PAD (pad), GST_FLOW_ERROR);
g_return_val_if_fail (GST_PAD_IS_SRC (pad), GST_FLOW_ERROR); //source pad调用chain函数
cache = pad_take_cache (pad, cache_ptr);
peer = cache->peer;//得到连接在这个sourcePad上的sink pad的list
ret = GST_PAD_CHAINFUNC (peer) (peer, buffer);//调用sink pad上的chain函数
}
//给sink Pad设置chain函数
void gst_pad_set_chain_function (GstPad * pad, GstPadChainFunction chain)
{
g_return_if_fail (GST_IS_PAD (pad));
g_return_if_fail (GST_PAD_IS_SINK (pad));
GST_PAD_CHAINFUNC (pad) = chain;
}
pull-based mode:sinkpad主动调用get_range()函数
GstFlowReturn gst_pad_pull_range (GstPad * pad, guint64 offset, guint size, GstBuffer ** buffer)
{
g_return_val_if_fail (GST_IS_PAD (pad), GST_FLOW_ERROR);
g_return_val_if_fail (GST_PAD_IS_SINK (pad), GST_FLOW_ERROR);//由sinkpad来调用
if (G_UNLIKELY ((peer = GST_PAD_PEER (pad)) == NULL)) //通过该sinkpad找到和它连接的sourcepad
goto not_connected;
ret = gst_pad_get_range_unchecked (peer, offset, size, buffer);//调用定义在source pad上的
get_range函数
}
GstFlowReturn gst_pad_get_range (GstPad * pad, guint64 offset, guint size, GstBuffer ** buffer)
{
return gst_pad_get_range_unchecked (pad, offset, size, buffer);
}
#define GST_PAD_GETRANGEFUNC(pad) (GST_PAD_CAST(pad)->getrangefunc)
static GstFlowReturn gst_pad_get_range_unchecked (GstPad * pad, guint64 offset, guint size,
GstBuffer ** buffer)
{
if (G_UNLIKELY ((getrangefunc = GST_PAD_GETRANGEFUNC (pad)) == NULL))
goto no_function;
ret = getrangefunc (pad, offset, size, buffer);
}
那么如何设置当前element的pad上采用哪一种scheduling mode,这就是pad-activation stage:
(1) 首先gstreamer需要去查询当前pad支持几种scheduling mode。
(2) Gstreamer来设置当前pad采用的scheduling mode方式,并通知当前pad知道。
PAD上需要实现notice函数供gstreamer来调用:
gst_pad_set_activatepull_function ()
gst_pad_set_activatepush_function ()
#define GST_PAD_ACTIVATEPUSHFUNC(pad) (GST_PAD_CAST(pad)->activatepushfunc)
void gst_pad_set_activatepush_function (GstPad * pad, GstPadActivateModeFuncti on activatepush)
{
g_return_if_fail (GST_IS_PAD (pad));
GST_PAD_ACTIVATEPUSHFUNC (pad) = activatepush; //函数指针
}
在activatepush()中调用下面的函数来设置mode。
gboolean gst_pad_activate_push/pull (GstPad * pad, gboolean active)
{
......
}
2 . 基于Gstreamer构建应用APP

第2部分:如何注册一个plugin
一个plugin中可以包含多个element。每一个element作为plugin的一个feature。
gst_element_register (GstPlugin * plugin, const gchar * name, guint rank,GType type)
->gst_plugin_feature_set_name (GST_PLUGIN_FEATURE_CAST (factory), name);
首先从APP的角度来看,如何调用一个plugin(使用plugin feature name来调用如fakesink):
sink = gst_element_factory_make ("fakesink", "swallow_audio");
GstElement * gst_element_factory_make (const gchar * factoryname, const gchar * name)
{
factory = gst_element_factory_find (factoryname);//根据factorName找到
GstPluginFeature *feature;
element = gst_element_factory_create (factory, name);//通过factory得到plugin并
创建element(name)
}
GstElementFactory * gst_element_factory_find (const gchar * name)
{
feature = gst_registry_find_feature (gst_registry_get_default (), name,
GST_TYPE_ELEMENT_FACTORY);
}
GstElement * gst_element_factory_create (GstElementFactory * factory, const gchar * name)
{
//gst_plugin_feature_load调用plugin = gst_plugin_load_by_name (feature->plugin_name);
newfactory = GST_ELEMENT_FACTORY (gst_plugin_feature_load (GST_PLUGIN_FEATURE
(factory)));
factory = newfactory;
if (name) //创建的instance的name
element =
GST_ELEMENT_CAST (g_object_new (factory->type, "name", name, NULL));
else
element = GST_ELEMENT_CAST (g_object_newv (factory->type, 0, NULL));
}
gst_element_factory_create->gst_plugin_feature_load()
->plugin = gst_plugin_load_by_name (feature->plugin_name);
-> plugin = gst_registry_find_plugin (gst_registry_get_default (), name);
newplugin = gst_plugin_load_file (plugin->filename, &error);
-> gst_plugin_register_func (plugin, plugin->orig_desc, NULL)
-> (desc->plugin_init) (plugin)
总结下来就是:先通过factoryname找到该plugin的factory数据结构(GstPluginFeature factor->feature),再找到对应的plugin,并调用 该plugin提供的plugin_init()函数。
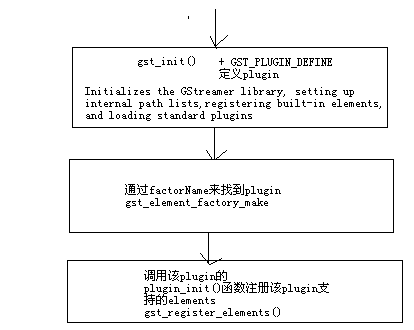
(1) gst_init()
Initializes the GStreamer library, setting up internal path lists,
registering built-in elements, and loading standard plugins.
