HDU 1046.Gridland【非搜索,找规律】【8月25】
Gridland
Problem Description
For years, computer scientists have been trying to find efficient solutions to different computing problems. For some of them efficient algorithms are already available, these are the “easy” problems like sorting, evaluating a polynomial or finding the shortest path in a graph. For the “hard” ones only exponential-time algorithms are known. The traveling-salesman problem belongs to this latter group. Given a set of N towns and roads between these towns, the problem is to compute the shortest path allowing a salesman to visit each of the towns once and only once and return to the starting point.
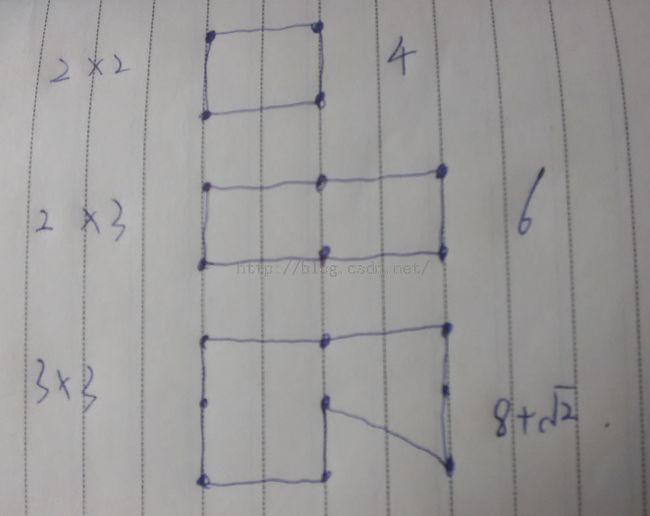
The president of Gridland has hired you to design a program that calculates the length of the shortest traveling-salesman tour for the towns in the country. In Gridland, there is one town at each of the points of a rectangular grid. Roads run from every town in the directions North, Northwest, West, Southwest, South, Southeast, East, and Northeast, provided that there is a neighbouring town in that direction. The distance between neighbouring towns in directions North–South or East–West is 1 unit. The length of the roads is measured by the Euclidean distance. For example, Figure 7 shows 2 × 3-Gridland, i.e., a rectangular grid of dimensions 2 by 3. In 2 × 3-Gridland, the shortest tour has length 6.

The president of Gridland has hired you to design a program that calculates the length of the shortest traveling-salesman tour for the towns in the country. In Gridland, there is one town at each of the points of a rectangular grid. Roads run from every town in the directions North, Northwest, West, Southwest, South, Southeast, East, and Northeast, provided that there is a neighbouring town in that direction. The distance between neighbouring towns in directions North–South or East–West is 1 unit. The length of the roads is measured by the Euclidean distance. For example, Figure 7 shows 2 × 3-Gridland, i.e., a rectangular grid of dimensions 2 by 3. In 2 × 3-Gridland, the shortest tour has length 6.

Input
The first line contains the number of scenarios.
For each scenario, the grid dimensions m and n will be given as two integer numbers in a single line, separated by a single blank, satisfying 1 < m < 50 and 1 < n < 50.
For each scenario, the grid dimensions m and n will be given as two integer numbers in a single line, separated by a single blank, satisfying 1 < m < 50 and 1 < n < 50.
Output
The output for each scenario begins with a line containing “Scenario #i:”, where i is the number of the scenario starting at 1. In the next line, print the length of the shortest traveling-salesman tour rounded to two decimal digits. The output for every scenario ends with a blank line.
Sample Input
2 2 2 2 3
Sample Output
Scenario #1: 4.00 Scenario #2: 6.00
只要多做几组你就会发现规律:
只要n,m有一个为偶数,答案为n*m;都为基数,答案为n*m-1+sqrt(2)。代码如下:
#include<cstdio>
int main(){
int T;
double n,m;
scanf("%d",&T);
for(int i=0;i<T;i++){
scanf("%lf%lf",&n,&m);
if((int)n%2==0||(int)m%2==0) printf("Scenario #%d:\n%.2f\n\n",i+1,n*m);//至少一个是偶数
else printf("Scenario #%d:\n%.2f\n\n",i+1,n*m+0.41);//全为奇数
}
return 0;
}

不知道为啥n,m用int不过。