gst_init_check()
{
group = gst_init_get_option_group ();
}
在plugin编写中:有2种注册plugin的方式:
如下面的例子中的macro GST_PLUGIN_DEFINE:
GST_PLUGIN_DEFINE (GST_VERSION_MAJOR,
GST_VERSION_MINOR,
"avi",
"AVI stream handling",
plugin_init, VERSION, "LGPL", GST_PACKAGE_NAME, GST_PACKAGE_ORIGIN)
* This macro needs to be used to define the entry point and meta data of a
* plugin. One would use this macro to export a plugin, so that it can be used
* by other applications.
*
* The macro uses a define named PACKAGE for the #GstPluginDesc,source field.
* When using autoconf, this is usually set automatically via the AC_INIT
* macro, and set in config.h. If you are not using autoconf, you will need to
* define PACKAGE yourself and set it to a short mnemonic string identifying
* your application/package, e.g. 'someapp' or 'my-plugins-foo.
*
* If defined, the GST_PACKAGE_RELEASE_DATETIME will also be used for the
* #GstPluginDesc,release_datetime field.
#define GST_PLUGIN_DEFINE(major,minor,name,description,init,version,license,package,origin) \
G_BEGIN_DECLS \
GST_PLUGIN_EXPORT GstPluginDesc gst_plugin_desc = { \
major, \
minor, \
name, \
(gchar *) description, \
init, \
version, \
license, \
PACKAGE, \
package, \
origin, \
__GST_PACKAGE_RELEASE_DATETIME, \
GST_PADDING_INIT \
}; \
G_END_DECLS
类似的有一个对应的静态注册函数:
#define GST_PLUGIN_DEFINE_STATIC(major,minor,name,description,init,version,license,package,origin) \
static void GST_GNUC_CONSTRUCTOR \
_gst_plugin_static_init__ ##init (void) \
{ \
static GstPluginDesc plugin_desc_ = { \
major, \
minor, \
name, \
(gchar *) description, \
init, \
version, \
license, \
PACKAGE, \
package, \
origin, \
NULL, \
GST_PADDING_INIT \
}; \
_gst_plugin_register_static (&plugin_desc_); \ //调用了静态注册函数
}
编译自己的plugin插件:http://blog.csdn.net/dyzhu/article/details/4357037
1. 从模板生成gstreamer插件
gst-template是gstreamer插件的开发模板,在gst-plugin/tools目录下有一个make_element,在gst-plugin/src目录下,运行../tools/make_element myfilter,就可以生成一个myfilter插件。
在gst-plugin目录下的autogen.sh可以自动生成congifure和makefile.in文件,如果这个脚本运行不成功。可以用下面的方法:
编译:
#libtool --mode=compile cc `pkg-config --cflags gstreamer-0.10` -DPACKAGE="Gstreamer" -DHAVE_USER_MTU -Wall -Wimplicit -g -o gstmyfilter.o -c gstmyfilter.c
链接:
#libtool --mode=link cc -module -avoid-version -rpath /usr/local/lib/gstreamer-0.10/ -export-symbols-regex gst_plugin_desc -o gstmyfilter.la gstmyfilter.lo `pkg-config --libs gstreamer-0.10`
安装:
#libtool --mode=install install gstmyfilter.la /usr/local/lib/gstreamer-0.10/
之后,就可以在自己的应用程序中创建myfilter的element。
转载两篇相关的文章:http://blog.csdn.net/dyzhu/article/details/4362865
http://blog.csdn.net/dyzhu/article/details/4362865
由于在嵌入式系统中运行gstreamer,受到资源的限制,所以打算只安装gstreamer核心库和一些必须的element,其它的element用到的时候再添加。我的想法是,把base,good,。。。插件包中的需要用到的elment编译成插件。
拿good插件包中的id3demux做试验(先在pc上试验,可惜pc上已经装了base插件包),把good插件包中的gst/id3demux目录下的5个文件copy到gst-template/gst-plugin/src目录下,用上一篇文章《编译自己的gstreamer插件》中提到的方法编译,郁闷,没通过,有空再研究一下(linux基本知识还很欠缺啊。。。)。
后来我想,既然gstreamer的插件是动态链接库,那么只是把这些源文件编译成动态链接库是否可以呢?试一下:
gcc -Wall $(pkg-config --cflags --libs gstreamer-0.10) -DPACKAGE='"GStreamer"' -Wimplicit -fpic -shared -g -o gstid3demux.so gstid3demux.c id3tags.c id3v2frames.c
把编译出来的gstid3demux.so拷贝到gstreamer库目录下,写个应用程序调用一下,OK,没问题。再用gst-template的工具生成一个myfilter,用同样的方法:
gcc -Wall $(pkg-config --cflags --libs gstreamer-0.10) -DPACKAGE='"GStreamer"' -DVERSION='"0.10.23"' -Wimplicit -fpic -shared -g -o gstmyfilter.so gstmyfilter.c
把编译出来的gstmyfilter.so拷贝到gstreamer库目录下,调用成功。
原来,只需要把你element编译成动态连接库就可以了。
看一个例子:
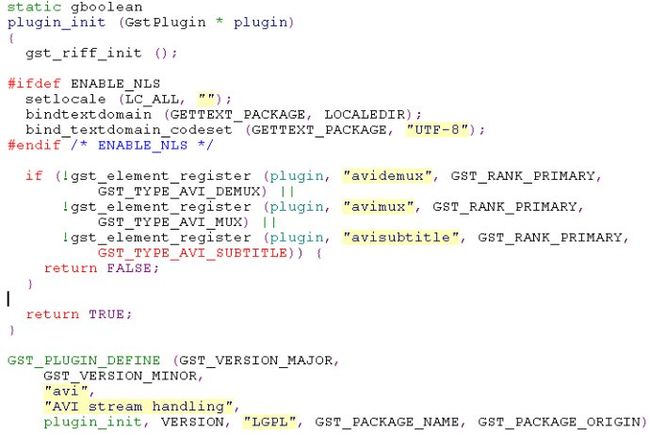
上面这个例子中,这个plugin中注册了几个element。 在plugin_init()中就是做element的注册。
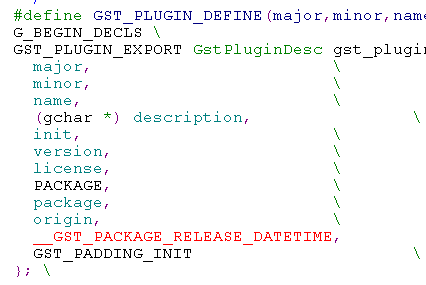
struct _GstPluginDesc {
gint major_version;
gint minor_version;
const gchar *name;
const gchar *description;
GstPluginInitFunc plugin_init; //初始化函数
const gchar *version;
const gchar *license;
const gchar *source;
const gchar *package;
const gchar *origin;
const gchar *release_datetime;
gpointer _gst_reserved[GST_PADDING - 1];
};
如下图,一个plugin中注册了多个components(elements)
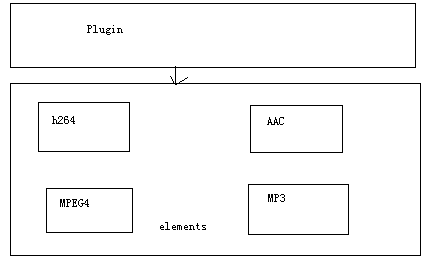
第3部分:GST-OMX
GST-omx是Gstreamer的一个plugin,用来和OMX IL封装的codec进行互连。从OMX IL的角度来说,GST-OMX
其实就是一个OMX IL Client,通过GetHandle得到component的handle来操作component。
由于是一个plugin,因此需要符合plugin的要求:
GST_PLUGIN_DEFINE (GST_VERSION_MAJOR,
GST_VERSION_MINOR,
"omx",
"OpenMAX IL",
plugin_init,
PACKAGE_VERSION, GST_LICENSE, GST_PACKAGE_NAME, GST_PACKAGE_ORIGIN)
static gboolean plugin_init (GstPlugin * plugin)
{
fetch_element_table (plugin);->path = get_config_path ();通过一个config文件来定义
}
缺省的config文件Gstomx_config.c 中default_config如下:
"omx_mpeg4dec,\
"
" type=GstOmxMpeg4Dec,\
"
" library-name=libomxil-bellagio.so.0,\
"
" component-name=OMX.st.video_decoder.mpeg4,\
"
" rank=256;\
通过解析这个config可以得到library name(.so),component name等信息。 config文件的路径可以由环境变量OMX_CONFIG设置,没有设置就使用default config(Gstomx.config)。
GST-OMX中的element做了一些抽象:

一些API和OMX IL的对应关系:

以H264dec为例:
在例化时会调用type_instance_init,由于基类是base filter,因此会先调用基类的type_instance_init函数
//Gstomx_h264dec.c
static void
type_instance_init (GTypeInstance * instance, gpointer g_class)
{
GstOmxBaseVideoDec *omx_base;
omx_base = GST_OMX_BASE_VIDEODEC (instance);//base videoDEC类型
omx_base->compression_format = OMX_VIDEO_CodingAVC;
}
//GstOmxBaseVideoDec 构造函数
static void
type_instance_init (GTypeInstance * instance, gpointer g_class)
{
GstOmxBaseFilter *omx_base;
omx_base = GST_OMX_BASE_FILTER (instance);
omx_base->omx_setup = omx_setup;
omx_base->gomx->settings_changed_cb = settings_changed_cb;
gst_pad_set_setcaps_function (omx_base->sinkpad, sink_setcaps);
}
基类basefilter的该函数:
static void
type_instance_init (GTypeInstance * instance, gpointer g_class)
{
GstOmxBaseFilter *self;
GstElementClass *element_class;
element_class = GST_ELEMENT_CLASS (g_class);
self = GST_OMX_BASE_FILTER (instance);
GST_LOG_OBJECT (self, "begin");
self->use_timestamps = TRUE;
self->gomx = gstomx_core_new (self, G_TYPE_FROM_CLASS (g_class)); //omx core生成,会调用
g_omx_core_init->request_imp
->imp_new->dlopen()
self->in_port = g_omx_core_new_port (self->gomx, 0);
self->out_port = g_omx_core_new_port (self->gomx, 1);
self->ready_lock = g_mutex_new ();
self->sinkpad =
gst_pad_new_from_template (gst_element_class_get_pad_template
(element_class, "sink"), "sink");
gst_pad_set_chain_function (self->sinkpad, pad_chain);
gst_pad_set_event_function (self->sinkpad, pad_event);
self->srcpad =
gst_pad_new_from_template (gst_element_class_get_pad_template
(element_class, "src"), "src");
gst_pad_set_activatepush_function (self->srcpad, activate_push);
gst_pad_use_fixed_caps (self->srcpad);
gst_element_add_pad (GST_ELEMENT (self), self->sinkpad);
gst_element_add_pad (GST_ELEMENT (self), self->srcpad);
GST_LOG_OBJECT (self, "end");
}
void *
gstomx_core_new (void *object, GType type)
{
GOmxCore *core = g_omx_core_new (object);
gstomx_get_component_info (core, type);
g_omx_core_init (core);
return core;
}
//对core进行初始化
gboolean
gstomx_get_component_info (void *core, GType type)
{
GOmxCore *rcore = core;
const gchar *element_name;
GstStructure *element;
const gchar *str;
element_name = g_type_get_qdata (type, element_name_quark);
element = get_element_entry (element_name);
if (!element)
return FALSE;
str = gst_structure_get_string (element, "library-name");
rcore->library_name = g_strdup (str);
str = gst_structure_get_string (element, "component-name");
rcore->component_name = g_strdup (str);
str = gst_structure_get_string (element, "component-role");
rcore->component_role = g_strdup (str);
return TRUE;
}
void
g_omx_core_init (GOmxCore * core)
{
core->imp = request_imp (core->library_name);// core的library_name如何得到的?config文件中读取
if (!core->imp)
return;
//调用了get_handle
core->omx_error = core->imp->sym_table.get_handle (&core->omx_handle,
(char *) core->component_name, core, &callbacks);
if (!core->omx_error) {
core->omx_state = OMX_StateLoaded;
if (core->component_role) {
OMX_PARAM_COMPONENTROLETYPE param;
GST_DEBUG_OBJECT (core->object, "setting component role: %s",
core->component_role);
G_OMX_INIT_PARAM (param);
strncpy ((char *) param.cRole, core->component_role,
OMX_MAX_STRINGNAME_SIZE);
OMX_SetParameter (core->omx_handle, OMX_IndexParamStandardCompon entRole,
¶m);
}
}
}
通过这些函数的调用,完成了element的例化。其中的关键函数:
core->imp = request_imp (core->library_name);//这里的library_name就是config文件中的library name
如何得到config文件?
在GST-OMX中plugin_init()->fetch_element_table()->get_config_path()中去查找config文件:
寻找的优先级如下:
1. OMX_CONFIG环境变量设置的文件
2. 系统目录下的gst-openmax.conf
3. 用户目录下的gst-openmax.conf
static gchar * get_config_path (void)
{
gchar *path;
const gchar *const *dirs;
int i;
path = g_strdup (g_getenv ("OMX_CONFIG")); //读取环境变量中设置的config文件的位置和文件名
if (path)
return path;
dirs = g_get_system_config_dirs (); //如果没有设置环境变量,则去系统目录下看是否这个文件存在
system_dir/gstreamer-0.10/gst-openmax.conf文件
for (i = 0; dirs[i]; i++) {
path =
g_build_filename (dirs[i], "gstreamer-0.10", "gst-openmax.conf", NULL);
if (g_file_test (path, G_FILE_TEST_IS_REGULAR))
return path;
g_free (path);
}
//如果上面两个都没有找到,那么返回usr目录下的gst-openmax.conf文件
//其中g_get_user_config_dir ()的返回值通常为home/user_name/.config
//在其它的代码中会去测试是否这个文件存在
return g_build_filename (g_get_user_config_dir (), "gst-openmax.conf", NULL);
}
config的内容:

上面的config中还可以设置一个component_role,在gst-omx.c的plugin_init()函数中有下面的代码:

在很多的omx component中需要这个component_role的设置:
在TI OMX_CORE.c 中就包含有下面的role表,前面一个是component name后面一个是该component支持的role:
char *tComponentName[MAXCOMP][2] = {
{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.avc"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.vc1"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.mpeg2"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.mpeg4"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.div3"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.rv"},
{"OMX.TI.MP3.decode", "audio_decoder.mp3"},
{"OMX.TI.AAC.encode", "audio_encoder.aac"},
{"OMX.TI.AAC.decode", "audio_decoder.aac"},
{"OMX.TI.WMA.decode", "audio_decoder.wma"},
{"OMX.TI.WBAMR.decode", "audio_decoder.amrwb"},
{"OMX.TI.AMR.decode", "audio_decoder.amrnb"},
{"OMX.TI.AMR.encode", "audio_encoder.amrnb"},
{"OMX.TI.WBAMR.encode", "audio_encoder.amrwb"},
}
//初始化
static inline GOmxImp *
request_imp (const gchar * name)
{
GOmxImp *imp = NULL;
g_mutex_lock (imp_mutex);
imp = g_hash_table_lookup (implementations, name);
if (!imp) {
imp = imp_new (name); //打开动态链接库得到函数指针
if (imp)
g_hash_table_insert (implementations, g_strdup (name), imp);
}
g_mutex_unlock (imp_mutex);
if (!imp)
return NULL;
g_mutex_lock (imp->mutex);
if (imp->client_count == 0) {
OMX_ERRORTYPE omx_error;
omx_error = imp->sym_table.init (); //调用omx_init
if (omx_error) {
g_mutex_unlock (imp->mutex);
return NULL;
}
}
imp->client_count++;
g_mutex_unlock (imp->mutex);
return imp;
}
static GOmxImp *
imp_new (const gchar * name)
{
GOmxImp *imp;
imp = g_new0 (GOmxImp, 1);
{
void *handle;
GST_DEBUG ("loading: %s", name);
imp->dl_handle = handle = dlopen (name, RTLD_LAZY); //打开omxcore的动态链接库,在GST-OMX
中只是提供了OMX_CORE.h,没有提供
OMX_CORE.c,这部分是由OMX提供,
在stagefright中这个库位libOMXCORE.so
在GST-OMX中由config中的library name指定
如下面的libomxil-bellagio.so.0
component_name是在getHandle时被调用( 打开lib+component_name.SO):
(core->omx_error = core->imp->sym_table.get_handle (&core->omx_handle,
(char *) core-> component_name, core, &callbacks);)

GST_DEBUG ("dlopen(%s) -> %p", name, handle);
if (!handle) {
g_warning ("%s\n", dlerror ());
g_free (imp);
return NULL;
}
imp->mutex = g_mutex_new ();
imp->sym_table.init = dlsym (handle, "OMX_Init"); //得到OMX 函数。
imp->sym_table.deinit = dlsym (handle, "OMX_Deinit");
imp->sym_table.get_handle = dlsym (handle, "OMX_GetHandle");
imp->sym_table.free_handle = dlsym (handle, "OMX_FreeHandle");
}
struct GstOmxBaseVideoDec
{
GstOmxBaseFilter omx_base; //继承baseFilter类
OMX_VIDEO_CODINGTYPE compression_format;
gint framerate_num;
gint framerate_denom;
};
//GstOmxBaseFilter 构造函数
static void
type_class_init (gpointer g_class, gpointer class_data)
{
GObjectClass *gobject_class;
GstElementClass *gstelement_class;
gobject_class = G_OBJECT_CLASS (g_class);
gstelement_class = GST_ELEMENT_CLASS (g_class);
gobject_class->finalize = finalize;
gstelement_class->change_state = change_state;
{
gobject_class->set_property = set_property;
gobject_class->get_property = get_property;
gstomx_install_property_helper (gobject_class);
//设置property
g_object_class_install_property (gobject_class, ARG_USE_TIMESTAMPS,
g_param_spec_boolean ("use-timestamps", "Use timestamps",
"Whether or not to use timestamps",
TRUE, G_PARAM_READWRITE | G_PARAM_STATIC_STRINGS));
g_object_class_install_property (gobject_class, ARG_NUM_INPUT_BUFFERS,
g_param_spec_uint ("input-buffers", "Input buffers",
"The number of OMX input buffers",
1, 10, 4, G_PARAM_READWRITE | G_PARAM_STATIC_STRINGS));
g_object_class_install_property (gobject_class, ARG_NUM_OUTPUT_BUFFERS,
g_param_spec_uint ("output-buffers", "Output buffers",
"The number of OMX output buffers",
1, 10, 4, G_PARAM_READWRITE | G_PARAM_STATIC_STRINGS));
}
}
在base filter中定义了这些property设置函数:
static void
set_property (GObject * obj,
guint prop_id, const GValue * value, GParamSpec * pspec)
{
GstOmxBaseFilter *self;
self = GST_OMX_BASE_FILTER (obj);
switch (prop_id) {
case ARG_USE_TIMESTAMPS:
self->use_timestamps = g_value_get_boolean (value);
break;
case ARG_NUM_INPUT_BUFFERS:
case ARG_NUM_OUTPUT_BUFFERS:
{
OMX_PARAM_PORTDEFINITIONTYPE param;
OMX_HANDLETYPE omx_handle = self->gomx->omx_handle;
OMX_U32 nBufferCountActual;
GOmxPort *port = (prop_id == ARG_NUM_INPUT_BUFFERS) ?
self->in_port : self->out_port;
if (G_UNLIKELY (!omx_handle)) {
GST_WARNING_OBJECT (self, "no component");
break;
}
nBufferCountActual = g_value_get_uint (value);
G_OMX_INIT_PARAM (param);
param.nPortIndex = port->port_index;
OMX_GetParameter (omx_handle, OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition , ¶m); //调用OMX IL API
if (nBufferCountActual < param.nBufferCountMin) {
GST_ERROR_OBJECT (self, "buffer count %lu is less than minimum %lu",
nBufferCountActual, param.nBufferCountMin);
return;
}
param.nBufferCountActual = nBufferCountActual;
OMX_SetParameter (omx_handle, OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition , ¶m);
}
break;
default:
G_OBJECT_WARN_INVALID_PROPERTY_ID (obj, prop_id, pspec);
break;
}
}
数据结构中:
struct GstOmxBaseFilter
{
GstElement element;
GstPad *sinkpad;
GstPad *srcpad;
GOmxCore *gomx; //OMXCORE
GOmxPort *in_port;
GOmxPort *out_port;
gboolean use_timestamps;
gboolean ready;
GMutex *ready_lock;
GstOmxBaseFilterCb omx_setup;
GstFlowReturn last_pad_push_return;
GstBuffer *codec_data;
gboolean share_input_buffer;
gboolean share_output_buffer;
};
struct GOmxCore
{
gpointer object;
OMX_HANDLETYPE omx_handle; //OMX HANDLE
OMX_ERRORTYPE omx_error;
OMX_STATETYPE omx_state;
GCond *omx_state_condition;
GMutex *omx_state_mutex;
GPtrArray *ports;
GSem *done_sem;
GSem *flush_sem;
GSem *port_sem;
GOmxCb settings_changed_cb;
GOmxImp *imp;
gboolean done;
gchar *library_name;
gchar *component_name;
gchar *component_role;
};
struct GOmxPort
{
GOmxCore *core;
GOmxPortType type;
guint num_buffers;
gulong buffer_size;
guint port_index;
OMX_BUFFERHEADERTYPE **buffers;
GMutex *mutex;
gboolean enabled;
gboolean omx_allocate;
AsyncQueue *queue;
};
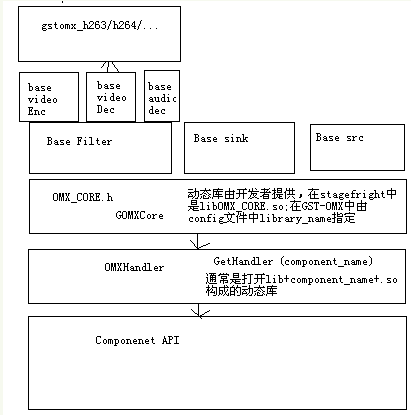
在stagefright中是libomxCore.SO,在GST-OMX中通过config文件中的library_name来指定使用的core的so文件
这是因为在omx_core.c中的一些API的实现是同实现相关的,因此需要开发这个core.so由开发者来实现,在
Gst-omx中可以通过config来定义使用的core.so文件:
比如stagefright中的TI的实现中:
OMX_ERRORTYPE TIOMX_Init()
{
eError = TIOMX_BuildComponentTable(); //component table的定义就是同实现相关的
}
//component name : role
char *tComponentName[MAXCOMP][2] = {
//{"OMX.TI.JPEG.decoder", "image_decoder.jpeg" },
{"OMX.TI.JPEG.Encoder", "image_encoder.jpeg"},
//{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.h263"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.avc"},
//{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.mpeg2"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.mpeg4"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.Decoder", "video_decoder.wmv"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.encoder", "video_encoder.mpeg4"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.encoder", "video_encoder.h263"},
{"OMX.TI.Video.encoder", "video_encoder.avc"},
从上面这个图中可以看到,GSTREMAER的GST-OMX确实只是通过GOMXCORE(omxcore)来调用GetHandler得到component 的handle后来操作omx component。因此可以认为GST-OMX只是一个OMX IL Client而已。
GST-OMX和OMX IL 工作机制:
通过playbin2来调用omx中实现的decoder,由于decodebin是一个filter类型,因此在filter类型初始化中:
type_instance_init()会创建一个gomx_core对象来调用OMX IL API;
{
self->gomx = gstomx_core_new (self, G_TYPE_FROM_CLASS (g_class)); //打开config中的
omxcore.so,并调用get_handler得到component的IL handler。
self->in_port = g_omx_core_new_port (self->gomx, 0);
self->out_port = g_omx_core_new_port (self->gomx, 1);
//gstreamer这边对应的sinkpad和srcpad,并且为pad上设置chain函数和event
self->sinkpad =
gst_pad_new_from_template (gst_element_class_get_pad_template
(element_class, "sink"), "sink");
//push-based schedule机制
gst_pad_set_chain_function (self->sinkpad, pad_chain);
gst_pad_set_event_function (self->sinkpad, pad_event);
self->srcpad =
gst_pad_new_from_template (gst_element_class_get_pad_template
(element_class, "src"), "src");
gst_pad_set_activatepush_function (self->srcpad, activate_push);
gst_pad_use_fixed_caps (self->srcpad);
gst_element_add_pad (GST_ELEMENT (self), self->sinkpad);
gst_element_add_pad (GST_ELEMENT (self), self->srcpad);
}
另外,由于decodebin是一个filter,包含input/output port,因此同样为OMX生成2个port。在Gstreamer这边
port对应的就是pad(src_pad,sink_pad)。

在pad_chain()函数中:完成OMX从loaded->idle的跳转和port上资源的分配工作
static GstFlowReturn pad_chain (GstPad * pad, GstBuffer * buf)
{
if (self->omx_setup) {
self->omx_setup (self);
}
setup_ports (self); // 调用get_parameter()得到port上的参数nBufferCountActual/nBufferSize来初始
化port(in,out),并将gstreamer的pad和Omx port连接起来(需要注意的是这里要
确定是allocate_buffer()还是use_buffer()的方式)
g_omx_core_prepare (self->gomx);//调用omx的sendCommand(),驱动omx状态机从loaded->idle,分配port
buffer
}
//PORT相关的函数
static void
setup_ports (GstOmxBaseFilter * self)
{
g_omx_port_setup (self->in_port);
gst_pad_set_element_private (self->sinkpad, self->in_port);
g_omx_port_setup (self->out_port);
gst_pad_set_element_private (self->srcpad, self->out_port);
if (g_getenv ("OMX_ALLOCATE_ON")) {
GST_DEBUG_OBJECT (self, "OMX_ALLOCATE_ON");
self->in_port->omx_allocate = TRUE; / /True:使用OMX的allocate_buffer方式;false:use_buffer
self->out_port->omx_allocate = TRUE;
self->share_input_buffer = FALSE;
self->share_output_buffer = FALSE;
} else if (g_getenv ("OMX_SHARE_HACK_ON")) {
GST_DEBUG_OBJECT (self, "OMX_SHARE_HACK_ON");
self->share_input_buffer = TRUE;
self->share_output_buffer = TRUE;
} else if (g_getenv ("OMX_SHARE_HACK_OFF")) {
GST_DEBUG_OBJECT (self, "OMX_SHARE_HACK_OFF");
self->share_input_buffer = FALSE;
self->share_output_buffer = FALSE;
} else {
GST_DEBUG_OBJECT (self, "default sharing and allocation");
}
GST_DEBUG_OBJECT (self, "omx_allocate: in: %d, out: %d",
self->in_port->omx_allocate, self->out_port->omx_allocate);
GST_DEBUG_OBJECT (self, "share_buffer: in: %d, out: %d",
self->share_input_buffer, self->share_output_buffer);
}
void
g_omx_core_prepare (GOmxCore * core)
{
change_state (core, OMX_StateIdle); //OMX状态机 从 loaded->idle
core_for_each_port (core, port_allocate_buffers); // 调用allocate_buffers来为port分配buffer。
wait_for_state (core, OMX_StateIdle);
}
static void
port_allocate_buffers (GOmxPort * port)
{
guint i;
gsize size;
size = port->buffer_size;
for (i = 0; i < port->num_buffers; i++) {
if ( port->omx_allocate) {
GST_DEBUG_OBJECT (port->core->object,
"%d: OMX_AllocateBuffer(), size=%" G_GSIZE_FORMAT, i, size);
OMX_AllocateBuffer (port->core->omx_handle, &port->buffers[i],
port->port_index, NULL, size);
} else {
gpointer buffer_data;
buffer_data = g_malloc (size);
GST_DEBUG_OBJECT (port->core->object,
"%d: OMX_UseBuffer(), size=%" G_GSIZE_FORMAT, i, size);
OMX_UseBuffer (port->core->omx_handle, &port->buffers[i],
port->port_index, NULL, size, buffer_data);
}
}
}
然而,对于很多情况来说,上面port上的参数很多都是default值,比如buffer的大小和数目,在实际中这个
设置可能不是正确的,因此如果实际buffer的需求超过了现在使用default参数初始化的port上的设置,底层
会发出"portSettingChange"来通知gst-omx,要求gst-omx重新根据实际的需求来分配port上的buffer.
Gst-omx需要提供几个callback函数:
static OMX_CALLBACKTYPE callbacks =
{ EventHandler, EmptyBufferDone, FillBufferDone };
在get_handler()是注册给component来使用。其中EventHandler()中就是需要来处理component发给client(gst-omx)的event,其中就包括OMX_EventPortSettingsChanged 。
buffer数据驱动:
在OMX中的数据驱动方式如下:

在OMX状态机状态从loaded->idle后,资源分配完成。下面开始进入
static GstFlowReturn pad_chain (GstPad * pad, GstBuffer * buf)
{
if (G_UNLIKELY (gomx->omx_state == OMX_StateLoaded)) {
if (self->omx_setup) {
self->omx_setup (self);
}
setup_ports (self);
g_omx_core_prepare (self->gomx);
if (gomx->omx_state == OMX_StateIdle) {
self->ready = TRUE;
gst_pad_start_task (self->srcpad, output_loop, self->srcpad);
}
}
}
static void output_loop (gpointer data)
{
if (G_LIKELY (out_port->enabled)) { //初始化为enable
OMX_BUFFERHEADERTYPE *omx_buffer = NULL;
omx_buffer = g_omx_port_request_buffer (out_port); //从port buffer queue中得到一个空的buffer
//对输入buffer,填充数据
//调用
g_omx_port_release_buffer (out_port, omx_buffer);
}
}
//调用fillthisbuffer和emptythisbuffer,开始传递buffer和数据
void g_omx_port_release_buffer (GOmxPort * port, OMX_BUFFERHEADERTYPE * omx_buffer)
{
switch (port->type) {
case GOMX_PORT_INPUT:
OMX_EmptyThisBuffer (port->core->omx_handle, omx_buffer);
break;
case GOMX_PORT_OUTPUT:
OMX_FillThisBuffer (port->core->omx_handle, omx_buffer);
break;
default:
break;
}
}